Section B
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Define: Development
The progress of a country in terms of reaching an acceptable standard of living and quality of life.
Which organisation organises countries into LIC, NEE and HIC?
World Bank.
Which sector dominates LIC countries?
Primary sector.
Which sector dominates NEE countries?
Secondary sector.
Which sector dominates HIC countries?
Tertiary sector.
Calculate: GDP
Total value of goods/services produced within a country divided by its population.
Calculate: GNI
Country’s total income divided its population.
What are the advantages of GNI?
Converted Into US dollars, making it easier to compare the standard of living of countries across the world.
What are the disadvantages of GNI?
It is an economic measure of development and doesn’t take social measures like quality of life into account.
Average figures so wealthy people can skew or distort the data.
Income of people in the informal economy or subsistence farming not included in data, making it less accurate.
Give one disadvantage of using an economic measure of development.
Doesn’t take social measures like quality of life into account.
Average figures/per person so doesn’t account for extremely wealthy people that can skew or distort the data.
Define: Birth Rate
Number of live births per 1,000 of the total population.
If a country has a higher birth rate, does this suggest a country is a more or less developed country?
Less developed.
If a country has a lower birth rate, does this suggest a country is a more or less developed country?
More developed.
What are the limitations of birth rate?
Birth rate policies can distort data, such as China’s pervious 1 child policy so more or less children may be born if incentives or disincentives are offered.
May not be accurate because there may nit be a reliable system of recording births.
Define: Death Rate
Number of deaths per 1,000 of the population.
If a country has a higher death rate, does this suggest a country is a more or less developed country?
Less developed.
If a country has a lower death rate, does this suggest a country is a more or less developed country?
More developed.
What are the limitations of death rate?
Poor measure of development as it may be high due to aging population, such as in Japan.
Not all child deaths are reported in remote areas so may be higher than reported number.
Define: Infant Mortality Rate
Number of children that do nit survive to one year of age per 1,000 live births that year.
What are the limitations of infant mortality rate?
Not all child deaths are reported in remote areas so may be higher than reported number.
Define: Life Expectancy
Average number if years a person is expected to live for.
What are the limitations of life expectancy?
May be misleading in countries with high infant mortality rates.
Define: Literacy Rate
Percentage of people with basic reading and writing skills.
What are the limitations of literacy rate?
Difficult to measure in conflict zones and squatter settlements.
What are the limitations of people per doctor?
Many now seek help or device via mobile phone rather than doctor.
What are the limitations of percentage if people with access to safe water?
People may have access but high costs mean they cannot take advantage of it.
Which measure of development combines income, life expectancy and education levels?
HDI.
Why is HDI a composite measure?
It uses 3 factors: life expectancy, GNI and average years of education.
If a country has a HDI that is closer to 1, is it more or less developed?
More developed.
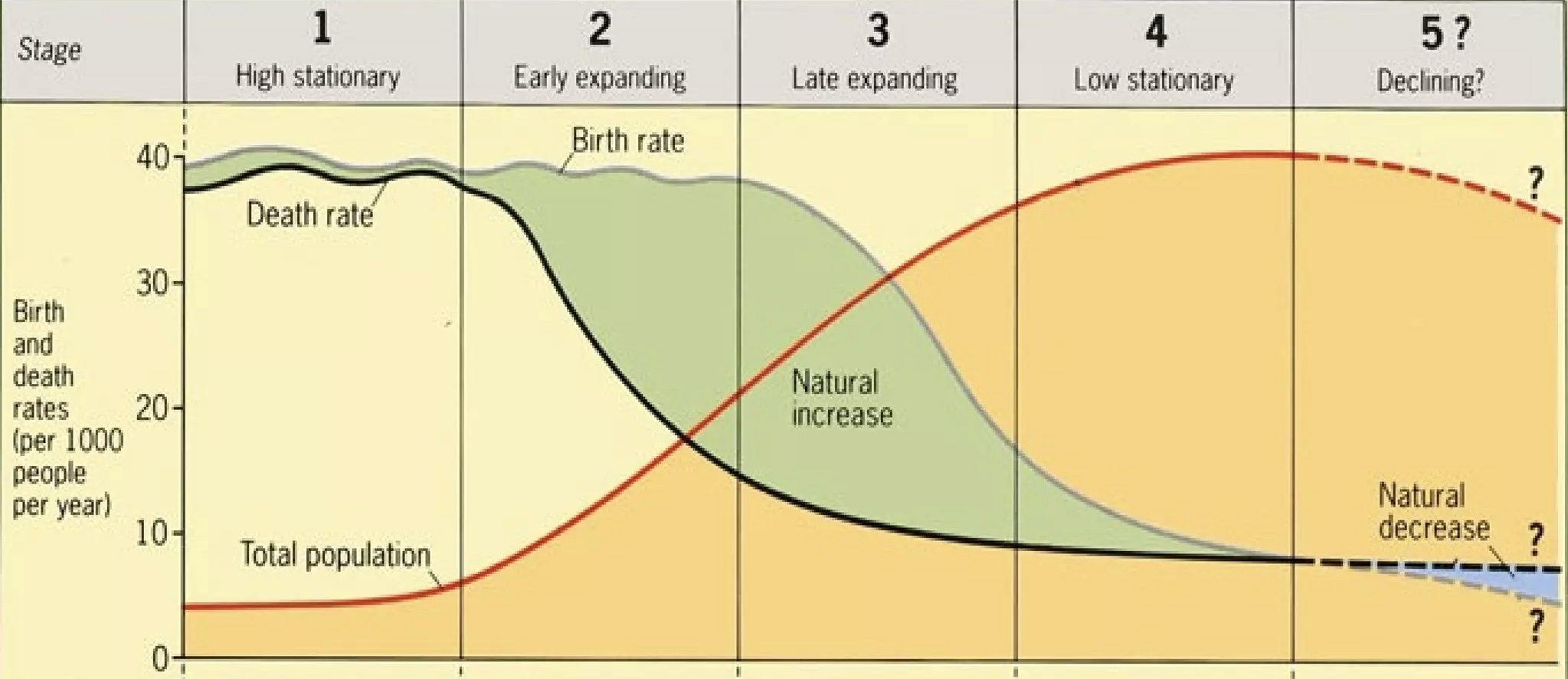
What does this diagram show?
The Demographic Transition Model.
In Stage 1 of the DTM, is there a low or high population?
Low population.
Which countries are in Stage 1 of the DTM?
No countries but some tribes.
Describe how Stage 1 of the DTM links to levels of development.
High birth rate due to subsistence farming so kids need to work on farms, limited knowledge of family planning/contraception and limited access to doctors, hospitals and medicines. High infant mortality rate also means that families have more children to ensure they survive to adulthood.
High death rate due to limited access to doctors,hospitals and medicines and poor living conditions, increasing spread of disease.
Which countries are in Stage 2 of the DTM?
Low Income Countries.
In which Stage of the DTM does natural increase occur?
Stage 2.
Describe how Stage 2 of the DTM links to levels of development.
Reflects the demographics of most Low Income countries.
Improvements in basic healthcare has lowered death rate and infant mortality rate.
However, birth rate is still high because the primary sector is still dominant and therefore, children are still needed to work o family farms.
Suggest how population change in Stage 2 of the DTM may have positive economic impacts.
High birth rate creates a large young population, providing a future large workforce and encouraging new businesses and ideas over time.
Rapid population growth increases demand for food, housing and services, stimulating the economy and creating more jobs.
Suggest how population change in Stage 2 of the DTM may have negative economic impacts.
High birth rate means government may struggle to fund education/school, healthcare and housing.
Increasing population may cause a strain on public services, like hospitals, schools and infrastructure, and limit economic development as jobs may not be created fast enough, leading to unemployment or work in the informal economy.
Which countries are in Stage 3 of the DTM?
Newly Emerging Economies.
Describe how Stage 3 of the DTM links to levels of development.
Reflects the demographics of Newly Emerging Economies.
Birth rate has decreased due to the availability of contraception, increased family planning and less need for children to work in farms due to a dominant secondary sector. Also, urbanisation and higher living costs encourages smaller families.
Low infant mortality rate also removes the need for larger families.
Death rate has decreased due to improvements in living standards and healthcare.
Suggest how population change in Stage 3 of the DTM may have positive economic impacts.
Falling birth rates mean that money needed to invest in maternity services and schools reduce, allowing for money to be spent on developing industry and other services in the country. Households also have more money available to spend in the economy.
Total population also increases so there’s more people to work, boosting GNI and tax revenue to invest in more infrastructure, education and healthcare.
Suggest how population change in Stage 3 of the DTM may have negative economic impacts.
Growing population leads to pressure on jobs, creating unemployment and a strain on public services like schools, healthcare and housing, causing overcrowding.
Which countries are in Stage 4 of the DTM?
High Income Countries.
Describe how Stage 4 of the DTM links to levels of development.
Reflects the demographics of High Income Countries.
Low birth rate due to accessible contraception, increased family planning, urbanised lifestyles with high living costs encourage smaller families. Social values change where women choose to study or work rather than get married and have children.
Low infant mortality rate also removes the need for larger families.
Low death rate due to excellent healthcare and high standards of living.
In Stage 4 of the DTM, is there a low or high population?
High population.
Suggest how population change in Stage 4 of the DTM may have positive economic impacts.
Low death rate and stable population growth creates a stable and reliable workforce which businesses benefit from and they may invest more in training skilled workers.
Low birth rate means less money spent on schools and childcare, increasing the amount of tax revenue that can be spent on infrastructure.
Suggest how population change in Stage 4 of the DTM may have negative economic impacts.
Slow and stable population growth may reduce the supply of workers.
Slightly ageing population means more elderly people may be unable to work, leading to less tax for the government, which is worsened by the fact that they have to pay the elderly pension. Also, cost more in healthcare and care homes as they may require treatment, which is harder to fund with the pressure of paying for pensions and receiving less tax from workers.
Give an example of a country in Stage 5 of the DTM.
Germany and Japan.
Which stage of the DTM links to natural decrease?
Stage 5.
Describe how Stage 5 of the DTM links to levels of development.
Birth rate falls below death rate as many women often prioritise education and careers, over family and marriage. High urbanisation also means high living costs and limited space so small households are more practical.
Excellent healthcare keeps death rate low but may also lead to ageing population.
Suggest how population change in Stage 5 of the DTM may have positive economic impacts.
Decreased birth rates and ageing populations means reduces the work force however labour shortages may lead to higher wages to improve SOL for workers and employers may invest more in training staff. Ageing population increases demand for jobs in healthcare or care services and give women or older workers more opportunities.
Businesses may invest in technology to replace labour, increasing productivity and efficiency in the long term.
Suggest how population change in Stage 5 of the DTM may have negative economic impacts.
Ageing populations means more elderly people may be unable to work, leading to less tax for the government, which is worsened by the fact that they have to pay the elderly pension. Also, cost more in healthcare and care homes as they may require treatment, which is harder to fund with the pressure of paying for pensions and receiving less tax from workers.
Birth rate decreases, meaning that there’s less people to work. School closures may lead to teachers losing their jobs.
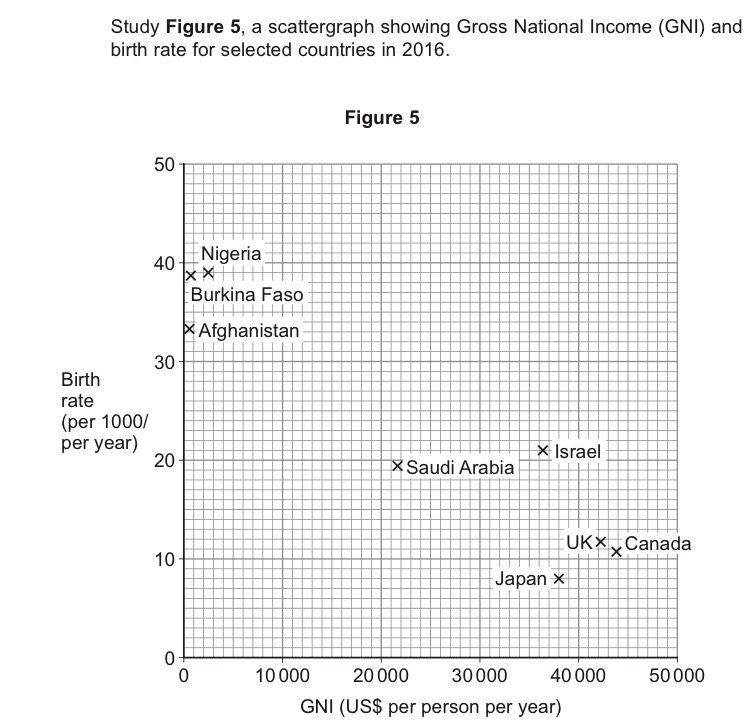
Japan is in Stage 5 of the DTM and is a highly developed country. Explain this statement using Figure 5.
Figure 5 shows a negative correlation between GNI and birth rate. Birth rate falls as the DTM progresses, alongside economic growth, shown here by Japan’s high GNI but low birth rate.
As people become wealthier they realise they don’t need to have so many children, decreasing birth rate.
As countries’ GNI grows, they can invest in health care which means lower infant mortality so fewer children need to be born in an effort to make sure some survive.
As the birth rate begins to fall, more money will become available in households and more widely in the economy for investment which will increase GNI.
In which Stage of the DTM, does birth rate begin to drop?
Stage 3.
In which Stage of the DTM, does death rate become higher than birth rate?
Stage 5.
What are the causes of uneven development?
Landlocked, Tropical Environment, Weather/climate, Relief, Water shortages.
Trade, Poverty.
Colonialism and Conflict.
Outline how one historical factor can lead to uneven development.
Many LICs, such as in Africa, were colonised by powerful European countries . This meant that their resource and people were exploited and LICs were locked into trade deals that don’t benefit them, hindering their independent development.
Civil wars and conflict within countries means men are often at war rather than working and damage to infrastructure requires expensive rebuilding, disturbing economic development.
Outline how one physical factor can lead to uneven development.
Some countries are landlocked which makes it difficult to trade with other countries as they have no coast and trade by road is much longer/transports less.
Natural hazards as a result of extreme weather can cause damage which makes it hard to develop as money is spent on repairs or lead to crop failure, so farmers cannot make an income, damaging SOL.
Tropical environments can lead to tropical diseases due to pests, like Malaria, and if people are ill they can’t work and earn money. Also, less tax will then be paid to the government so less improvements to services and infrastructure.
Mountainous ares like Nepal can make it a struggle to build infrastructure like hospitals which may decrease life expectancy.
Outline how one economic factor can lead to uneven development.
Countries with high levels of poverty often rely on exporting raw materials through trade and HICs pay as little as possible for these goods so the country earns little money from trade.
Low profit means the government has less income from taxes to spend on healthcare, education, and infrastructure. This keeps people poor and limits development.
In contrast, wealthier countries trade manufactured goods and services, which have higher value and generate more profit. This allows them to reinvest money into development, widening the gap and causing uneven development.
How can a country’s relief lead to uneven development?
Relief is the shape and height of land. Mountainous ares like Nepal can make it a struggle to build infrastructure like hospitals which may decrease life expectancy.
How can a country being in a tropical environments lead to uneven development?
Tropical environments can lead to tropical diseases due to pests, like Malaria, and if people are ill they can’t work and earn money. Also, less tax will then be paid to the government so less improvements to services and infrastructure.
How can a country’s weather and climate lead to uneven development?
Natural hazards as a result of extreme weather can cause damage which makes it hard to develop as money is spent on repairs or lead to crop failure, so farmers cannot make an income, damaging SOL.
How can a country being landlocked lead to uneven development?
Some countries are landlocked which makes it difficult to trade with other countries as they have no coast and trade by road is much longer/transports less.
What are the consequences of uneven development?
Disparities in health and wealth + International migration.
Outline how uneven development can cause disparities in health.
Low Income Countries tend to have poorer healthcare and less highly skilled healthcare staff. LIC’s also often invest in war over healthcare, making the quality worse.
This means that people in those countries do not access high quality medical care, leaving to high rate of diseases and lower life expectancies to HICs.
Outline how uneven development can cause disparities in wealth.
HIC’s have a higher GNI and more evenly distributed wealth and therefore are very developed with better infrastructure, education, and job opportunities, which attract businesses and investment. This leads to higher wages and more wealth being created. In contrast, less developed areas may lack jobs, services, and investment, so people earn lower incomes and remain in poverty.
Outline how uneven development can cause international migration.
People move from poorer countries to richer ones for better paid jobs and improved quality of life. These are known as economic migrants.
Many people flee conflict in LICs and move to safer HICs and people can send remittances back home.
Migrants may also be encouraged to move to other countries as a source of cheap labour.
Name 8 strategies goes to reduce the development gap.
Investment, Industrial Development, Tourism, Aid, Debt Relief, Microfinance Loans, Intermediate Technology, Fairtrade.
Suggest how investment can help to reduce the development gap.
Countries, organisations and companies invest in LICs to increase their profits so that LICs can have more job opportunities and the government can improve infrastructure.
Higher employment and better infrastructure increase tax income for governments, which can be spent on healthcare and education. This helps poorer countries develop faster and reduces the development gap.
For example, 2,000 Chinese companies have invested in Africa such as hydroelectric power in Madagascar, providing electricity to countries therefore improving QOL, and the Tazara railway linking Tanzania and Zambia, providing jobs in the building of the road and improving trade between the two countries.
Suggest how industrial development can help to reduce the development gap.
Investing in factories can provide locals with job opportunities; working in the factory or constructing them. This increases SOL as people earn more income and more tax is paid for the government to use for industry and infrastructure.
Investing in healthcare or education can improve quality of life, life expectancy and HDI.
Also, manufactured goods sell at higher price in comparison to the raw materials so the country can boost its GNI through trade.
Does aid have to be repaid or is it a gift/donation?
Gift/donation.
Outline ways in which international aid has had an impact on a named LIC/NEE.
Can fund major infrastructure projects such as the Igna 3 Dam in the Democratic Republic of Congo to make electricity for the country.
The UK has given £350 million to Pakistan which has been spent on improving education facilities.
Water Aid has helped people provide clean water to over 12,000 people in their villages in Malawi so children can spend more time at school than collection water.
Suggest how debt relief can help to reduce the development gap.
Debt relief is when debts are reorganised or reduced.
Many LICs have debts that are so expensive that they cannot repay due to high levels of interest. They therefore spend more money on debt than services, infrastructure and development projects.
Debt relief allows them to spend less on debt and more on services like healthcare, increasing quality of life and life expectancy, which boosts HDI and reduces disparities in health.
If more people are fit to work, GNI can increase, reducing disparities in wealth.
In 2006, the International Monetary Fund agreed to cancel the debt of 19 of the world poorest countries, including Niger, Rwanda, Ghana, Ethiopia and Zambia.
Suggest how microfinance loans can help to reduce the development gap, using a named example.
Small scale financial loans support individuals or community to start a business, creating jobs to increase income.
The Grameen Bank in Bangladesh lent small loans to women to buy mobile phones. This allowed them to check market prices before selling farm produce, so they were not exploited and could earn a fair profit to support their families and improve SOL. The women could also charge villagers to use the phones, creating extra income to repay the loan. This increases income, reduces poverty, and helps local communities develop, which helps to reduce the development gap. As loans are repaid, the money is reused to help others.
State one characteristics of intermediate technology.
Tools/systems are simple and affordable.
Easy for locals to use and maintain without outside help.
Suggest how intermediate/appropriate technology can help to reduce the development gap.
Supports local development projects by using affordable, simple equipment and techniques that suit the needs and wealth of the local population.
It is cheap, easy to use, and easy to repair so local people can operate and maintain the technology themselves without relying on expensive imports or skilled workers from richer countries. This creates jobs, improves productivity, and increases incomes. As incomes rise, people can invest in education, healthcare, and businesses, helping poorer areas develop and reducing the development gap.
For example, local materials (sand, stones) build small dam to improve water supply in Adis Nila, an Ethiopian village. The project is low-cost and can be maintained by the local community. The improved water supply provides clean water for drinking and irrigation, which reduces disease and increases crop yields. Healthier people can work more, and higher food production can be sold for income.
Explain how fairtrade can reduce the development gap.
Farmers are usually paid very low wages and cannot escape poverty. An organisation promoting reasonable and fair wages for farmers and their goods in LICs gives them the chance to improve their SOL, providing an income for their families, and be invested back into the local community.
Investments to the locals may improve healthcare or education, improving HDI or literacy.
Give a named example of fairtrade to reduce the development gap.
Over 90% of small coffee farmers in Eastern Uganda have joined the Gumutindo Coffee Cooperation, allowing for coffee to be milled before roasting to add to its value.
Selling higher-value coffee means farmers earn more money than if they only sold raw coffee beans. Higher incomes reduce poverty and allow farmers to afford better healthcare, education, and housing. It also keeps the money in the local economy, creating more jobs and growing businesses.
Where is Tunisia?
North Africa.
Is Tunisia an LIC, NEE or HIC?
NEE.
What is the current population of Tunisia?
12.6 million people.
Which languages are spoken in Tunisia?
French and Arabic.
Temperatures can reach up to __ in Tunisia during the summer.
40°C.
What is the GNI of Tunisia?
US$ 4,320.
How many tourists has Tunisia attracted?
Around 7 million.
As a result of tourism in Tunisia, how many jobs were created?
370,000 jobs.
As a result of tourism in Tunisia, in 2020, what percenatge of Tunisias’s GDP was brought by tourists?
35%.
In Tunisia, what do tourists often buy?
Rugs.
In Tunisia, where do tourists often shop?
Local markets known as Souks.
How does the agricultural system benefit from tourism in Tunisia?
They supply food to hotels.
By how much have literacy rates risen by in Tunisia?
66% to 79/82%.
Suggest how the growth of tourism in an LIC/NEE may help to reduce the development gap.
Infrastructural improvements may directly improve economic measures of development + improvements to roads/airports improve the country’s trade, closing the development gap.
Other infrastructure may be in education which will improve social measures of development e.g. a rise in HDI or literacy scores. In Tunisia , literacy rates have risen from 66% to 79/82%.
In Tunisia, tourism has created 370,000 jobs in places like restaurants, transport, hotels, tour guides, souvenir shops etc. which educes unemployment and helps to lift people out of poverty, giving a better HDI and GNI score.
What are the limitations of tourism in Tunisia?
Water and land pollution due to litter on beaches and sewage from hotels pumped into the sea.
Leakage of profits as many Europeans book package holidays with companies like Jet 2 and Tui do European companies get the profit rather than Tunisia.
In 2015, two terrorist attacks aimed at tourists so multiple European government said that it was no longer safe to risk.
Describe the location of Nigeria.
Located in West Africa, bordering Benin, Niger, Chad and Cameroon as well as the Gulf of Guinea, in the Atlantic Ocean.
Outline the regional importance of Nigeria.
3rd largest secondary sector in Africa.
Highest GNI in Africa.
One Africa’s fastest growing economies and highest population.
Outline the global importance of Nigeria.
12th largest oil producer.
Bollywood is the second largest film industry.
5th largest contributor to UN peacekeeping.
Describe the social and cultural background of a named LIC/NEE country.
There are a number of different ethnic groups in Nigeria who have religious differences as some are Christian and others Muslim.
Three tribal groups dominate Nigeria - the Hausa, Fulani, Igbo and Yoruba.
There is religious conflict in Nigeria which has led to the rise of the Boko Haram terror group.
Nigerian football team won African cup of nations on three occasions and several players belong to Premier League club in the UK.
What are the two main religions in Nigeria?
Christianity and Islam.
Which 4 tribes are prevalent in Nigeria?
Hausa, Fulani, Igbo and Yoruba.
What is the name of Nigeria’s film industry?
Nollywood.