Anatomical Study of Nerves, Blood Vessels, Salivary Glands, & Lymph Nodes in Biology
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
division 1
opthalmic nerve is what division of trigeminal nerve
division 2
maxillary n. is what division of trigeminal nerve
division 3
mandibular n. is what division of trigeminal nerve
opthalmic n.
1st division of trigeminal n.
Function: supply general sensations (touch, pain, pressure, temperature) to skin of Upper 3rd of face - NOT ORAL CAVITY
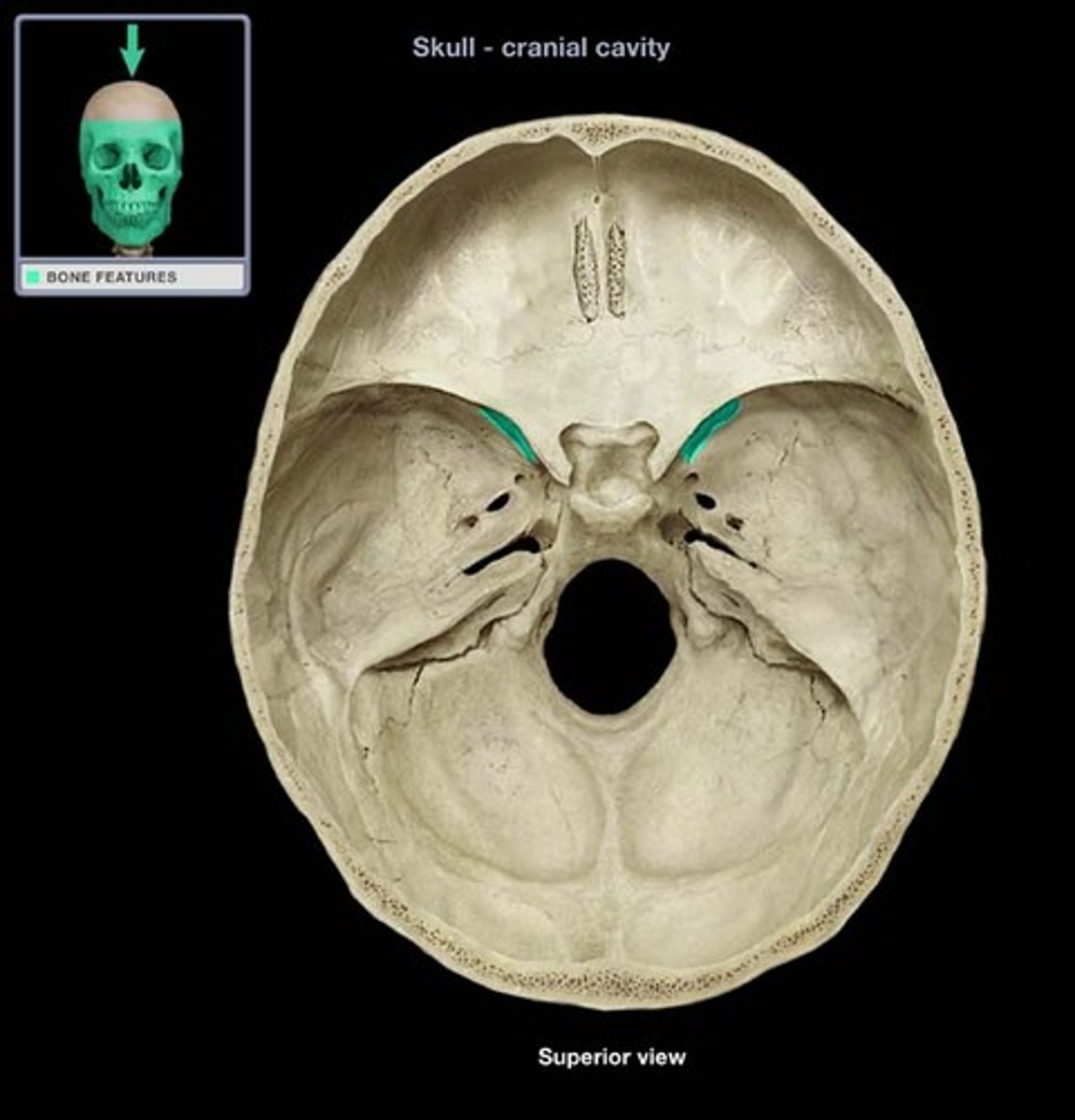
superior orbital fissure
Pathway: From brain, CN V, Div 1 (opthalmic n.) exits the skull by way of the ________
maxillary n.
2nd division of trigeminal nerve
Function: supply general sensations (touch, pain, pressure, temperature) to Middle 3rd of face and palate and pulp of maxillary teeth
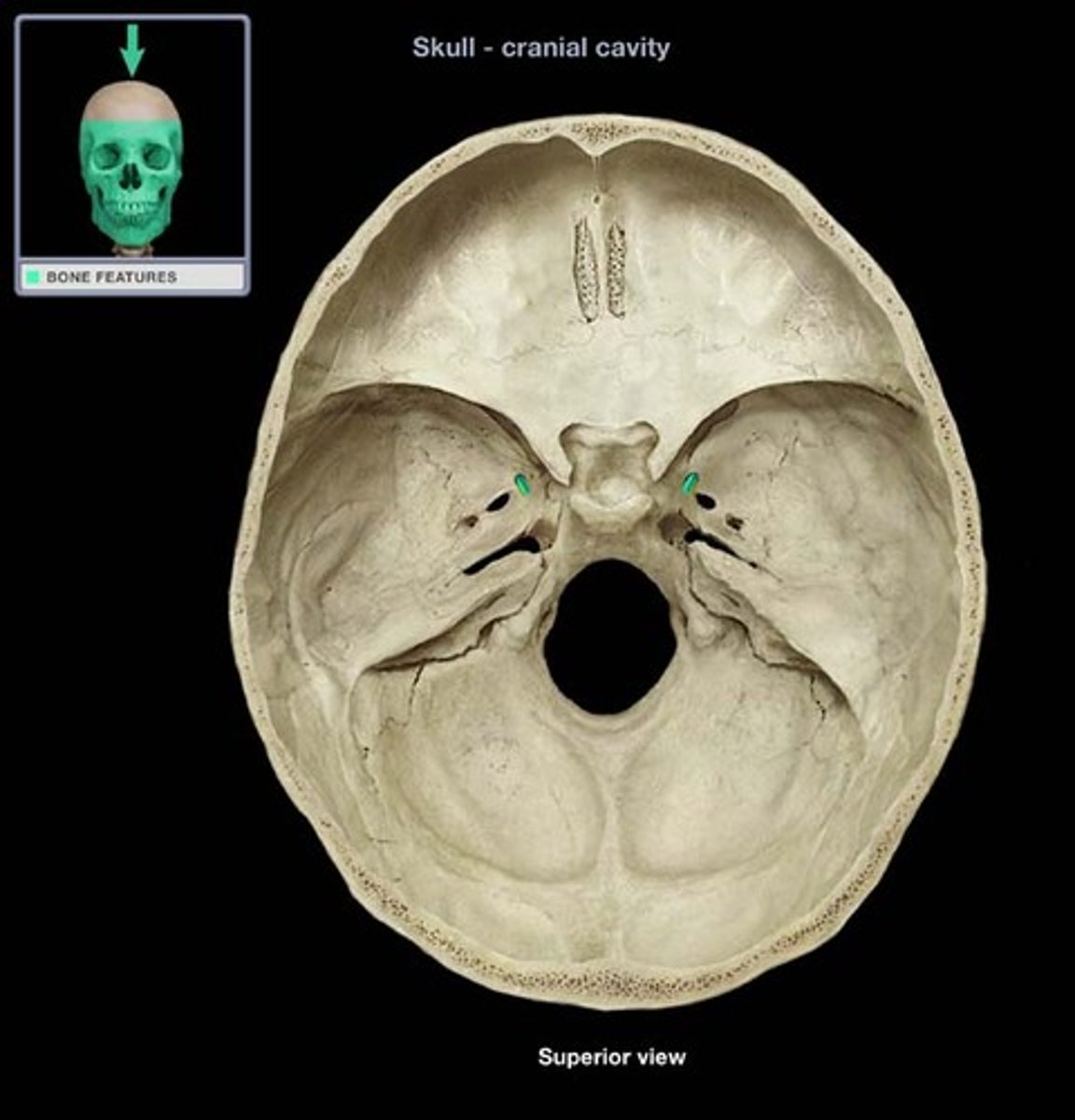
foramen rotundum
Pathway: From brain, CN V, Div 2 (maxillary n.) exits the skull by way of the _____
mandibular n.
3rd division of trigeminal n.
Function: motor supply to 8 muscles of mastication, mylohyoid, anterior digastric m. and sensory general sensation to skin of lower 3rd of face, floor of mouth, anterior 2/3rds of tongue, all mandibular teeth
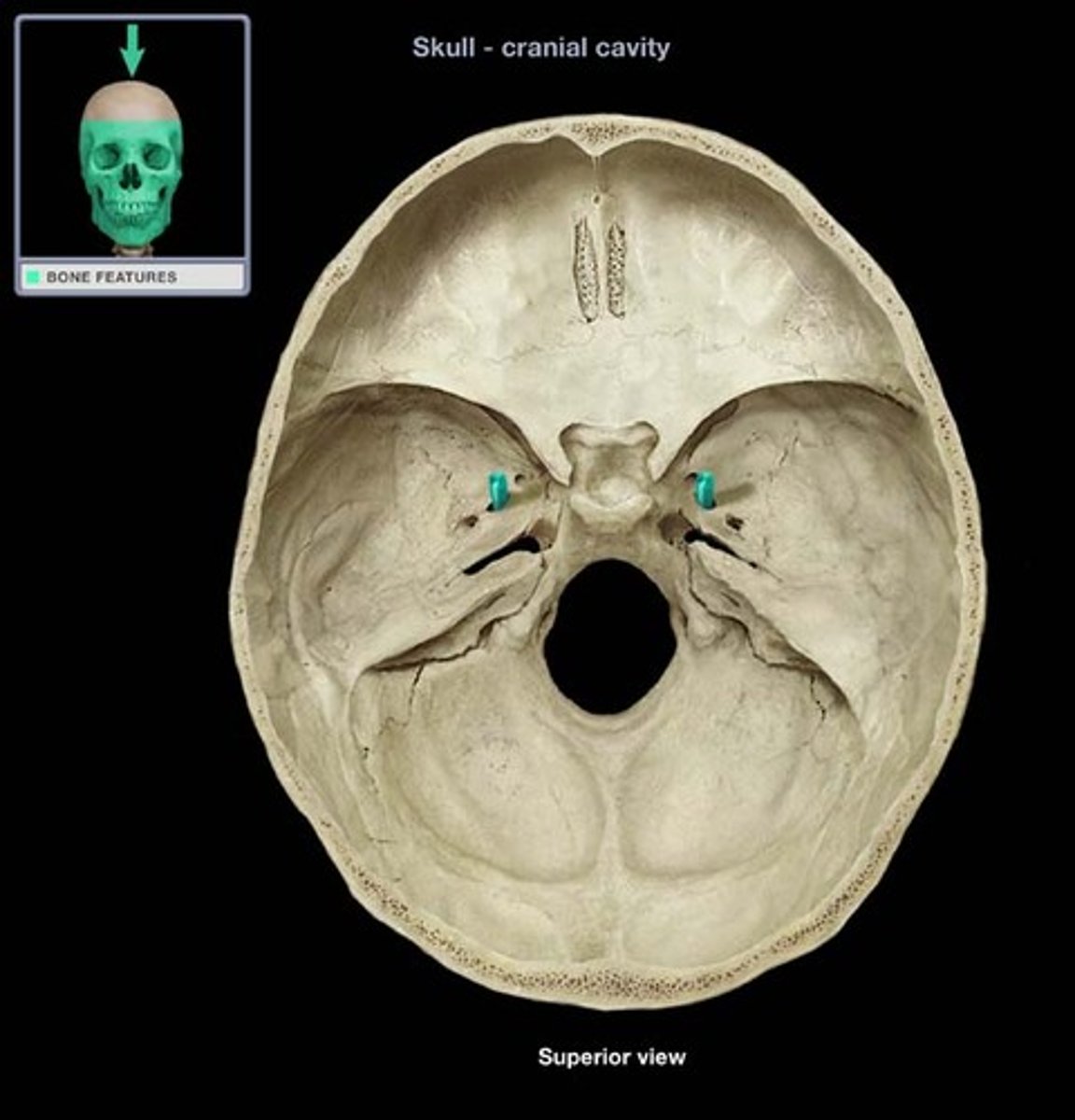
foramen ovale
Pathway: From brain, CN V, Div 3 exits the skull by way of the _____
facial n. (CN VII)
Motor Function: innervate muscles of facial expression and visual expression of face and scalp
Sensory Function: supply sense of taste to anterior 2/3rds of tongue
Secretory Function: stimulate secretions from sublingual and submandibular glands
internal acoustic meatus
from the brain, the facial nerve travels through the petrous portion of the temporal bone through the ________
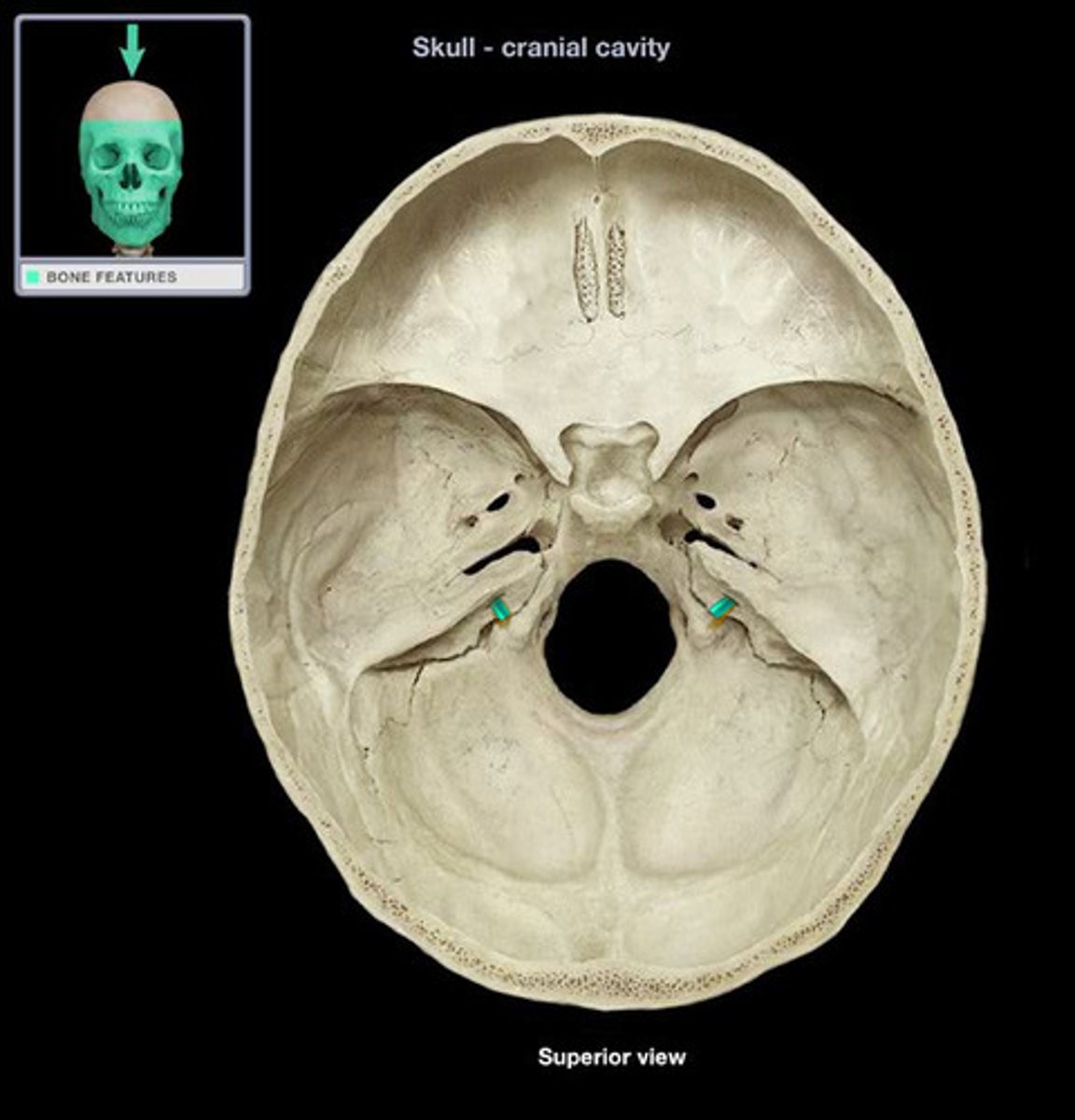
styomastoid foramen
the efferent fibers of facial n (CNVII) exit the skull through the _____
petrotympanic fissure
the afferent fibers of facial n (CNVII) exit the skull through the _____
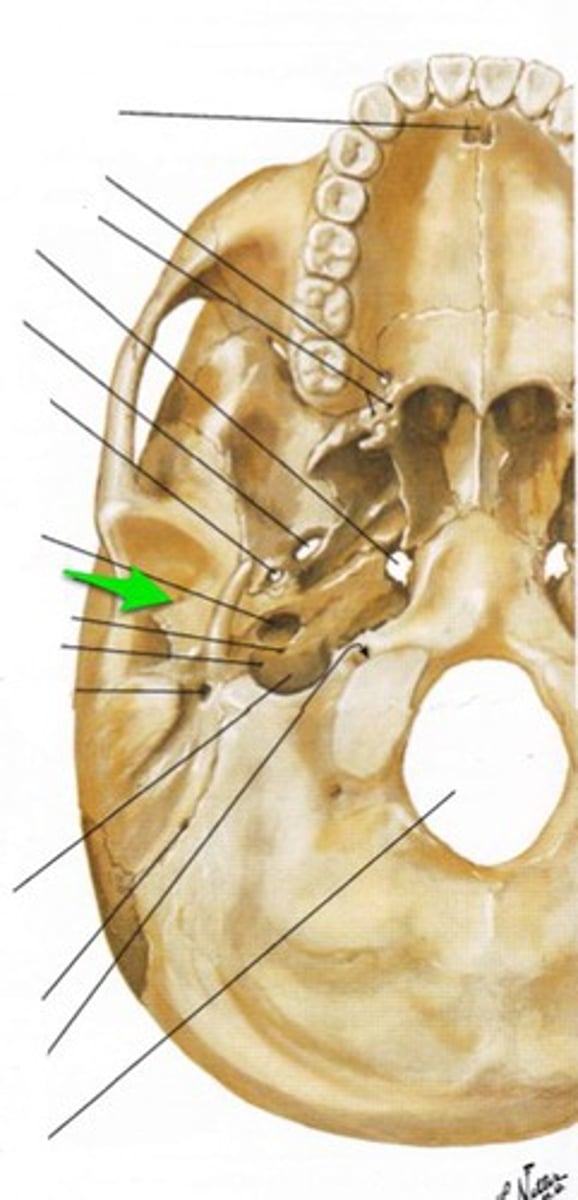
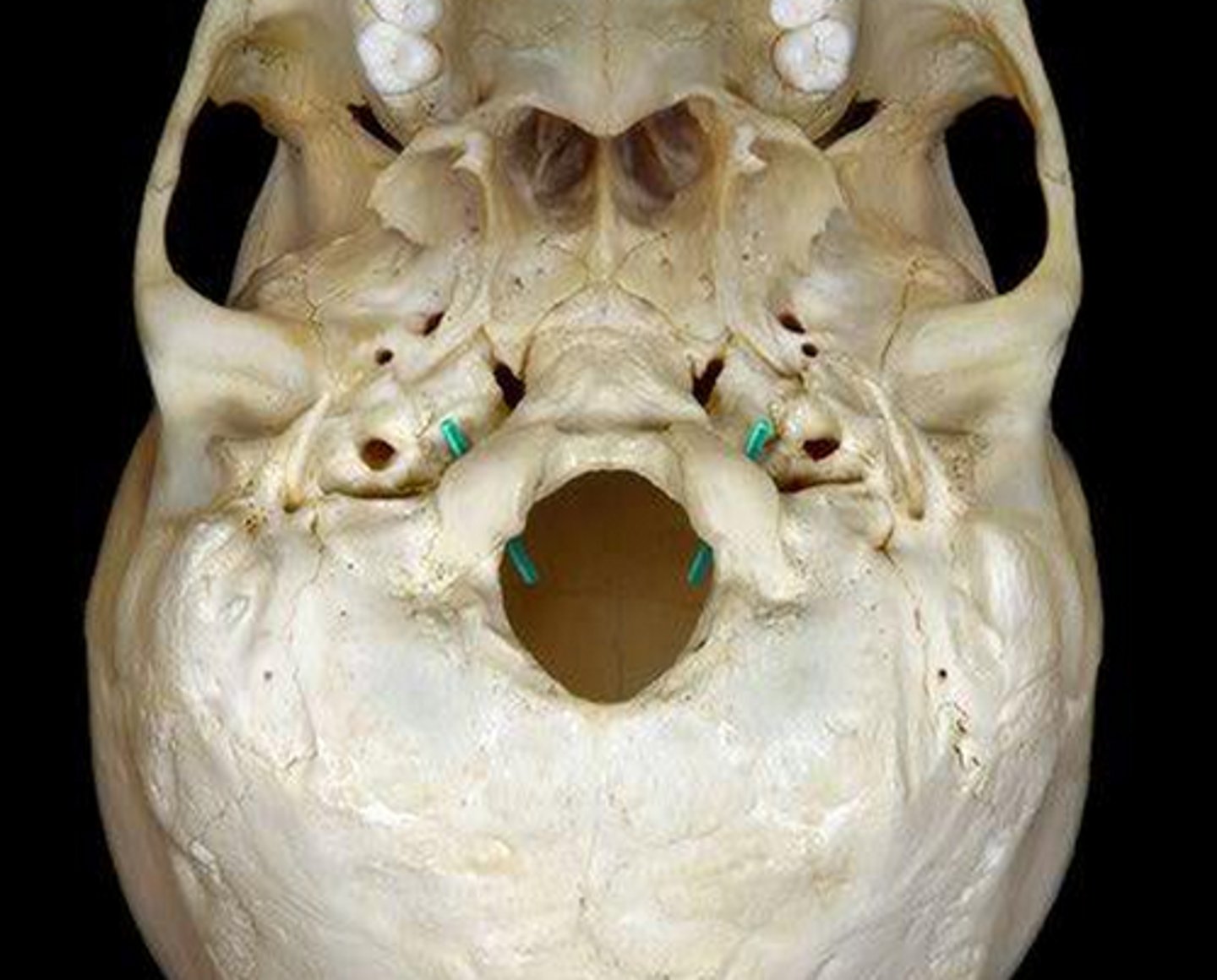
glossopharyngeal nerve (CNIX)
Motor Function: innervate stylopharyngeus muscle of pharynx
Sensory Function: supply sense of taste and feeling (touch and pain) to posterior 1/3rd of tongue and general sensation to mucosa of pharynx and tonsils
Secretory Function: innervate parotid gland (influence secretion)
jugular foramen
From the brain, the glossopharyngeal nerve exits the skull through the ________
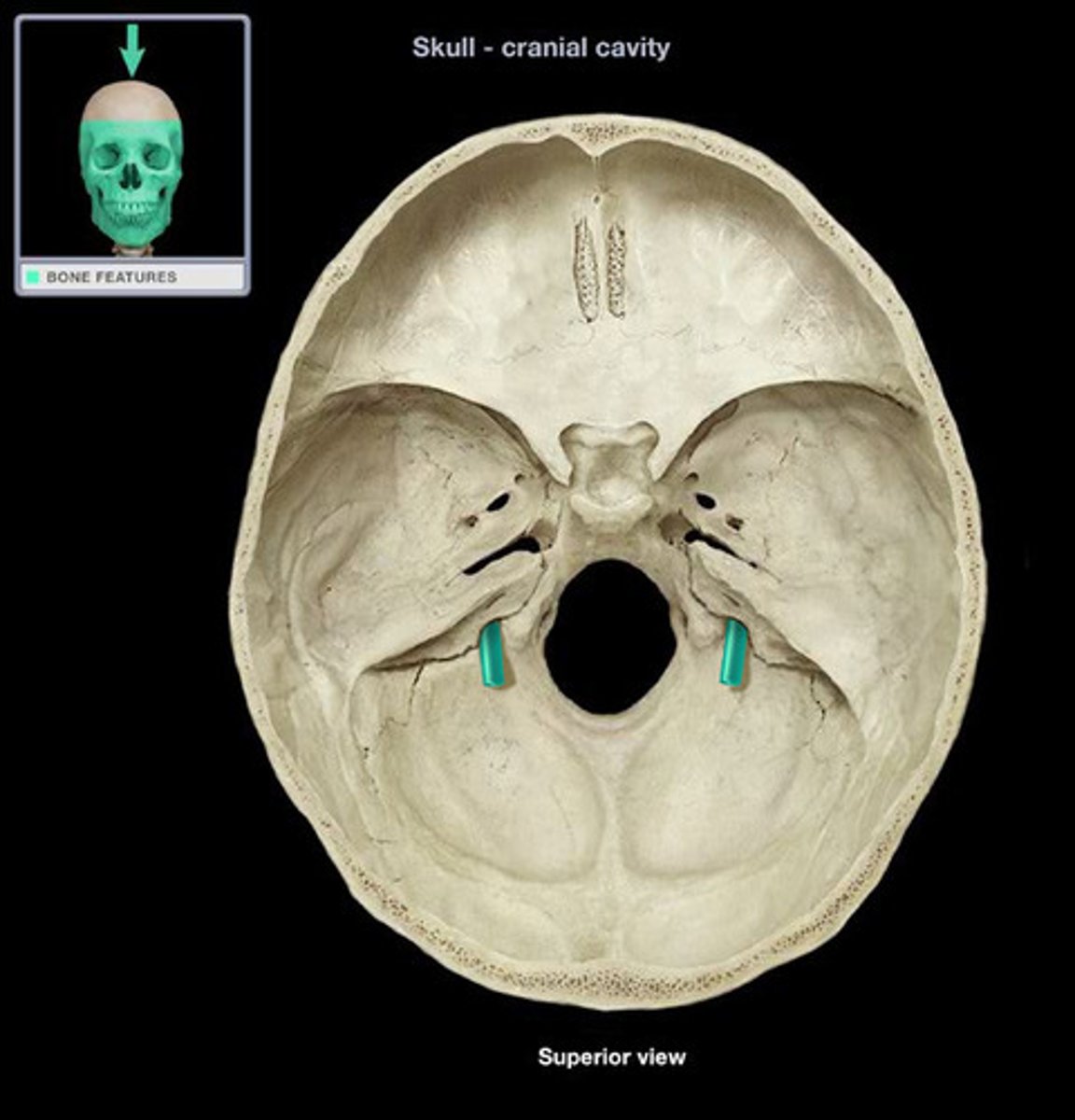
hypoglossal n. (CN XII)
Motor Function: innervate muscles that move the tongue
hypoglossal canals
From the brain, the hypoglossal n. exits the skull through the _____
pterygopalatine space
posterior superior alveolar n.
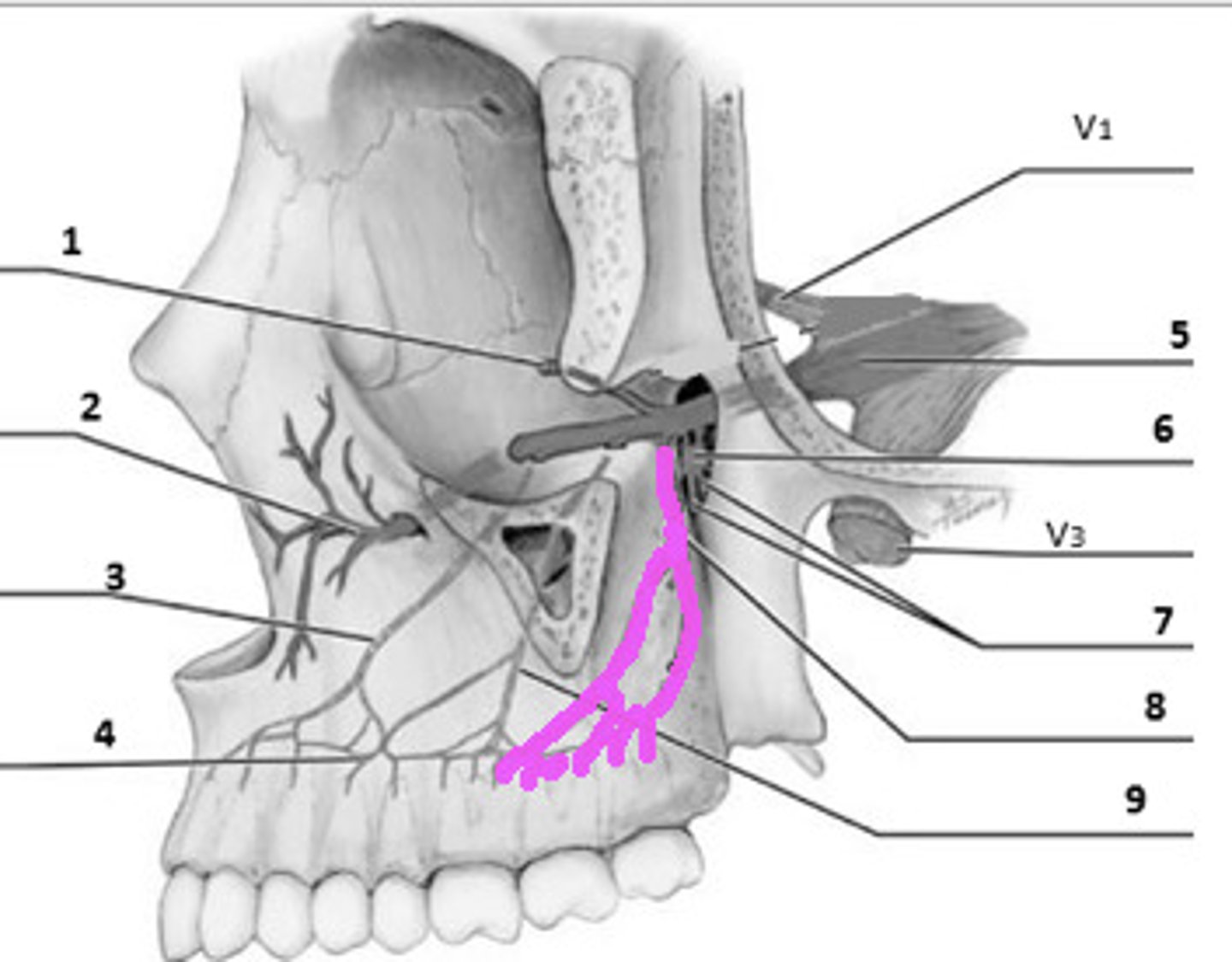
alveolar canal opening
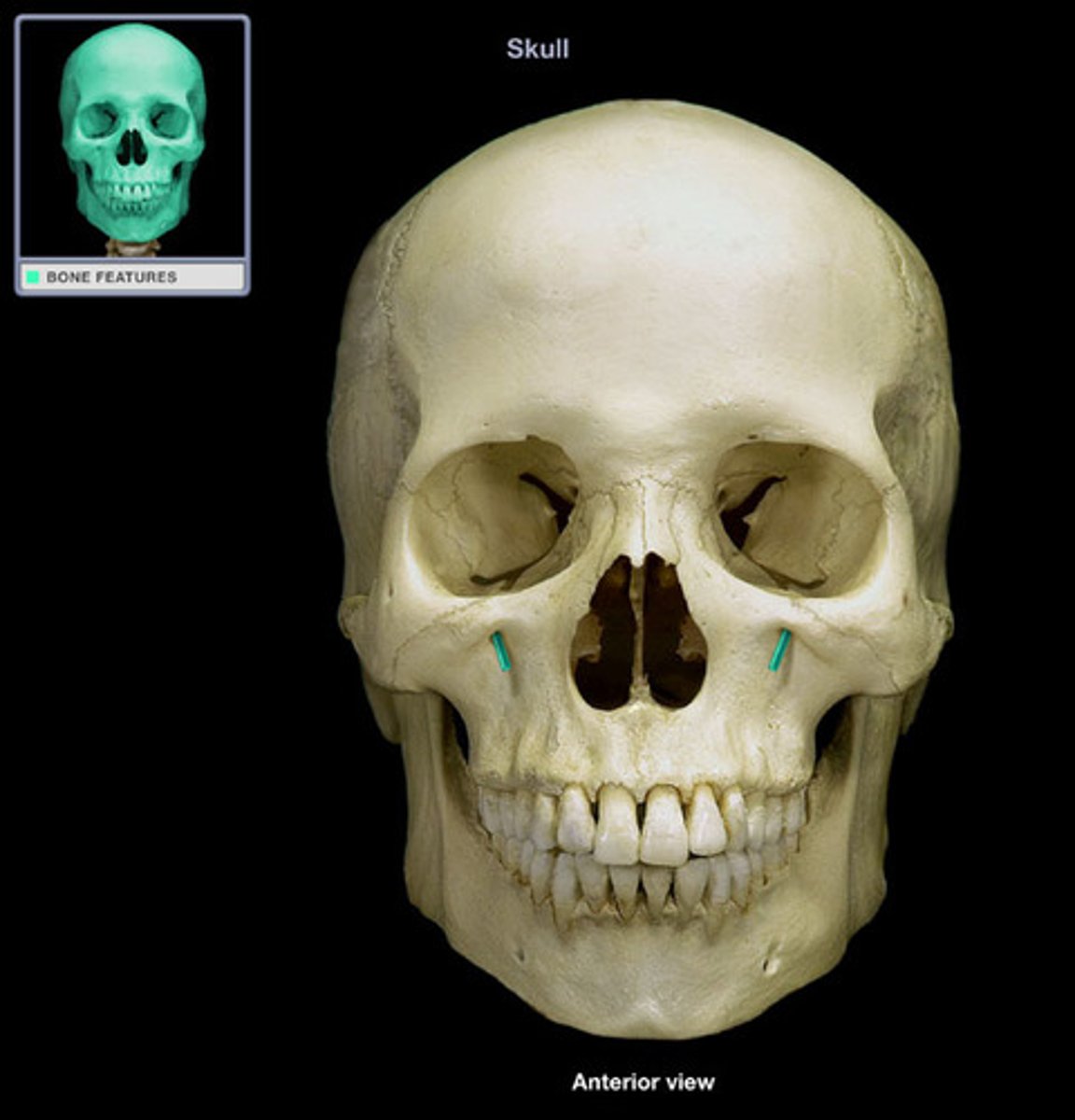
infraorbital n.
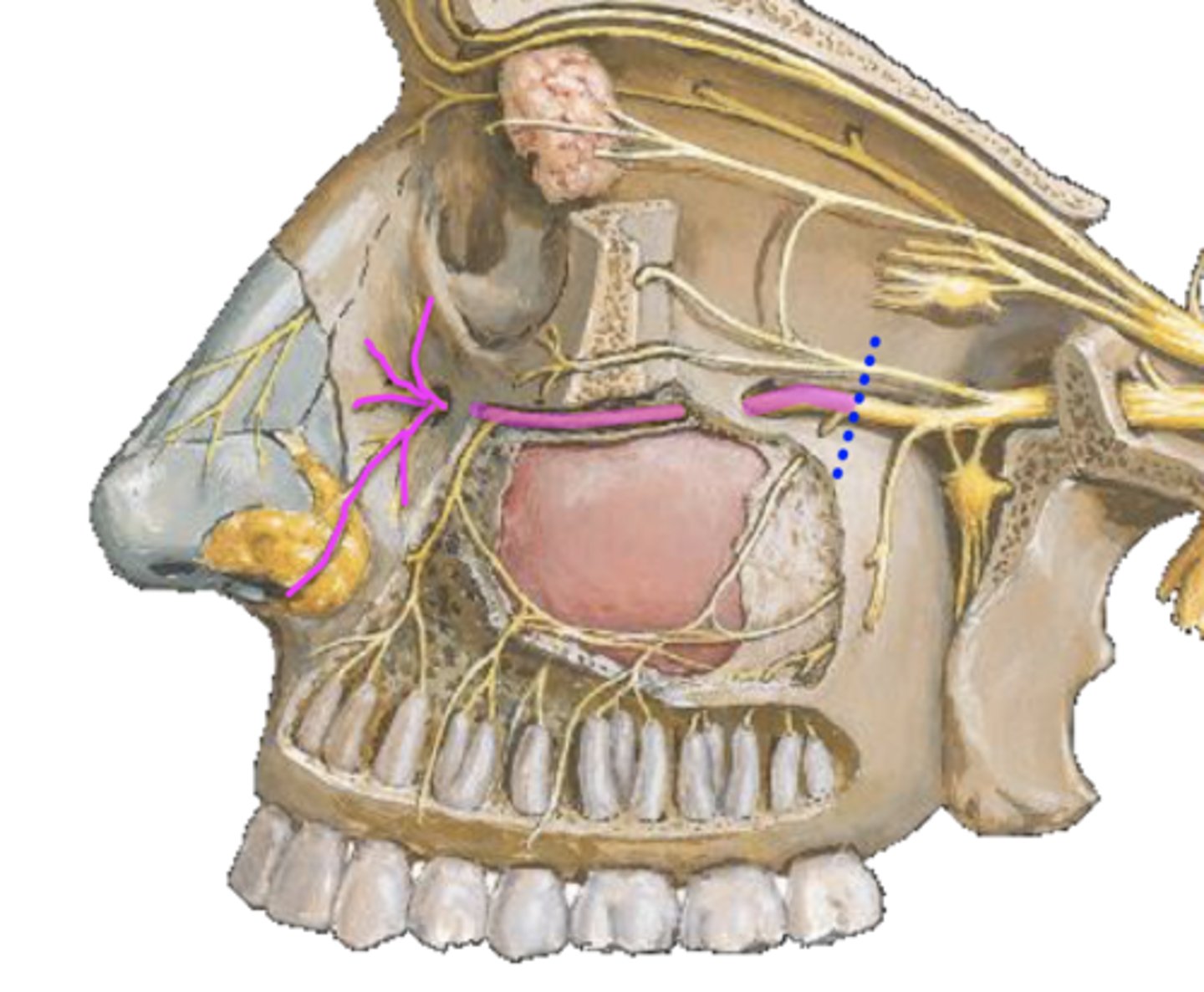
lateral nasal n.
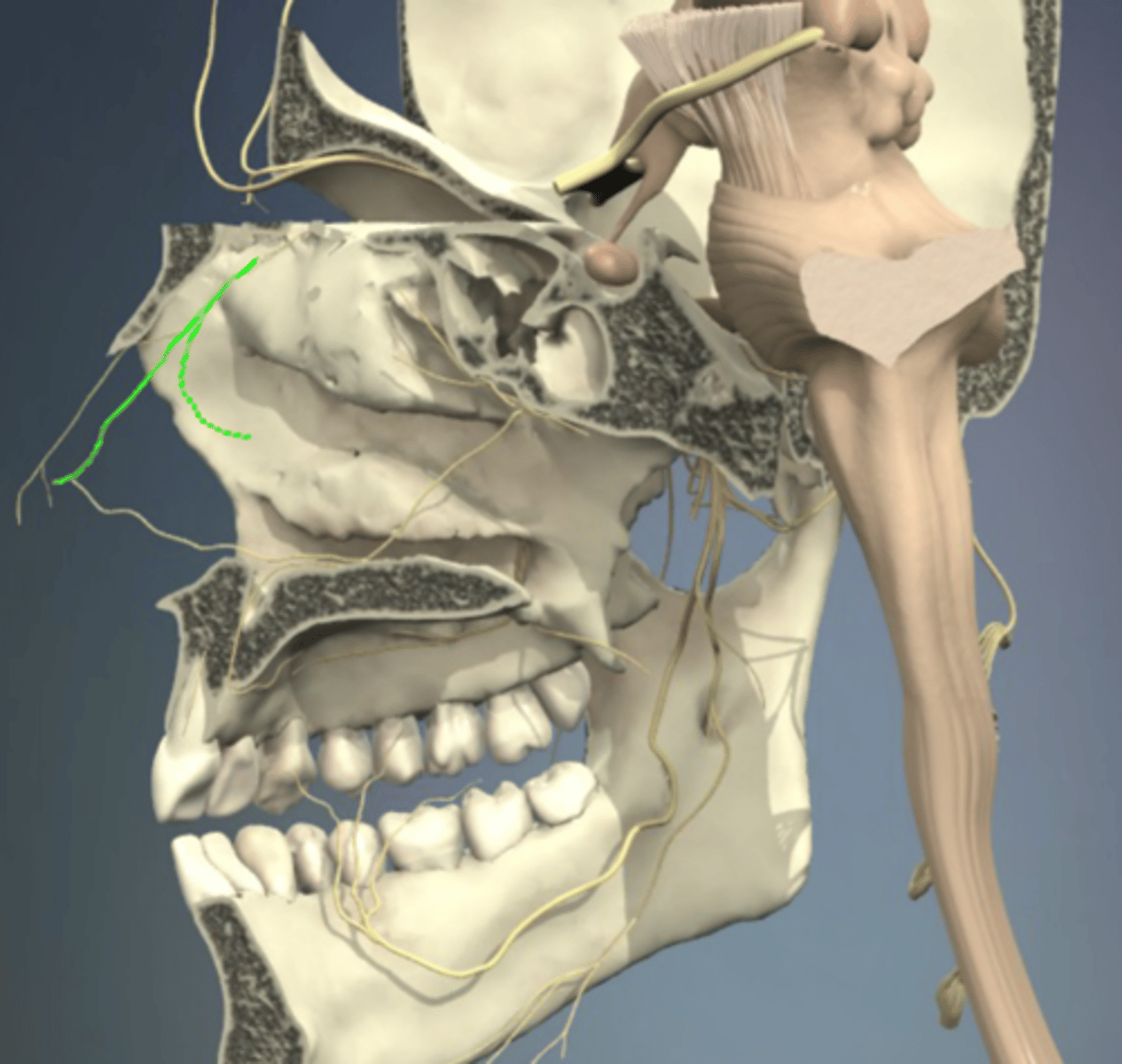
palpebral n.
infraorbital foramen
superior labial n.
anterior superior alveolar n. (ASA)
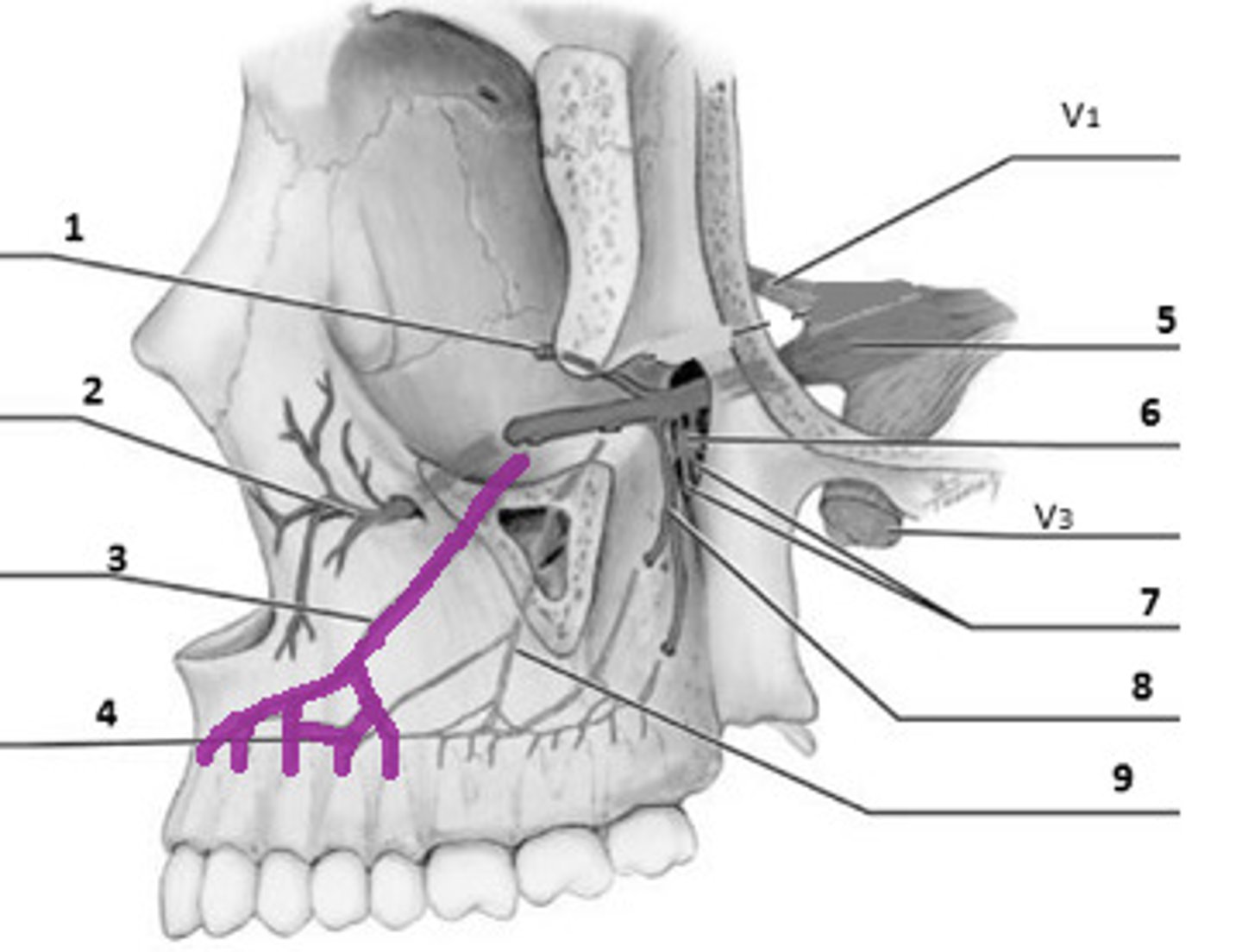
maxillary sinus
middle superior alveolar n. (MSA)
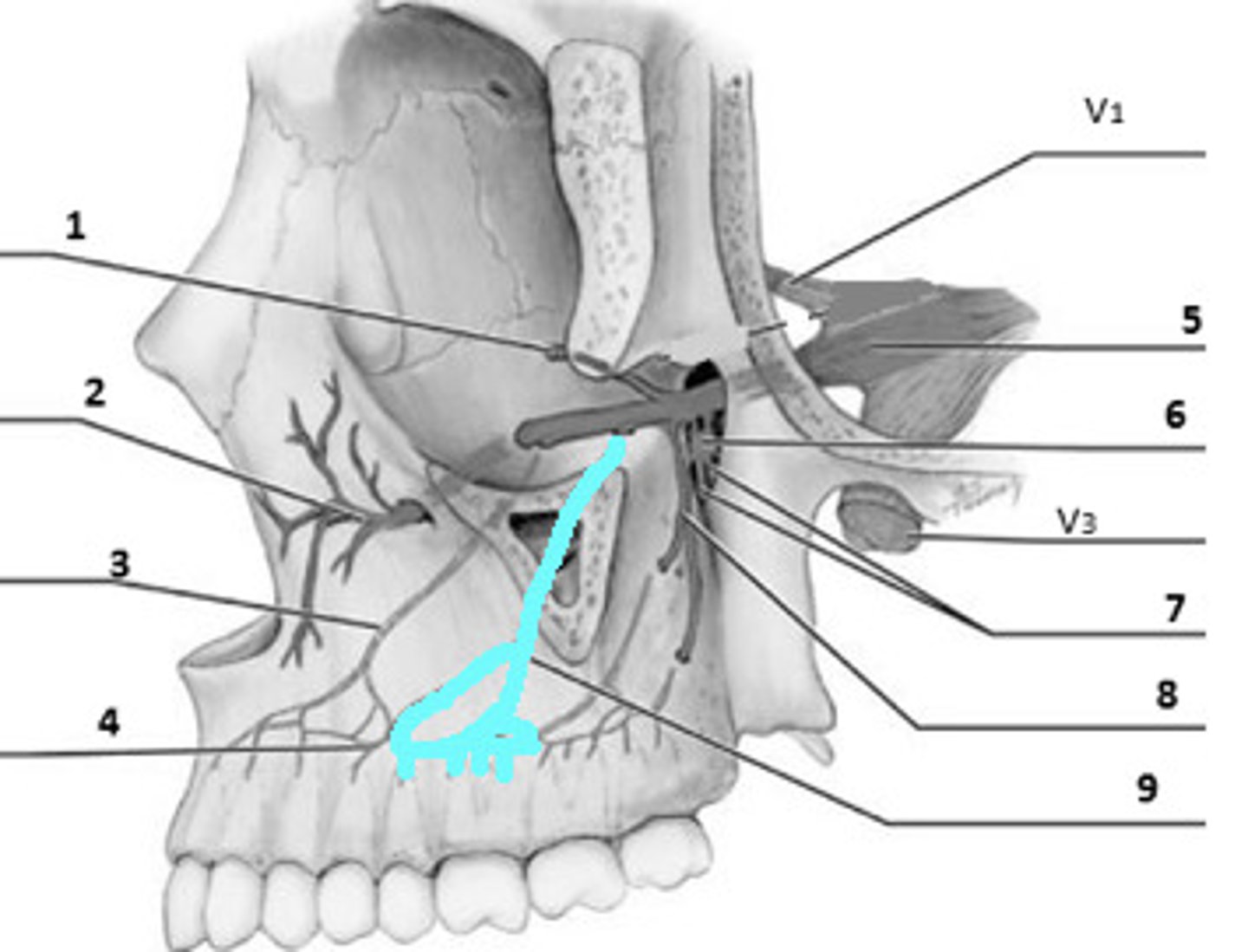
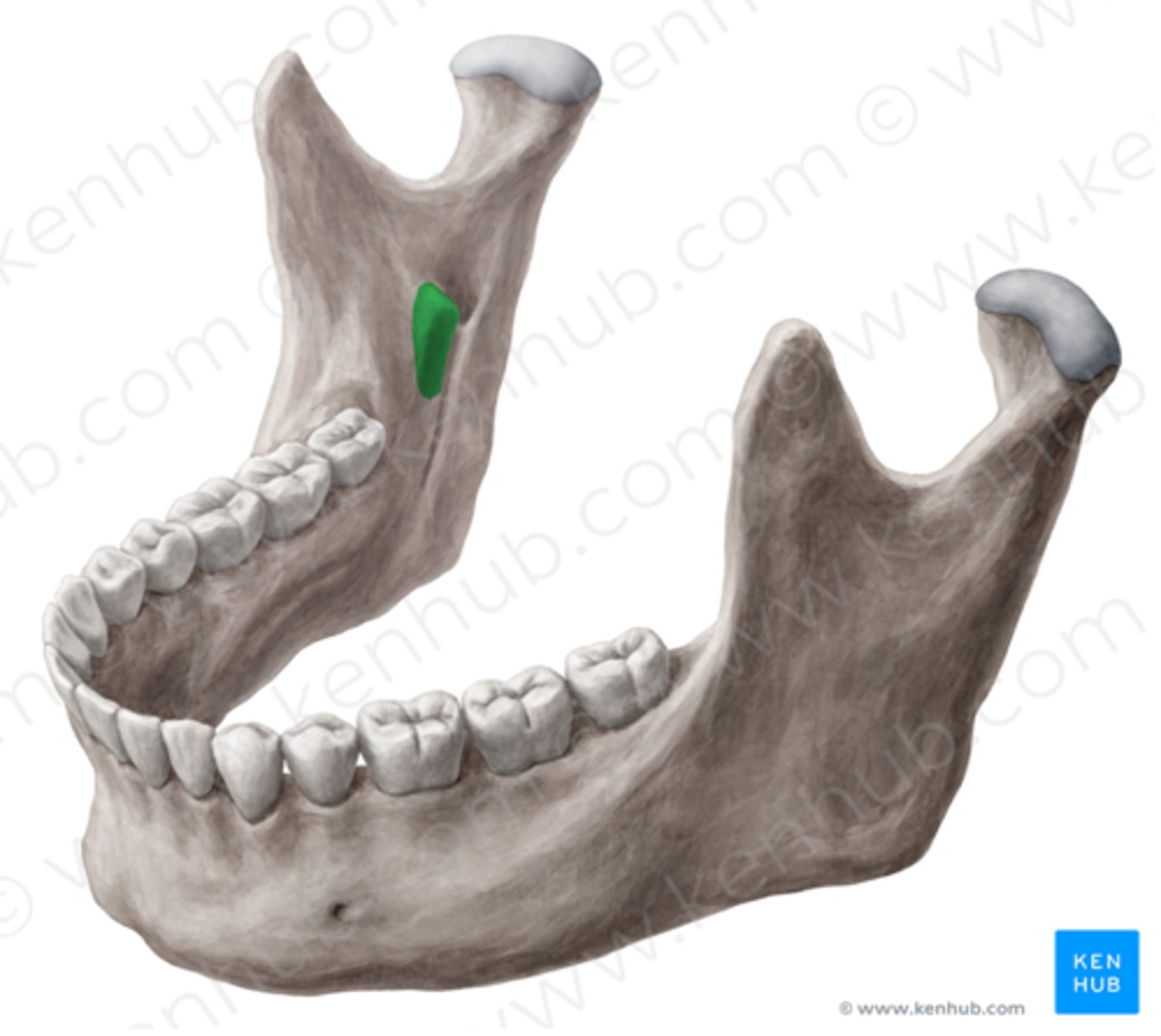
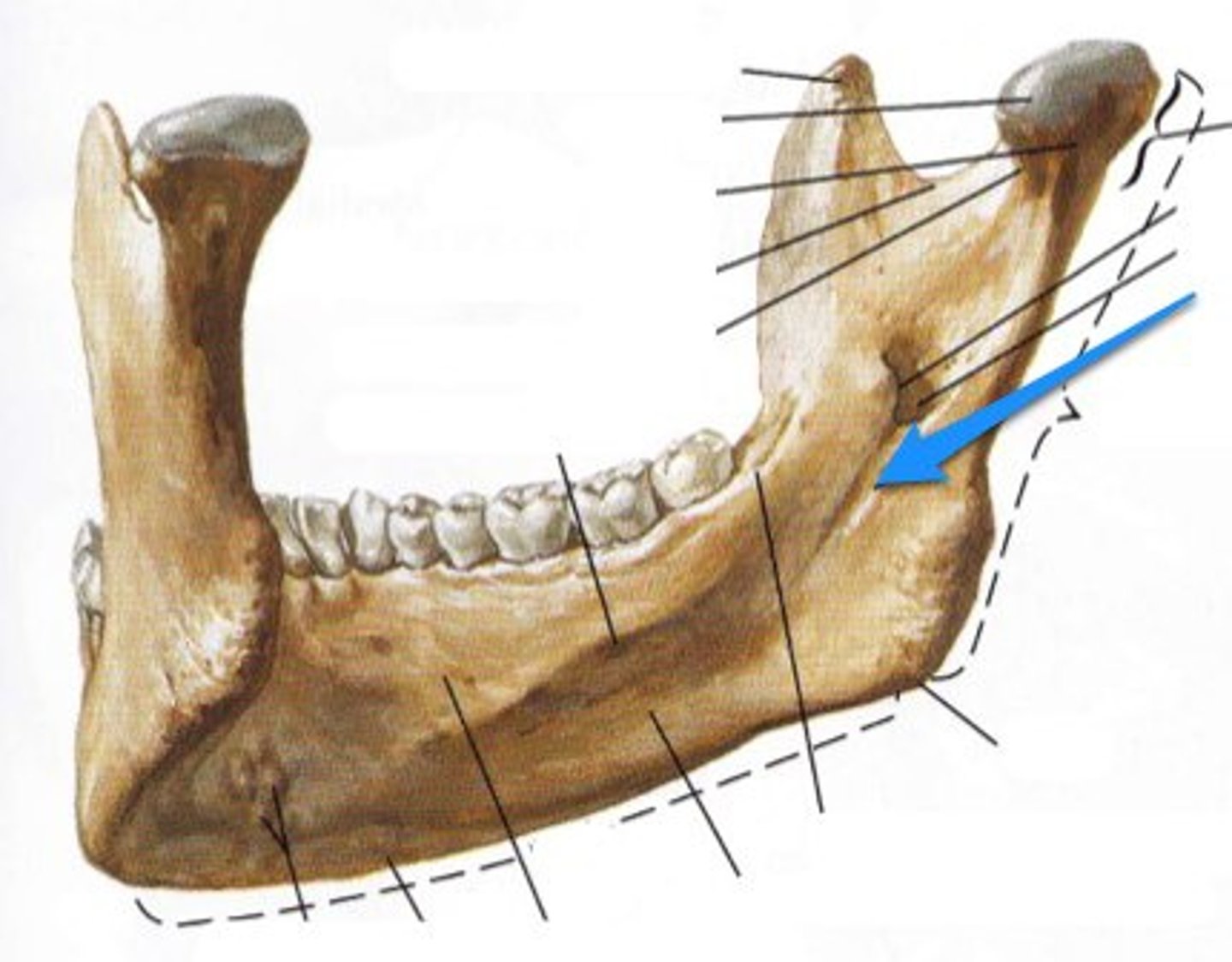
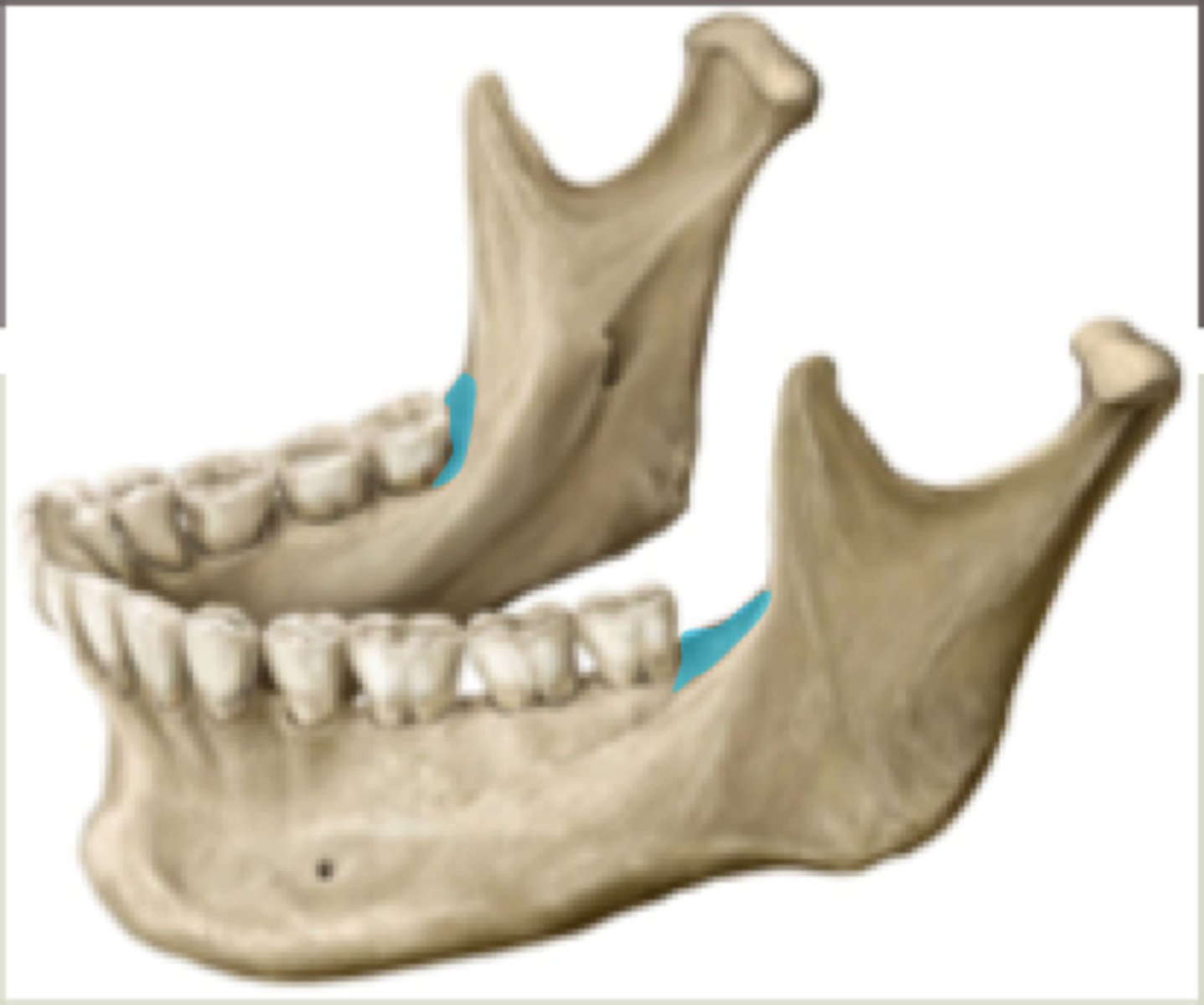
lingula
mylohyoid groove
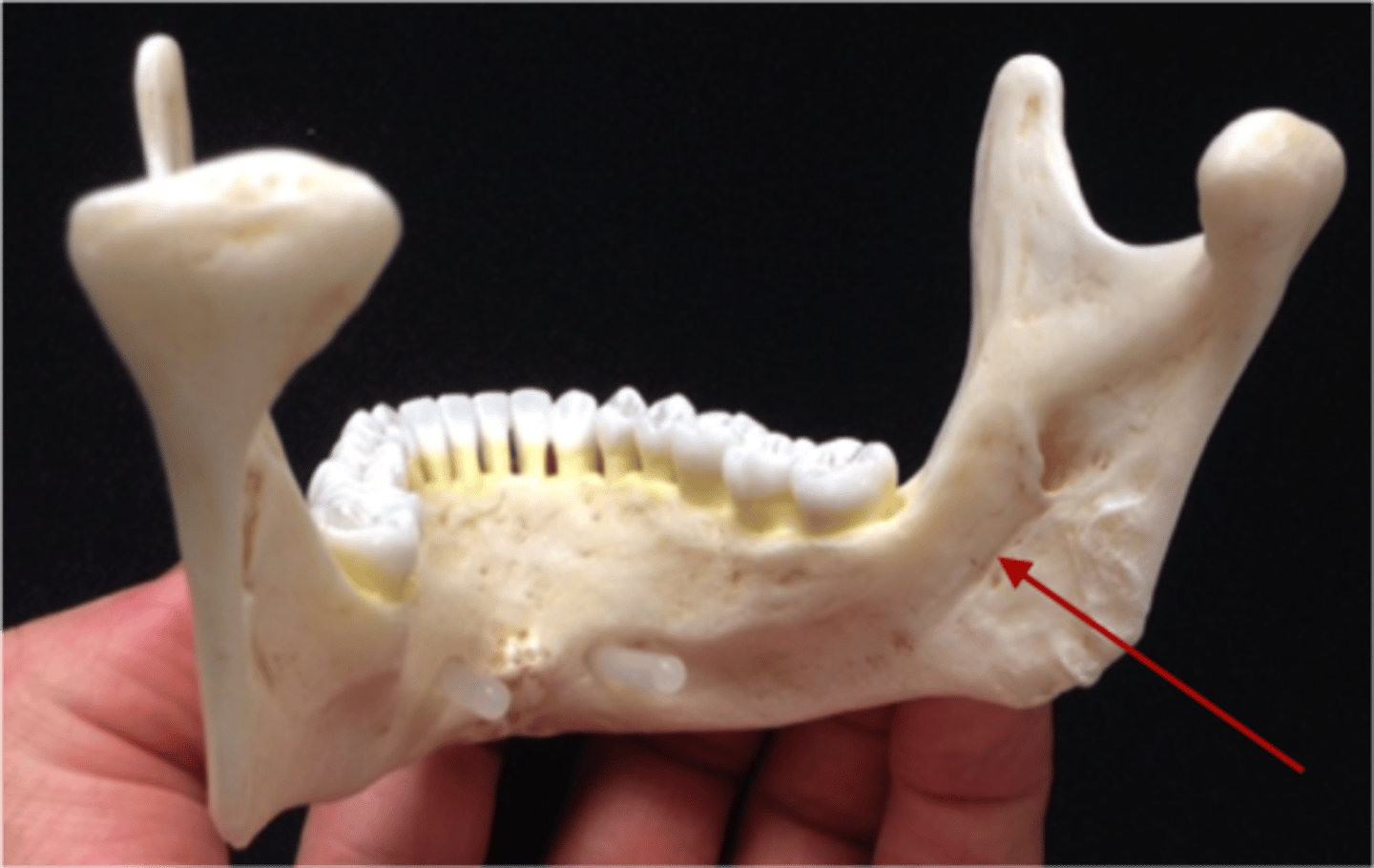
mylohyoid n.
runs through here
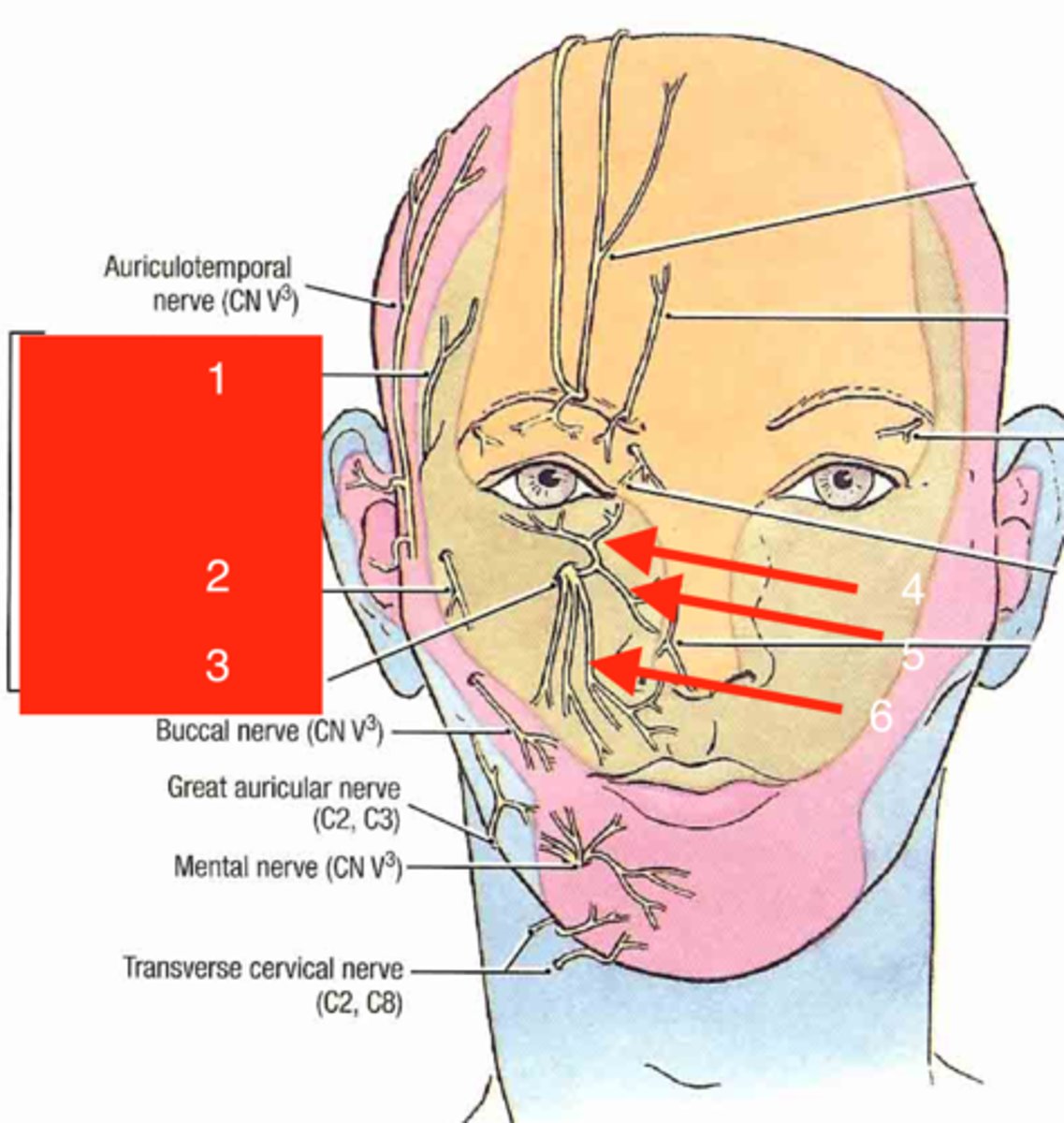
lingual n.
CN V to anterior tongue
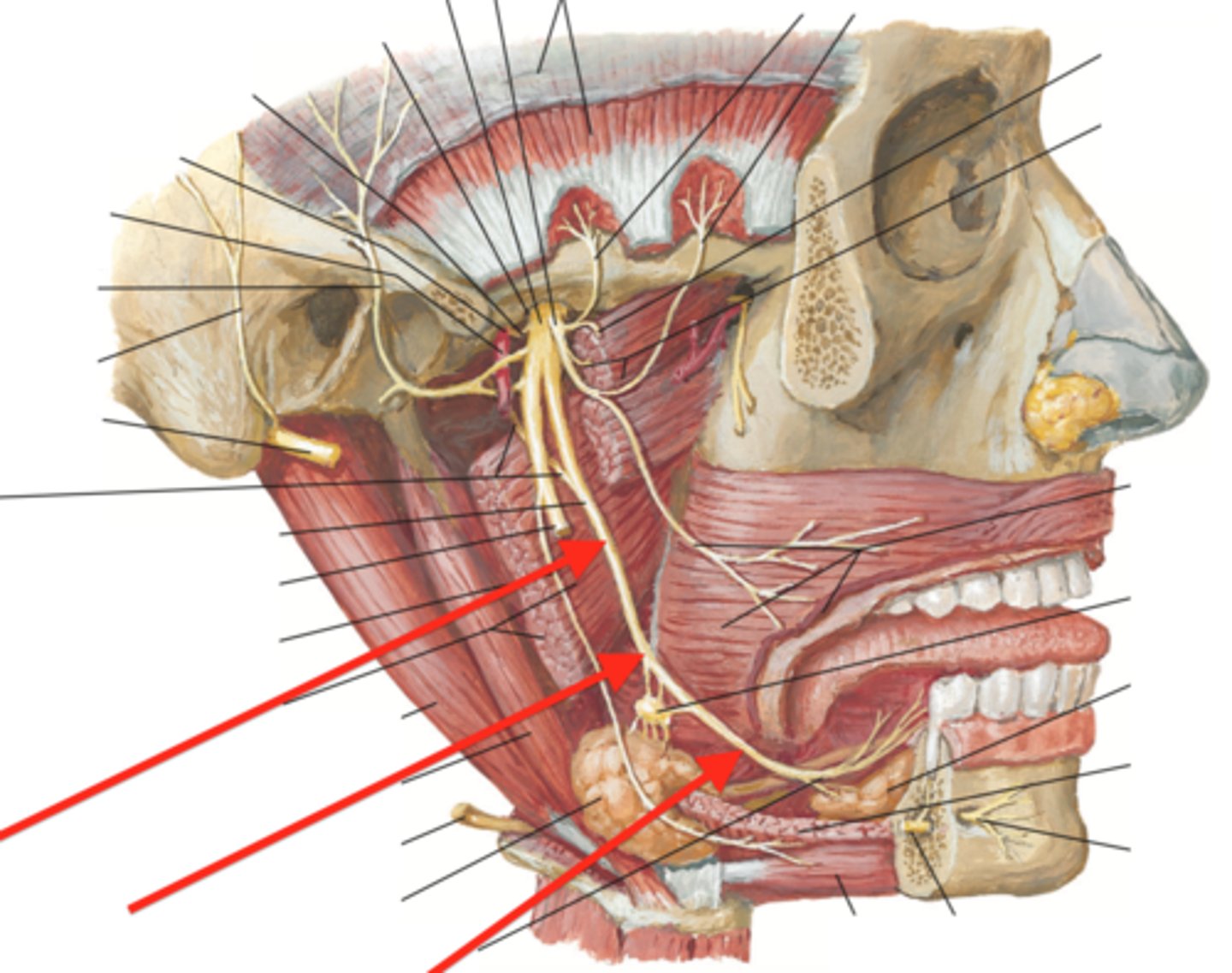
buccal n.
CN V to cheek
retromolar fossa
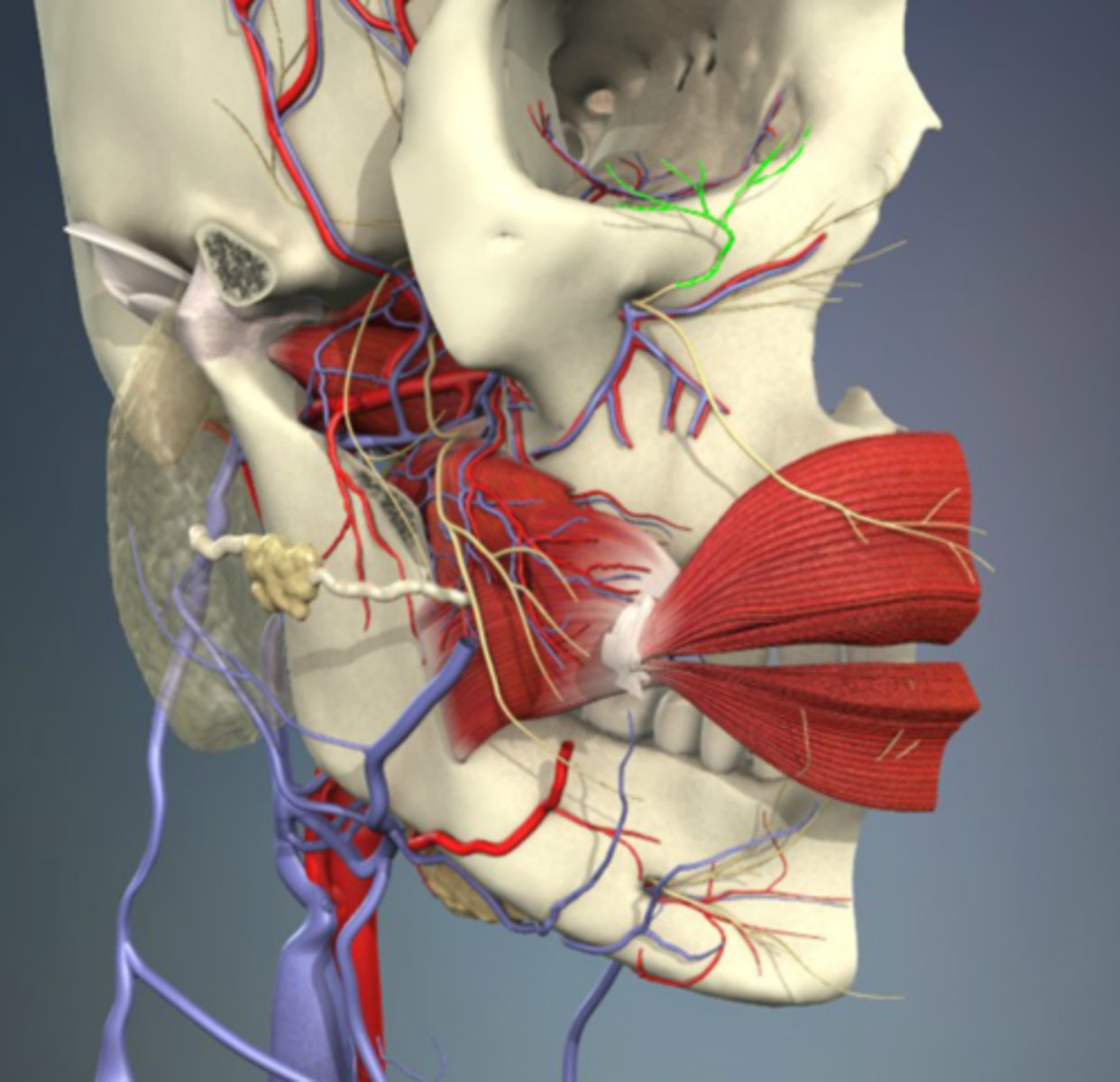
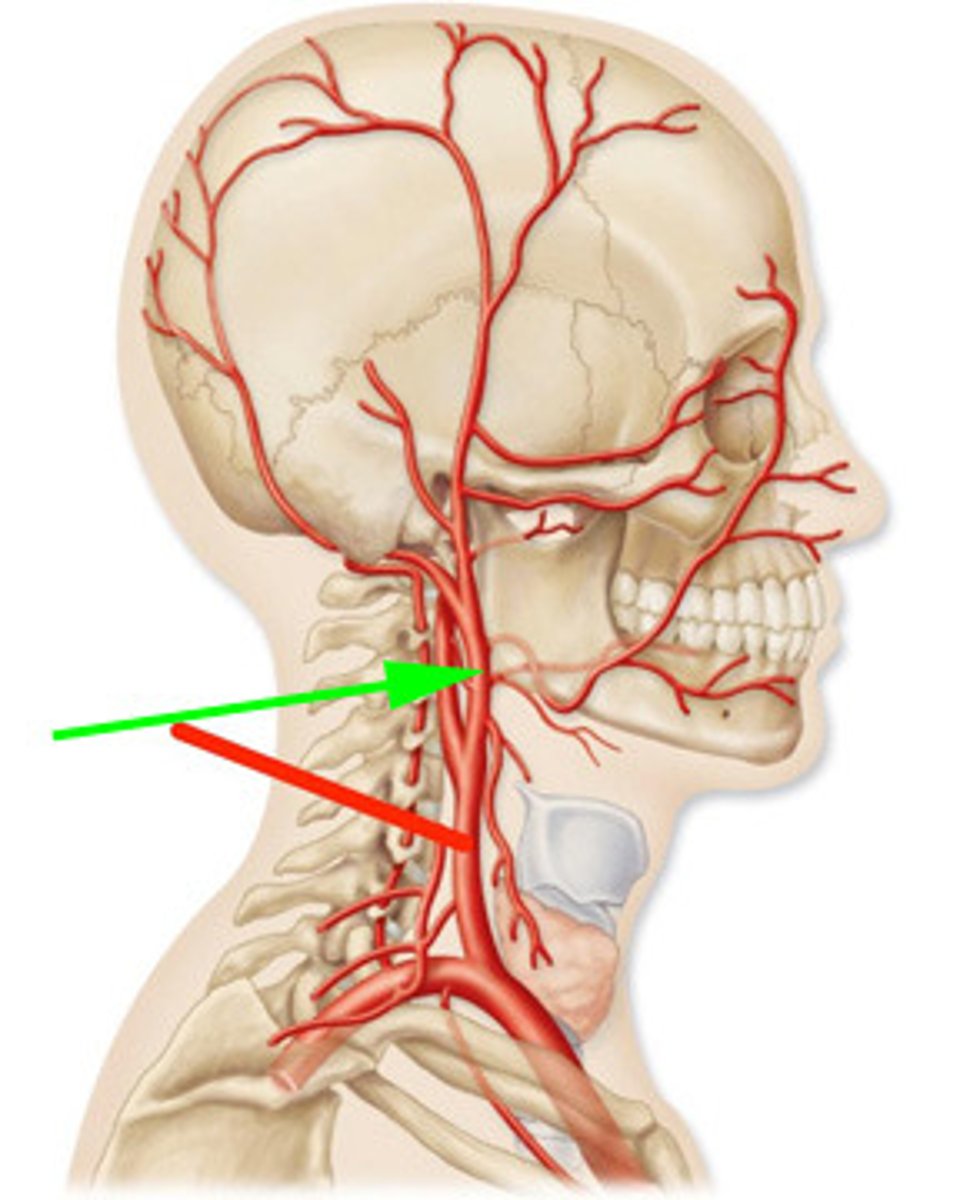
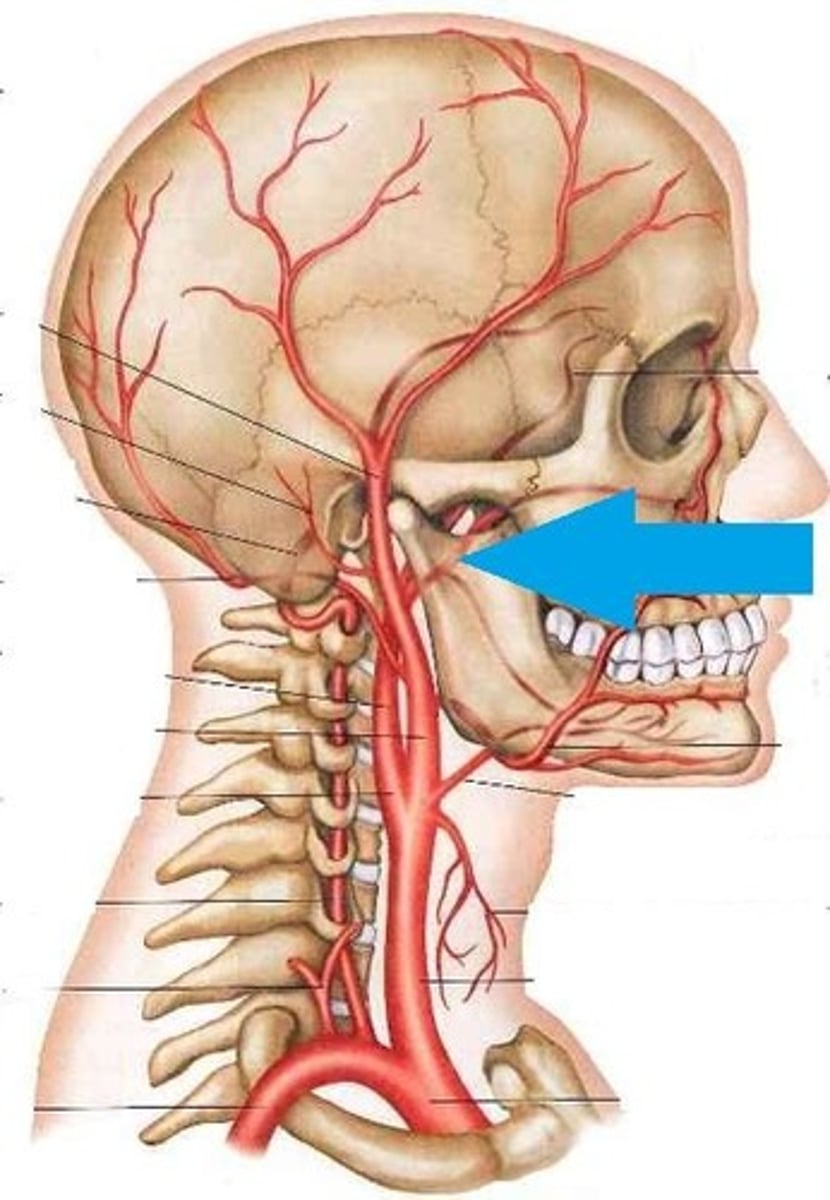
external carotid a.
The common carotid artery travels through the neck and divides into two branches. These branches are the internal carotid artery and the ______
lingual artery
This artery branches off near the hyoid bone and enters the tongue to supply the floor of the mouth, adjacent gingiva, and sublingual gland
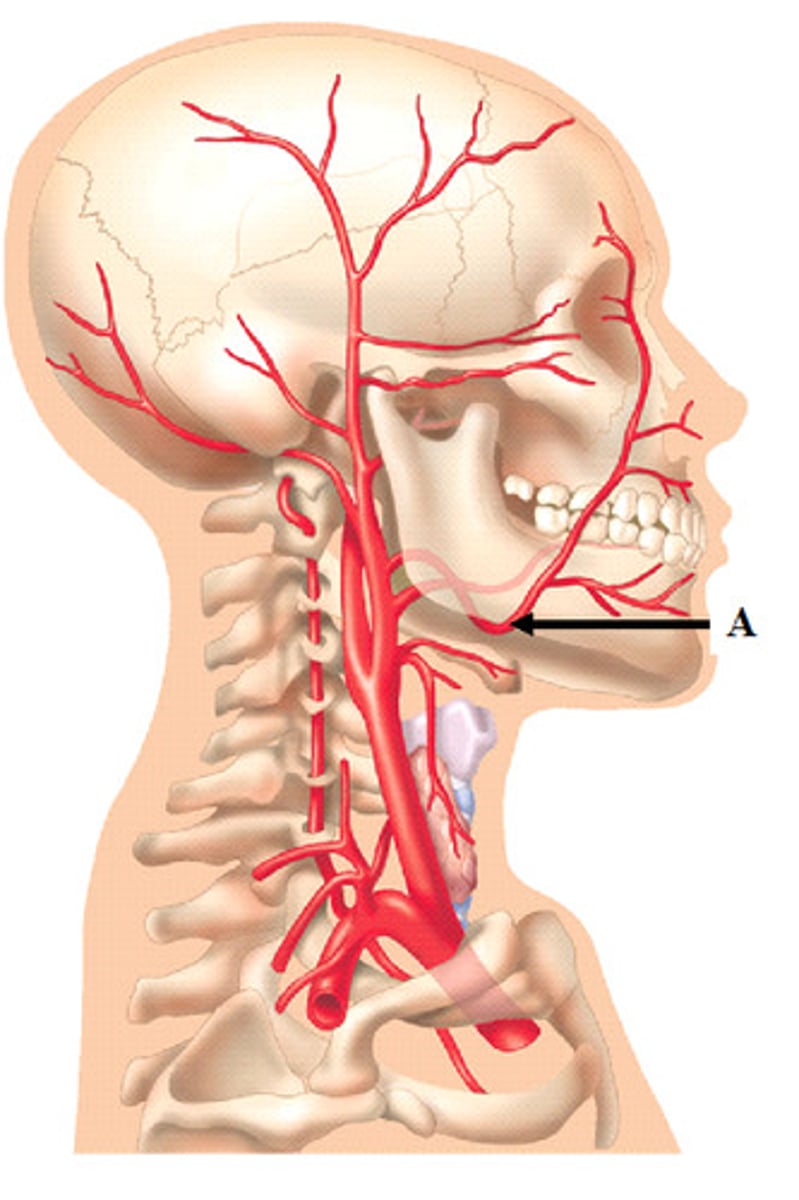
facial artery
This artery gives off branches that supply blood to structures adjacent to the pharynx (soft palate, pharyngeal muscles, mucosa of the pharynx, and palatine tonsil (ascending palatine a.), the floor of the mouth (mylohyoid muscle, ant. belly of digastric muscle, and lymph nodes below mylohyoid muscle (submental a.), the lips and orbicularis oris muscle (inferior and superior labial a., lateral nasal and angular a.)
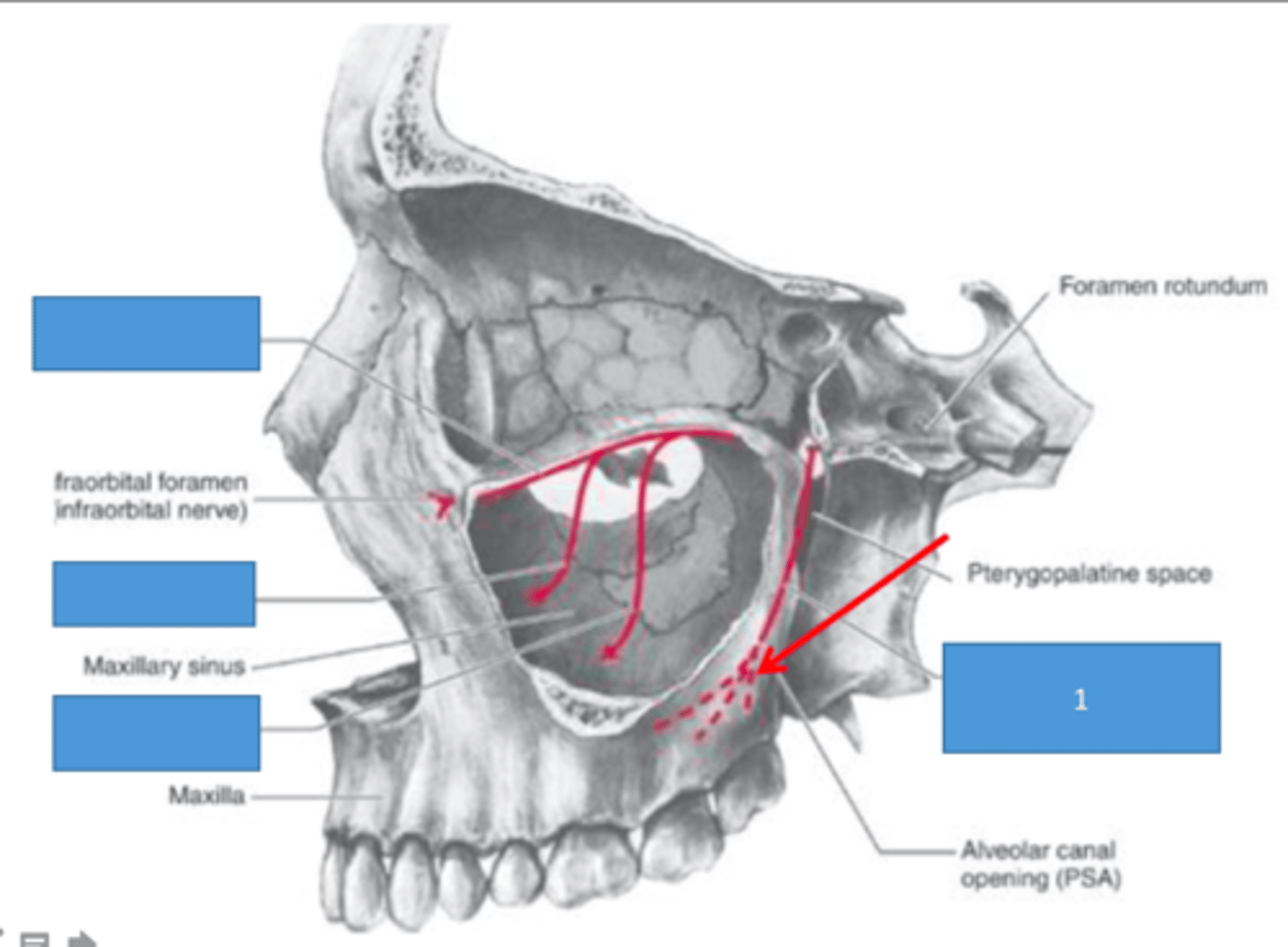
maxillary artery
This artery may be the most important artery to dentist and hygienist. Its own branches consist of three parts that
separately supply blood to the mandibular teeth (mandibular part-inferior alveolar artery, mental artery, and incisive artery), the four muscles of mastication (pterygoid part), and the maxillary teeth and
palate (pterygopalatine part-PSA artery, infraorbital artery, MSA artery, ASA artery, and descending palatine artery)
mandibular part
1st part on left
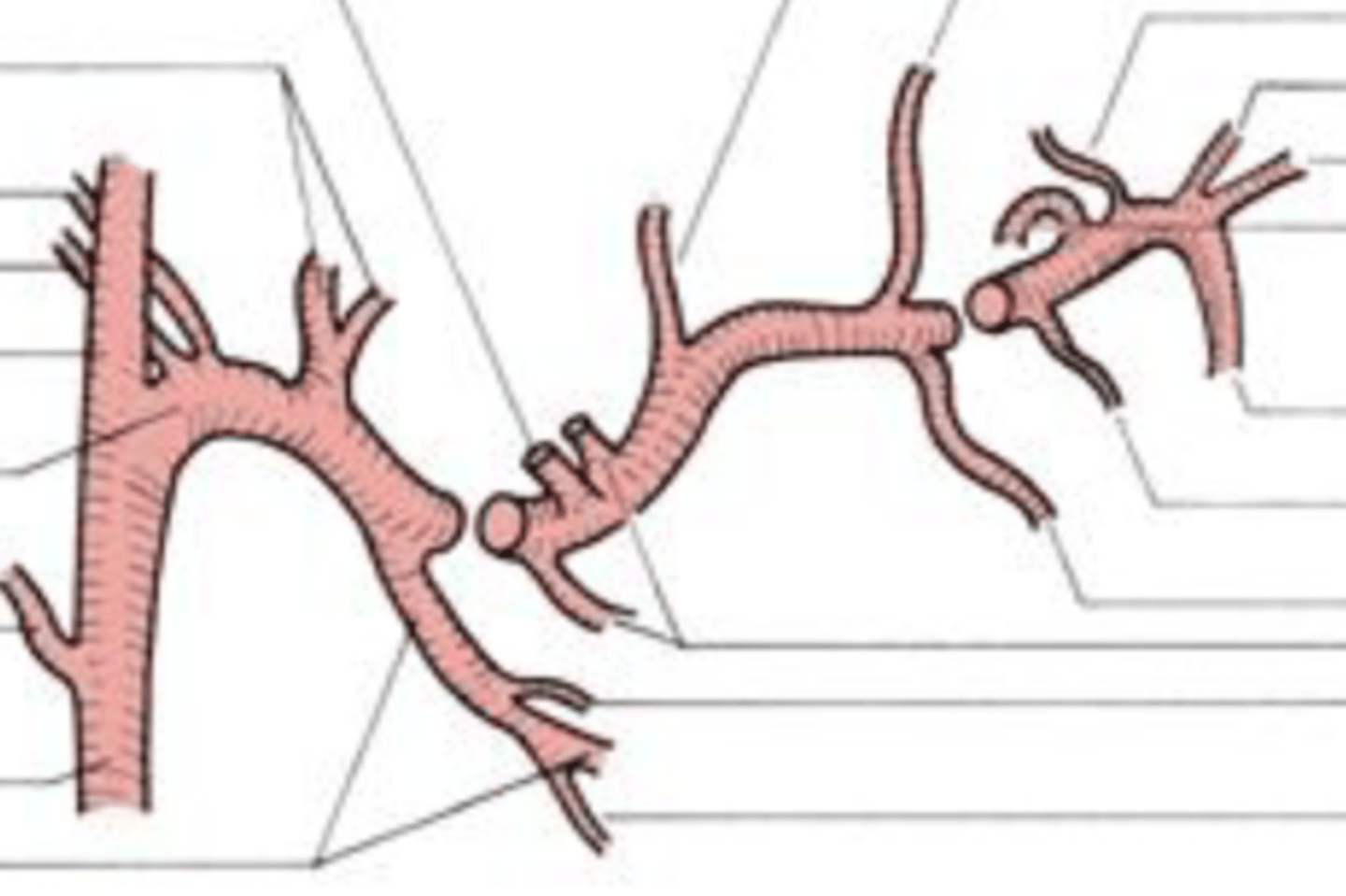
pterygoid part
middle part
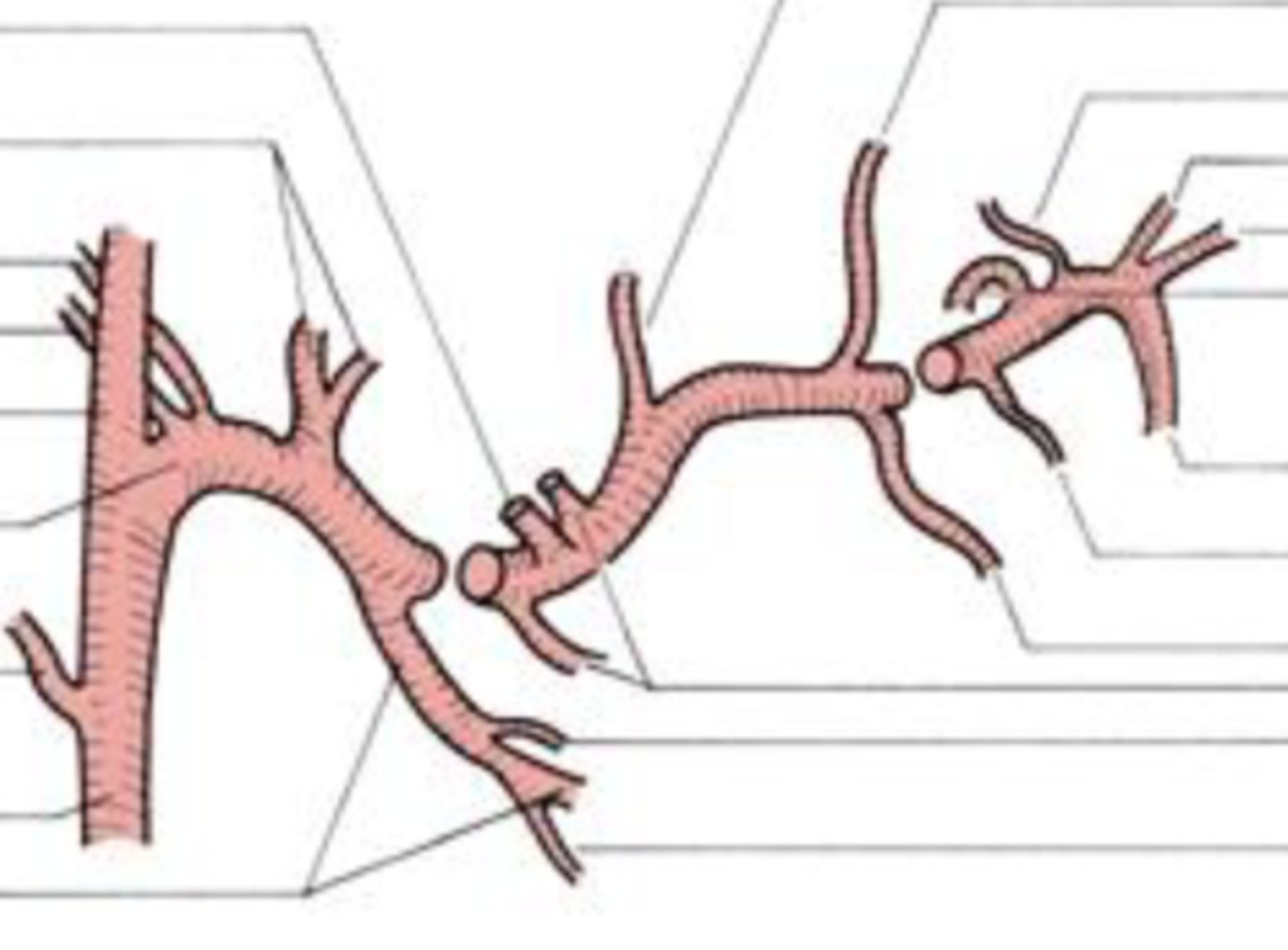
pterygopalatine part
3rd part on the right
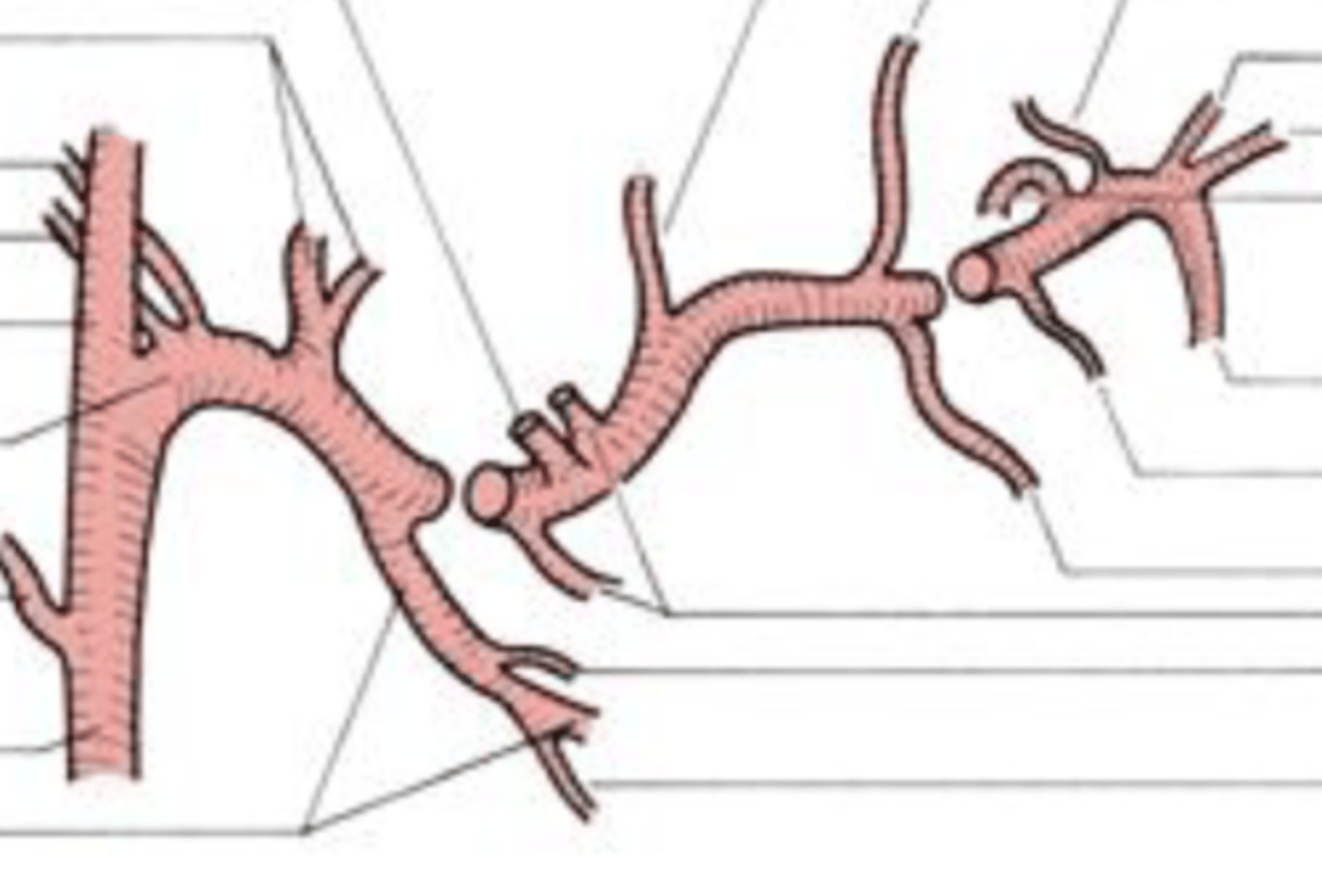
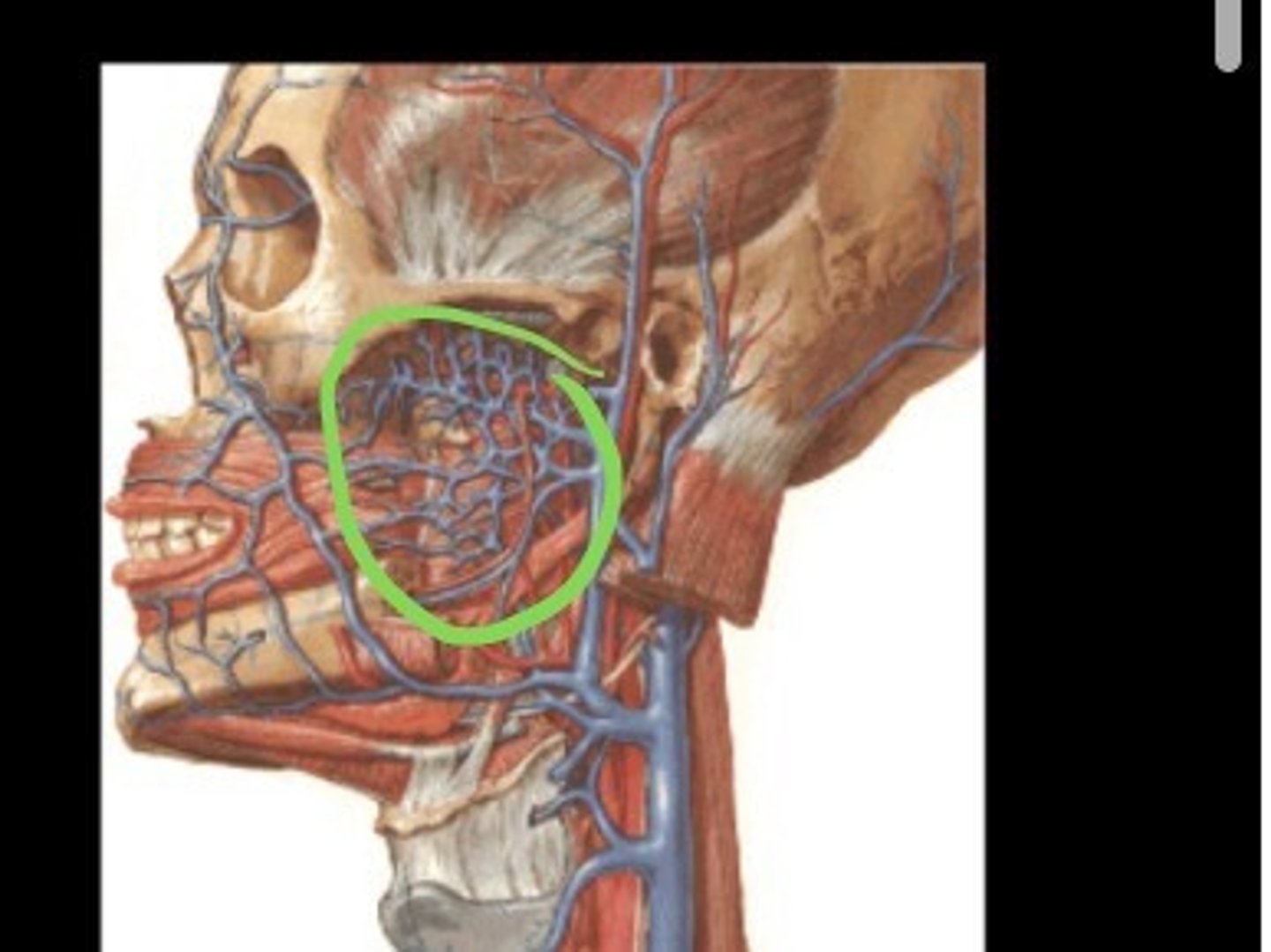
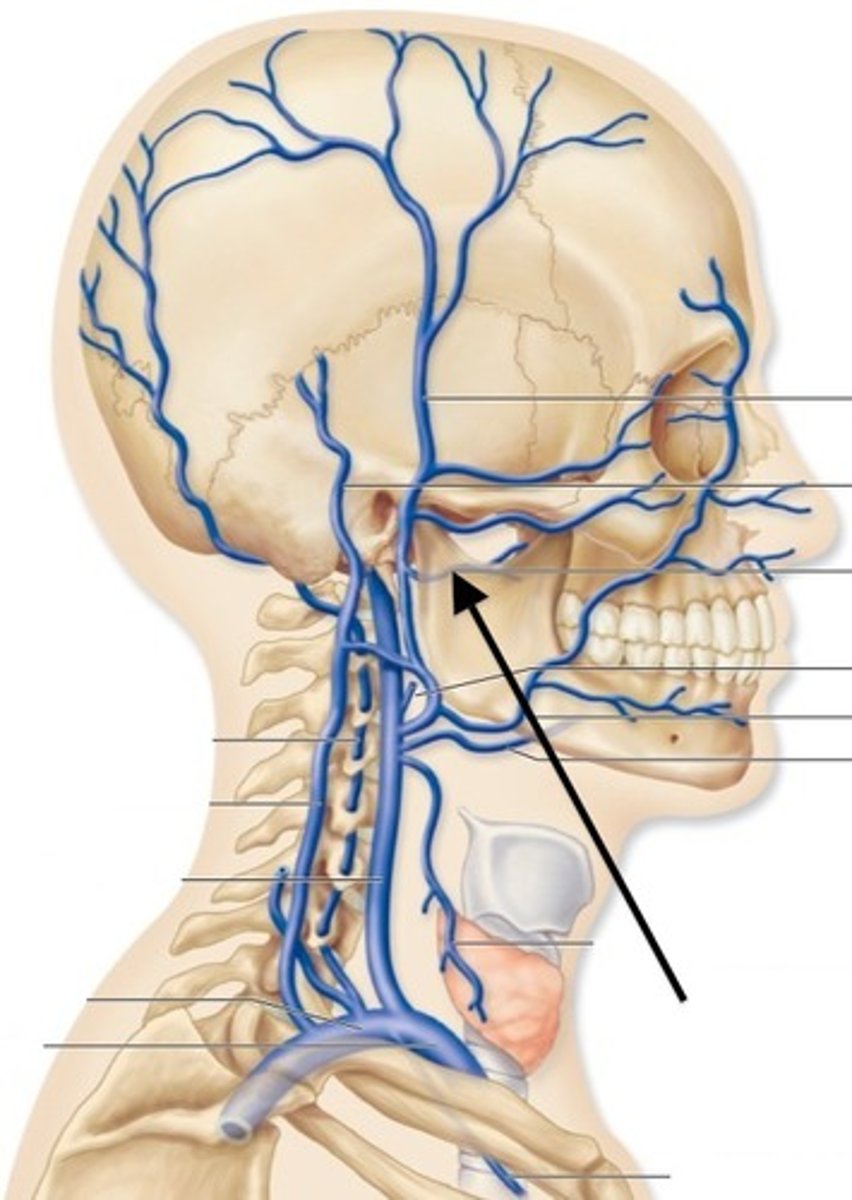
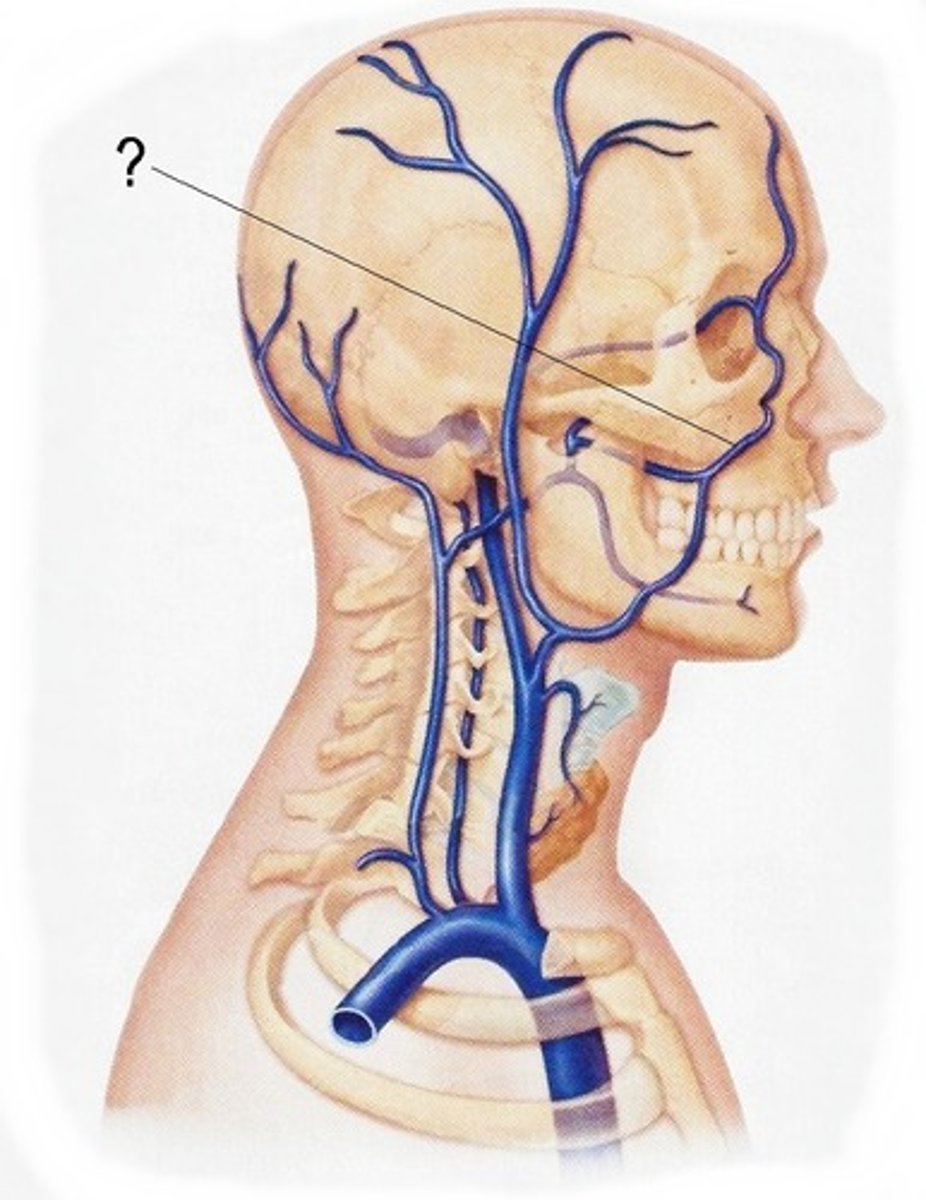
pterygoid plexus
Numerous deep veins drain blood from the upper part of the face, the tissue of the lips, and muscles around the
mouth, the posterior part of the nasal cavity, the palate, the maxillary alveolar process, and the maxillary teeth into the _______
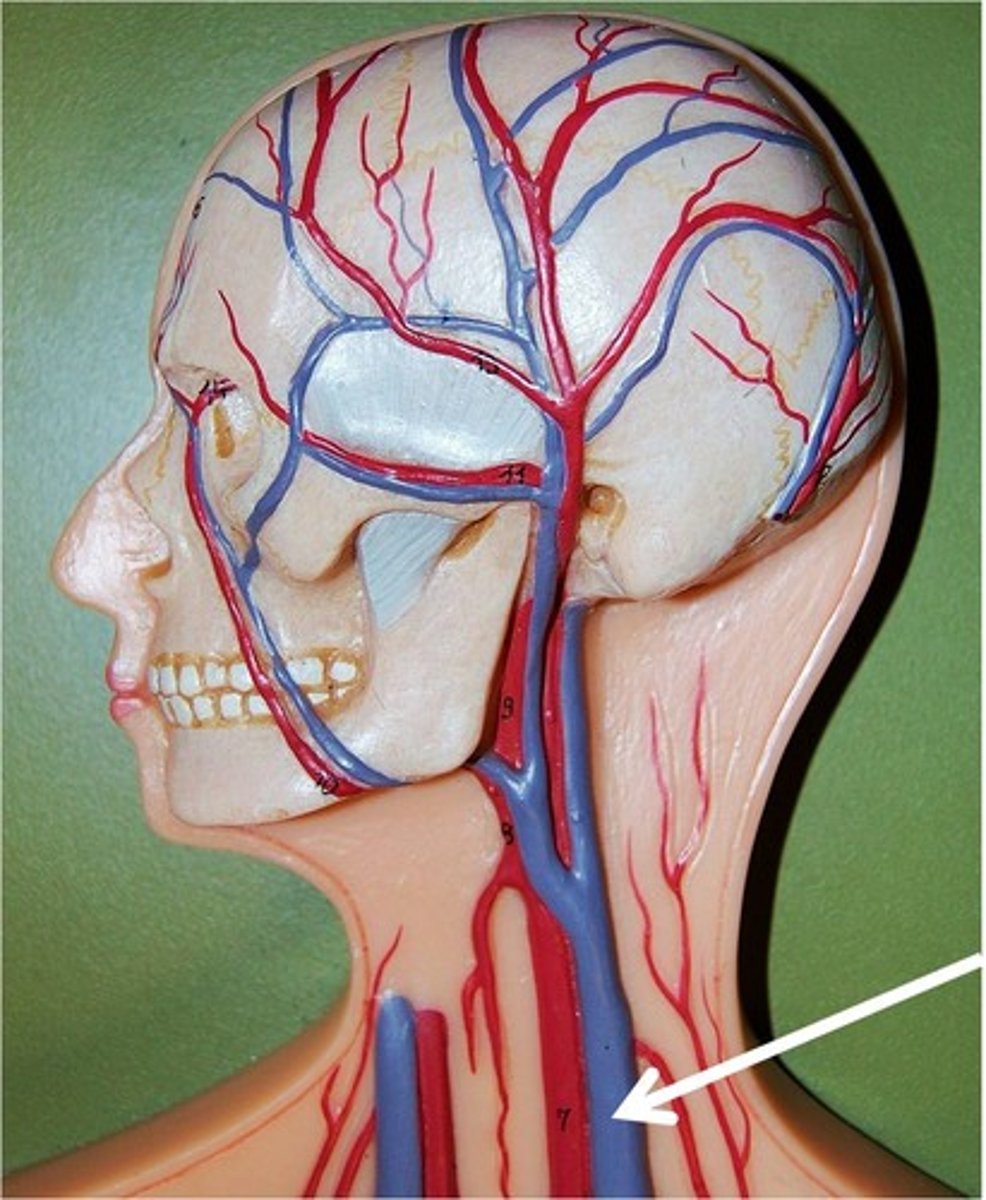
maxillary vein
Veins of the pterygoid plexus empty into the short ______
retromandibular vein
The blood then passes to the next vein to drain those areas that received blood through the maxillary and superficial temporal arteries
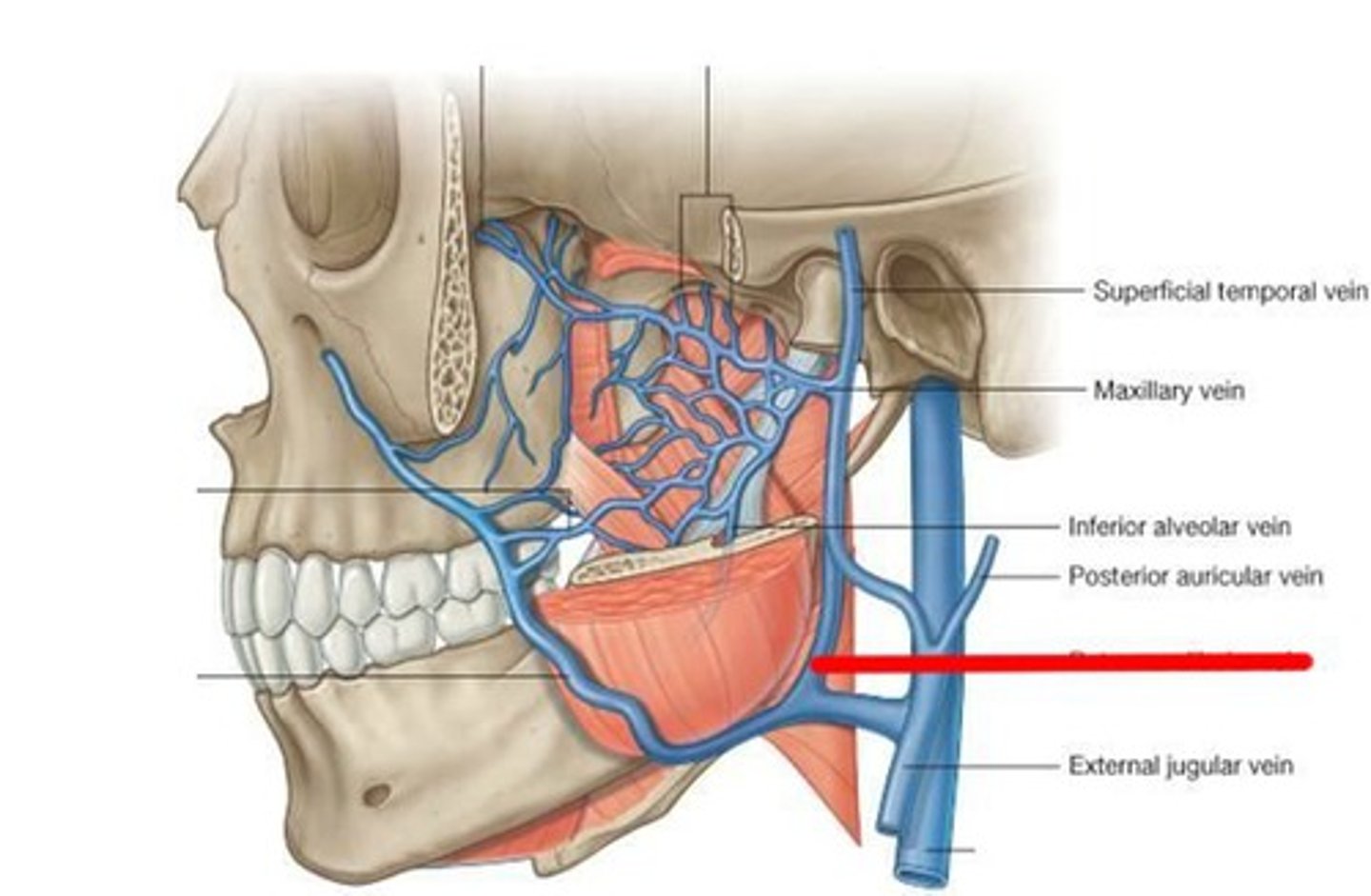
facial vein
An important superficial vein that also drains blood from the face. Receives blood from the area around the eyes, nose, lips and the muscles of mastication
internal jugular vein
The maxillary vein, retromandibular vein, facial vein, lingual veins, and deep facial vein drains into the common facial vein and then into the ______
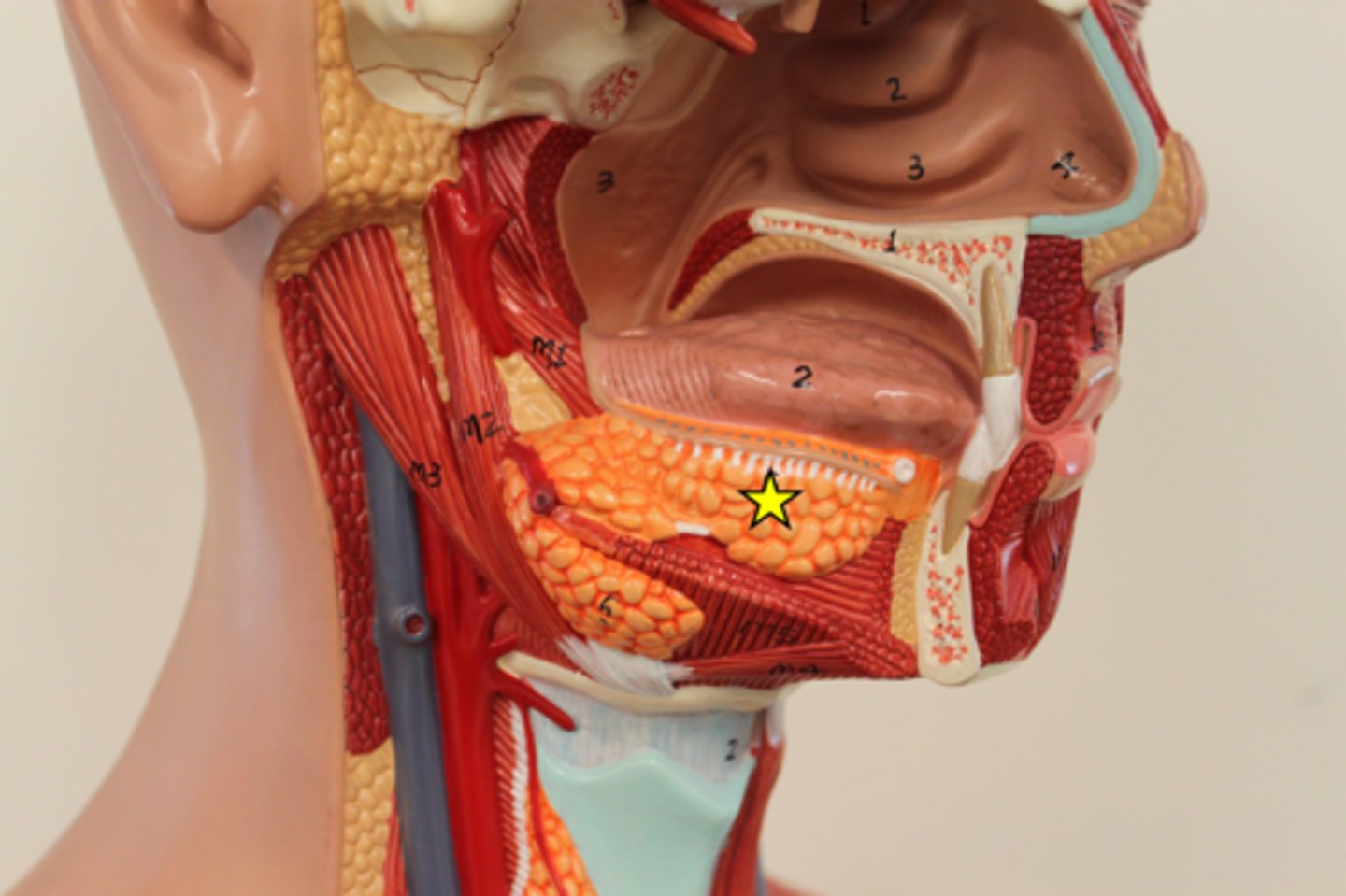
submandibular gland
wharton's duct
drains submandibular gland
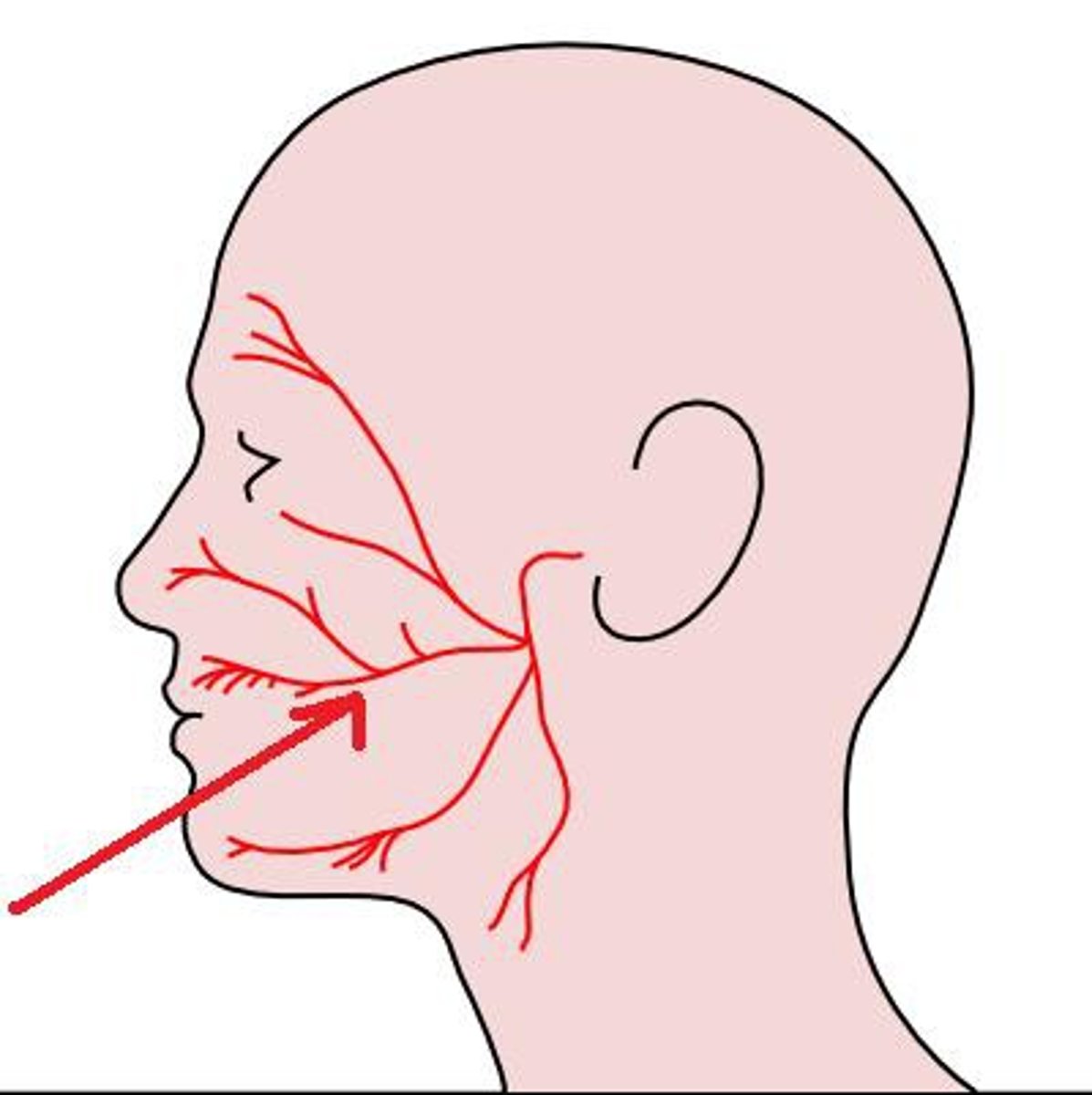
parotid gland
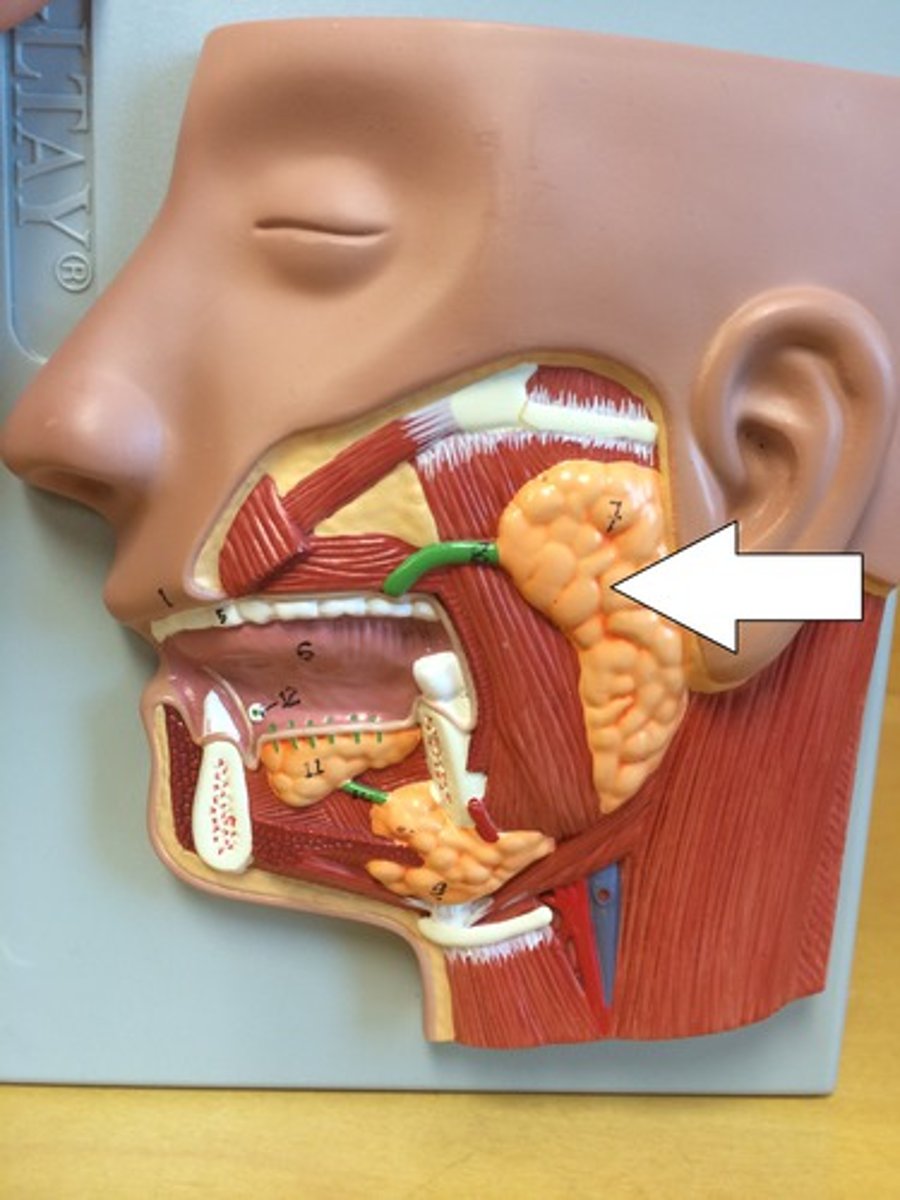
stenson's duct
Drains the parotid gland
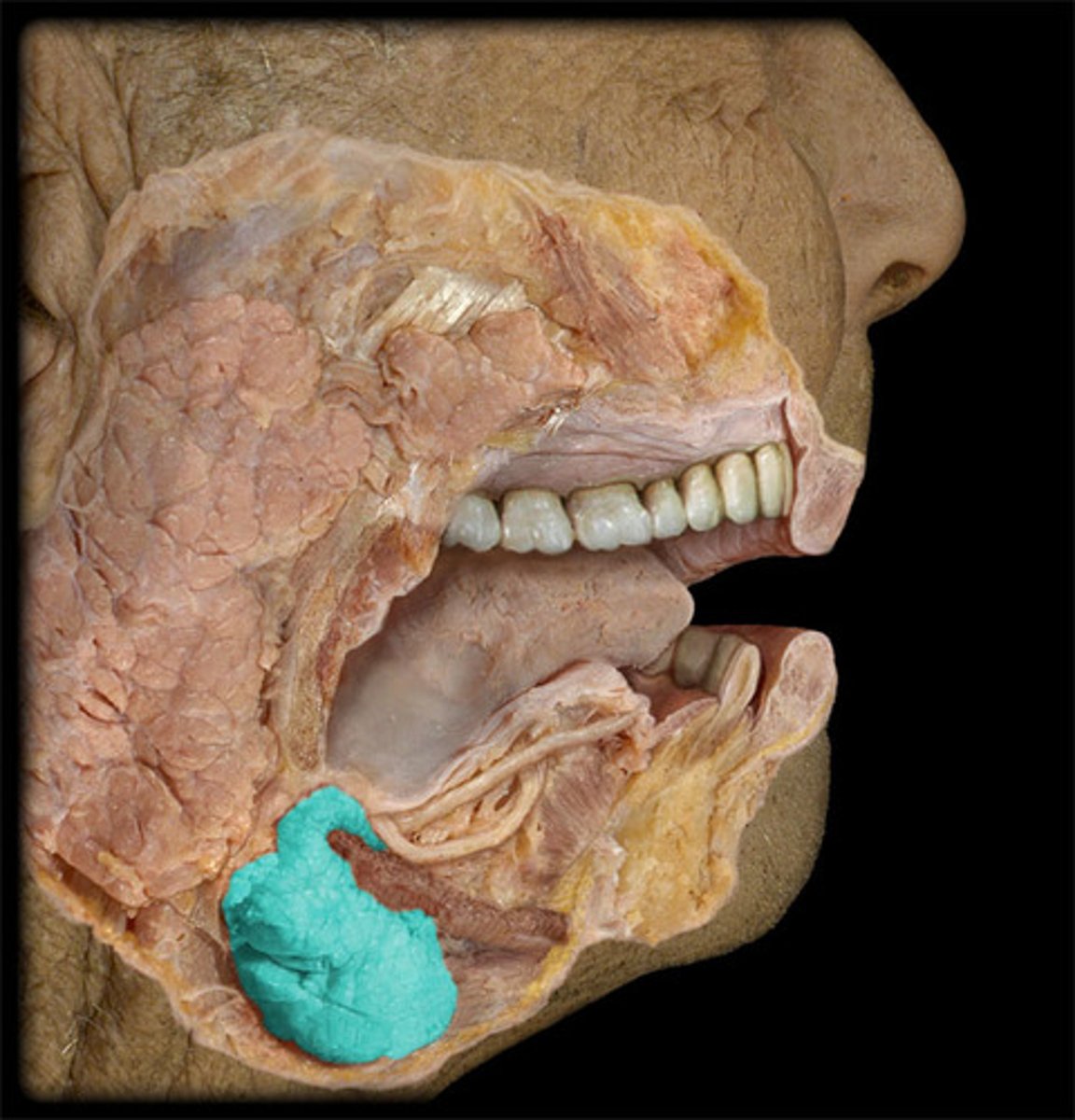
sublingual gland
Bartholin's duct
drains sublingual gland
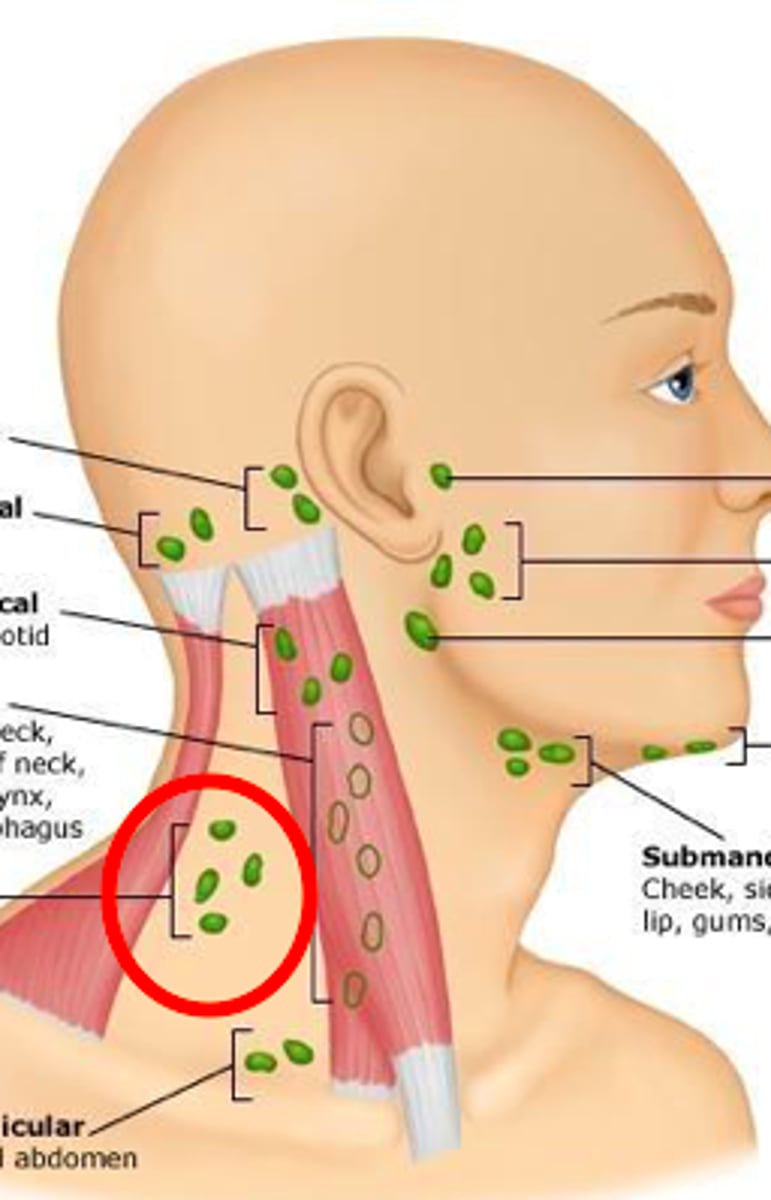
submental nodes
Infection in the area of the chin, tip of the tongue, anterior floor of the mouth, lower lip, and adjacent gingiva all drain into the ______
*when enlarged, these nodes can be palpated just posterior to the mandibular symphysis)
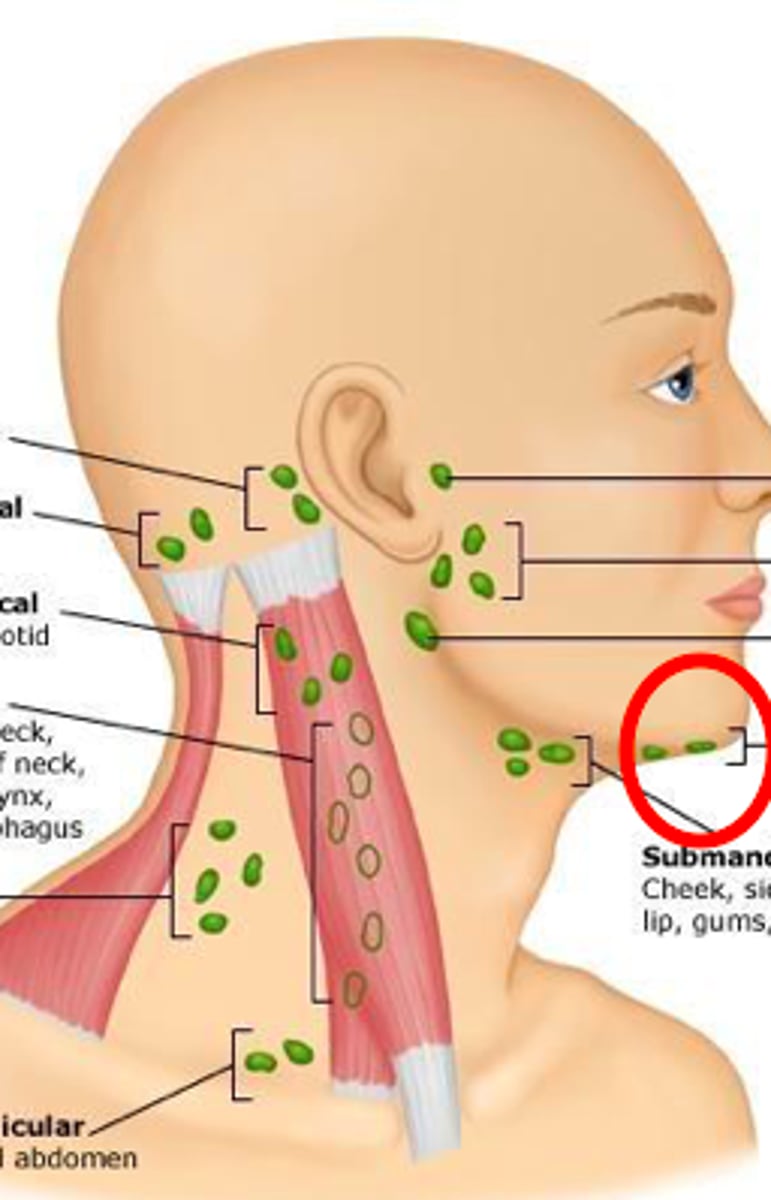
submandibular nodes
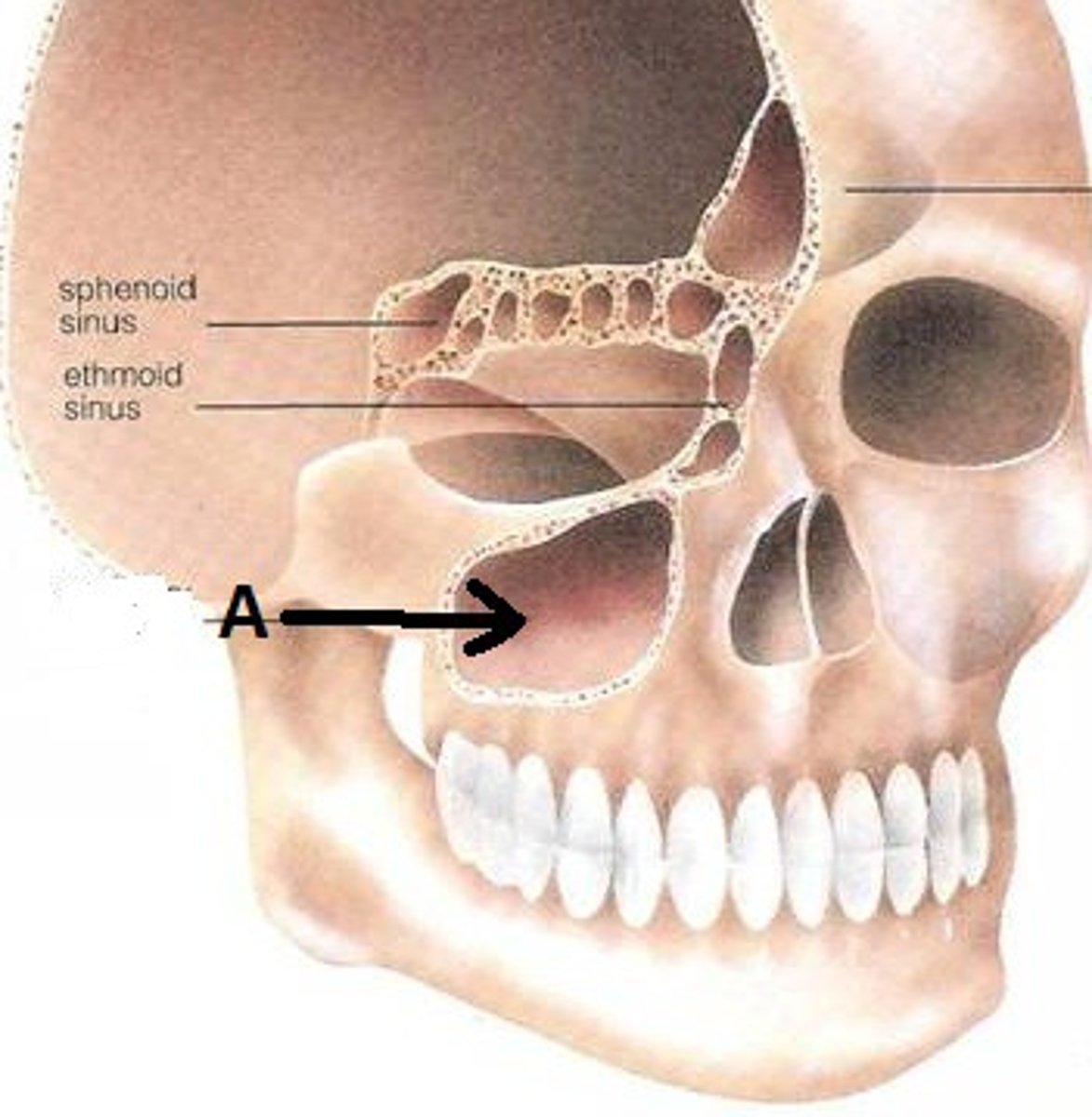
infection will drain from the submental nodes into the _______ which also collect fluid from maxillary and mandibular teeth, facial and palate all tissue, posterior floor of mouth, sides of tongue anteriorly, cheek
and side of nose, upper and lower lip, and maxillary sinus.
*When enlarged, these nodes can be palpated medial and anterior to the angle of the mandible
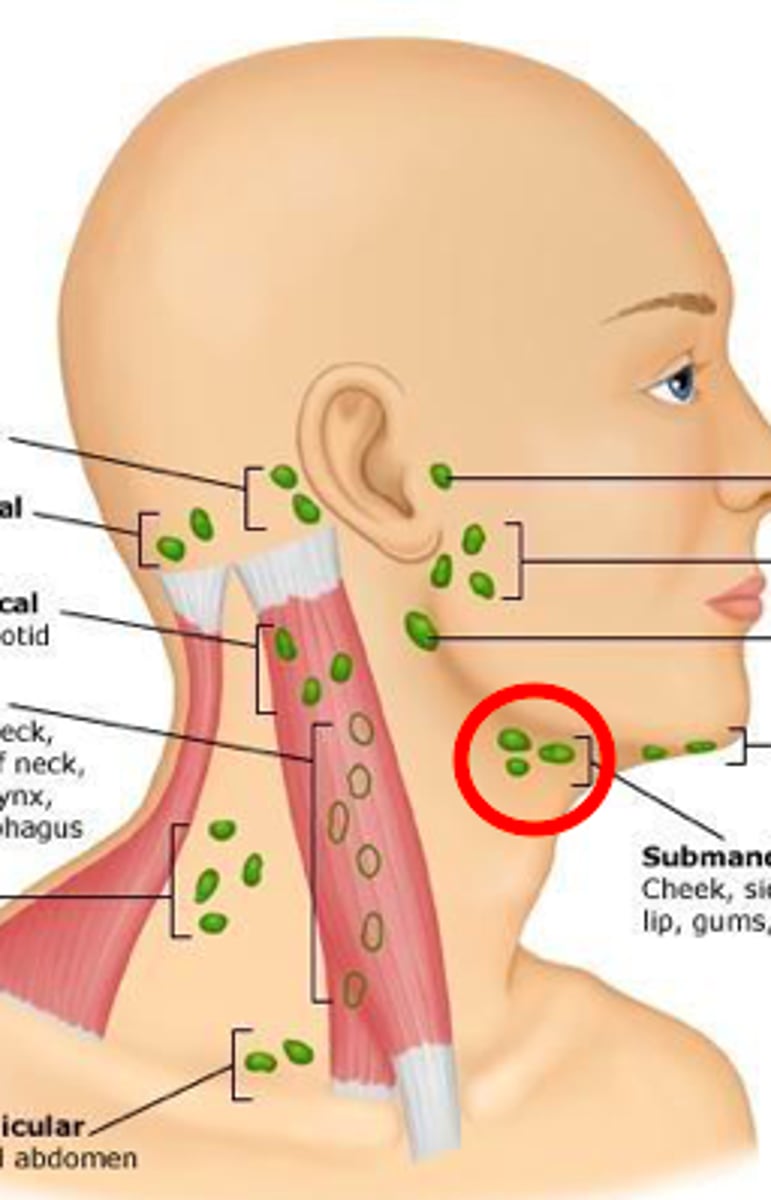
parotid nodes
infection will drain from submandibular nodes into the ________ which also receives lymph from the areas around the parotid gland (ear, prominence of the cheek, eyelids)
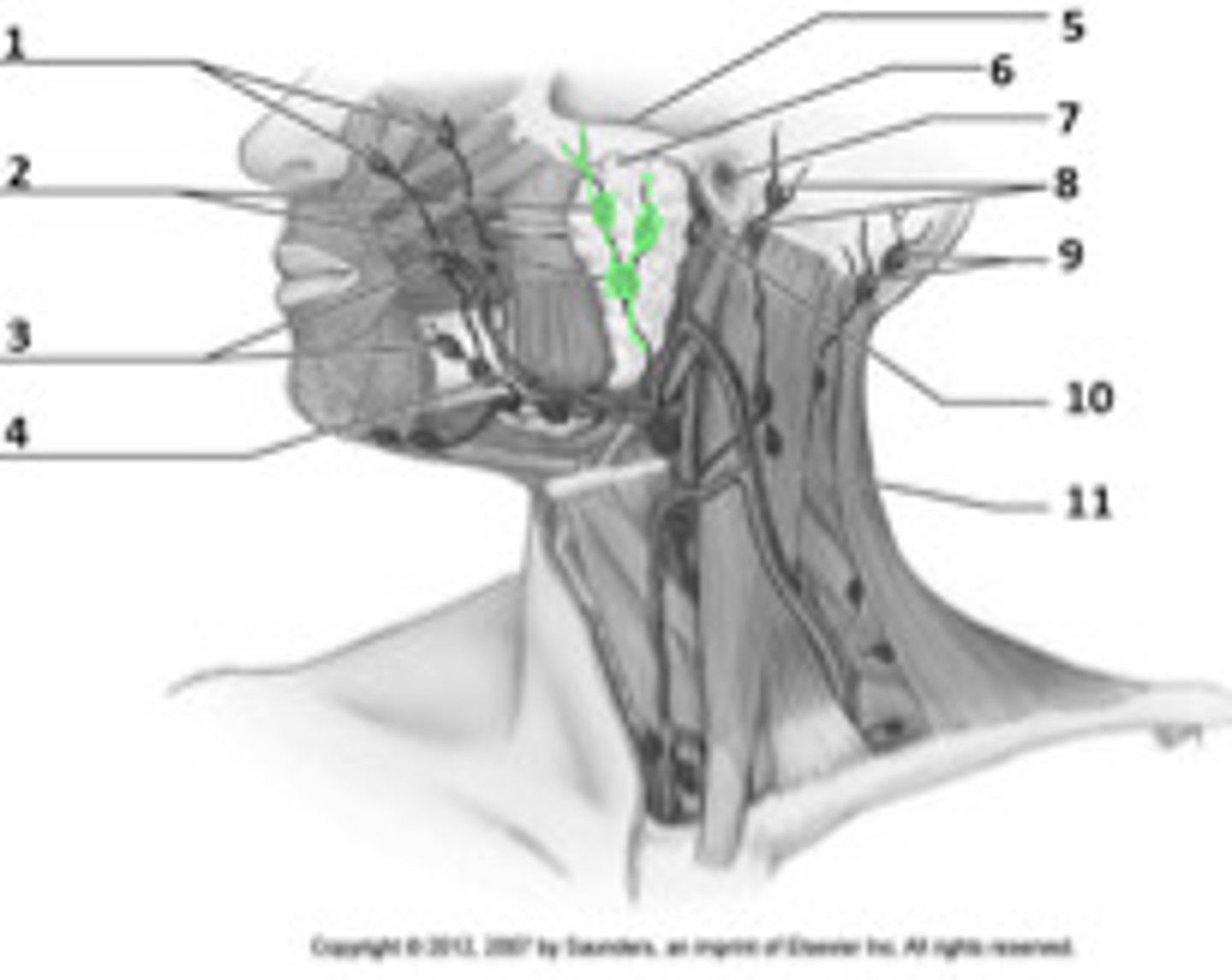
cervical nodes
infection will drain from the parotid nodes into the _______ chain of lymph nodes