BME - DNA fingerprinting
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
DNA fingerprinting
determination of an individual’s unique collection of DNA pattern.
Used in healthcare system - diagnosis of hereditary disease, chromosome aberrations, and cancer.
Used in judicial system - identification of suspects and establishing paternity
How to do DNA fingerprinting
Collect tissue sample (>20 cells)
PCR analysis with STR RFLP
STR - Single tandem repeats
Certain regions of genome are highly variable and made of repeating base pairs
RFLP - Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism
a technique that cuts DNA into fragments using restriction enzyme digestion to cut DNA.
Difference in DNA fragment size results from presence of different DNA sequences
Restriction enzymes (endonucleases)
Enzymes that cut DNA
Recognize specific base sequences in DNA and cut DNA only at those recognition sites
Restriction enzyme recognition site
enzymes recognize specific 4-8 bp (base pair) sequences
e.g. EcoRI recognizes GAATTC (and its pair)
e.g. PvuII recognizes CAGCTG (and its pair)
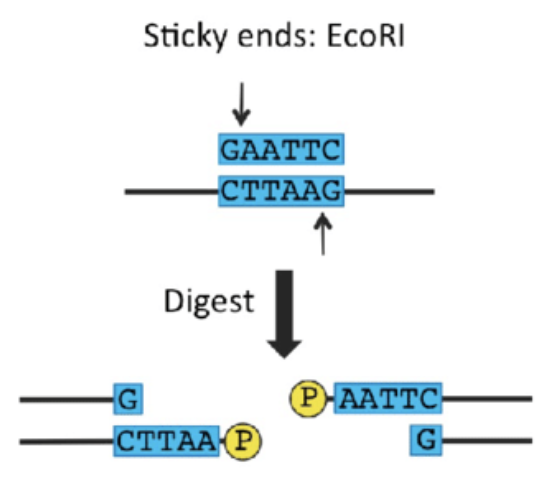
Restriction enzyme - staggered fashion
e.g. EcoRI (GAATTC)
cuts DNA at both strands, leaving overhangs. (looks like sign when cut)
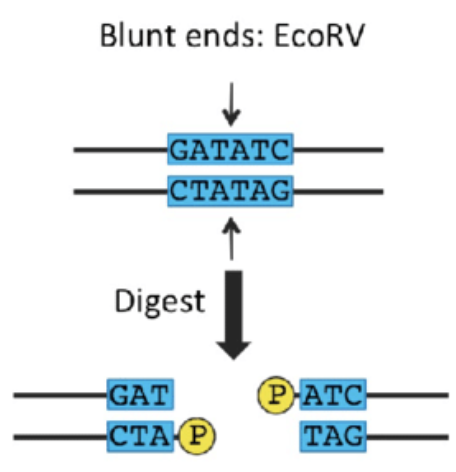
Restriction enzyme - direct fashion
e.g. PvuII (CAGCTG)
cuts DNA in a straight line
Allele
one of 2+ alternative forms of a gene that can arise by mutation and are found at the same place on a chromosome
wild type allele - “normal” allele
mutant allele
different alleles act as different restriction sites, even if they differ by one nucleotide