Ethical, legal and environmental impact 🏛️
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Digital Technology Unit 1: Digital Technology (Core)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Legislation law
government is responsible to creating and updating laws to encourage appropriate use of computers
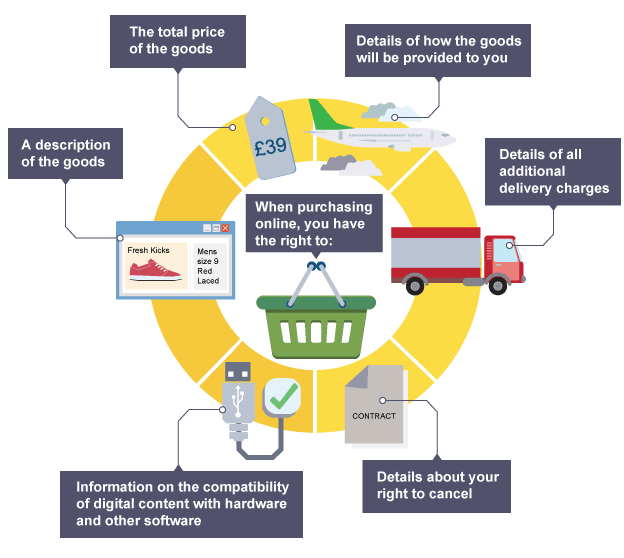
Rights of customers shopping online
Consumer Contracts Regulation 2013
traders must provide full descriptions of products sold
all costs must be made available e.g delivery and return charges
right to cancel order and receive full refund (physical products only) for 14 days
Protecting data online
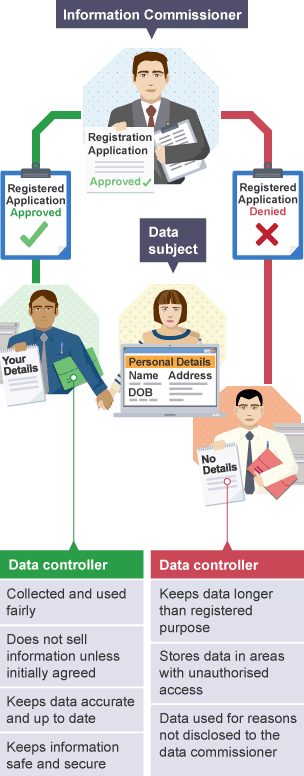
Data Protection Act 1998
controls how information can be used, protecting rights on owners
organisations that don’t comply can be prosecuted
not shared between companies without prior permission
Principles of Data Protection Act
processed fairly and lawfully with consent of data subject
used only for purpose specified to information commissioner
be adequate and relevant to intended purpose
accurate and up to date
not kept for longer than necessary
processed in accordance with rights of subject
held safely and securely
not transferred outside European union without proper protection
Data subject
individual who is subject of personal data
Information commissioner
government regulator responsible for enforcing Act, promoting good practice and making public aware
Data controller
person within organisation responsible for processing personal data
Property rights of original ideas
Copyright Designs and Patents Act 1988
protects those that create and produce their own material (intellectual property)
illegal to copy, download or distribute software without permission/ licence
organisation must have licence to cover number of users and monitor who has access
requires policies to ensure awareness of Act and consequences of breaching

Software licence
document providing legally binding guidance for use and distribution of software
FACT
Federation against Copyright Theft, protecting illegal use of software
Preventing misuse of computer systems
Computer Misuse Act 1990
illegal to hack computer to plant viruses or malicious software
not allowed to gain unauthorised access to change passwords, settings or modify data
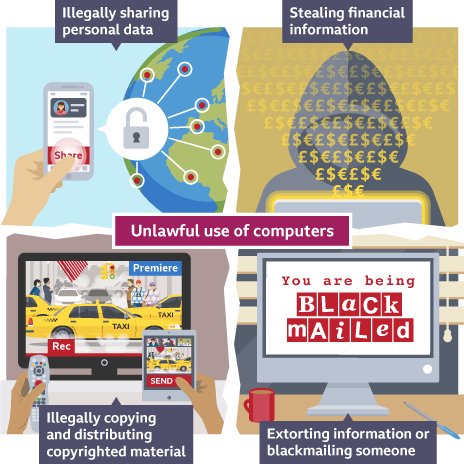
Examples of computer misuse
Hacking/stealing usernames and passwords
websites promoting violence and negative behaviour
personal use of internet in workplace e.g booking holidays
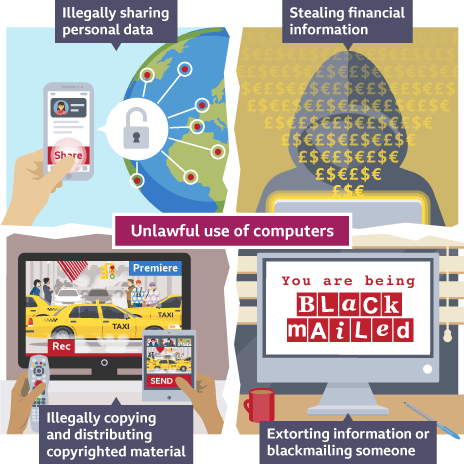
Software piracy
illegally downloading copyright materials from the internet
Plagiarism
copy and paste materials and signing it of as their own work
Ways personal data is collected without us being aware
loyalty cards from supermarkets give data on our shopping habits, used for marketing
CCTV cameras monitor our activity in cities/ shopping centres
mobile phones transmit location, monitoring movement during phone calls
analysing debit or credit card transactions which can be sold to direct advertising
Social media
subscribing to websites such as Instagram, connecting with others to share videos or messages
Misusing social media
searching profile pages to gain access to personal information e.g address
communicating racial or religious hatred/ discrimination
fake accounts to steal someone identity for crimes
privacy issues, people provide too much personal details
GPS (global positioning system)
provides real time information such as geographical locations using satellites
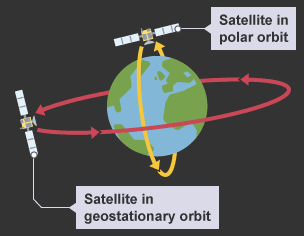
Positives of GPS
individuals who need to be monitored through tracking devices e.g vulnerable patients
tracking buses or taxis to make customers aware of arrival and departure times or employee acitivty
Issues with GPS systems
when making calls data about location can be tracked and infringe their rights to privacy
confusion over who owns data, people/ companies/ government satellites
Laws in other countries
laws vary so data may be processed in countries with less strict laws, impacting security