oral histology and embryology exam 1 terms
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Fertilization-2.5 weeks
cell proliferation, migration, and some cellular differentiation
patterning
key process in development
patterning
a series of spatial and temporal events
differentiation
process where cells change into subpopulations with specific functions
induction
neighboring cells influence the fate of adjacent cells through signaling.
competent
refers to a cell's ability to respond to inductive signals and differentiate appropriately.
Hox genes
a group of genes that control the body plan and segment identity during embryonic development
growth factors
proteins that regulate cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation during development.
paracrine
a form of cell signaling where cells communicate with nearby cells through the release of signaling molecules.
autocrine
signaling where a cell produces signals that bind to receptors on its own surface, influencing its own behavior.
morula
develops 4 days post-fertilization
no growth phase
what is different about the mitosis that occurs during early cell division
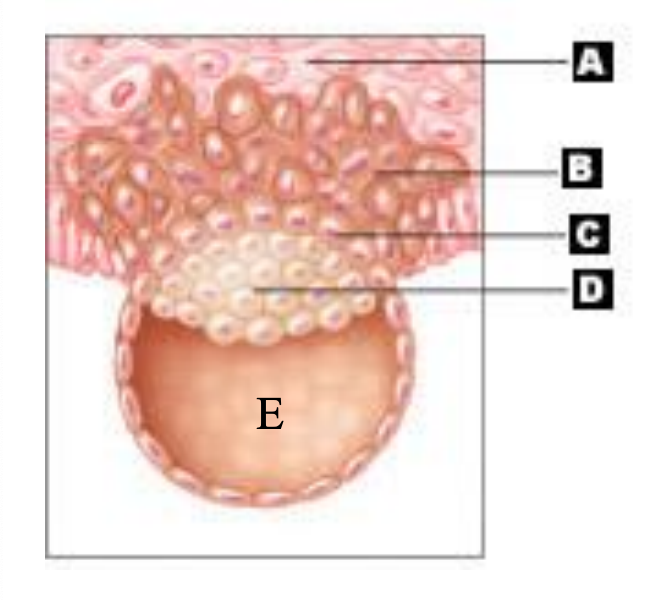
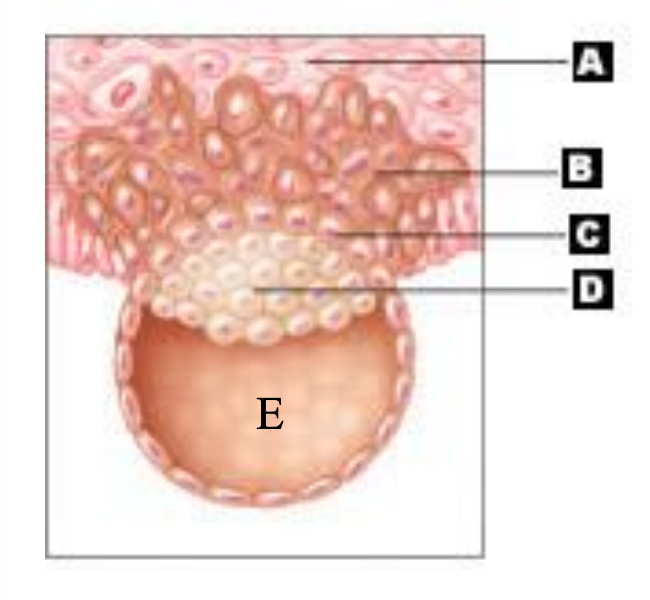
cytotrophoblast
C
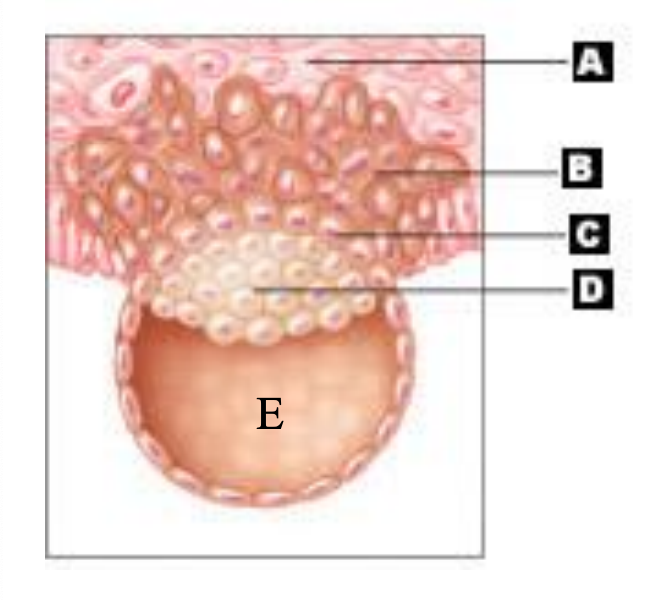
inner cell mass/embryoblast
D
inner cell mass
which side of the blastocyst is the site of implantation
8 days
when does formation of bilaminar germ disk occur
epiblast
becomes the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
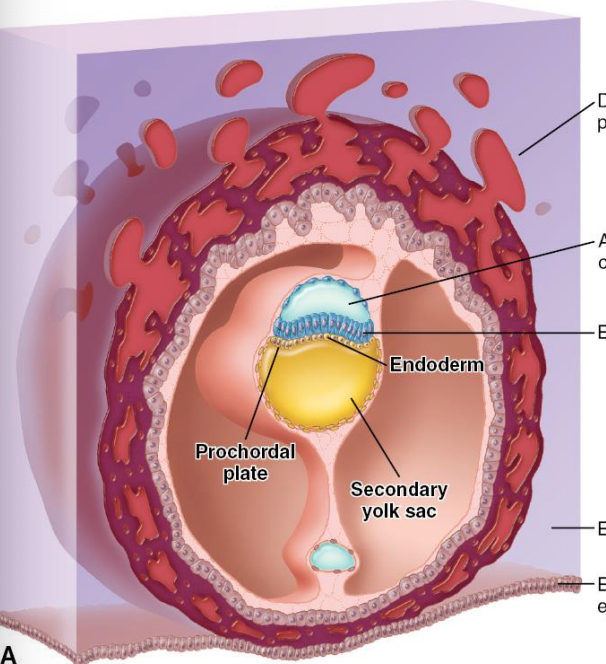
hypoblast
becomes the extra embryonic endoderm and secondary yolk sac
sycytiotrophoblast
B) the outer layer of the trophoblast, involved in implantation and nutrient exchange.
13 days
when does prochordal plate formation occur
prochordal plate
vital for heart development, transverse septum and buccopharyngeal membrane
primary blastocoel
(2)
trophoblast
(3)
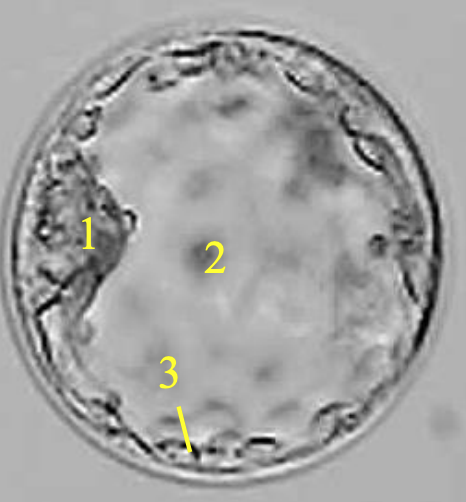
primary yolk sac
(E)
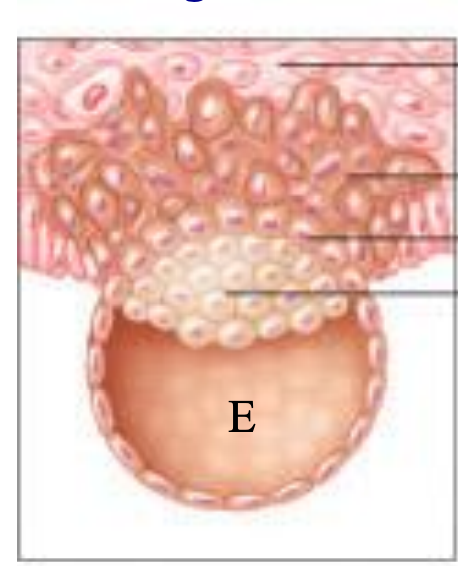
primitive streak formation
hypoblast cells delaminate from epiblast and secrete fluid into developing blastocoel
gastrulation
the process that forms the three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm) from the epiblast during embryonic development.
end of week 2
when is the bilaminar disk fully developed
week 3
formation of trilaminar disc establishing longitudinal axis and bilateral symmetry
mesoderm
which primary germ layer is the notochord a part of
end of week 3
when does the neural tube formation begin
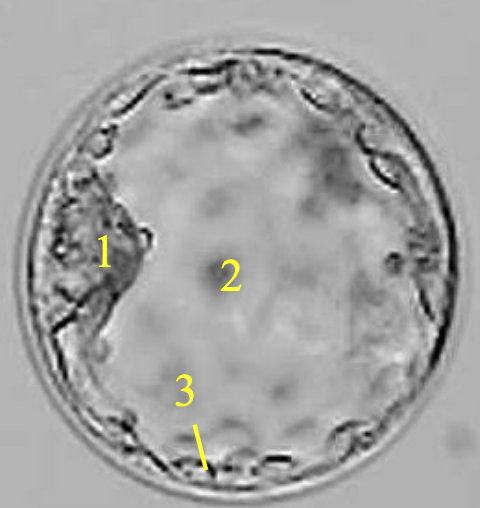
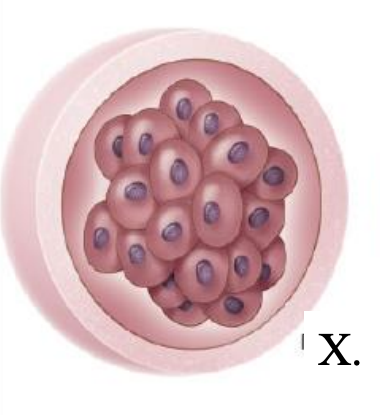
morula
what is this structure
blastocyst
what is this structure
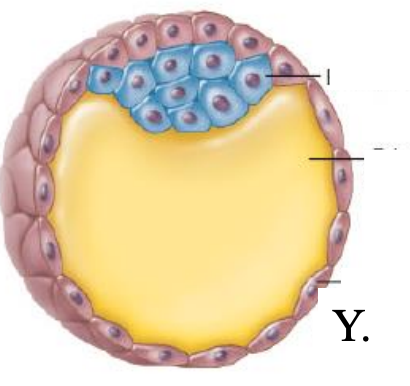
amniotic cavity
(X)
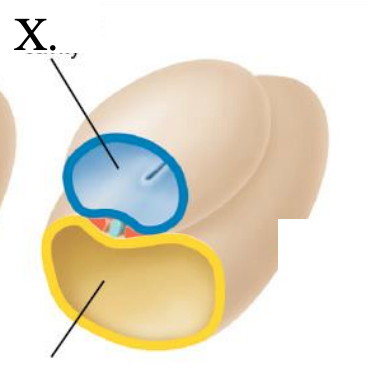
week 2
which week of development is this
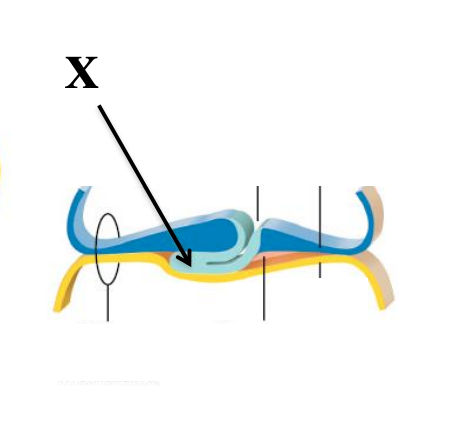
notochord
(X)
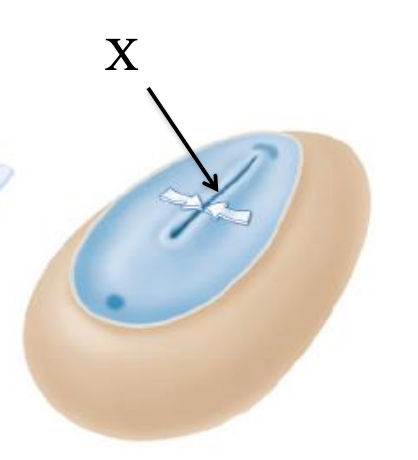
Primitive streak
(X)
prochordal plate
contribute to premandibular condensation of head mesenchyme and heart mesenchyme
primary neurulation
formation of rostral neural tube
neural plate
A thickened region of ectoderm that gives rise to the central nervous system during embryonic development.
week 4
neural tube forms
notochord
signals overlying ectoderm to change into neural plate then into two neural folds
epiboly
A process during embryonic development where cells move to enclose the yolk, contributing to the formation of the germ layers. And the force for the folding of neural folds
neural tube foramation
signals differentiation of lateral mesoderm into paraxial, intermediate, and lateral plate mesoderm
neural crest cells
The group of cells that arise from the edges of the neural tube during embryonic development and migrate to form various structures, including peripheral nerves, bons and skull, and facial cartilage.
stomatodeum
what is the arrow pointing to
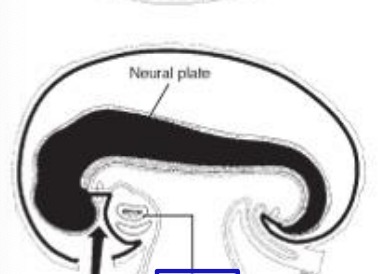
stomatodeum
space created by the movement of primordial heart posteriorly and the development of the foregut. precursor to the mouth
buccopharynegeal membrane
what is the arrow pointing to
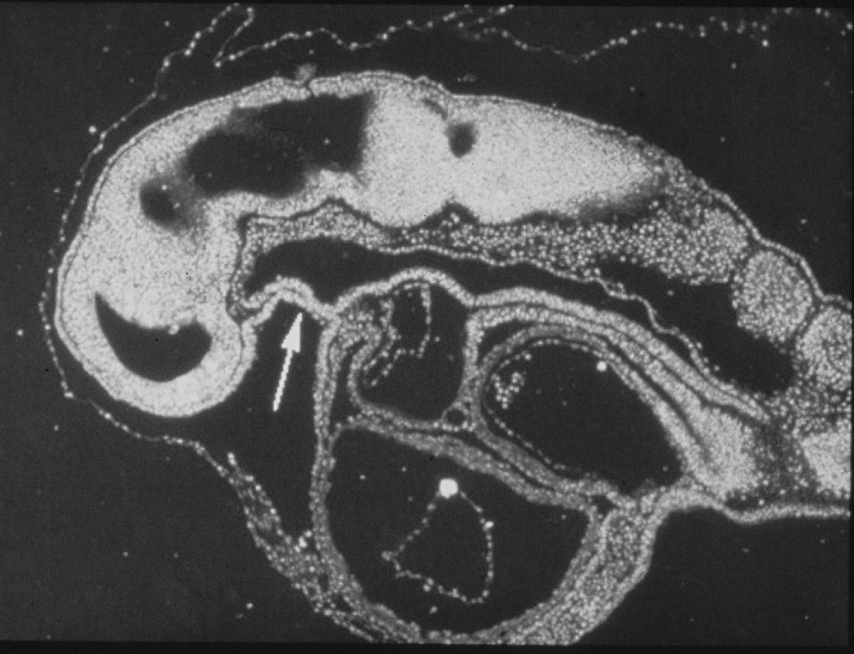
week 4 (25 days)
buccopharyngeal membrane begins to break down allowing the stomatodeum to connect with the foregut.
frist branchial arch
The first of the pharyngeal arches that forms during embryonic development, giving rise to structures such as the maxilla, mandible, and muscles of mastication.
hox genes
what controls regional patterning from the 2nd branchial arch to the caudal region
Msx genes
what controls the developmental pattern in the head
neural crest cells in the head
forms cells leading to dermal bones of skull and face
treacher collins syndrome
caused by lack of neural crest cell migration into facial region
ectoderm
layer of cells that contributes to the development of skin and nervous system.
mesoderm
layer of cells in the embryo that gives rise to muscles, bones, and the circulatory system.
endoderm
layer of cells that forms the lining of the digestive and respiratory tracts