BIOL 465: Fish Diversity Taxa
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
Class Conodonta
conodonts (extinct)
Name origin: from Greek kōnos = “cone” + odous (odont-) = “tooth” → “cone tooth”
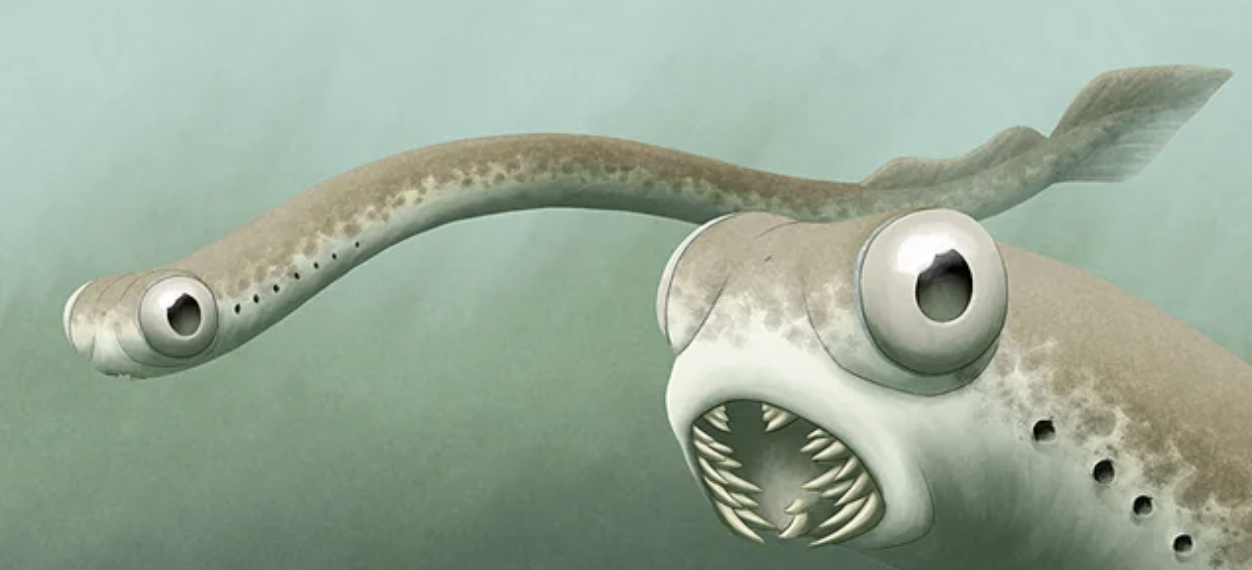
ostracoderms
Name origin:from Greek ostrakon = “shell” + derma = “skin” → “shell-skinned” or “armored skin”
4 extinct classes
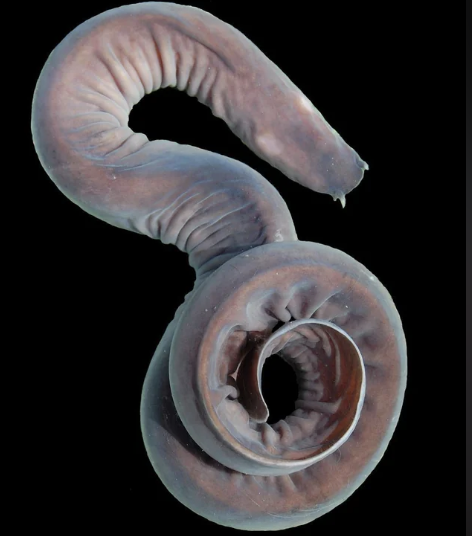
Class Myxini
Name origin:from Greek myxa = “slime” → “slime fish”
hagfish
Infraphylum Vertebrata
vertebrates
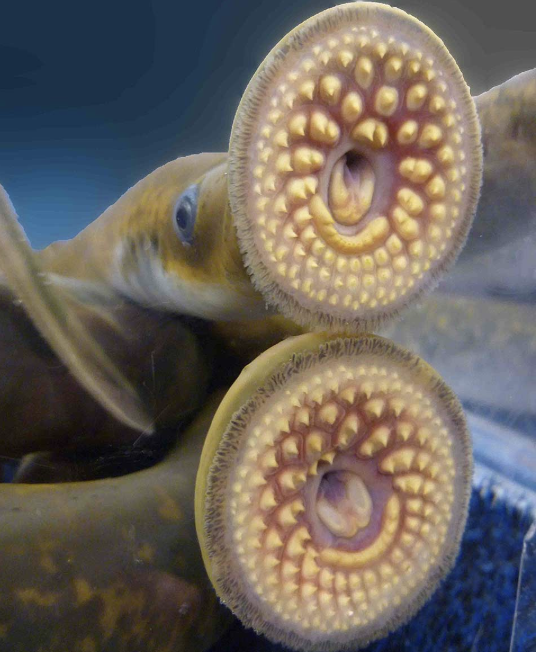
Class Petromyzontida
Name origin: petra = “rock” + myzo = “to suck” → “rock-suckers”
lampreys
Superclass Gnathostomata
Name origin: gnathos = “jaw” + stoma = “mouth” → “jaw-mouths”
jawed vertebrates
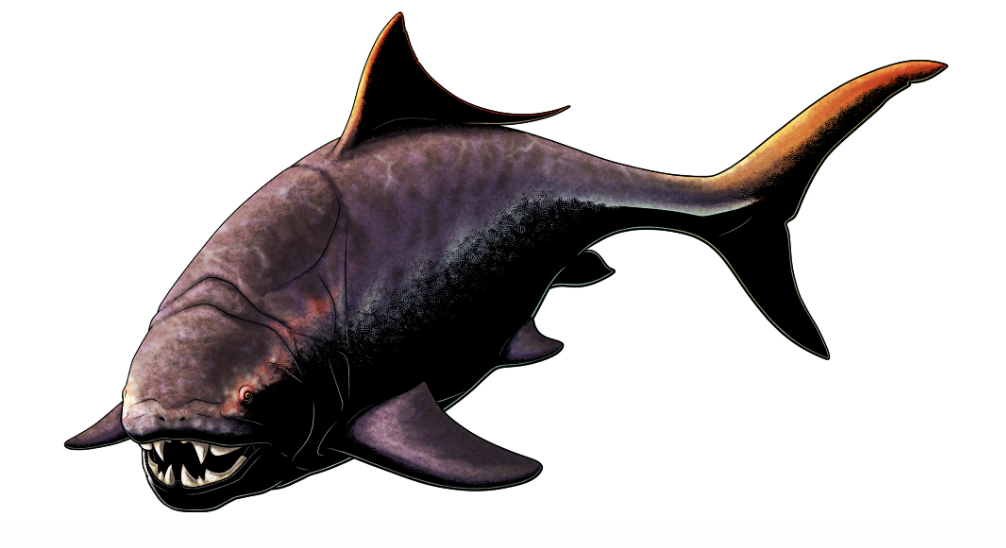
Class placodermi
Name origin: plax (placos) = “plate” + derma = “skin” → “plate-skinned” (armored fish)
placoderms (extinct)

Class Chondrichthyes
Name origin: chondros = “cartilage” + ichthys = “fish” → “cartilage fish”
cartilaginous fishes
Infraclass Elasmobranchii
Name origin: elasmos = “plate” or “thin metal sheet” + branchia = “gills” → “plate-gilled”
living sharks and rays
Division Selachii
Name origin: selachos = “shark” → literally “sharks”
sharks
Superorder Galeomorphi
Name origin: galeos = “shark” + morphē = “form” → “shark-shaped” or “shark form”
galeomorph sharks
Order heterodontiformes
Name origin: heteros = “different” + odous (odont-) = “tooth” + -formes = “having the form of” → “different-toothed form
bullhead sharks (horn sharks)
Key traits:
9 species
2 dorsal fins with spines; blunt head; crests above eyes; up to 1 m long
• heterodont teeth (graspers & grinders): eat hard-shelled invertebrates
• oviparous: screw-shaped keratin egg cases
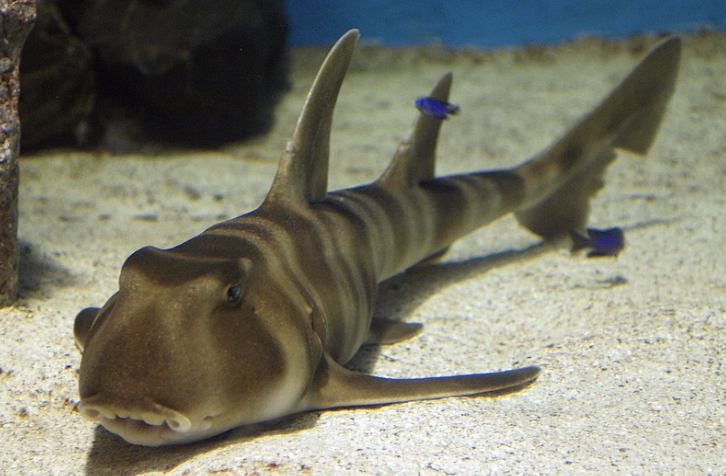

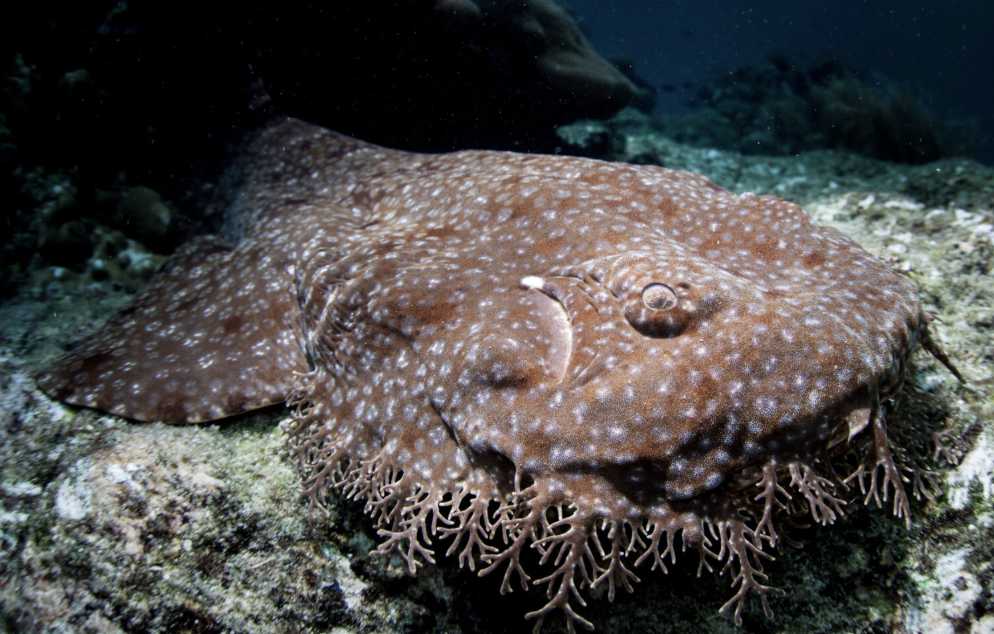
Order Orectolobiformes
Name origin: orektos = “stretched out” + lobos = “lobe” + -formes = “form” → “stretched-lobed form” (referring to lobed nasal flaps or fins)
carpet sharks (wobbegongs, zebra sharks, angel sharks, nurse sharks)
Key Traits:
44 species
2 dorsal fins without spines; prominent spiracles; most w/ barbels (sensory whiskers)
• broad size range & diets: filter feeding, suction feeding, etc.
• mostly ovoviviparous; some oviparous

Order Lamniformes
Name origin: lamna = “fish of prey, shark” + -formes = “form” → “lamnid-form” or “predatory shark form”
mackerel sharks (great whites, mako sharks, thresher sharks, porbeagle, goblin sharks)
Key Traits:
15 species
cosmopolitan marine, 2 dorsal fins without spines, large mouth, ovoviviparous
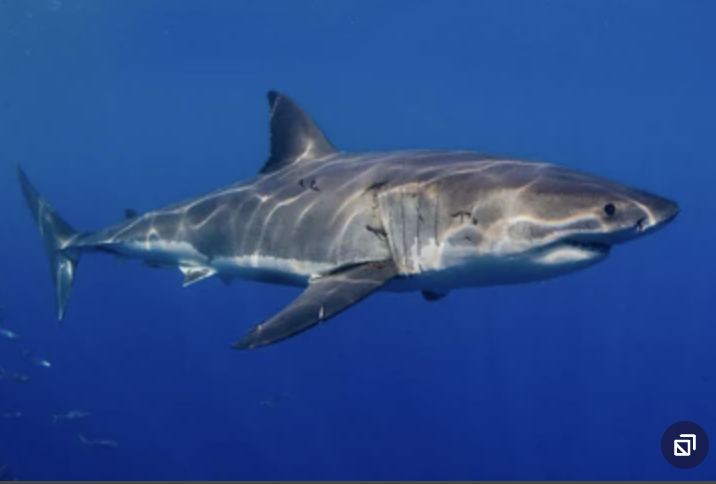

Family Lamnidae
Name origin: lamna = “fish of prey, shark”
mackerel sharks
Order Carcharhiniformes
Name origin: karcharos = “sharp” + rhinos = “nose” + -formes = “form” → “sharp-nosed form” (ground sharks)
ground sharks (tiger sharks, blue sharks, hammerheads, bull sharks, cat sharks)
Key Traits:
>280 species
cosmopolitan marine, 2 dorsal fins without spines, anal fin, nictitating eye membrane, various reproductive modes
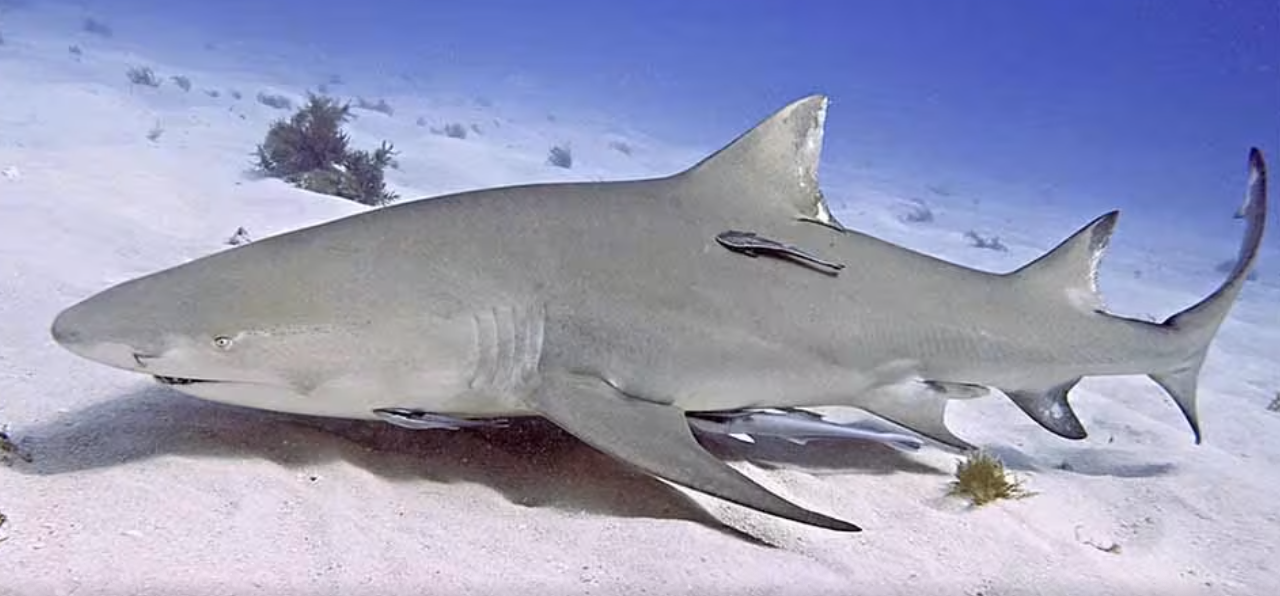

Family Carcharhinidae
Name origin: karcharos + rhinos → “sharp-nosed”
requiem sharks
Superorder Squalomorphi
Name origin: squalus = “shark” + Greek morphē = “form” → “shark-form”
squalomorph sharks
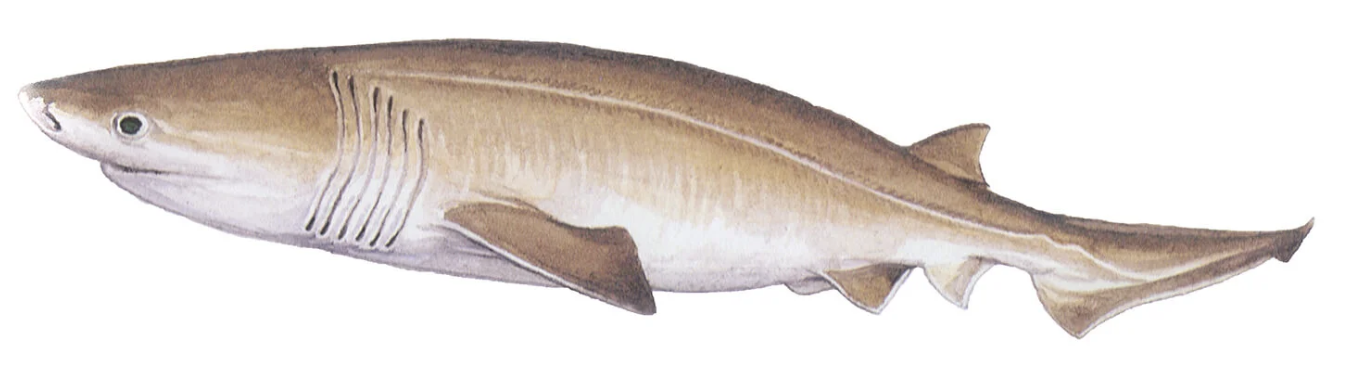
Order Hexanchiformes
Name origin: hexa = “six” + anchos (from branchia) = “gill” + -formes → “six-gilled form”
6 and 7 gill sharks
Key Traits:
6 species
continental slopes
6-7 gill slits, 1 dorsal fin without spine set back, anal fin present, ovoviviparous
Order Squaliformes
Name origin: squalus = “shark” + -formes = “form” → “shark form”
dogfish sharks
Key Traits:
120 species
global, mostly deep sea (photophores), 2 dorsal fins ± spines, anal fin absent, ovoviviparous
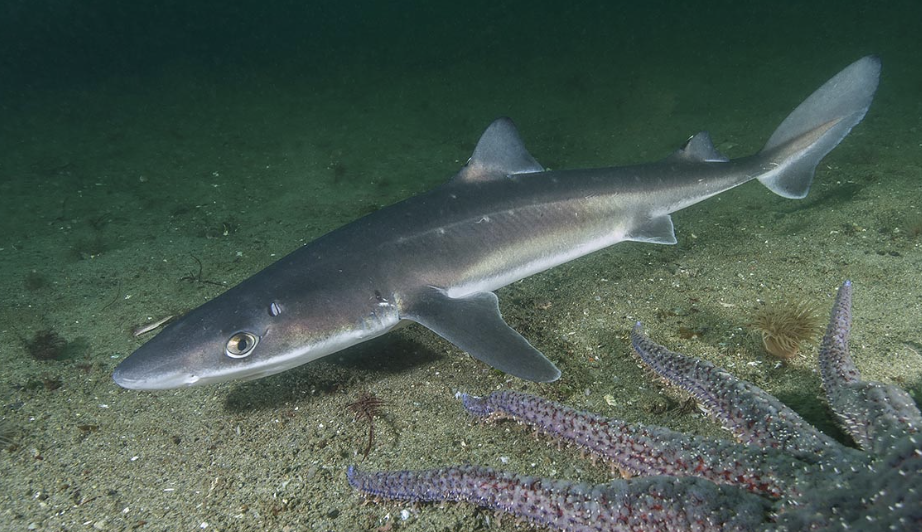

Family Squalidae
Name origin: squalus = “shark”
Dogfish sharks
Division Batomorpha
Name origin: batos = “ray” + morphē = “form” → “ray form”
rays
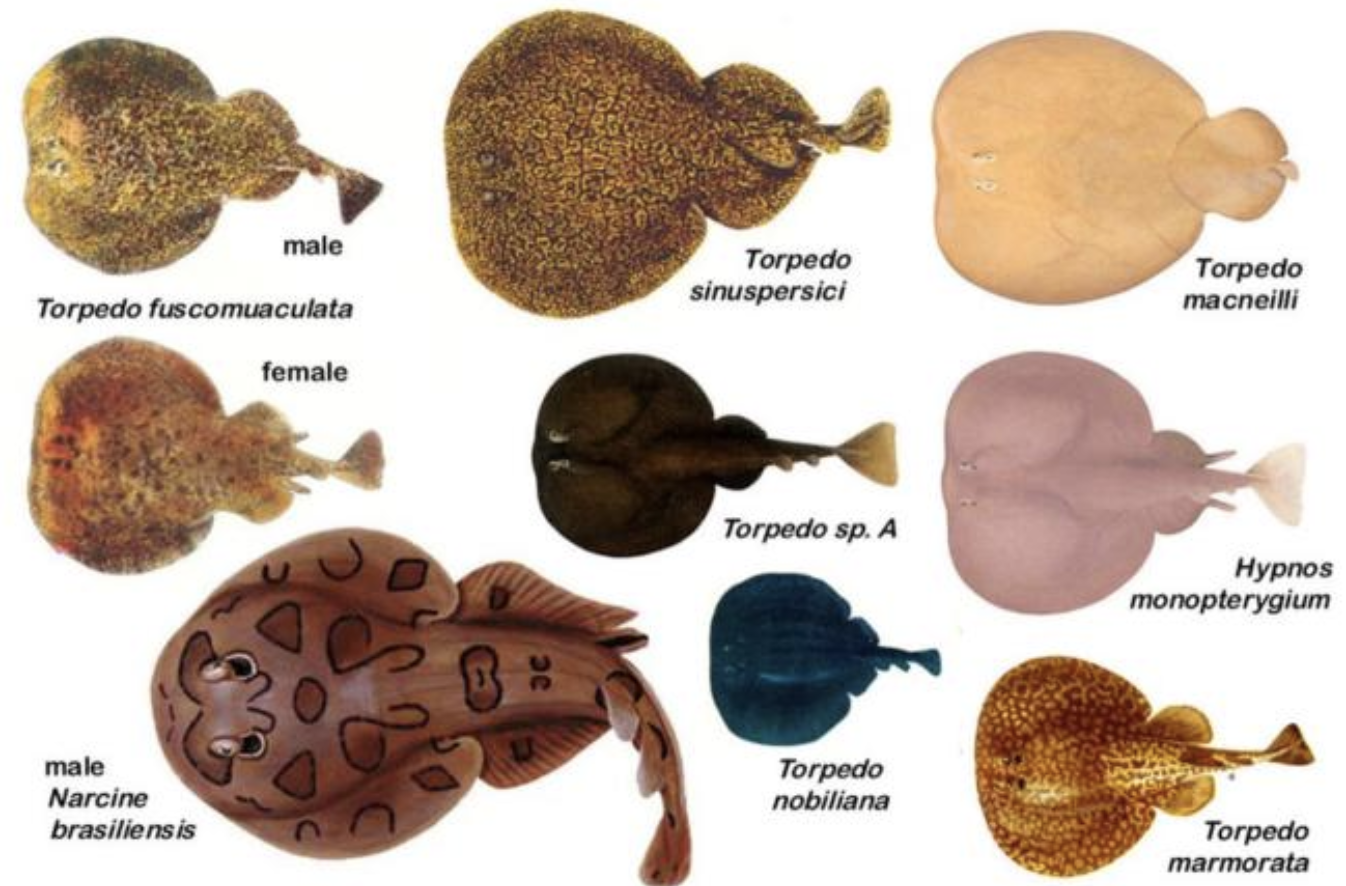
Order Torpediniformes
Name origin: torpedo = “numbness” or “paralysis” (from the electric shock) + -formes = “form” → “electric-ray form”
electric rays
Key Traits:
65 species
continental shelves and slopes, strong electric organs, no scales, 1-2 dorsal fins, well developed caudal fin, eat mostly fish (electrocute prey) ovoviviparous
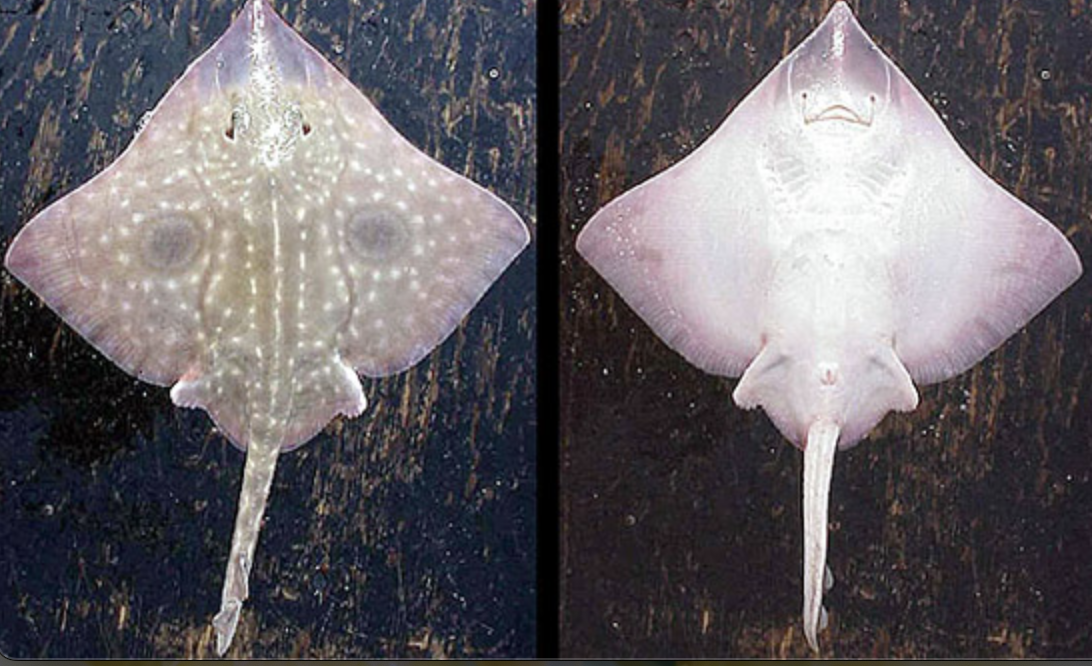
Order Rajiformes
Name origin: raia = “skate” + -formes = “form” → “skate form”
skates
Key Traits:
287 species
global shallow to deep, weak electric organs in narrow tail, row of thorns, 0-2 dorsal fins, eat soft bottom invertebrates oviparous with keratin egg case

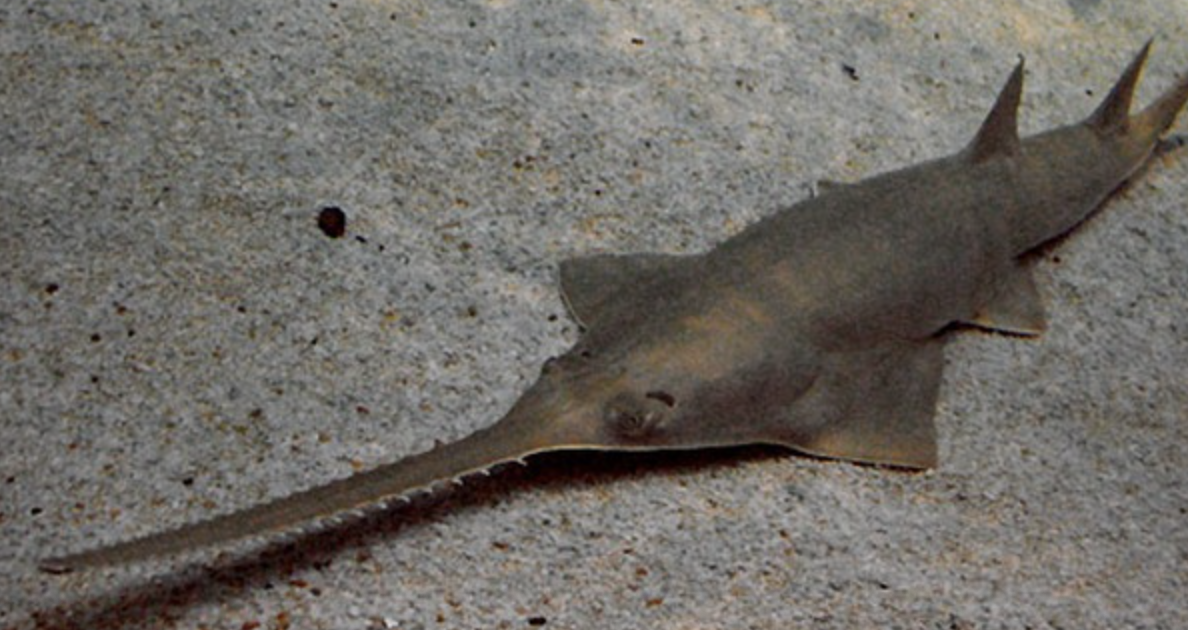
Order Pristiformes
Name origin: pristis = “sawfish” (from prion, “saw”) + -formes = “form” → “sawfish form”
guitarfish and sawfish
Key Traits:
63 species
tropical to temperate estuaries and coasts, intermediate body plan, 2 dorsal fins, heterocercal caudal, eat invertebrates and fish, ovoviviparous

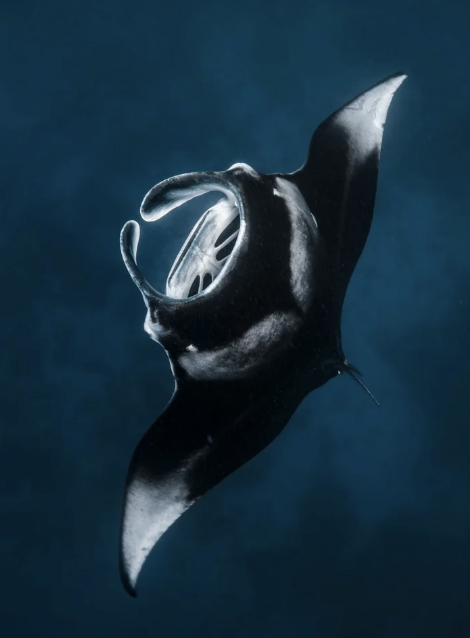
Order Myliobatiformes
Name origin: “millstone” (flat shape) + batis = “ray” + -formes = “form” → “millstone-ray form” (refers to broad, flat bodies)
stingrays and mantas
Key traits:
220 species
cosmopolitan including freshwater, no (or reduced) dorsal fin, very thin tail (often barbed), eat mostly benthic invertebrates

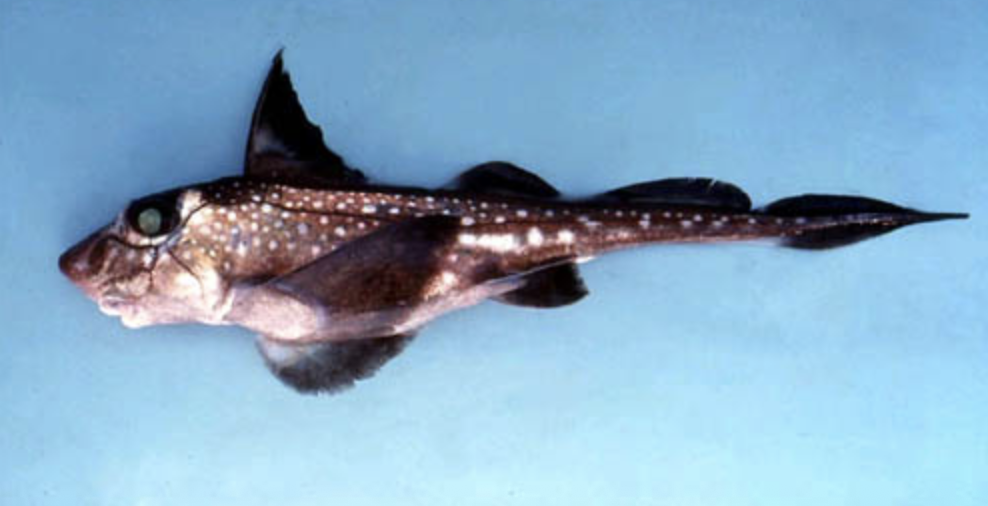
Subclass Holocephali
Name origin: holos = “whole” + kephalē = “head” → “whole head” (refers to fused upper jaw)
ratfish/chimera
Key traits:
50-60 species
holostylic jaw suspension, upper jaw is fused to the braincase, have a single gill slit covered by an operculum.

Grade Teleostomi
Name origin: teleos = “complete, perfect” + stoma = “mouth” → “complete mouth”
teleostomes
Class Acanthodii
Name origin: akantha = “spine, thorn” + -odes = “like” → “spiny ones”
acanthodians (extinct)

Class Osteichthyes
Name origin: osteon = “bone” + ichthys = “fish” → “bony fish”
bony fishes
Subclass Actinopterygii
Name origin: aktis (actin-) = “ray” + pteryx = “fin” or “wing” → “ray-fin”
ray-finned fish
Key traits:
>30,500 species
Scales ganoid, cycloid, ctenoid (or absent), brachiostegal rays usually present, swim bladders or lungs, ossified vertebrae
Infraclass Cladistia
Name origin: klados = “branch” → “branch-like” (refers to their lobed fins)
bichirs and reedfish
Key traits:
14 species
ganoid scales, 5-18 dorsal finlets, ‘lungs’ (can breathe air), lobed pectorals, spiracles, maxilla fused to skull, spiral valve, no branchiostegals, 2 gular plates

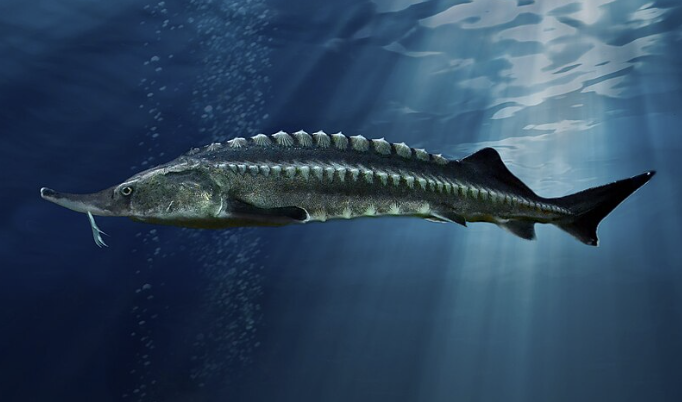
Infraclass Chondrostei
Name origin: chondros = “cartilage” + osteon = “bone” → “cartilage-bone” (partly cartilaginous skeleton)
paddlefishes and sturgeons
Key traits:
2 specialized relic families
heterocercal caudal, spiracles, secondarily cartilaginous skeletons, spiral valve intestine

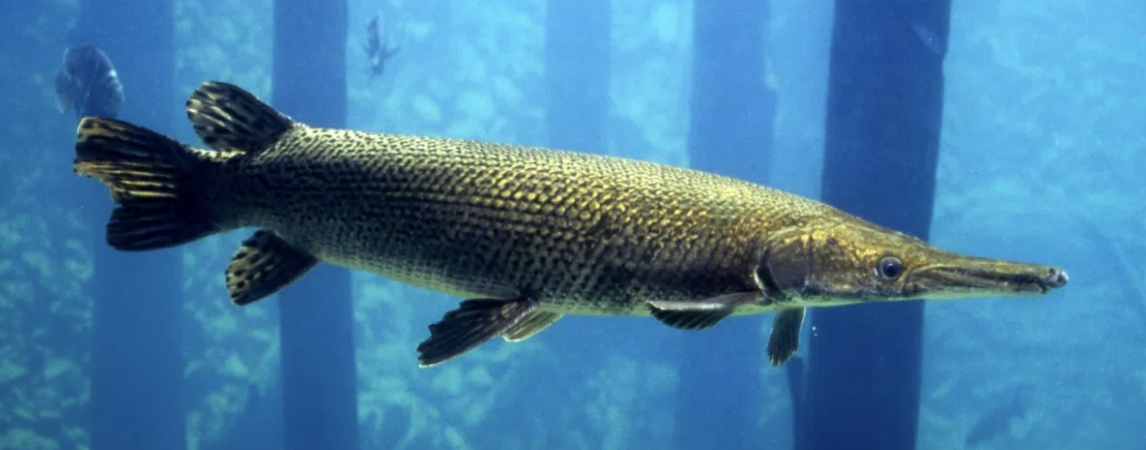
Infraclass Holostei
Name origin: holos = “whole” + osteon = “bone” → “whole bone” (entirely bony skeleton)
gars and bowfin
Key traits:
lepisosteiformes and amiiformes

Division Teleostei
Name origin: teleos = “complete” + osteon = “bone” → “completely bony” (modern bony fishes)
derived fin fishes
Key traits:
96% of all extant fish
increased feeding efficiency and maneuverability
Cohort Elopomorpha
Name origin: lops = “kind of fish” (often used for eels or serpentlike fish) + morphē = “form” → “elops-form”
usually many brachiostegal rays, maxilla in gape, diagnostic leptocephalus larva
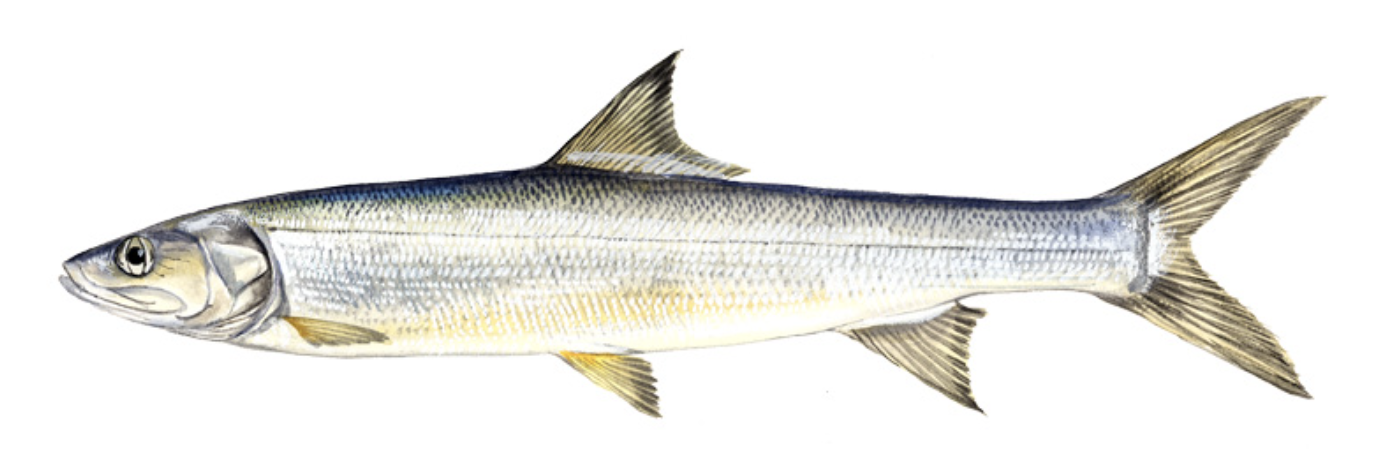
Order Elopiformes
Name origin: → “elops form”
tenpounders and ladyfishes
Key traits:
9 spp
mostly marine, terminal mouth, gular plate, leptocephalus tail, fin forked, heavy scales, carnivores

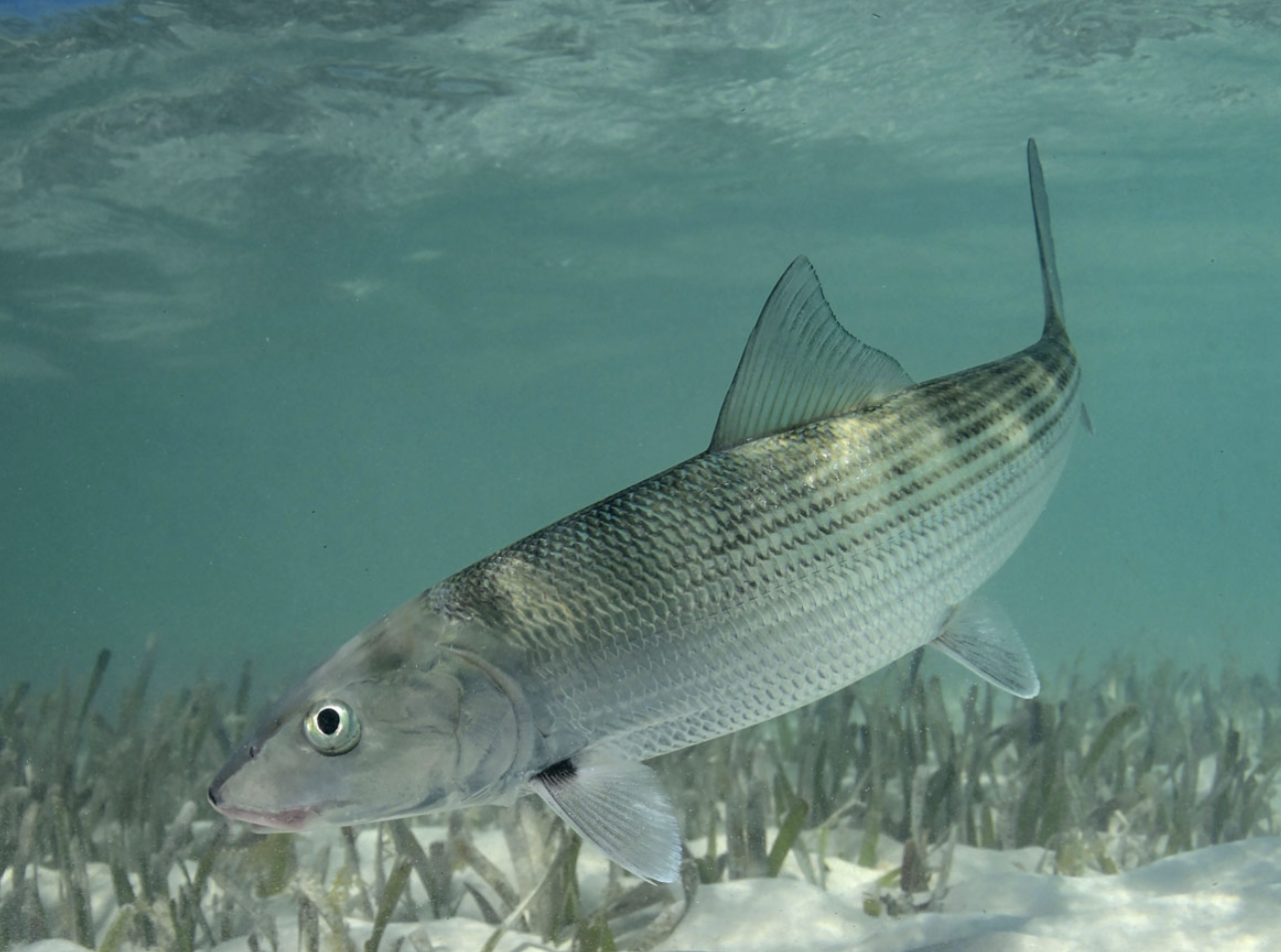
Order Abuliformes
Name origin: albus = “white” + -formes = “form” → “white-fish form”
bonefishes
Key traits:
20 spp
marine, tropical, subterminal mouths, gular plate small or absent, leptocephalus tail, fin forked, heavy scales, carnivores, gamefishes

Order Anguilliformes
Name origin: anguilla = “eel” + -formes = “form” → “eel form”
eels
Key traits:
940 species
mostly marine, global, no gular plate, no scales, no pelvic fin, carnivores, leptocephalus tail round or pointed
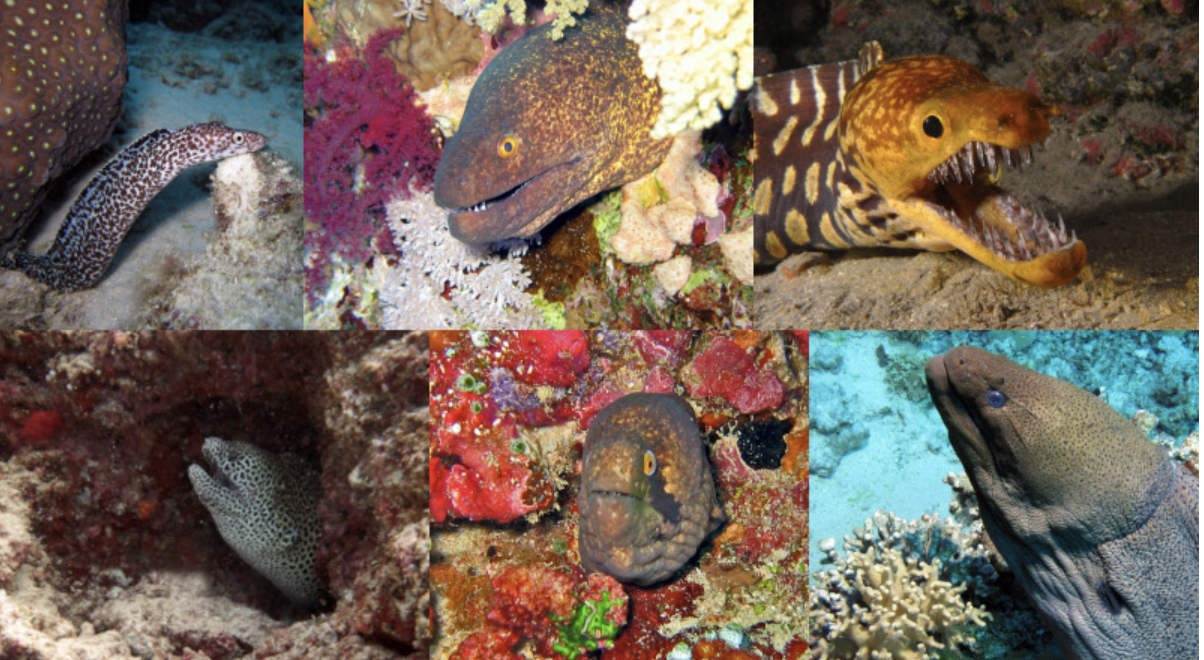

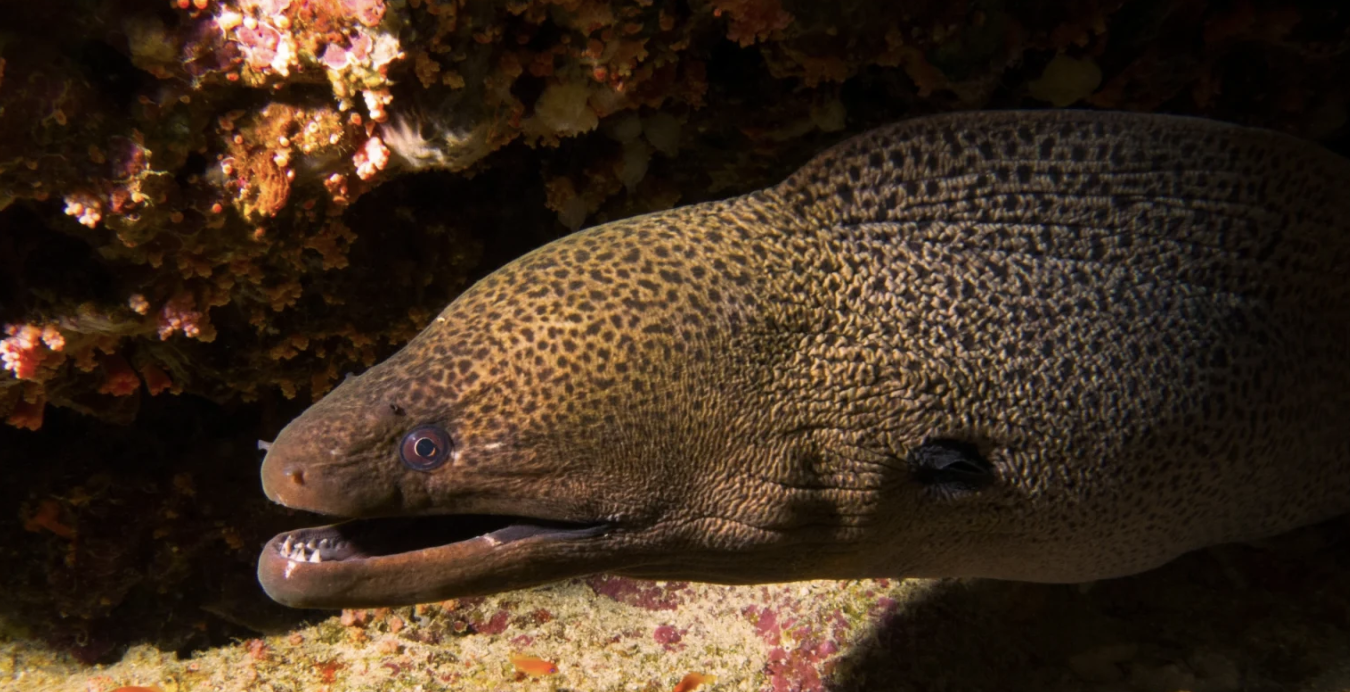
Family Muraenidae
Name origin: muraena = “moray eel” → “moray eels”
moray eels
Key traits:
215 spp, 42 spp in Hawaii
tropical and temperate, small round gill openings, neuromast on head only, no pectorals, nostril tubes, teeth sharp or molarform

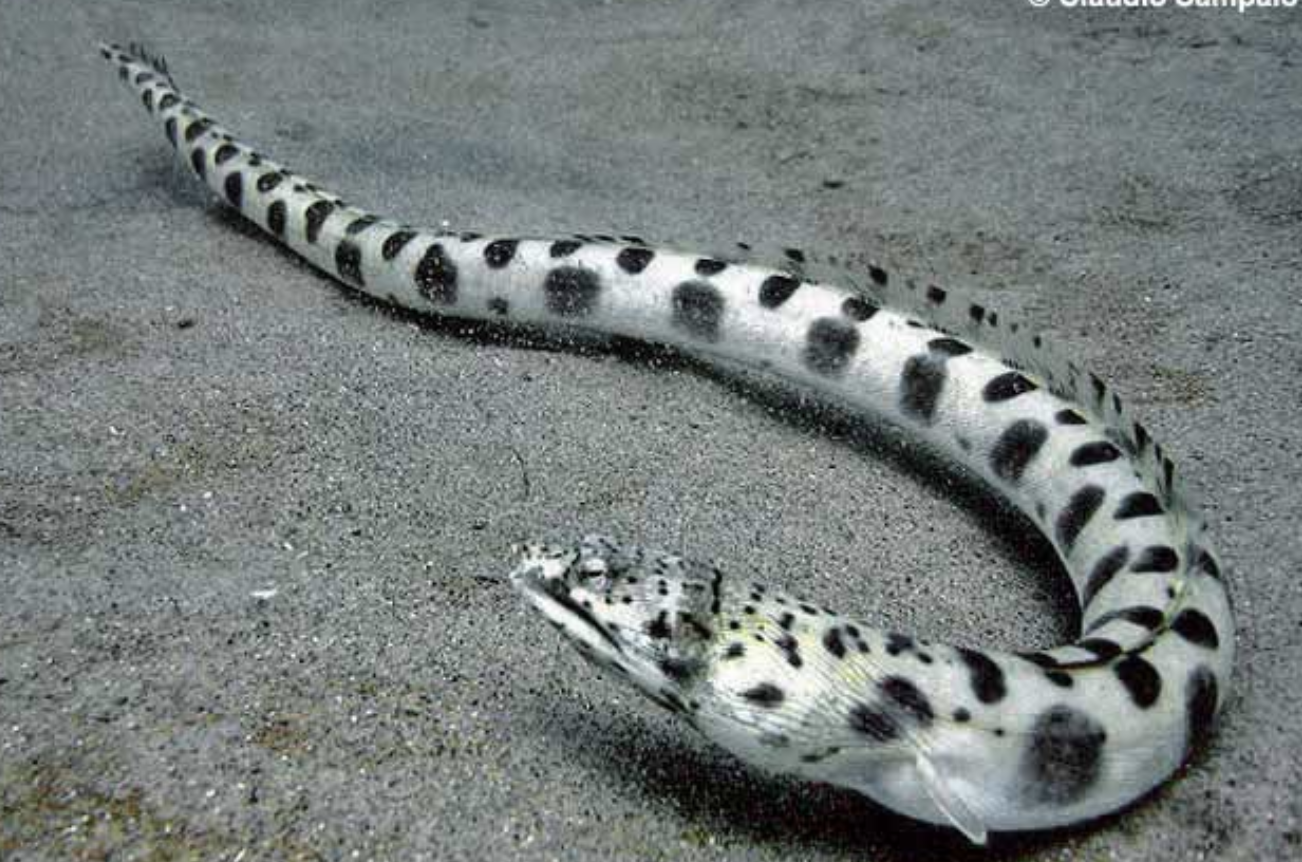
Family Ophichthidae
Name origin: ophis = “snake” + ichthys = “fish” → “snake fish”
snake and worm eels
Key traits:
320 spp, 16 in Hawaii
tropical and warm temperate, coastal, complete lateral line, pectorals present or absent, many brachiostegals, pointed head and stiffened tail, burrow in sand

Family Congridae
Name origin: gongros = “eel” → “conger eels”
conger and garden eels
Key traits:
200 spp, 4 in Hawaii
tropical and temperate, coastal, complete lateral line, pectorals usually present

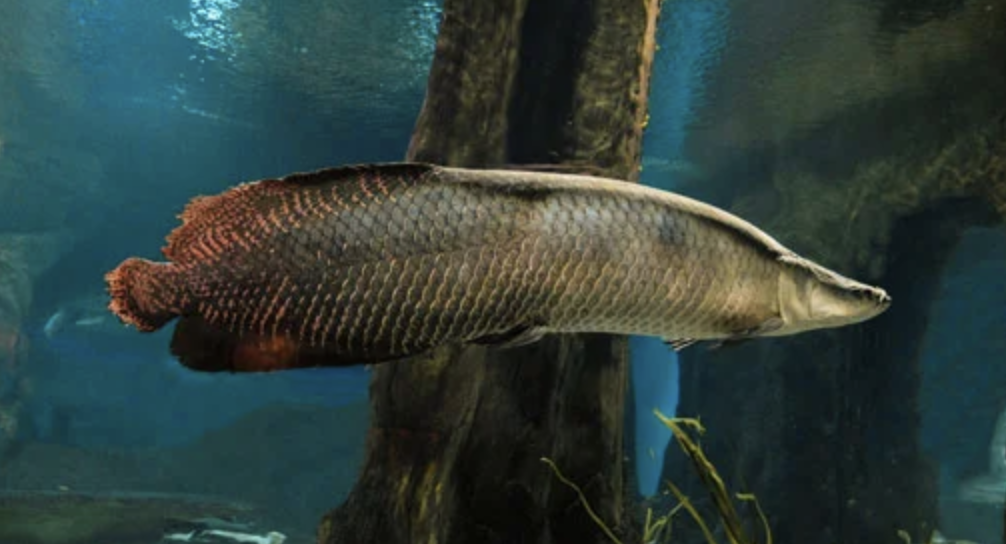
Cohort Osteoglossomorpha
Name origin: osteon = “bone” + glossa = “tongue” + morphē = “form” → “bony-tongue form”
Name origin:
freshwater
2 orders
Order Osteoglossiformes
Name origin:“bony-tongue form”
bony tongues
Key traits:
244 spp
mainly south america and africa, teeth on tongue bones, premaxilla small and fused to skull, 1 ovary, mostly carnivores

Cohort Otocephala
Name origin: ous (ot-) = “ear” + kephalē = “head” → “ear-head” (refers to ear–swim bladder connection)
otocephalans
Key traits:
7 orders
marine and freshwater, global, swimbladder inner ear connection
Order Clupeiformes
Name origin: clupea = “herring” + -formes = “form” → “herring form”
clupeiformes
Key traits:
400 spp
paired swimbladder extensions connect directly to inner ear, no lateral line, no fin spines, single dorsal fin, caudal fin usually forked, mostly schooling planktivores
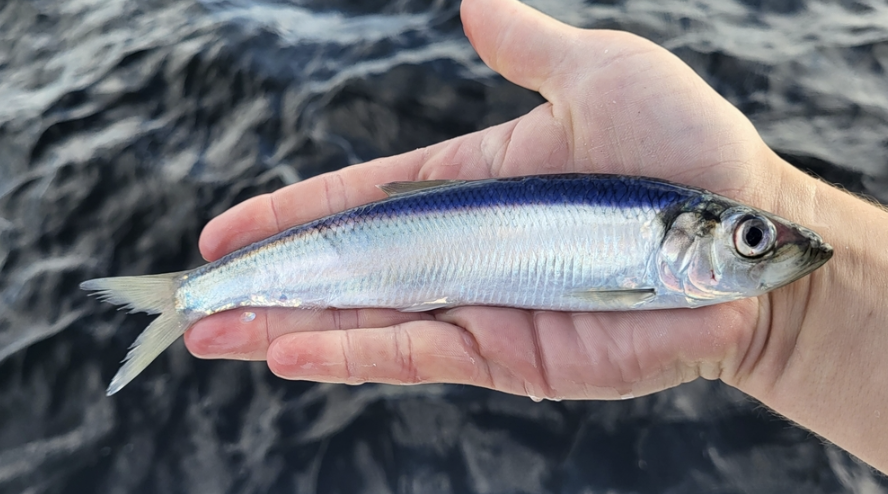
Family Clupeidae
Name origin: clupea = “herring” → “herrings, sardines”
herrings, menhadens, pilchards, sardines, shads, sprats
Key traits:
218 spp, 4 in Hawaii
shorter jaws, terminal mouth

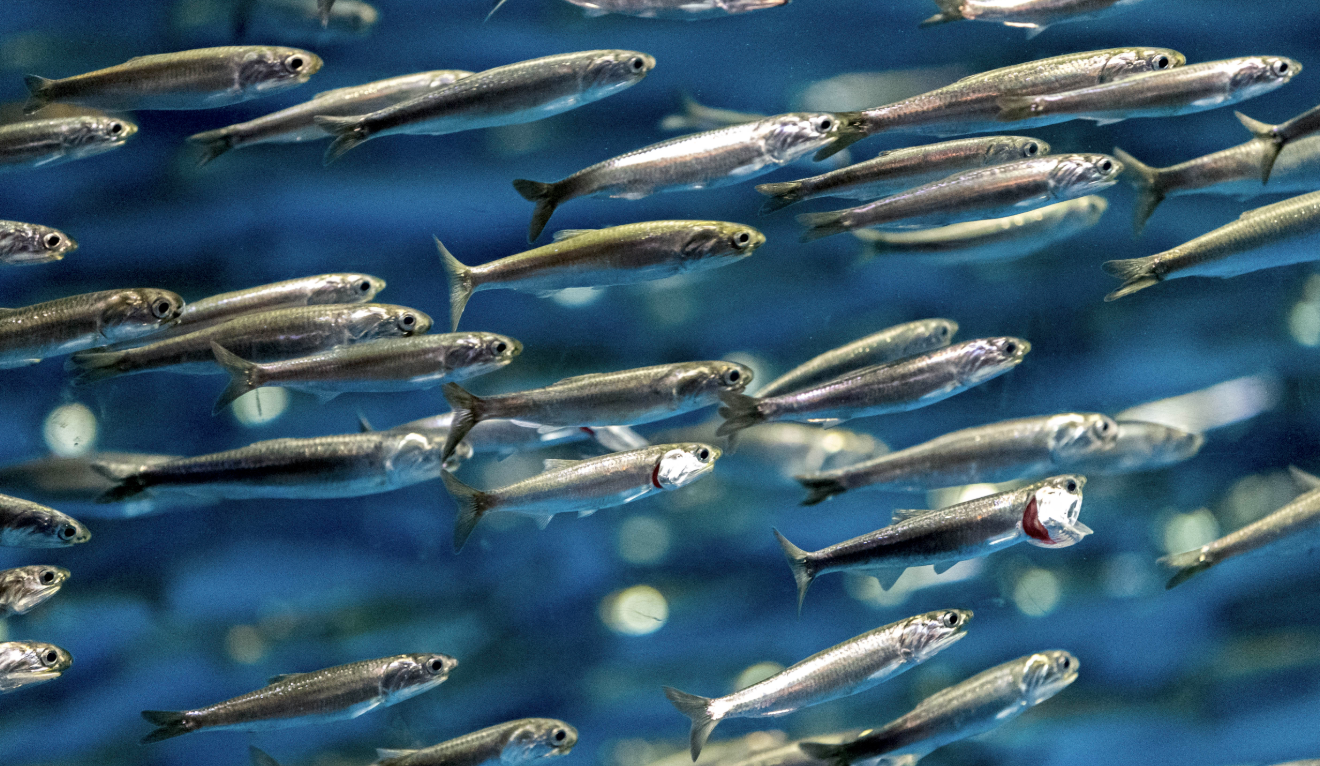
Family Engraulidae
Name origin: engraulis = “anchovy” → “anchovies”
anchovies, anchovetas
Key traits:
146 spp, 2 in Hawaii
elongated jaws, subterminal mouth

Superorder Ostariosphysi
Name origin: ostarion = “small bone” + physa = “bladder” → “small-bone bladder” (refers to Weberian apparatus linking ear and swim bladder)
Name origin:
5 orders, 10400 spp, 68% of freshwater species
dominate freshwater, weberian apparatus bone series, connects swim bladder to ear, most species release alarm substance when skin injured
Order Gonorynchiformes
Name origin: gonia = “angle” + rhynchos = “snout” + -formes = “form” → “angled-snout form”
milkfishes
Key traits:
37 spp, 1 in Hawaii (family Chanidae)
marine and brackish water, lateral line present, no fin spines, single dorsal fin, caudal fin deeply forked, mostly herbivores

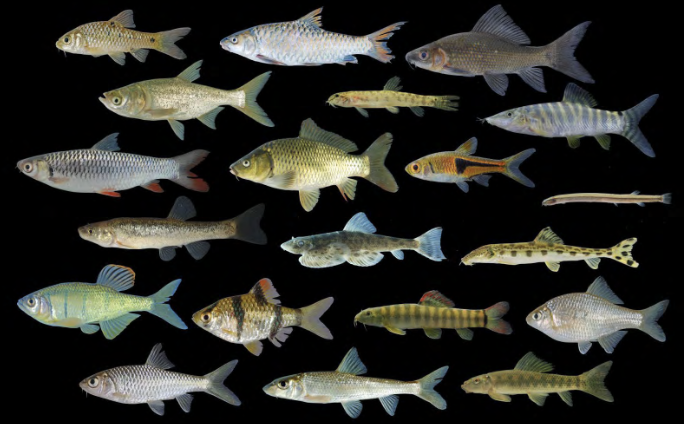
Order Cypriniformes
Name origin: kyprinos = “carp” + -formes = “form” → “carp form”
carps and relatives
Key traits:
4,450 spp
freshwater, 3 brachiostegal rays, head usually scaleless, jaws toothless, jaws usually protrusible, no adipose fin, omnivores

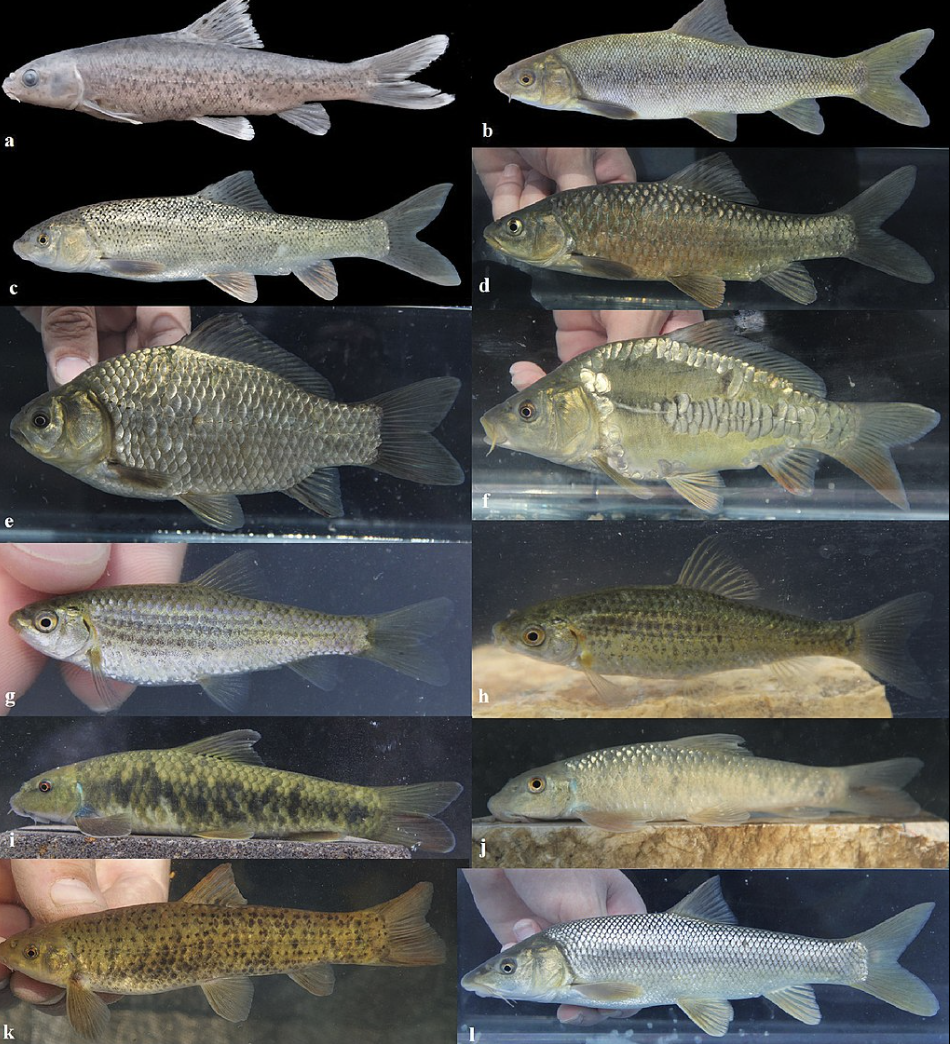
Family Cyprinidae
Name origin: kyprinos = “carp” → “carps”
barbel, bitterling, bleak, bream, carp,
chub, dace, goldfish, gudgeon, labeo, minnow, riffle dace, roach, roach, rudd, shiner, tench
Key traits:
1,795 spp
first to evolve pharyngeal teeth, maxilla excluded from gape, protrusible jaws, pelvics abdominal

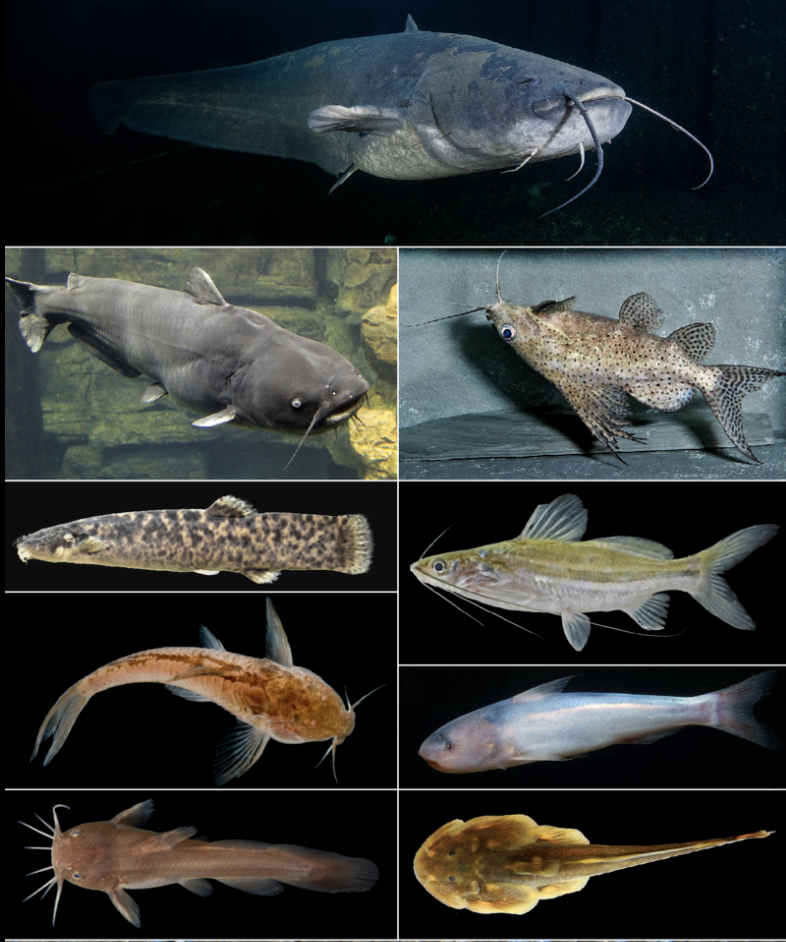
Order Siluriformes
Name origin: silurus = “catfish” + -formes = “form” → “catfish form”
catfishes
Key traits:
4,100 spp
mostly freshwater, 1-4 pairs of barbels, # brachiostegal rays vary, most gave adipose fin, jaws not protrusible, some with venomous spines, reduced # of head bones, mostly benthic omnivores

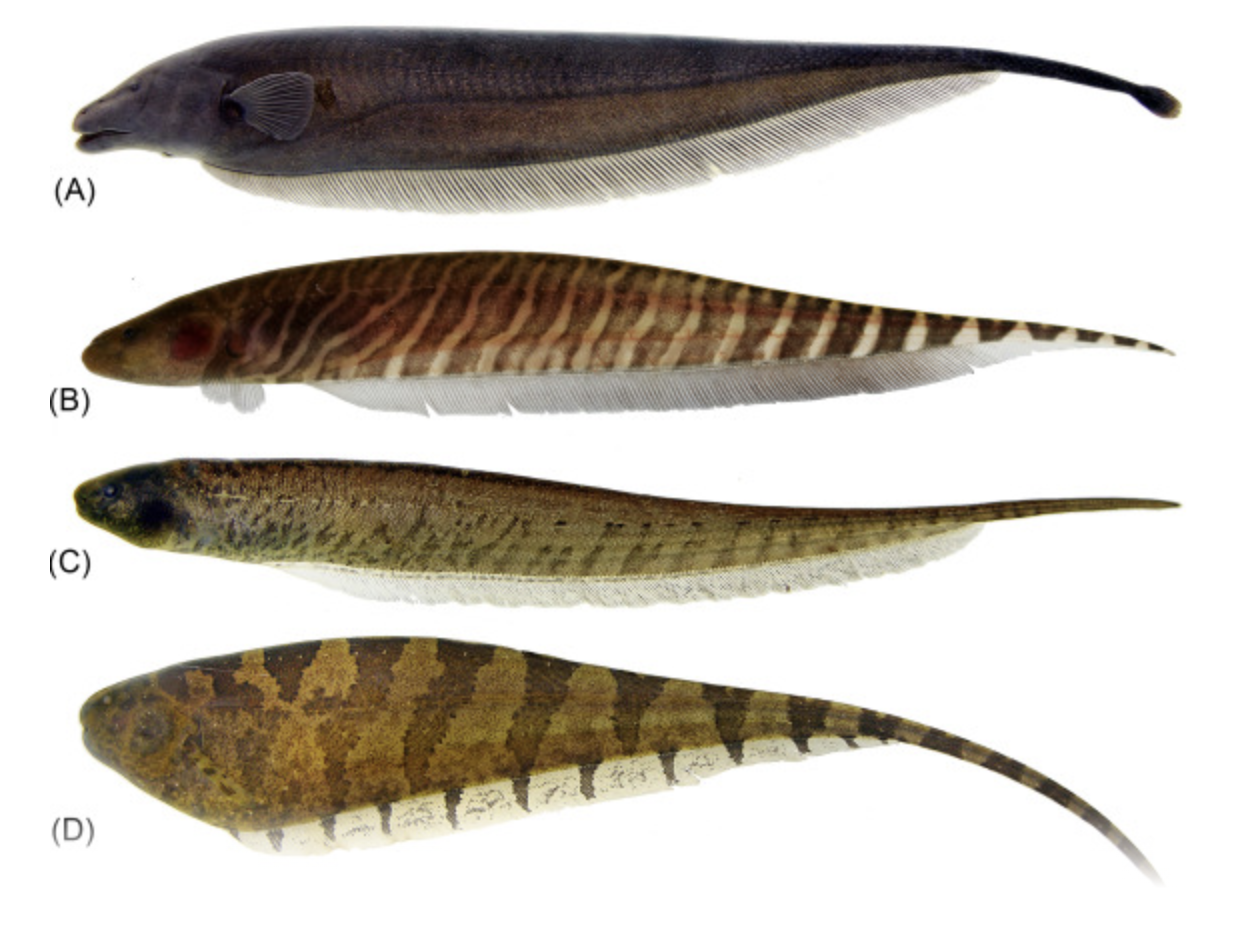
Order Gymnotiformes
Name origin: gymnos = “naked” + noton = “back” + -formes = “form” → “naked-back form” (refers to scaleless, eel-like knifefishes)
South American knifefishes, electric eel
Key traits:
256 spp
freshwater, 2-5 brachiostegal rays, no scales, jaws toothless, eel like body, swim with elongated anal fin, no pelvic/dorsal/adipose fins, produce and detect electrical impulses, generalized carnivores

Cohort Euteleostei
Name origin: eu = “true” + teleos = “complete” + osteon = “bone” → literally “true complete-boned fish”
euteleosteans
Key traits:
50 orders, marine and freshwater, monophyly suggested by skeletal structures
Superorder Procanthopterygii
Name origin: protos = “first” + akantha = “spine” + pteryx = “fin” → “first spiny fin”
salmon, pikes, smelts, various deep sea fish
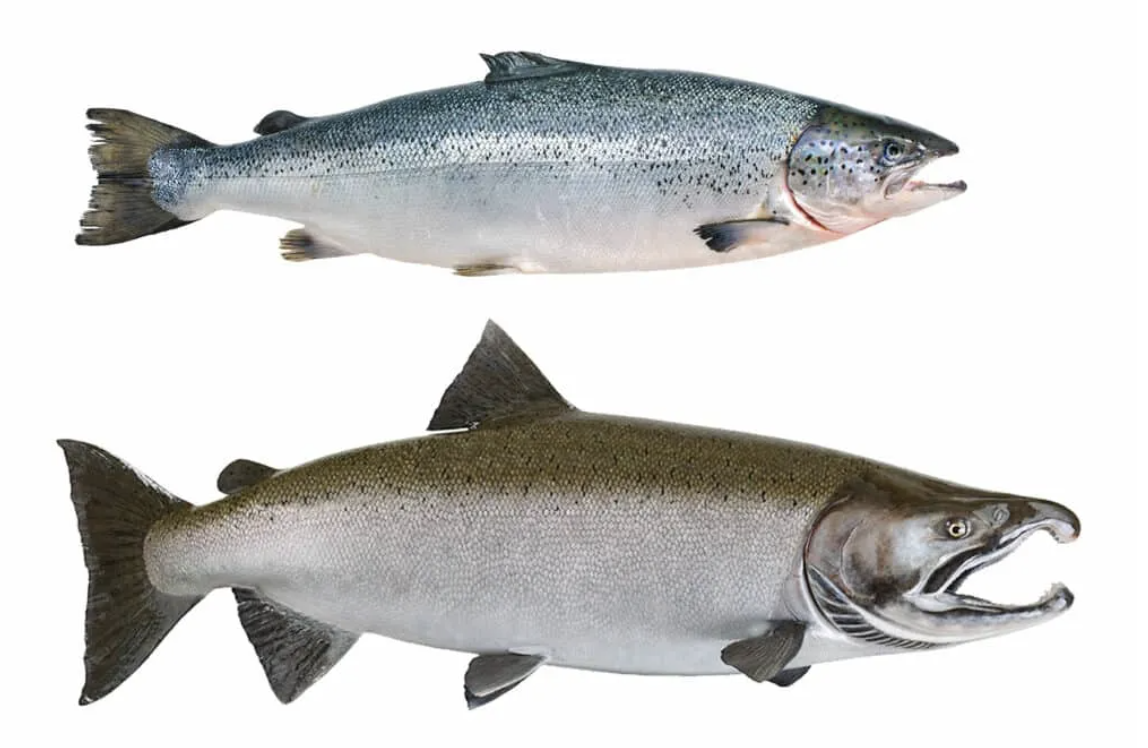
Order Salmoniformes
Name origin: salmo = “salmon” + -formes = “form” → “salmon form”
salmon, etc.
Family Salmonidae
Name origin: salmo = “salmon” → “salmon family”
salmon, trout, etc
Key traits:
223 spp
freshwater and anadromous, adipose, pelvic axillary process, no spiny fin rays, gill membranes free from isthmus, physotomous swim bladder, mostly cycloid scales

Order Stomiiformes
Name origin: stoma = “mouth” + -formes = “form” → “mouth form” (refers to large-mouthed deep-sea fishes)
various deep sea fishes: dragonfish, hatchetfish, viperfish, bristlemouths, lightfishes
Key traits:
414 spp
teeth on maxilla and premaxilla, cycloid scales or scaleless, photophores

Superorder Scopelomorpha
Name origin: skopelos = “a kind of fish” (used for lanternfish-like species) + morphē = “form” → “scopelus form”
scopelomorphs
Key traits:
1 order
Order Myctophiformes
Name origin: mykter = “nose” + ophis or phos (“light” depending on interpretation) + -formes = “form” → most likely “light-bearing form”
myctophiforms
Key traits:
260 families
ancestral- adipose fin, usually cycloid scales, derived - maxilla excluded from gape
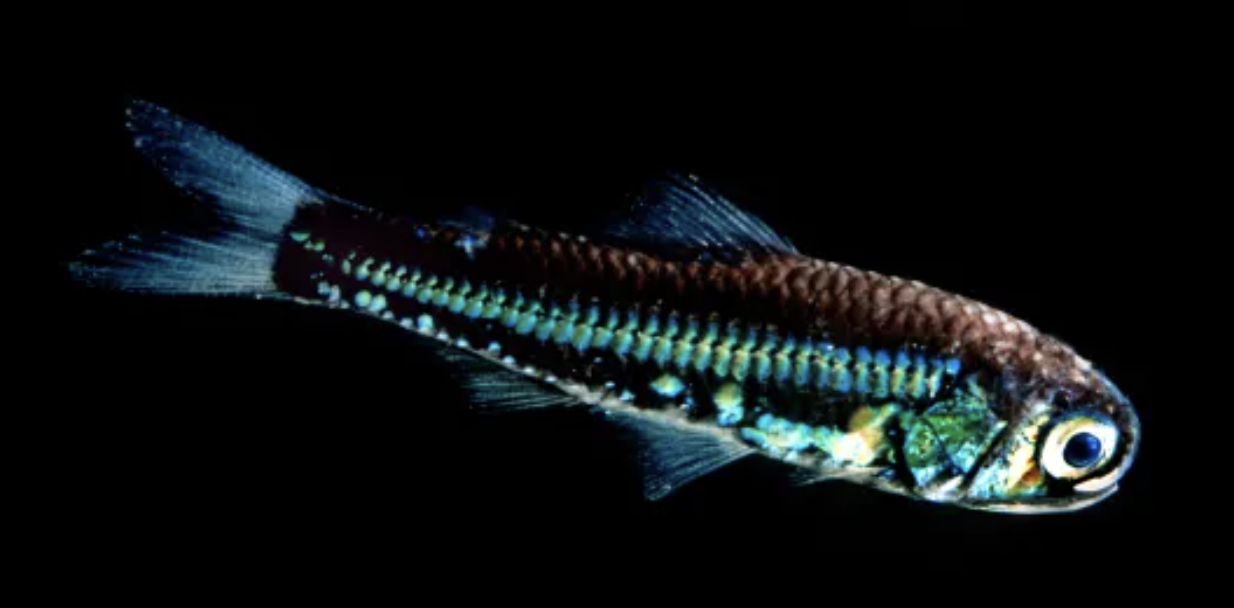
Family myctopidae
Name origin: myctophos = “light-bearer” → (bioluminescent fish)
lanternfishes
Key traits:
>250 spp
global mesopelagic, many small photophores, dark to silvery body, schooling planktivores, diel vertical migration, major prey fish

Superorder Lamprimorpha
Name origin:
Key traits:
1 order
Order lampriformes
Name origin: lampros = “bright, shining” + morphē = “form” → “bright form” (refers to the metallic sheen of opahs and oarfishes)
oarfishes, opah, etc.
Key traits:
no true fin spines, maxilla excluded from gape, mouth protrusible, tropical and temperate epipelagic planktivores
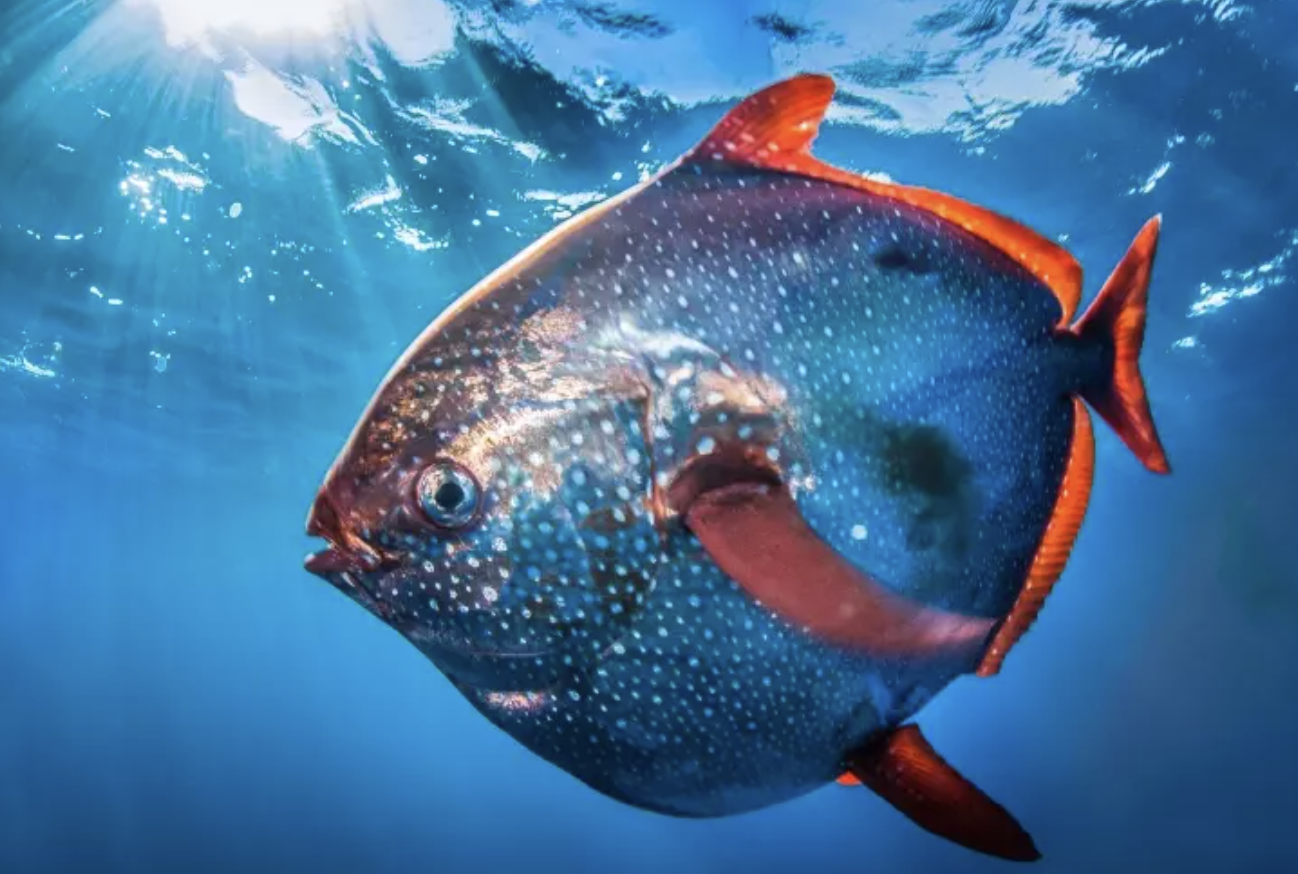

Superorder Paracanthopterygii
Name origin: para = “beside” + akantha = “spine” + pteryx = “fin” → “beside the spiny fins” (near relatives of spiny-finned fishes)
paracanthopterygians
Key traits:
5 orders
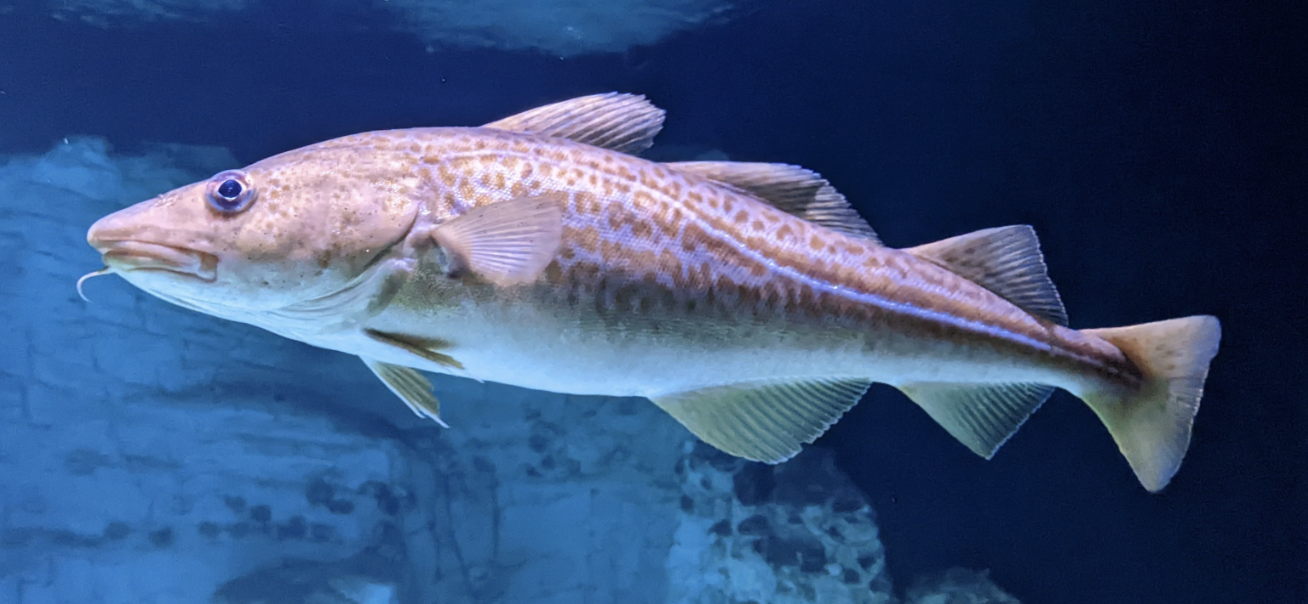
Order Gadiformes
Name origin: gadus = “codfish” + -formes = “form” → “cod form”
cods, pollocks, hakes, rattails, etc
Key points:
global temperate marine, pelvics below or in front of pectorals (or absent), no spines, scales usually cycloid, maxilla excluded from gape, swim bladder physoclistic (not connected to the digestive tract)

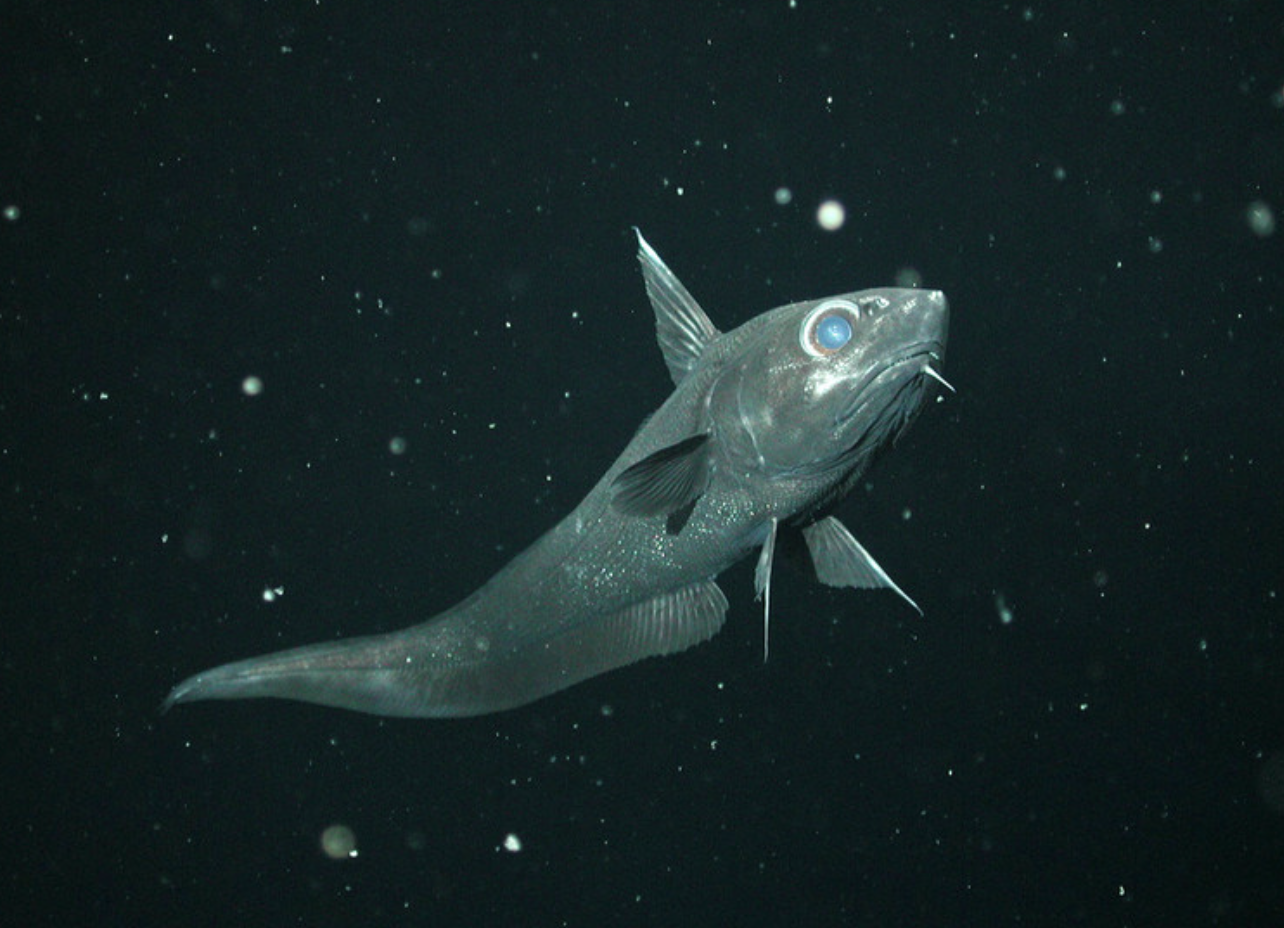
Family Macrouidae
Name origin: makros = “long” + oura = “tail” → “long-tail” (rattails)
rattails/grenadiers
Key traits:
405 spp
global deep seafloors, large head with tapering bodies, 1st dorsal with spine like soft ray, followed by short elongated 2nd dorsal, elongated anal fin, some with barbel and photophores, carnivores

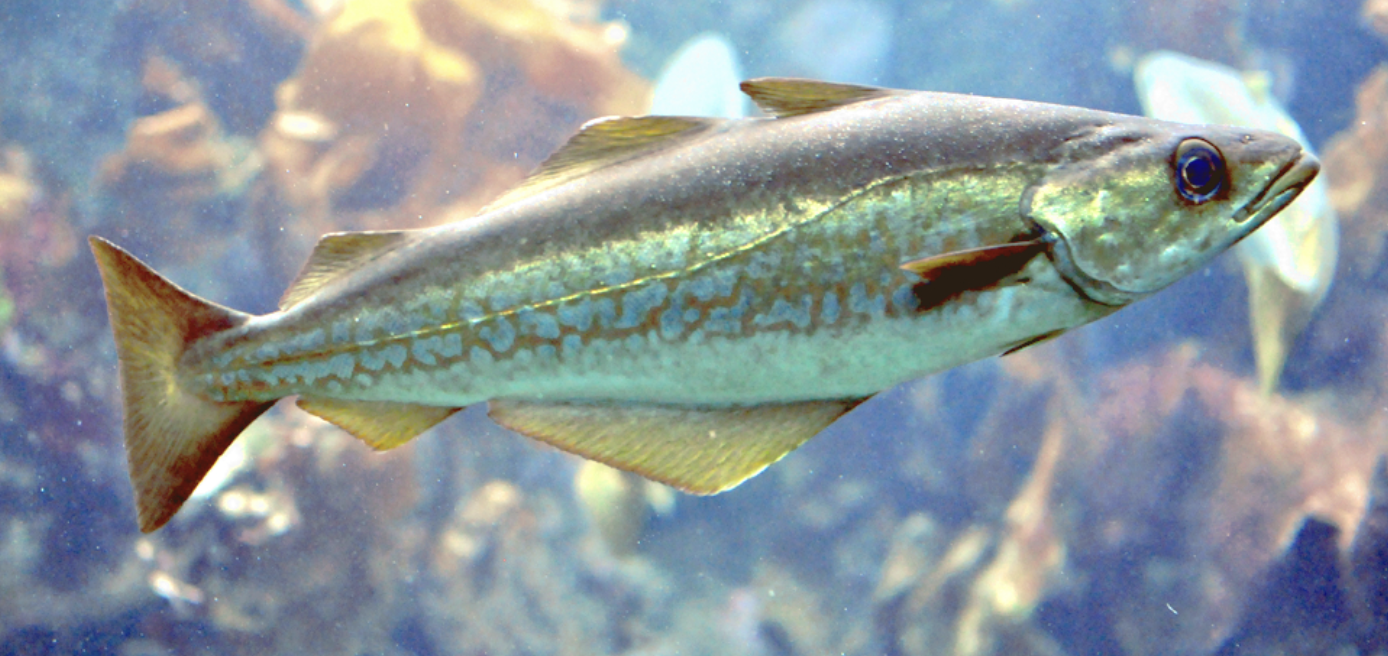
Family Gadidae
Name origin: gadus = “cod” → “cod family”
cod, haddock, whiting, pollock
Key points:
25 spp
1-3 dorsal fins, 1-2 anal fins, pelvics (often jugular), most have barbels, dermersal carnivores

Superorder Acanthopterygii
Name origin: akantha = “spine” + pteryx = “fin” → “spiny fin”
spiny finned fishes
Key points:
~17,000 spp
two major feeding innovations: jaw mobility/protrusion, pharyngeal jaw and tooth diversity
physoclistous swimbladder
pectoral fins high and vertical
2 dorsal fins
at least one spine on anal fin
symmetrical caudal fin with fused basal elements
Order Beryciformes
Name origin: beryx = “a kind of red sea fish” + -formes = “form” → “beryx form”
bigscales, alfonsinos, whalefishes, gibberfishes, pricklefishes
Key traits:
104 spp
global tropical temperate, mostly deep sea, planktivores and carnivores
weak/absent fish spines, reduced centoid like scales, some have photophoresglobal temperate marine, pelvics below or in front of pectorals (or absent), no spines, scales usually cycloid, maxilla excluded from gape, swim bladder physoclistic (not connected to the digestive tract)

Order Holocentriformes
Name origin: holos = “whole” + kentron = “spine” or “sting” + -formes = “form” → “whole-spined form”
squirrelfishes and soldierfishes
Key traits:
90 spp, 15 in Hawaii
global coral reefs, dorsal divided by notch, forked caudal, 1 pelvic spine, 4 anal spines, rough centoid scales, large eyes and reddish body

Order Ophidiiformes
Name origin: ophis = “snake” + -formes = “form” → “snake form” (eel-like fishes)
cusk eels
Key traits:
558 species
pectoral fins high and vertical, pelvic fins under head or absent, long dorsal and anal fins, carnivores
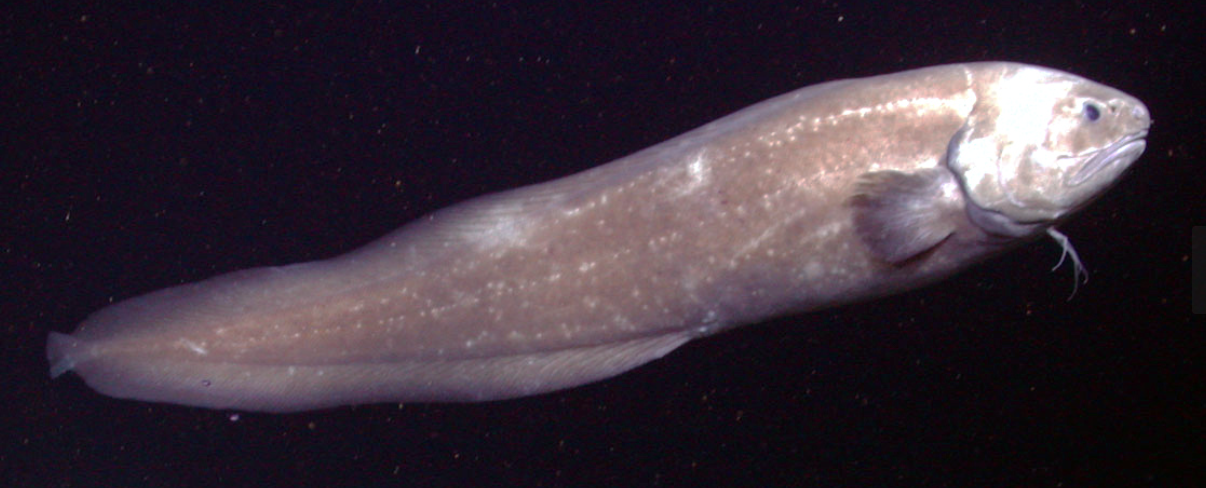

Order Mugiliformes
Name origin: mugil = “mullet” + -formes = “form” → “mullet form”
mullets
Key traits:
Family Mugilidae
80 spp, 2 in Hawaii
shallow tropical temperate marine and brackish, widely separated 4 spine dorsal and soft dorsal, cycloid-ish scales, pectorals high on body
pelvics subdominal, lateral line pores diffuse, teeth small or absent, long gill rakers, muscular gizzard

Order Antheriniformes
Name origin: athēr = “spike” or athērina = “a small silvery fish” + -formes = “form” → “silverside form”
atheriniformes
Key traits:
382 spp (half freshwater)
dorsal fins flexible and usually separated, pectorals usually high on body, pelvics abdominal
lateral line reduced or absent
Family Atherinidae
Name origin: athērina = “a small silvery fish”
old world silversides
Key traits:
body translucent with silvery lateral stripe
schooling planktivores
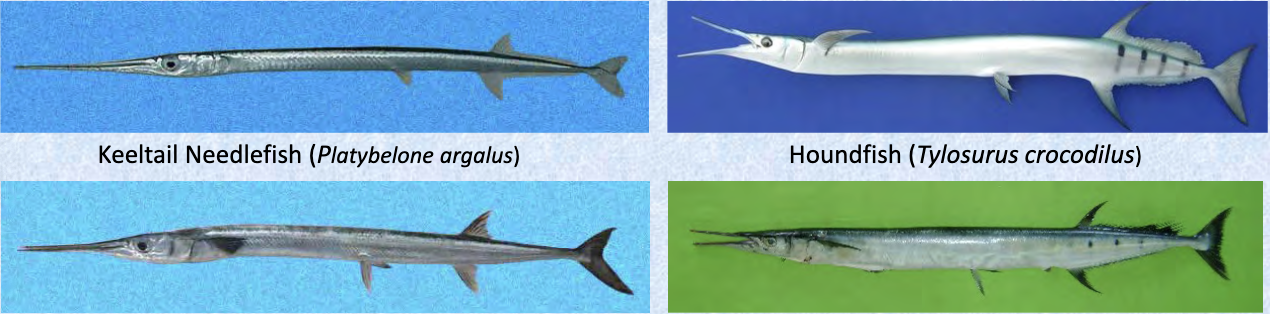
Order Beloniformes
Name origin: belone = “needle” + -formes = “form” → “needle form”
beloniformes
Key traits:
286 spp
mouth not protrusible, lower caudal lobe often extended
silvery near surface dwellers
Family Belonidae
Name origin: belone = “needle”
needlefishes
Key traits:
44 spp, 4 in Hawaii
epipelagic oceanic to coastal/freshwater
sharp needlelike teeth, elongated jaw, dorsal and anal fins set back
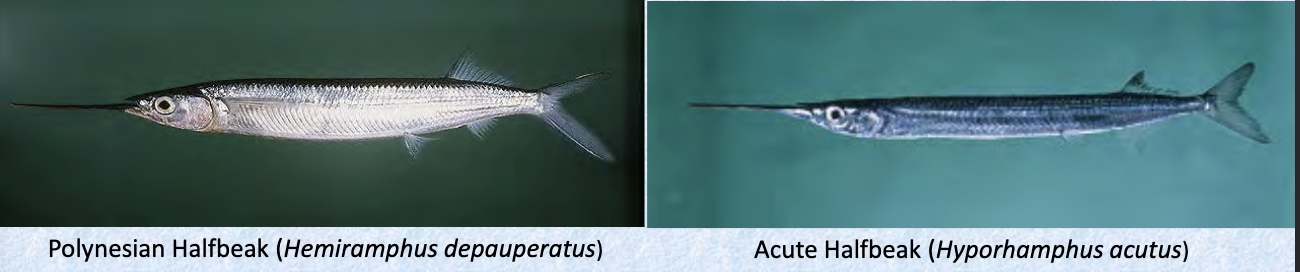
Family Hemiramphidae
Name origin: hemi- = “half” + ramphos = “beak” → “half-beak”
halfbeaks
Key points:
61 spp, 2 in Hawaii
epipelagic coastal/ few freshwater
elongated lower jaw only, smaller teeth, dorsal and anal fin set back
no stomach, pharyngeal mill
Family Exocoetidae
Name origin: exo = “outside” + koite = “bed” (but here coetus means “to lie” or “rest”) — however, Exocoetus literally means “sleeping outside (the sea)”
flyingfishes
Key traits:
74 spp, 9 in Hawaii
epipelagic oceanic to coastal, unique jaw protrusion
elongated pectorals that allow for gliding propelled by asymmetrical caudal
schooling planktivores, attatch eggs to floating objects
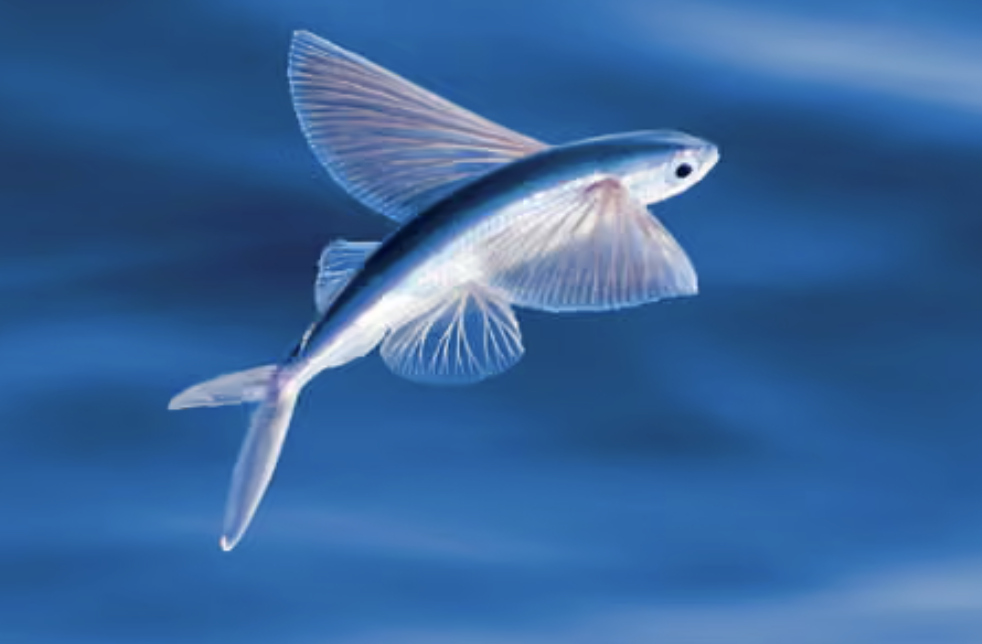

Order Cyprinodontiformes
Name origin: kyprinos = “carp” + odous (odont-) = “tooth” + -formes = “form” → “carp-tooth form”
topminnows, killifishes, pupfishes, livebearers
Key traits:
1,424 spp
global (mostly freshwater), dorsal and caudal often set back
caudal truncated or rounded, pectorals low on body, pelvics may be absent
lateral line mostly on head

Subseries Percomorpha
Name origin: “perch” + Greek morphē = “form” → “perch form”
Key points:
8 orders
most derived fishes
mostly marine, each pelvic fin with 1 fin and 5 soft rays
anteriorly placed pelvic girdle connected to pectoral girdle by ligament
Order Gasterosteiformes
Name origin: gastēr = “stomach” + osteon = “bone” + -formes = “form” → “stomach-bone form” (refers to bony plates along the belly)
gasterosteiforms
Key traits:
26 spp
mostly freshwater, dermal armor plates
dorsal and anal often posterior
small mouths, eat small invertebrates
Family Gasterosteidae
Name origin: “stomach-boned”
sticklebacks
Key traits:
16 spp
temperate zone, marine but some freshwater
carnivorous
isolated spines in their dorsal fins, no scales
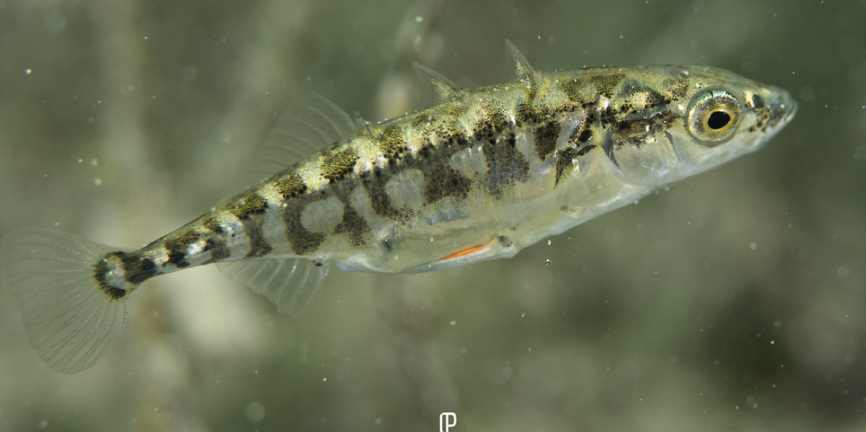

Order Syngnathiformes
Name origin: syn = “together” + gnathos = “jaw” + -formes = “form” → “fused-jaw form”
Snygnathiforms
Key traits:
353 spp
temperate to tropical marine, small mouth, usually at the end of tubular snout, bony plates
Family Syngnathidae
Name origin: “fused-jaw family”
seahorses and pipefish
Key traits:
322 spp, 9 in Hawaii
seahorses with elongated tail vs pipefish elongate, dorsal fin propelled
suction feed zooplankton, sexual roles reversed
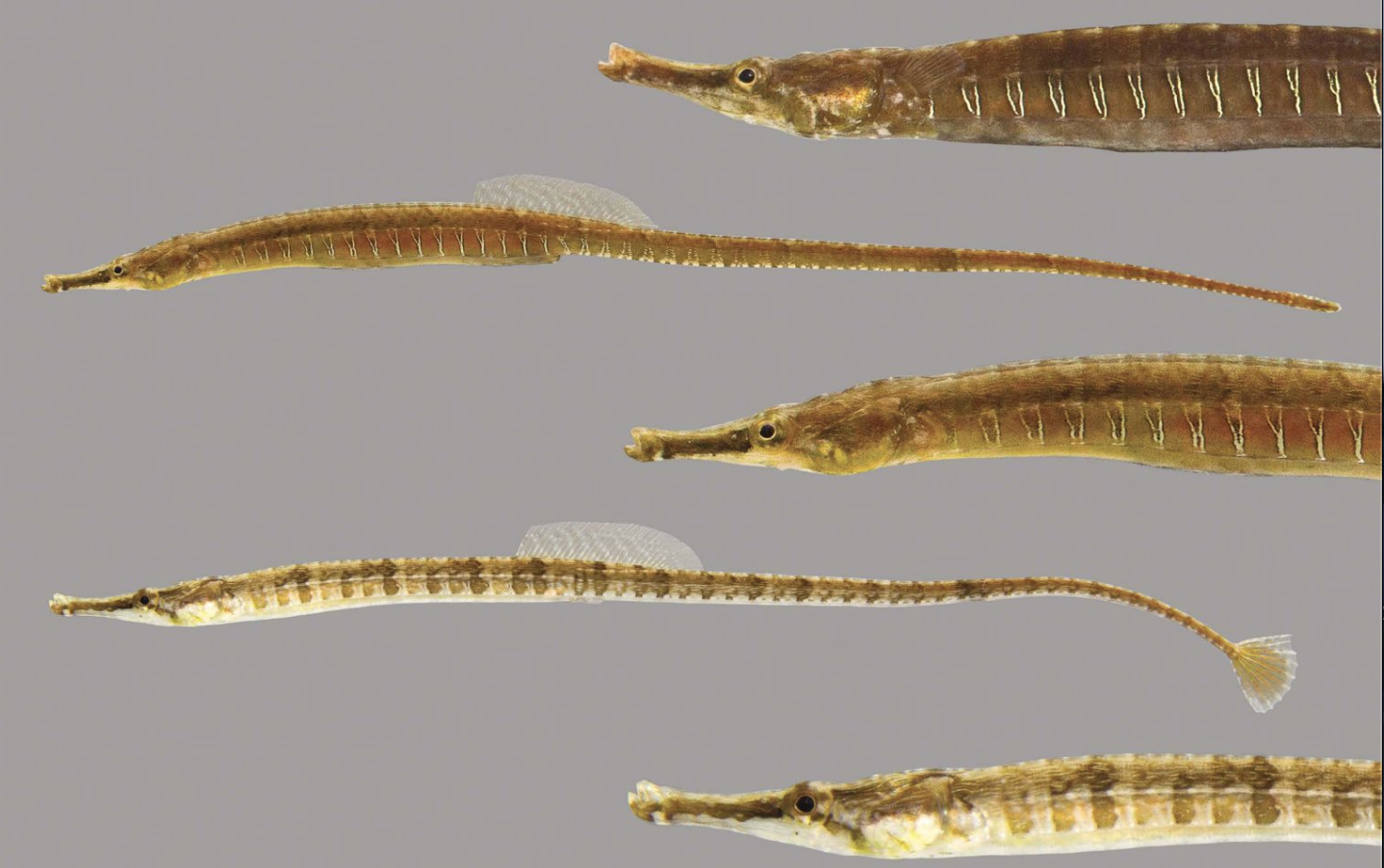

Order Aulostomidae
Name origin: aulos = “pipe” + stoma = “mouth” → “pipe-mouth”
trumpetfish
Key traits:
3 spp, 1 in Hawaii
elongate, compressed, posterior dorsal and anal, rounded caudal, chin barbel, stalking piscivore

Family Fistulariidae
Name origin: fistula = “tube, pipe” → “tube fish”
cornetfishes
Key traits:
4 spp, 1 in Hawaii
temperate to tropical coastal marine, small mouth usually at the end of tubular snout, bony plates
Order Scorpaeniformes
Name origin: scorpaena = “scorpionfish”
scorpaeniforms
Key traits:
1,480 spp
mostly marine, all depths, most with suborbital stay
spiny head, dorsal, anal, and pelvic fins
pectorals usually rounded, carnivores
Family Scorpaenidae
Name origin: scorpaena = “scorpionfish”
Scorpionfishes
Key traits:
223 spp, 25 in Hawaii
coastal indian and pacific
some with venomous dorsal, anal, and pelvic spines
demersal/benthic and cryptic ambush predators
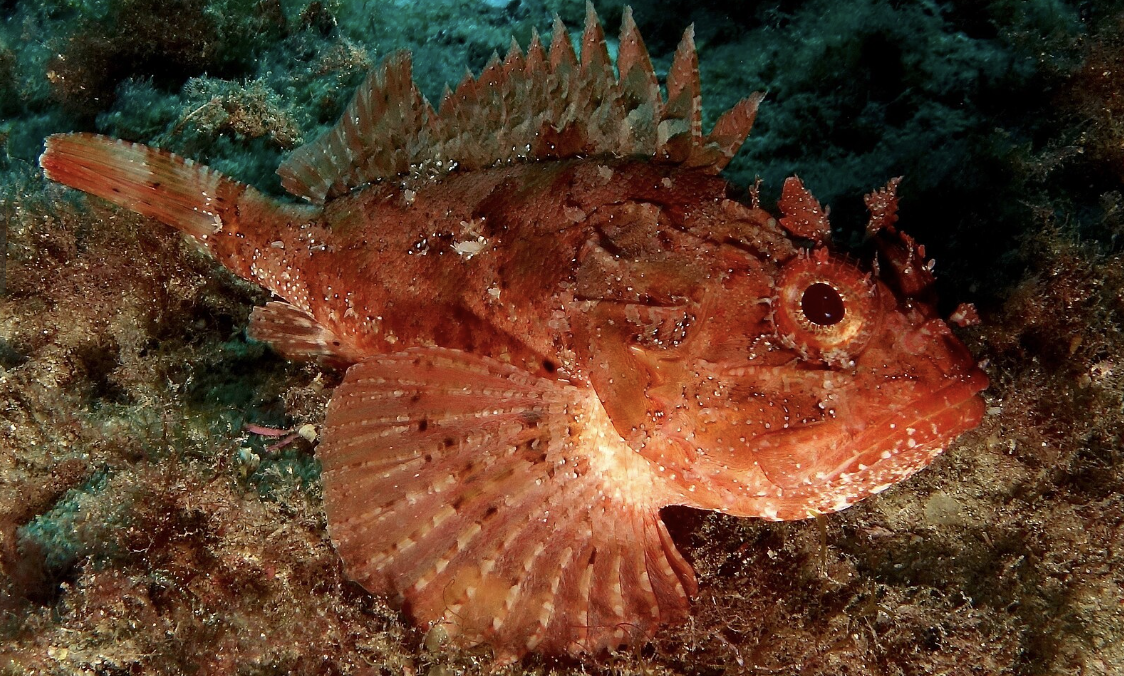

Family Cottidae
Name origin: cottus = “a kind of small fish”
sculpins
Key traits:
294 spp
not very spiny, relatively depressed, blunt head, tapering body
gill membrane fused, lack scales
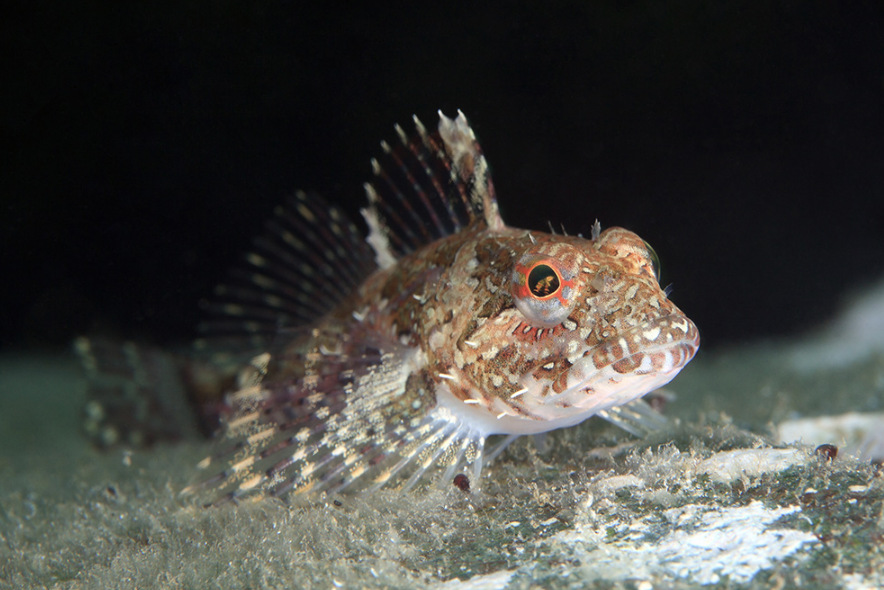

Family Liparidae
Name origin: liparos = “fat, oily, smooth” → “smooth ones”
snailfishes
Key traits:
444 spp
all depths, not spiny, relatively compressed, elongated body, most with fused pelvics
dorsal-caudal-anal confluent

Order Perciformes
Name origin: perca = “perch” + -formes = “form” → “perch form”
Perch-like fish
Key traits:
>10,000 spp
dominate shallow habitats, mostly ctenoid or cycloid scales
dorsal, anal, pelvic fin spines, pelvics thoracics with 1 spine and 5 or fewer soft rays
pectoral fins lateral and vertical
caudal fin rays, maxilla excluded from gape
swim bladder physoclitstous
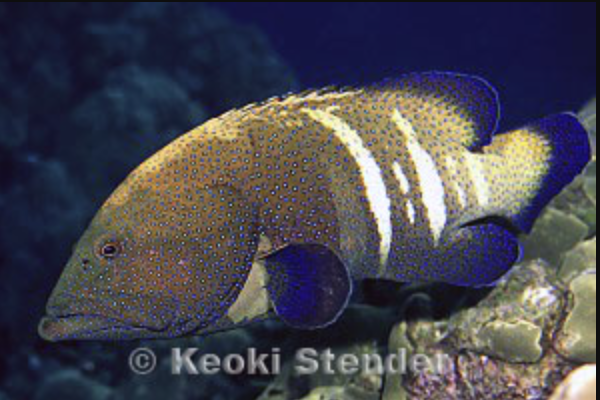
Family Serranidae
Name origin: serra = “saw” → “saw-edged” (refers to serrated fin spines)
sea basses, groupers, etc
Key traits:
598 spp
tropical temperate
most with 33 opercular spines, dorsal continuous, 3 anal spines, pelvic 1 spine + 5 soft rays
hermaphroditic, carnivores

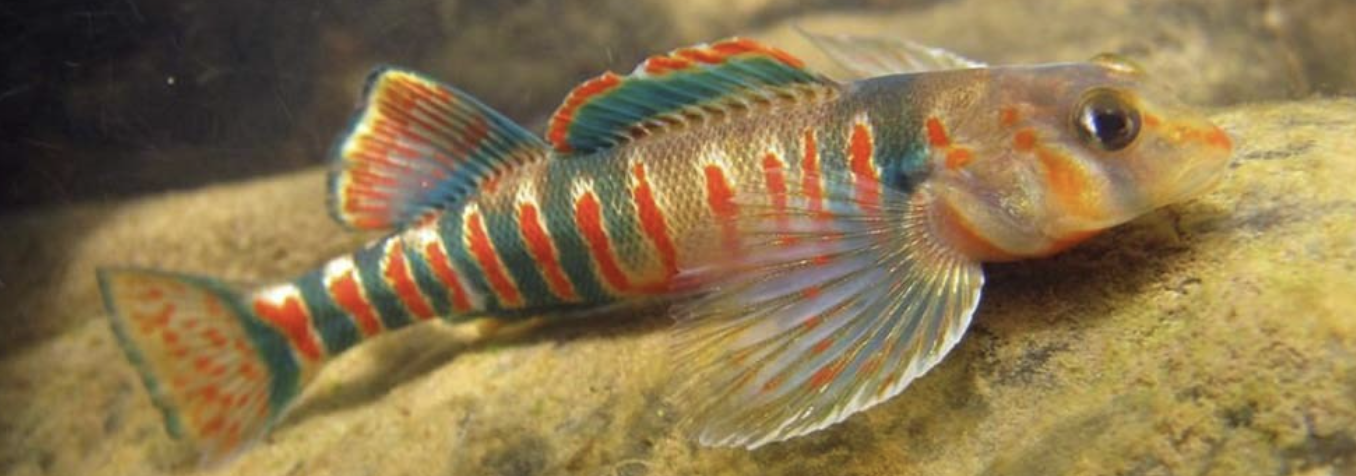
Family Percidae
Name origin: perca = “perch” → “perch family”
darters, perches, etc
Key traits:
242 spp
freshwater, N. Hemisphere
mostly separated dorsal fins and 2 anal spines
pelvic 1 spine + 5 soft rays, insectivores

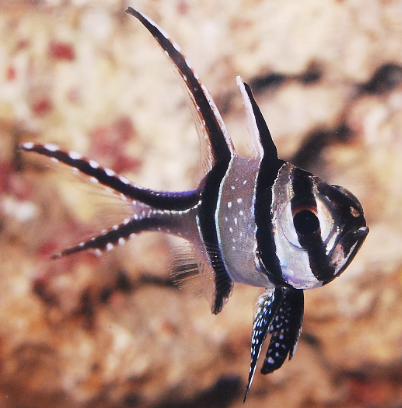
Family Apogonidae
Name origin: apogon = “without beard” → “beardless ones” (cardinalfishes lack chin barbels)
cardinalfishes
Key traits:
385 spp
coral reefs ( few brackish and freshwater)
separate dorsal fins, 2 anal spines, large eyes
nocturnal planktivores

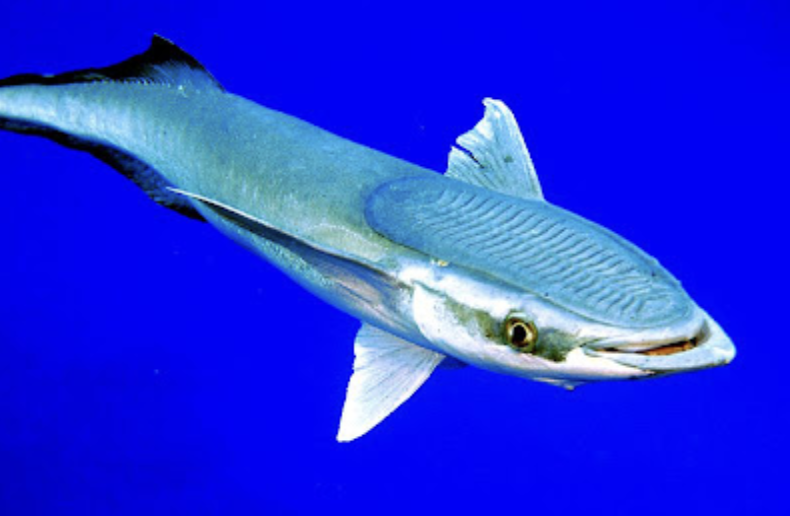
Family Echeneidae
Name origin: echein = “to hold” + naus = “ship” → “ship-holder” (remoras cling to ships or sharks)
remoras and sharksuckers
Key points:
8 spp, 4 in Hawaii
global warm marine
1st dorsal modified into sucking disk, superior mouth, no dorsal/anal spines
no swim bladder (ride on sharks, mantas, marine mammals, turtles)
eat food scraps and clean hosts

Family Caragidae
Name origin: carangus = “a fish like a jack” → “jacks and trevallies”
jacks, trevallies, scads, pompanos, etc
Key traits:
151 spp, 22 in Hawaii
compressed silvery body, some with dorsal anal finlets
1st dorsal 4-8 spines, 2nd dorsal 1 spin, 3 anal spines
forced caudal with slender peduncle
schooling midwater predators

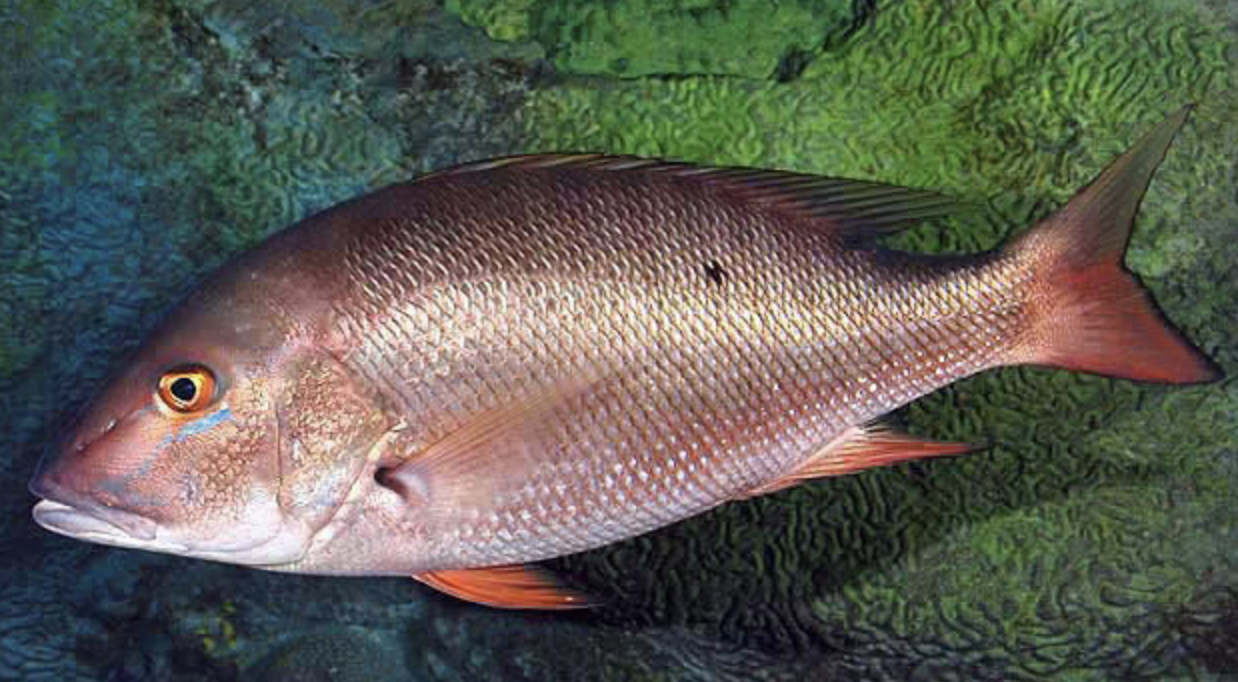
Family Lutjanidae
Name origin: lutjan = “snapper”
snappers
Key traits:
113 spp, 14 in Hawaii
reefs
bass-like body with straight forehead profile dorsal continuous or notched
3 anal spines, canine teeth, maxilla slips beneath preorbital

Family Haemulidae
Name origin: haimulos = “grunting” → “grunters” (refers to the croaking sound they make)
grunts and sweetlips
Key points:
136 spp
bass-like body with variable forehead profile, eyes larger than snappers
small mouth and teeth, “grunt by grinding pharyngeal teeth
nocturnal schooling demersal carnivores

Family Scaienidae
Name origin: skiaena = “sea-fish that makes a sound”
croakers and drums
]
Key points:
297 spp
global coastal marine/brackish/freshwater
molar like pharyngeal teeth, lateral line extends to end of caudal
long notched dorsal, swimbladder usually branched with sound producing vibrating muscles
![<p>croakers and drums</p><p></p><p>]</p><p>Key points:</p><ul><li><p>297 spp</p></li><li><p>global coastal marine/brackish/freshwater</p></li><li><p>molar like pharyngeal teeth, lateral line extends to end of caudal</p></li><li><p>long notched dorsal, swimbladder usually branched with sound producing vibrating muscles</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/34f41d30-ab95-4e29-96ca-70efcb140ac2.png)