multi store model
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Atkinson & Shiffrin (1968) multi store model
describes how information flows through the memory system, suggests memory is made up of 3 stores
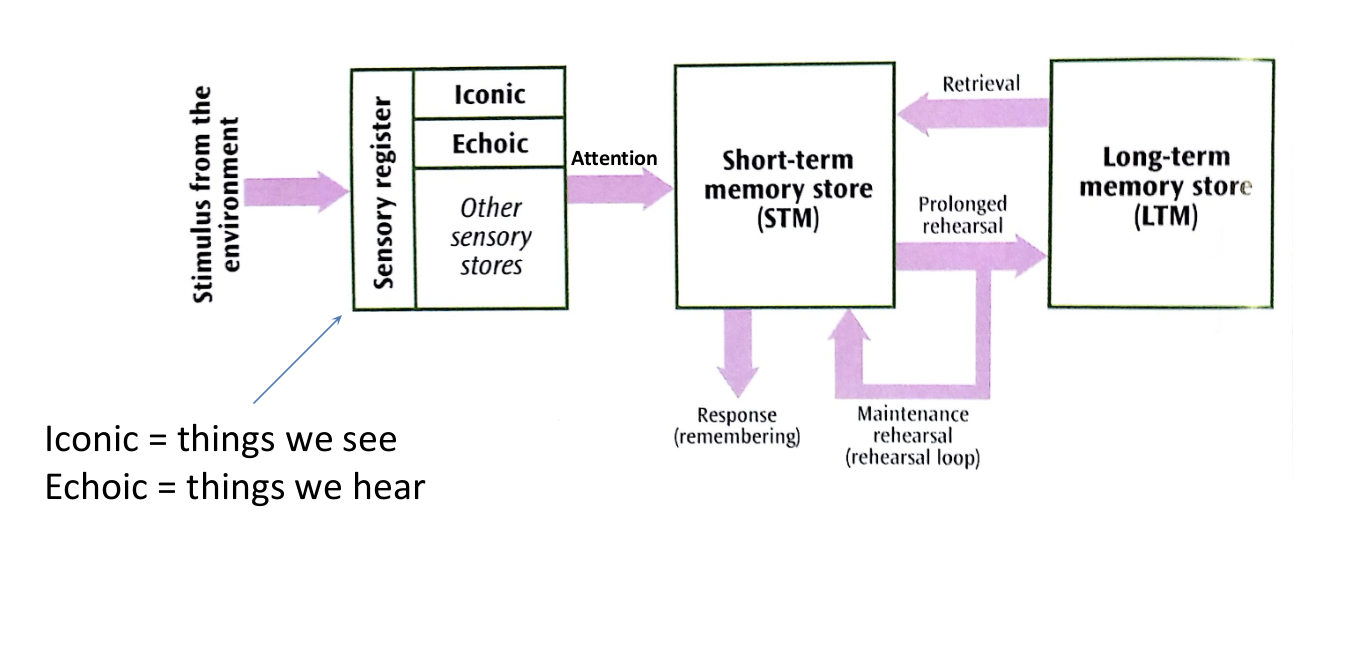
sensory register
all stimuli from the environment pass into the sensory register, we have 5 stores, one for each sense
duration: stays for a very brief period, 1/2 a second, before decaying or passing on to the STM store
coding: modality specific, depends on the sense
capacity: very high
we use mainly our iconic memory for visual information and our echoic memory for auditory information
little information from SR passes into memory
how is information passed from sensory register to STM?
information passes further into memory only if attention is paid
short term memory
capacity: thought to be 7+/- 2 items
duration: very small duration up to 30 seconds, can be lost within a few seconds if not rehearsed, items usually held in the STM store as sounds, most information lost before 18 seconds
coding: mainly visual and acoustic
if information is rehearsed (maintenance rehearsal) it is passed onto the LTM
we can often hold larger amounts of information by chunking where the information is consolidated into chunks
how is information passed from STM to LTM?
maintenance rehearsal occurs when we repeat (rehearse) material to ourselves, we can keep information in STM as long as we rehearse it, if its rehearsed enough it passes to LTM
long term memory
has a potentially limitless capacity and duration, difficult to prove
coding: semantic, the meaning and understanding
3 types of LTM:
episodic: memory of events
semantic: general knowledge
procedural: knowing how to do things
when we want to recall information from the LTM, it has to be transferred back to the STM by retrieval
primary-recency effect
well known experiment demonstrating the MSM, participants are read a list of words then have to recall them either immediately or after a distraction
recall of 1st and last words are best, recall for middle is poor
in immediate recall the first words are in the LTM as they have been rehearsed and transferred, last words are still being rehearsed in the STM, words in the middle are less well recalled as you were too busy rehearsing the 1st to remember them well
case study of KF- Shallice & Warrington 1970
MSM states STM is a unitary store i.e. only one type of STM
people suffering from amnesia shows this can't be true, KF had problems with information presented to him verbally (acoustic), his recall was much better when he could read them himself (visual)
strength of MSM- support showing STM and LTM are different
Baddeley (1966) found we tend to mix up words that sound similar when using our STM's so STM coding is acoustic
but we mix up words that have similar meanings when we use our LTM's so LTM coding is semantic
supports the MSM's view that these 2 memory stores are separate and independent
support showing STM and LTM are different counterpoint
despite such apparent support, the studies tend not to use everyday information eg faces, names, they use digits/ letters (Jacobs) or meaningless consonant syllables (Peterson & Peterson)
therefore MSM may not be a valid model of how memory works in everyday life where memory tends to involve meaningful information
limitation of MSM- evidence suggesting there is more than one STM store
KF had amnesia (Shallice and Warrington 1970), STM recall for digits was poor when he heard them, but much better when he read them
other studies confirm there may also be a separate STM store for non verbal sounds eg noises
therefore the MSM is wrong to claim there is just one STM store processing different types of information
limitation of MSM- prolonged rehearsal isn't needed for STM to LTM transfer
Craik & Watkins (1973) argued there are 2 types of rehearsal, maintenance and elaborative, maintenance (amount of rehearsal) is the one described in the MSM
but elaborative rehearsal is needed for long term storage, occurs eg when you link information to existing knowledge or think about its meaning
suggests the MSM doesn't fully explain how long term storage is achieved
evaluation of MSM- bygone model
MSM was a useful model that explained a lot of evidence at the time eg differences between STM and LTM
however it has become clear that it can't account for many research findings eg amnesia and oversimplifies the nature of STM, LTM and rehearsal
therefore, MSM was a good starting point for developing more valid models of memory that explain the research evidence better