Influence of genes on behaviour, inlcuding genotype and phenotype, genetic basis of behaviour
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is a gene?
Gene= a part of a chromosome of an organism that carries information in the form of DNA. The human genome has 23 pairs of chromosomes with 21,000 genes distributed across them
What is the genotype?
Genotype= the genetic makeup of an individual; the inherited genetic material that is passed from generation to generation
What is the phenotype?
Phenotype= the observable characteristics of an individual; this results from the interaction between the genotype and the environment
What is evolution?
Evolution= refers to the changes in the genetic makeup of a population or genotypes changing in response to natural selection
What is natural selection?
Natural selection= the process by which inherited characteristics that confer a survival advantage are passed on to the next generation and spread through a population
What is neurochemistry?
Neurochemistry= the study of chemical and neural processes associated with the nervous and endocrine systems
What are the main assumptions of the biological approach?
The main assumptions of the biological approach=
psychology and biology can be combined to give physiological explanations of human behaviour
how we think, feel + behave can be explained in terms of physical factors (nature-based)
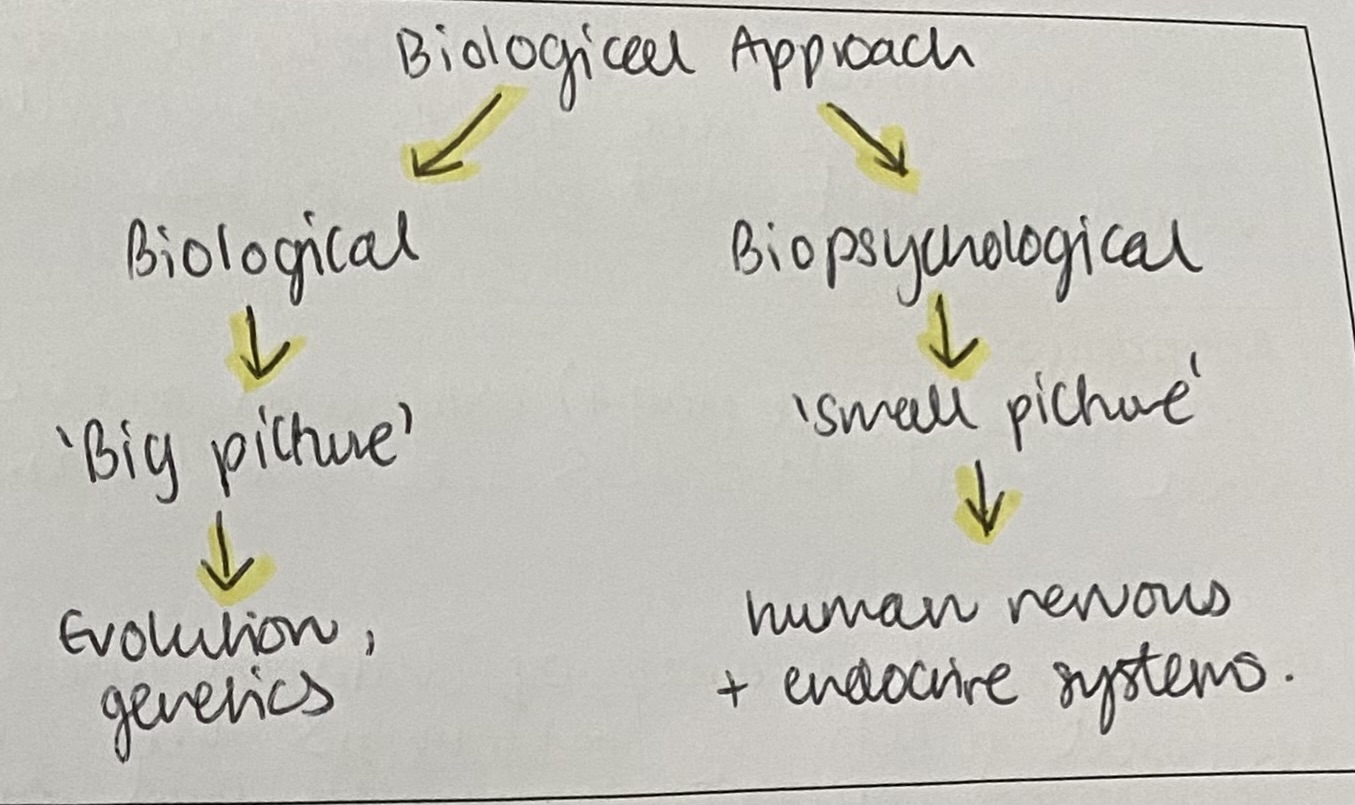
What is the diagram for the main assumptions of the biological approach?
Diagram for the main assumptions of the biological approach=
How are genes and environment linked to nature and nurture?
Genes= nature
environment= nurture
How does our behaviour affect our DNA?
Our behaviour affects our DNA (epigenetics)
for e.g. smoking
How does our behaviour affect how we interact with our environment?
Our behaviour affects how we interact with our environment
being a vegetarian can put less pressure on ecosystems and be more healthy
What is the genetic basis of behaviour?
The genetic basis of behaviour=
individuals have a unique combination of genetic instructions; hence we differ from each other in terms of personality, intelligence etc
What does heritability mean?
Heritability= refers to the amount of variability, within a trait in a population, which can be attributed to genetic differences between individuals within that population
the more a trait is influenced by genetic factors, the greater the heritability
i.e studies of identical twins shows that the difference in individual intellligence could be 60-80% due to genes
Who did the ‘Twin studies?’
Twin studies were done by Gottlesman & Shields (1991) that examined genetic explanations of schizophrenia
How was the ‘Twin studies’ done?
The ‘Twin studies’ was done by examining 210 monozygotic (identical) & 319 dizygotic (non-identical) twins to see whether, if one had schizophrenia, would the other develop it
What does the ‘Twin studies’ show?
The ‘Twins studies’ showed that they found a concordance rate of 35-50% in MZ and 9-26% in DZ
i.e. in 35-58% of cases where one MZ twin had it , the other had it too
Why were the ‘Twins studies’ done?
Twin studies were done as= schizophrenia is highly likely to have a genetic cause, but the fact that MZ twins are 100% genetically similar & DZ are 50%, would suggest other causes exist
Who did the ‘Adoption studies?’
The ‘adoption studies’ were done by Tienari et al (1994) that examined genetic explanations for a range of severe mental disorders i.e. psychosis
How were the ‘adoption studies’ done?
The ‘adoption studies’ were done by= examining a group of children whose biological parents have been diagnosed with a psychosis but had been adopted by undiagnosed carers or who had grown up with their diagnosed parents
What does the ‘adoption studies’ show?
The ‘adoption studies’ shows that= those that lived with their biological parents, the concordance rate was 30% and in those that lived with adoptive parents it was only 15%
Why were the ‘adoption studies’ done?
The ‘adoption studies’ were done as it suggest that such psychosis have both biological and environmental causes