Nephron, Kidney, Raas
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Kieser, Jan 29
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What is Filtration?
High pressure movement of water and small solutes from the blood into the Bowman’s capsule.
What is Reabsorption? Where does it take place?
Moving needed substances (glucose, water, ions) from the filtrate back into the blood. The PCT, DCT, loop of henle, and collecting duct.
What is Secretion?
Active movement of waste ions (H+, K+) and drugs from the blood into the renal tubule for excretion.
Where does filtration occur? How does the blood get there?
Occurs in the Glomerulus. High blood pressure forces it into the Bowman’s capsule.
Where is the primary sight for reabsorption? What two things does it reclaim.
The PCT, reclaims nearly 100% of the bodies glucose and amino acids.
Where is the primary place where secretion happens. What is its purpose?
The DCT and the PCT. To fine tune blood pH and electrolyte balance.
During reabsorption and secretion, substances are exchanged between the renal tube and…
Peritubular capillaries.
(The renal tube is the ascending and descending loop of Henle)
What is the general flow of Blood?
Renal artery → afferent arteriole → glomerulus → efferent arteriole → peritubular/vasa recta → renal vein
What is the general flow of filtrate?
Bowman's capsule → PCT → Loop of Henle → DCT → collecting duct → renal pelvis → ureter
In reabsorption what is the process where water follows NA?
Osmosis
What 2 factors affect reabsorption?
Quantity of substance of filtrate
Rate of flow (Slow=more absorption, vice versa)
Examples of things that are secreted out.
Hydrogen Ions, potassium, drugs
What compound is Urine mostly?
Nitrogen-based including urea (broken down urea acids) - dark yellow means more solute in the filtrate.
What are some things filtered out of blood?
NaCl, water, vitamins, glucose, etc…
Why are red blood cells and large proteins (like albumin) NOT typically found in the filtrate after filtration?
To large to be filtered so they do not enter
If your body did not perform reabsorption, you would lose about ___ liters of fluid a day. List three vital substances the body must reabsorb to maintain homeostasis.
180 liters. Glucose b. Water c. Amino acids
Which process is considered "passive" because it relies on blood pressure rather than metabolic energy (ATP)?
Filtration because it uses blood pressure to move substances.
What process would remove H+ from blood if it was too acidic.
Secretion
Glomerulus to Bowman's Capsule: Blood pressure forces water and small solutes (like glucose and urea) across the capillary wall into the nephron. This is…
Filtration
In the ____, nearly 100% of the glucose that entered the filtrate is moved back into the peritubular capillaries. This is..
PCT, Reabsorption
To help regulate blood pH, the ____ actively moves H+ ions from the blood into the tubular fluid. This is…
DCT, secretion.
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT), Secretion.
As filtrate travels down the ___, water moves out of the tubule and back into the bloodstream. This is
Descending Loop of Henle/renal tubule. Reabsorption
Small molecules, regardless of whether they are "good" or "waste," are pushed out of the blood in the ____ based primarily on size. This is
Renal corpuscle (Glomerulus/ Bowman’s capsule). Filtration
Penicillin or other medications are often moved from the ____ into the renal tubule to be excreted. This is
Peritubular capillaries, secretion.
These building blocks of proteins are reclaimed from the filtrate in the ___ so they are not lost in the urine. This is
PCT, Reabsorption.
Under the influence of aldosterone, extra potassium is moved from the blood into ____. This is
the collecting duct, secretion
The very first process in urine formation where ____ is separated from blood cells and large proteins. This is
Plasma. Filtration
In the ______, sodium and chloride are moved out of the tubule to help maintain the medullary osmotic gradient. This is
Ascending limb. Reabsorption
Which typically has a larger diameter, the afferent or efferent arteriole?
Afferent is wider. The efferent restricts the exit, making the glomerulus force out fluid and solutes. Keeps glomerulus pressure high.
Which is permeable (allow to pass through) to Na, the descending or ascending loop of Henle?
The ascending loop
In which of the following is the majority of reabsorption done, the PCT, loop of Henle, or DCT?
PCT
Are large proteins filtered in the Bowman’s capsule?
No, large proteins are usually reabsorbed into the PCT
Which kidney sits lower and why?
Right side is lower, it gives space for the liver.
Which kidney is generally a little bit heavier than the other?
Left, about 10g heavier.
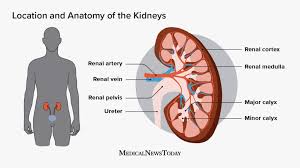
Label
Check.
How much blood does each kidney filter per day?
120-150
How much urine is produced per day?
1-2 quarts
How much urine can a bladder hold?
1.5-2 cups
Do you have voluntary control of the internal or external urethral sphincter
External
What does the descending tube do?
Rebabsorbtion of water mostly
What does the ascending tube do?
Absorption of Na+ mostly.
Job of Pct
reabsorbs most water..
Job of DCT
reabsorption and secretion of ions