National 5 Chemistry Unit 3 - Chemistry in Society
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What is a metallic bond?
A metallic bond is the electrostatic attraction between positively charged metal ions and a sea of delocalised electrons
Why are metallic elements conductors of electricity?
Because they contain delocalised electrons
What is the word equation for a metal reacting with oxygen?
metal + oxygen —→ metal oxide
What is the word equation for a metal reacting with water?
metal + water —→ metal hydroxide + hydrogen
What is the word equation for a metal reacting with dilute acid?
metal + dilute acid —→ salt + water
How can metals be used to prepare soluble salts?
By reacting excess metal with acid to produce hydrogen gas and a salt, filtering the mixture, and then evaporating the filtrate to dryness
What does OIL RIG stand for?
Oxidation Is Loss (of electrons), Reduction Is Gain (of electrons)
What is reduction?
A gain of electrons by a reactant in any reaction
What is oxidation?
A loss of electrons by a reactant in any reaction
What is a redox reaction?
A reaction in which reduction and oxidation take place at the same time
What takes place during the extraction of metals?
Metal ions are reduced, forming metal atoms
What is an ore?
A naturally occurring compound containing enough metal to make it worthwhile extracting
How are the least reactive metals extracted?
By heat alone
How are the most reactive metals extracted?
By electrolysis
How are moderately reactive metals extracted?
By heating with carbon or carbon monoxide
What is electrolysis?
The splitting of an ionic compound into its constituent elements using electricity
Why is a d.c. supply necessary for electrolysis?
So the products at each electrode can be identified
Which metals are extracted using electrolysis?
Lithium, potassium, calcium, sodium, magnesium, aluminium
Which metals are extracted by heating them with carbon or carbon monoxide?
Copper, lead, tin, nickel, iron, zinc
Which metals are extracted using heat alone?
Silver, mercury, gold
During electrolysis, what takes place at the positive electrode?
Negative ions lose electrons (are oxidised)
During electrolysis, what takes place at the negative electrode?
Positive ions gain electrons (are reduced)
What is an electrolyte?
An electrically conducting solution containing ions
How can you make a simple cell?
By placing two metal electrodes in an electrolyte
What does a simple cell look like?
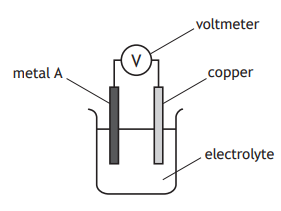
Other than a simple cell, what other kind of cell is there?
Using two half-cells (metals in solutions of their own ions)
When connecting two half-cells, what is needed to complete the circuit?
An ion bridge, also known as a salt bridge, which allows ions to flow and complete the circuit
What is the purpose of an ion bridge?
To complete the circuit by allowing ions to flow
In a simple cell, where do electrons flow through?
The wires
Which non-metal can be used as an electrode?
Carbon in the form of graphite
Why can carbon in the form of graphite be used as an electrode?
It conducts electricity
What is the relationship between the distance between two metals in the electrochemical series and the voltage produced?
The greater the distance between the two metals in the electrochemical series, the greater the voltage produced when they are used as electrodes
What is a displacement reaction?
When a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound during a chemical reaction
How can you determine the direction of electron flow in an electrochemical cell?
The electrons will flow from the metal which is higher in the electrochemical series to the metal which is lower in the electrochemical series
Write an ion-electron equation to show iron(II) ions forming iron(III) ions.
Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e-
Explain why an ion bridge is used to link half-cells.
To allow ions to flow from one beaker to another and complete the circuit
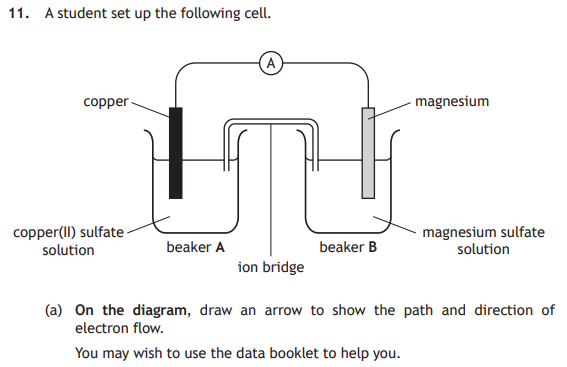
The electrons would flow through the wires from magnesium to copper
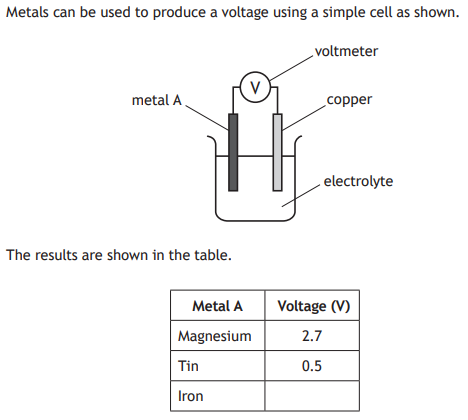
Suggest a value for the voltage produced by the cell when metal A is iron.
Any value higher than 0.5 and less than 2.7
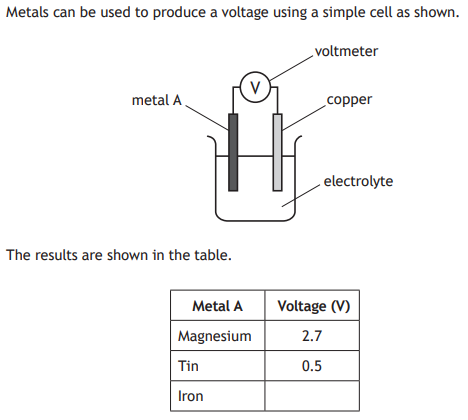
Name one factor that should be kept constant to make the experiment fair.
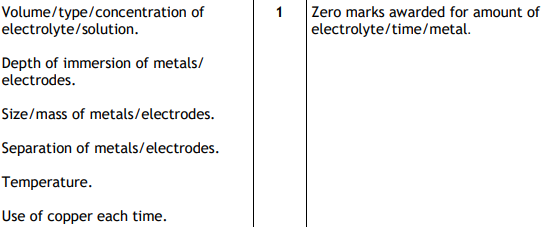
What are the three elements essential for healthy plant growth?
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium - NPK
What two criteria must a substance fulfill in order to be a fertiliser?
It must contain at least one of the elements essential for healthy plant growth and it must be soluble
What are fertilisers?
Substances which restore elements, essential for healthy plant growth, to the soil
Why do fertilisers need to restore elements essential for healthy plant growth to the soil?
Each time crops are harvested, the nutrients contained within the plant matter are removed from the ecosystem
What is ammonia?
A pungent, clear, colourless gas which dissolves in water to produce an alkaline solution
When ammonia dissolves in water, what kind of solution is produced?
An alkaline solution
Why do fertilisers need to be soluble?
So that the essential nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) can dissolve in water and be absorbed by the plant's root hair cells
Write the word equation for when ammonia solution reacts with an acid.
Ammonia solution + an acid —> an ammonium salt + water
Why are fertilisers important?
Because the world’s population is increasing and so we need enough food to feed them all
Which process is used to make ammonia?
The Haber process
What is the Haber process?
The process by which ammonia is produced?
What is the chemical formula for ammonia?
NH3
Write down the balanced equation for the Haber process?
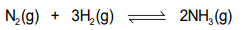
What two gases are needed for the Haber process?
Nitrogen and hydrogen
What temperature does the Haber process take place at?
A moderate temperature of 450°C
Is the Haber process a reversible reaction?
Yes
Why does the Haber process take place at a moderate temperature of 450°C?
Because if the temperatures are too low then the reaction would be too slow to be economical, but if the temperatures were too high then the backward reaction would be dominant