Nonpolar, aliphatic amino acids
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Nonpolar, aliphatic amino acids
On inside of proteins, stabilizes core of protein
Hydrophobic effect stabilizes protein structure
Aliphatic: carbon atoms form open chains, as in alkanes
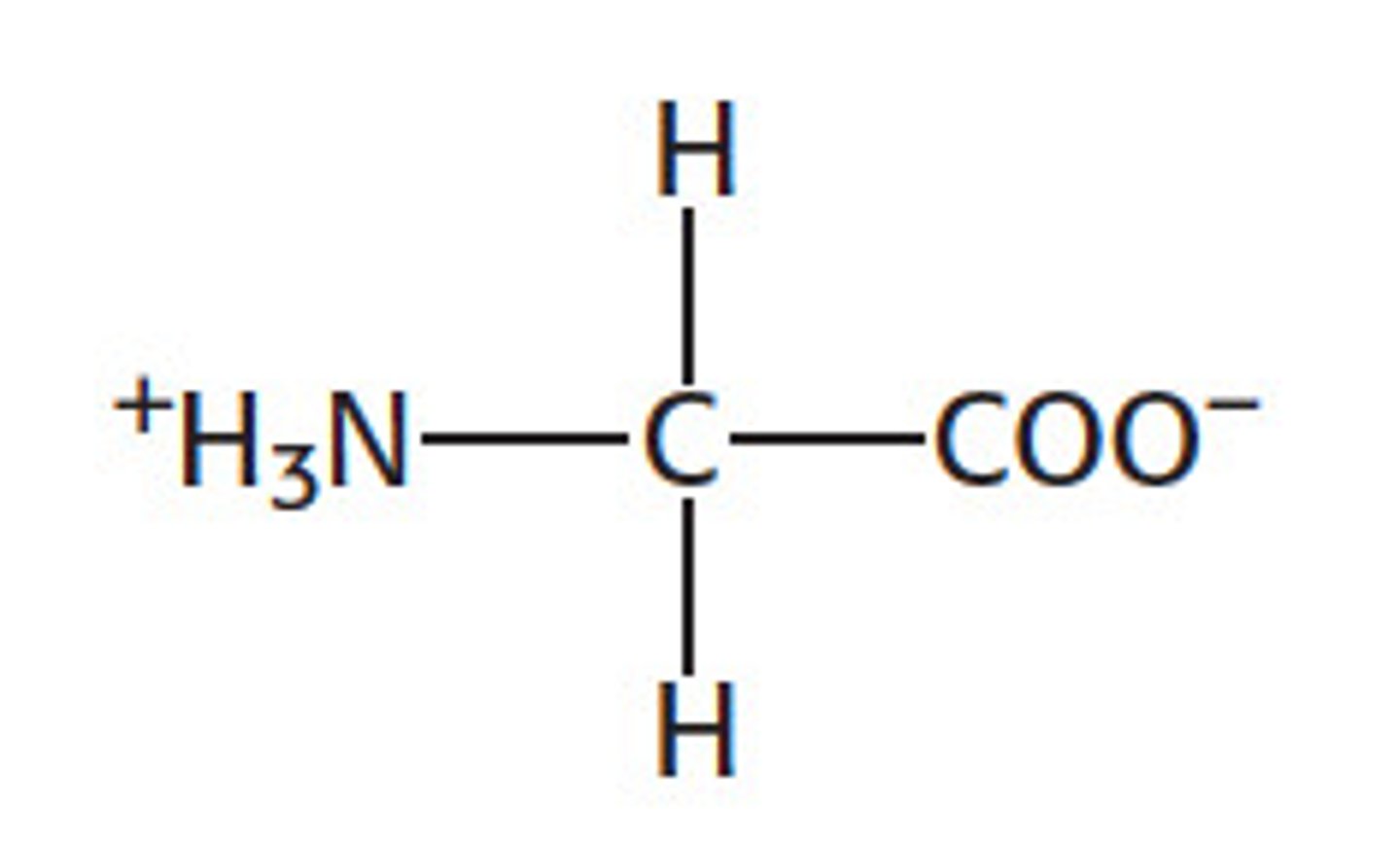
Glycine (Gly, G)
nonpolar, hydrophobic
R group consists of H
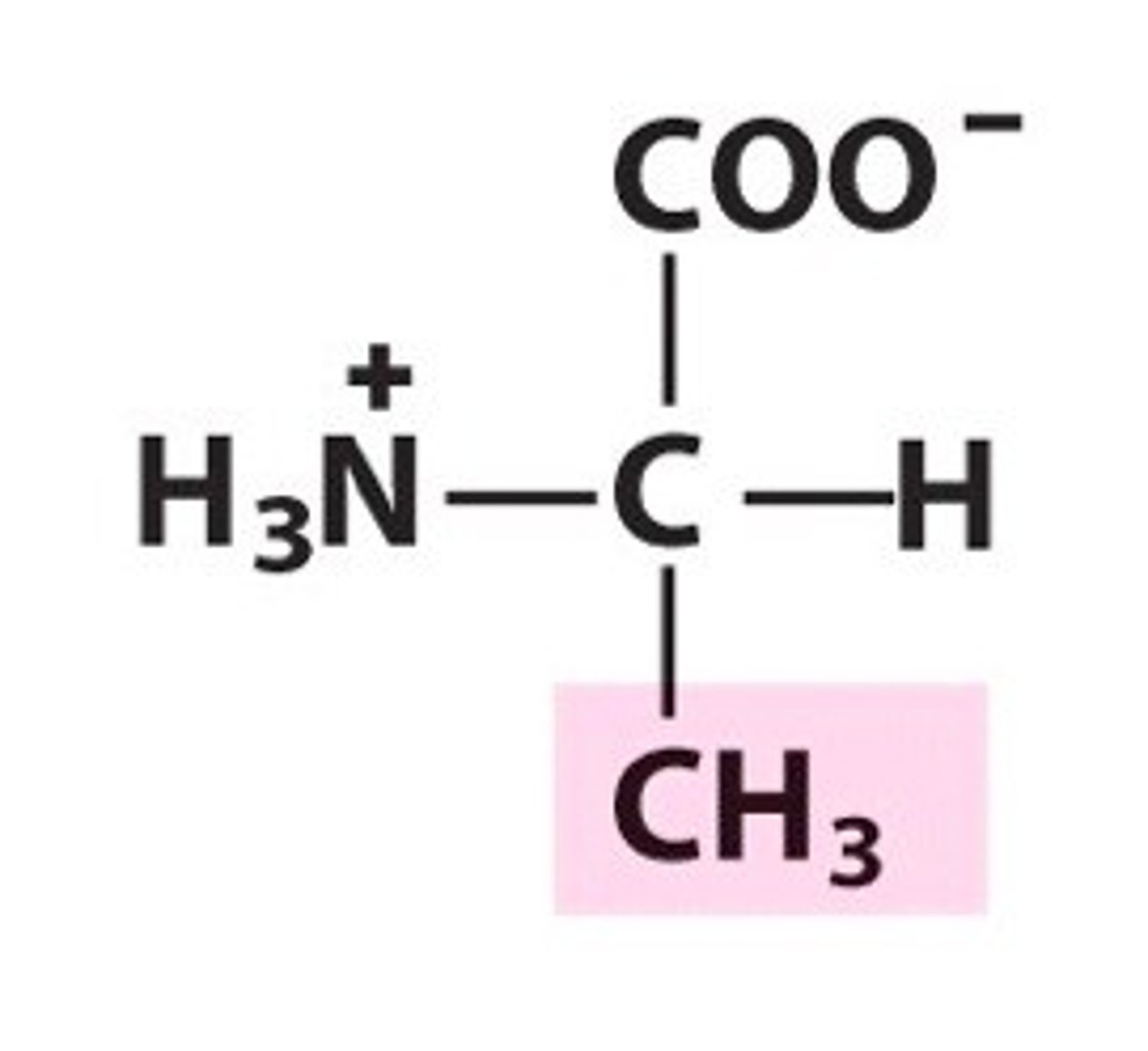
Alanine (Ala, A)
nonpolar, hydrophobic
R group consists of CH3
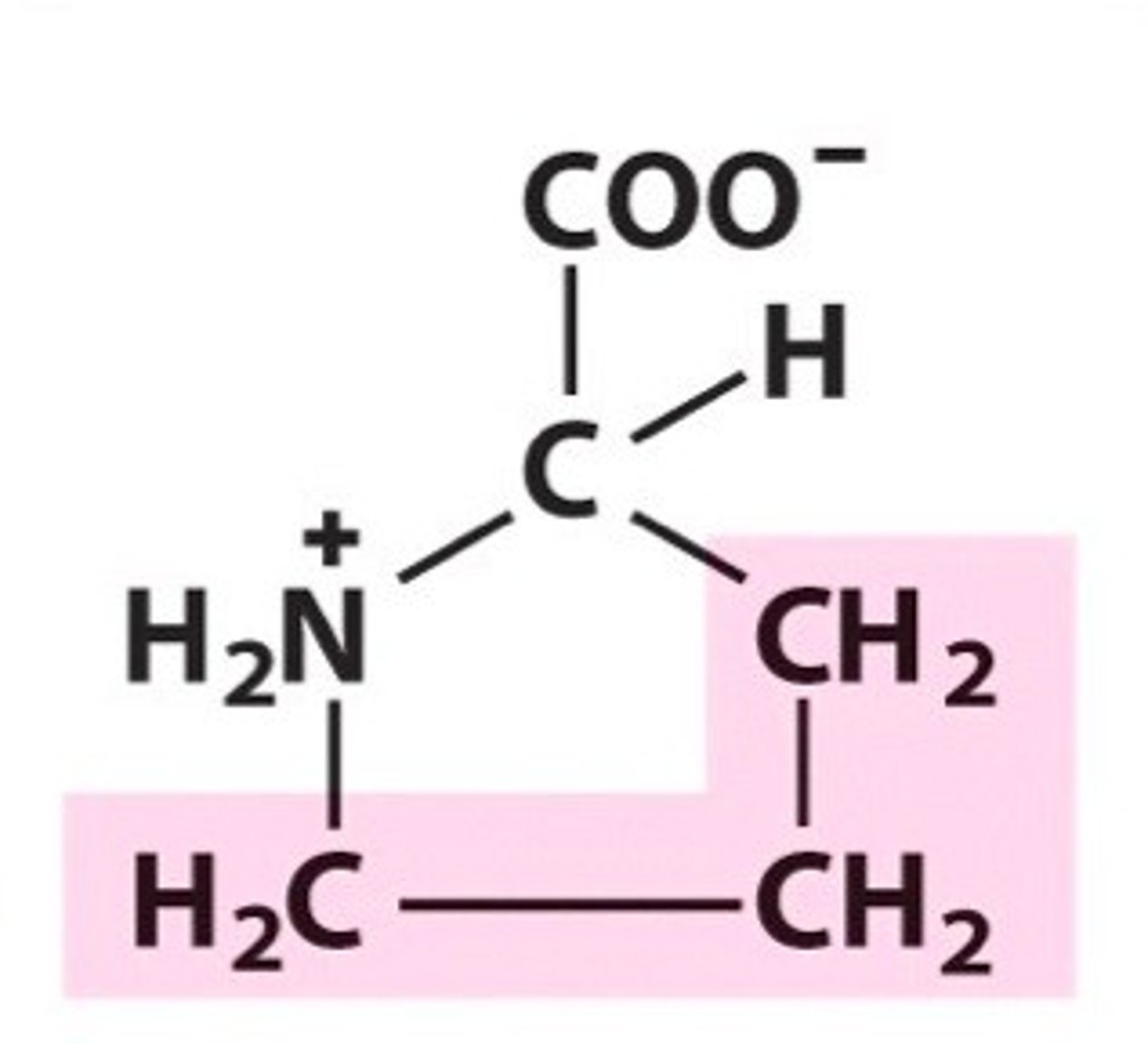
Proline (Pro, P)
nonpolar, hydrophobic;
alpha helix breaker - rigid, causes kinks in the secondary protein structure alpha helices
Alpha amino is not free, attached in 4-C pentagon (including alpha)
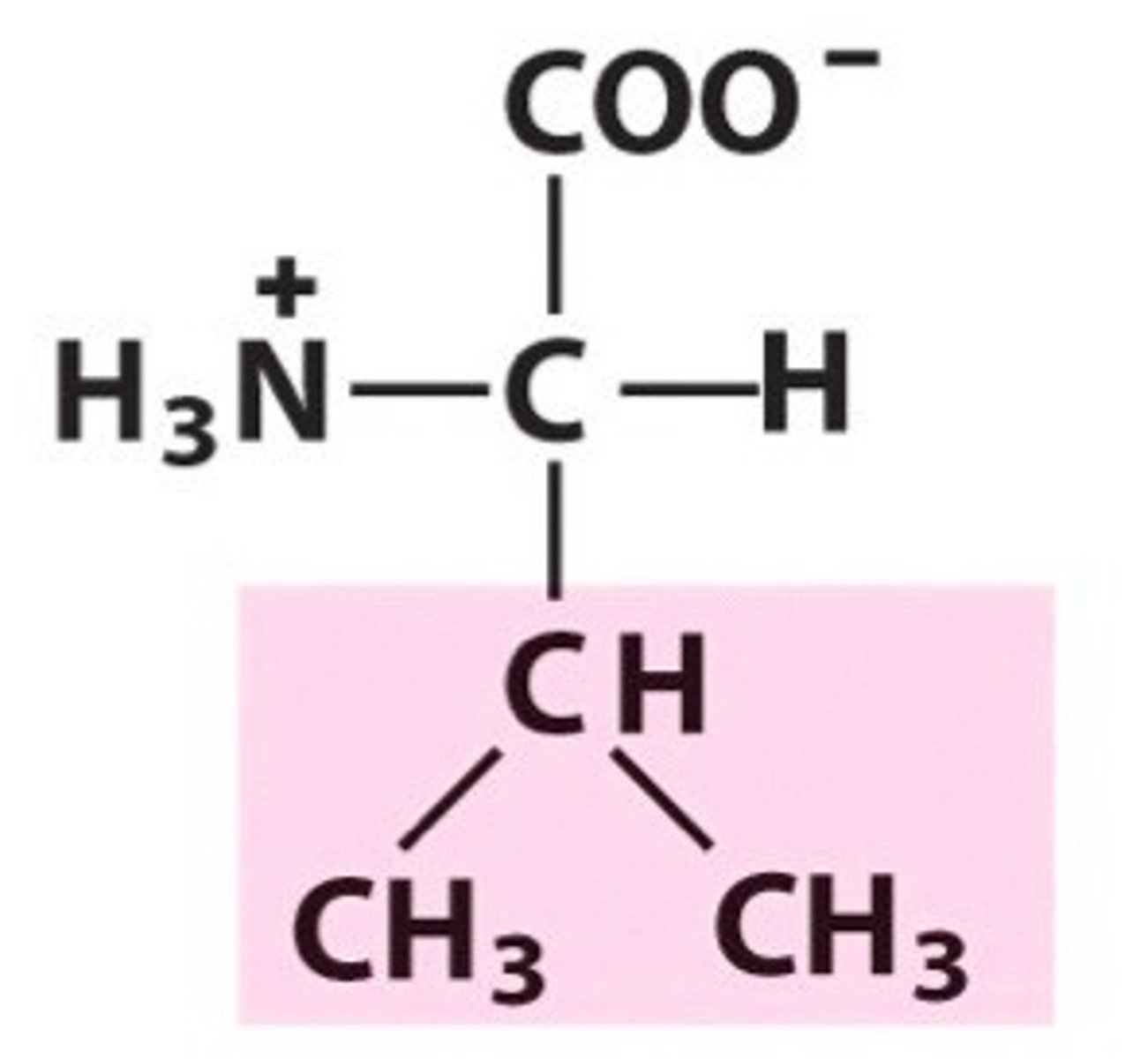
Valine (Val, V)
nonpolar, hydrophobic
R group is isopropyl group
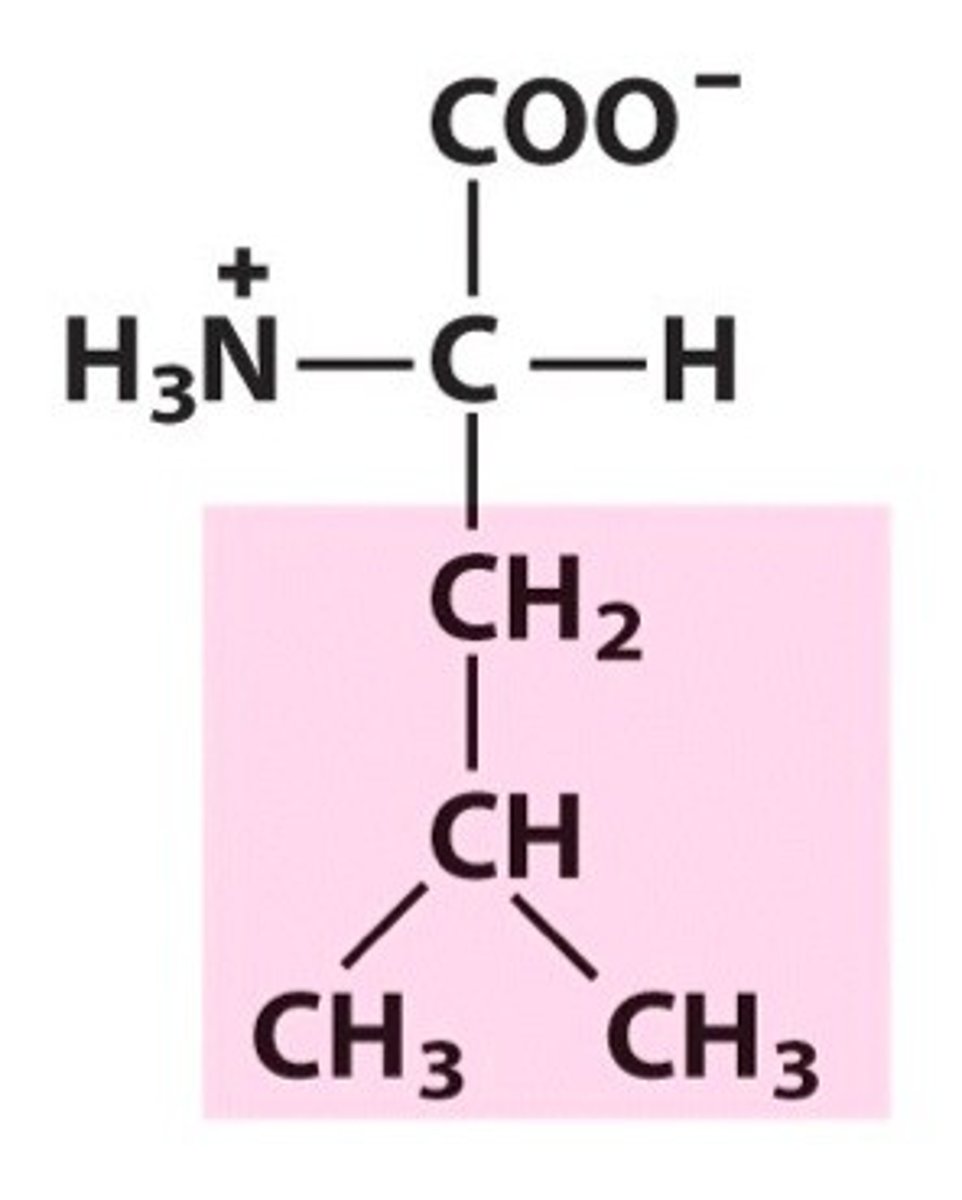
Leucine (Leu, L)
nonpolar, hydrophobic
R group is Ch2-isopropyl
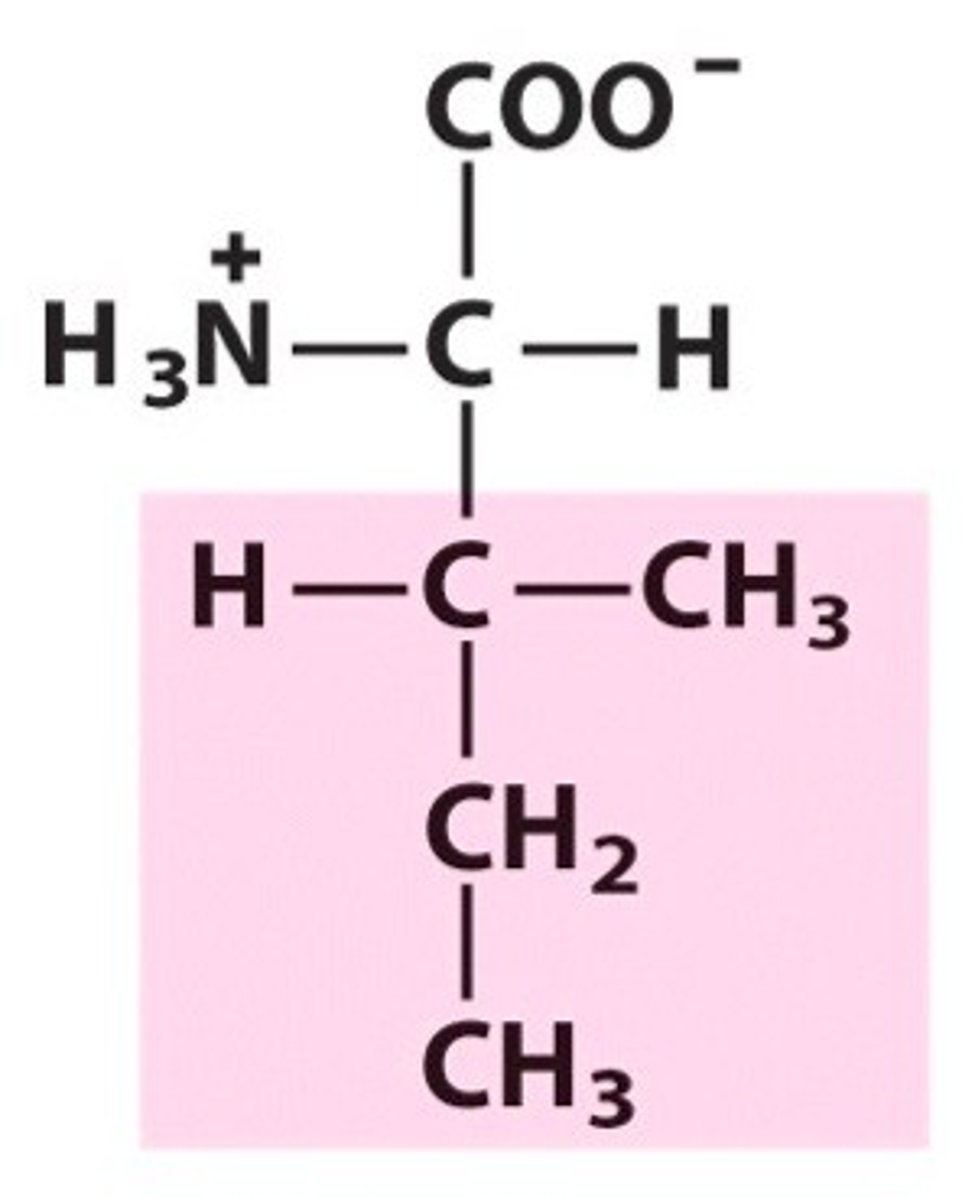
Isoleucine (Ile, I)
nonpolar, hydrophobic
R group is alpha-C bonded to H-C-C3. Middle C is bonded to ethyl group.
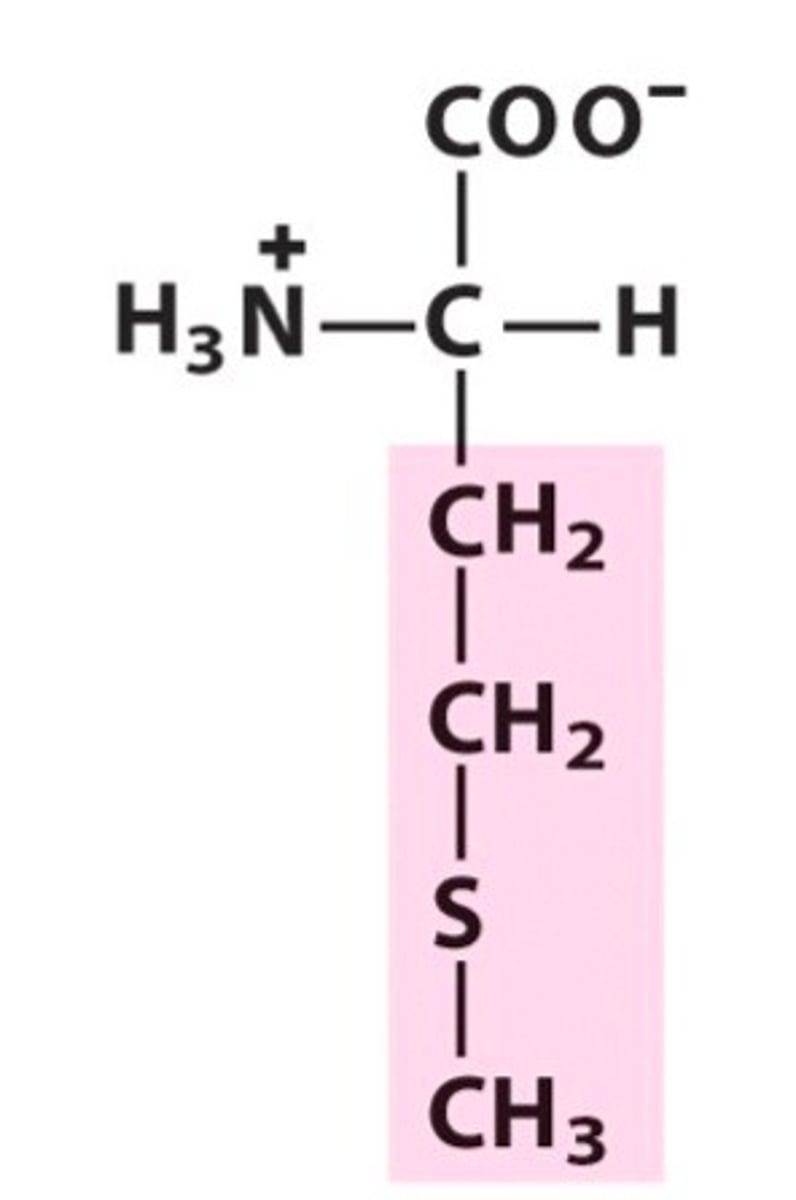
Methionine (Met, M)
nonpolar, hydrophobic
R group is Ch2-Ch2-S-Ch3
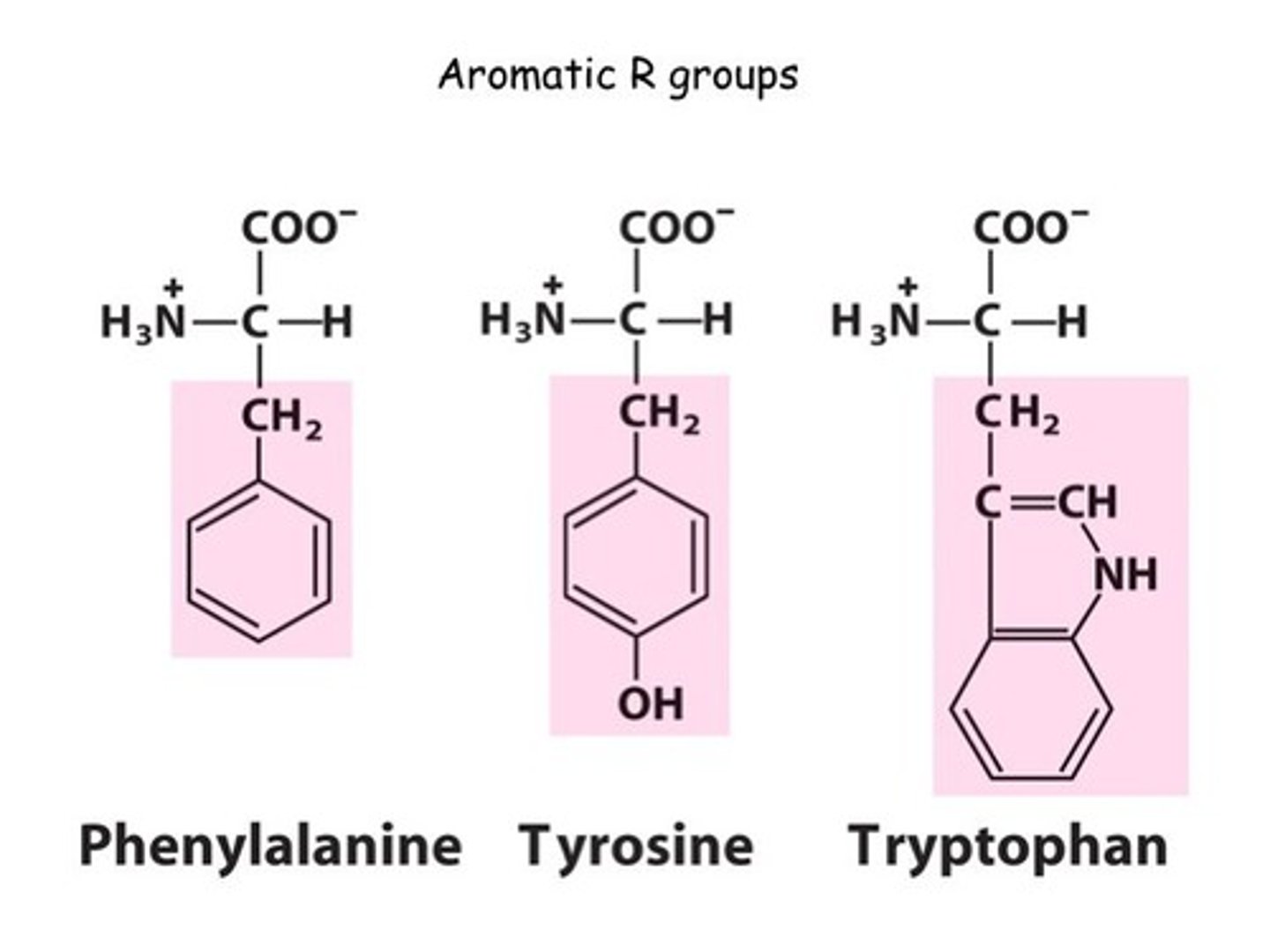
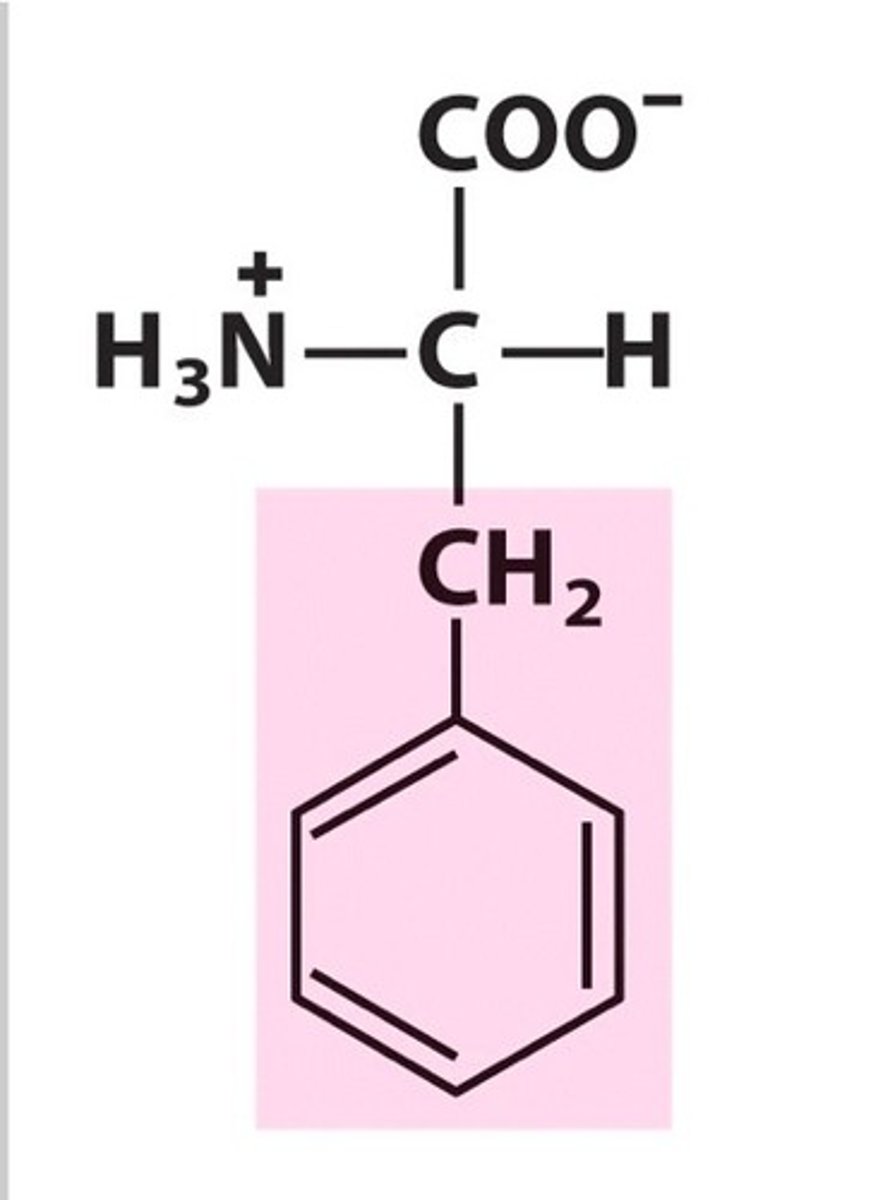
Phenylalanine (Phe, F)
non-polar, aromatic, hydrophobic
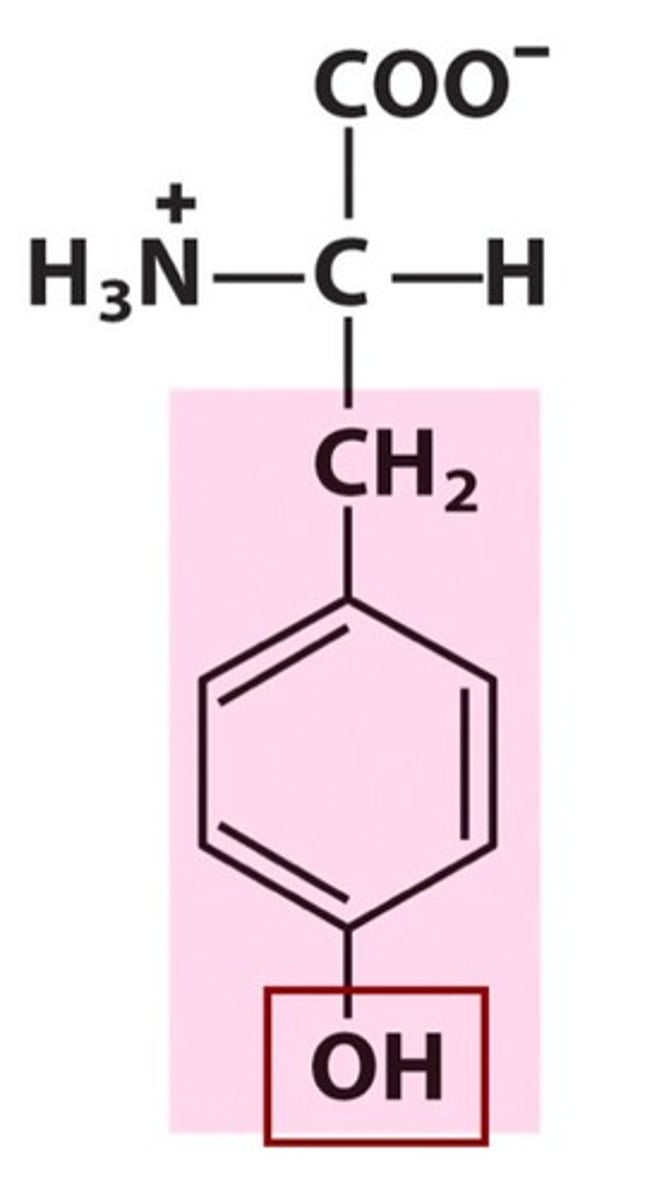
Tyrosine (Tyr, Y)
polar aromatic, partial hydrophilic. pka = 10. IONIZABLE
R-OH <---> R-O- + H+
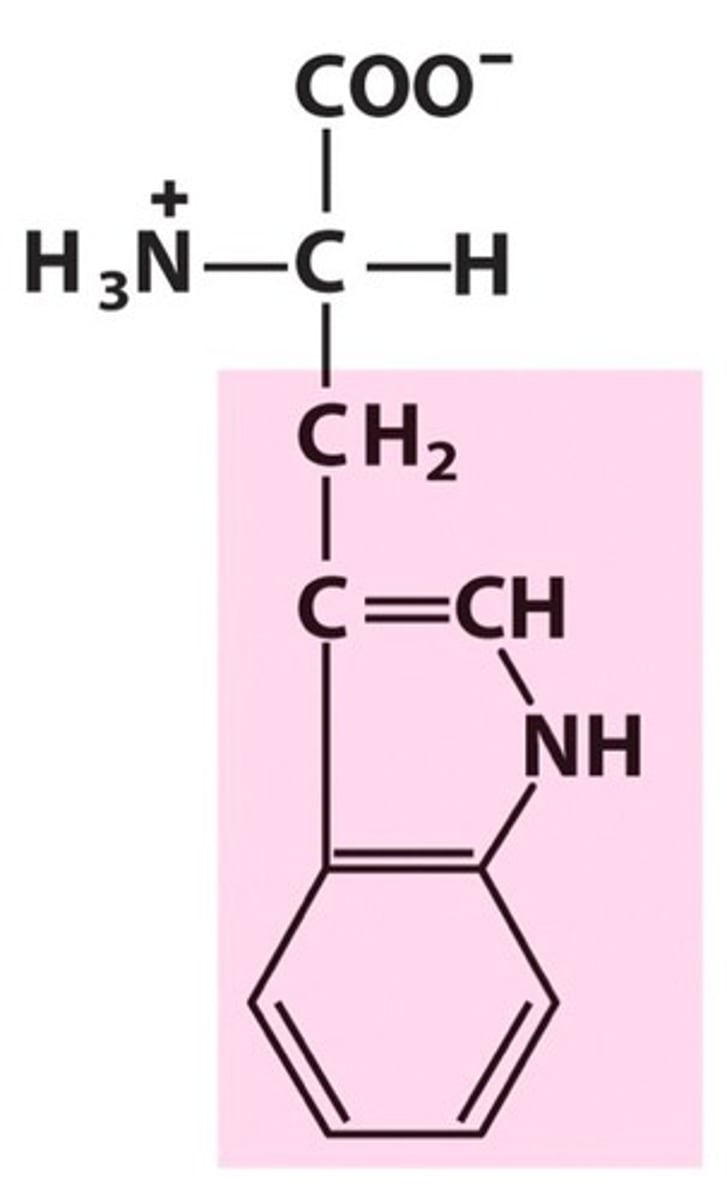
Tryptophan (Trp, W)
aromatic, hydrophobic
Aromatic R groups
useful for detection, absorbs UV light around 280 nm