Learning-Communication-and-Change-Processes
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
A relatively permanent changes in behavior, skills, knowledge, or attitudesresulting from identifiable psychological or social experiences.
Learning
key feature is permanence
Elements of Learning Process
Refers to the context in which learning takes place, including environment, instructional materials, and external factors. In health promotion,
Situation
Elements of Learning Process
The attributes the learner brings to the situation, such as prior knowledge, experiences, attitudes, and motivations.
Personal Characteristics
patient's health condition, physical ability, or emotional readiness
Elements of Learning Process
The objective the learner is trying to achieve
Goal
a goal might be to adopt healthier habits or manage a chronic
condition through physical therapy (in hep)
Elements of Learning Process
The learner’s understanding or perception of the situation and the instruction provided
Interpretation
Elements of Learning Process
The behavior or response taken by the learner based on their interpretation of the situation.
Action
Elements of Learning Process
The outcome of the learner’s action, which either supports (confirmation) or challenges (contradiction) their expectations.
Consequence: Confirmation or Contradiction
essential for adjusting future actions
Elements of Learning Process
When the learner encounters obstacles that hinder progress, They might feel frustrated, or they could develop resilience and seek new strategies for success.
Reaction to Thwarting
key for long term improvement
Theories of Learning
This focuses on how the brain processes, stores, and retrieves information.
Cognitive Learning Theory
problem solving, decision making and memory
Theories of Learning
Emphasizes learning through interaction with the environment. Learning seen as result of reinforcement
Behaviourism Learning Theory ( B.F. Skinner & John Watson)
Theories of Learning
Learners construct their own understanding of the world based on experiences
Constructivism Learning Theory (Jean Piaget and Lev Vygotsky)
Theories of Learning
Centers on personal growth, self-actualization, and the learner’s autonomy. it focuses on creating environments that foster self-directed learning
Humanism Learning Theory (Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow )
Theories of Learning
Learning happens across connections in a digital or social network, where information can come from many sources, not just direct instruction.
Connectivism Learning Theory
Theories of Learning
It encourages critical reflection and questioning of assumptions, leading to personal growth and a change in how individuals see themselves and the world.
Transformative Learning Theory (Jack Mezirow)
Theories of Learning
Emphasizes learning through observation, imitation, and modeling within a social context.
Social Learning Theory (Albert Bandura)
Theories of Learning
Focuses on learning through experience, emphasizing the importance of reflection on doing.
Experiential Learning Theory (KOLB)
Transfer of information from one person to another
Communication
Communication in Health
The most important resource for promoting health is relevant health information that can guide people’s health decisions and can motivate them to adopt healthy behaviors.
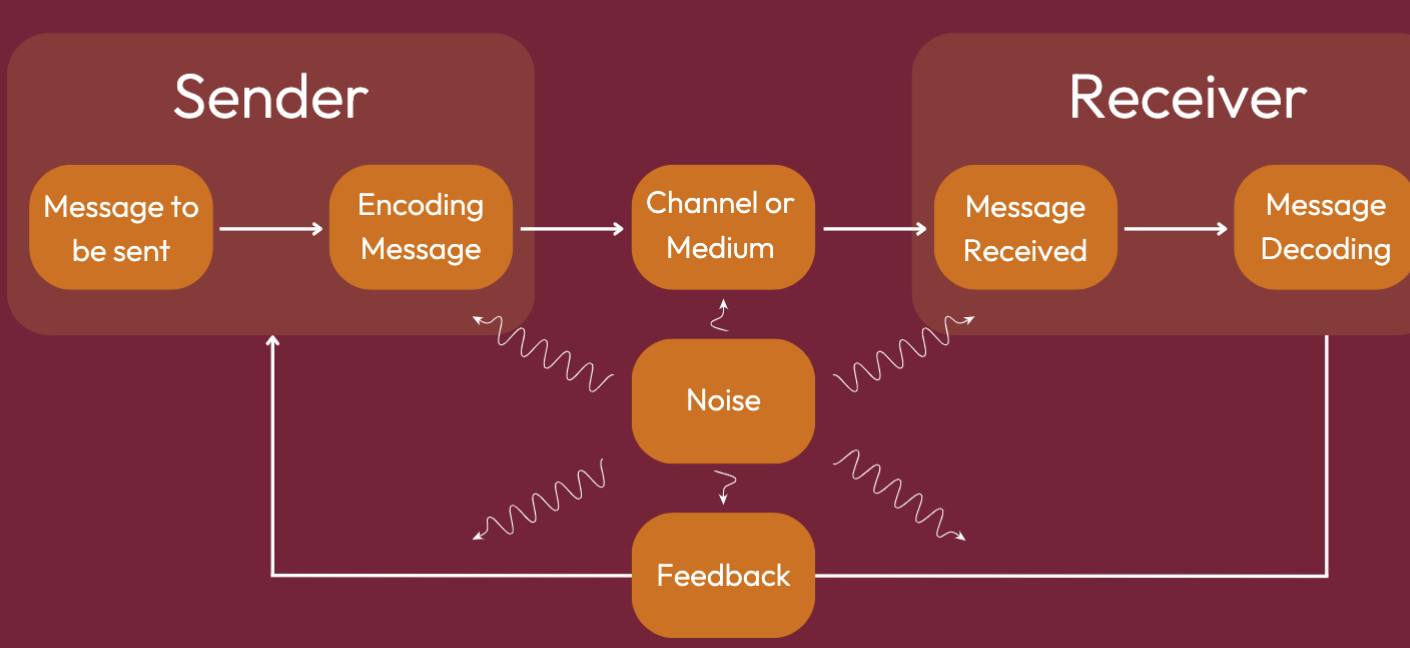
Elements of Communication Process
The individual who initiates the communication by encoding and transmitting a message to the receiver.
Sender
Elements of Communication Process
The information or content being communicated from the sender to the receiver.
Message
Elements of Communication Process
The individual who receives and interprets the message from the sender.
Receiver
depends on the receiver’s ability to understand and process the information.
Elements of Communication Process
The medium through which the message is transmitted from sender to receiver.
Channel
verbal, non verbal, written or digital
Elements of Communication Process
The response or reaction from the receiver back to the sender, indicating whether
the message was understood and how it was received.
Feedback
Elements of Communication Process
Refers to any external or internal factors that disrupt or distort the communication process
Noise
Steps in the Communication Process
Communication Theories
This theory suggests that mass media messages are first received by key
individuals, known as opinion leaders, who then interpret the information and pass it
on to others.
Two-Step Flow of Communication
Communication Theories
This theory explains how new ideas, practices, or technologies spread through a population over time.
Diffusion of Innovation Theory
Innovators – first to try, risk-takers, open to new ideas.
Early Adopters – opinion leaders, adopt early but carefully.
Early Majority – adopt after seeing evidence of success.
Late Majority – adopt due to peer pressure or necessity, more skeptical.
Laggards – last group, resistant to change, prefer tradition.
Communication Theories
A strategy that uses communication to promote positive changes in behaviours and social norms.
Social and Behaviour Change Communication (SBCC)
mass media and community mobilization.
Barriers to Effective Communication in Health Promotion
Use of medical jargon
Language differences
Cultural differences
Disabilities and other challenges
Low health literacy
Complexity of health topics
Lack of time
A systematic approach to managing the transition from a current state to a desired future state.
Change Process
Series of steps or stages individuals, groups, or organizations go through when adopting new behaviors, practices, or systems.
Change Process in Health Promotion
Changes
Refers to changes in thought patterns or knowledge, such as understanding
the benefits of a healthy lifestyle in managing chronic conditions.
Cognitive Change
Changes
This involves altering a person’s feelings, beliefs, or opinions towards a subject.
Attitudinal Change
changing how someone feels about the importance of exercise or smoking cessation.
Changes
This is the modification of an individual's actions or habits.
Behavioral Change
encouraging patients to engage in regular physical activity
Changes
Involves shifts in societal norms, values, or policies that affect collective behaviour.
Social Change
Change at Different Levels
This involves a person modifying their own attitudes, behaviours, or cognitive patterns.
Individual Level
Change at Different Levels
Involves a collective shift in attitudes or behaviors within a small community or
organization,
Group Level
Change at Different Levels
Refers to large-scale transformations in societal norms, laws, or practices, such as the acceptance of public health policies like vaccination programs.
Societal Level
Models of Attitudinal Change
This model focuses on the factors influencing attitude change: the source
of the message, the message content, and the audience.
Yale Attitude Change Approach
how persuasive messages can influence attitudes and behavior
Models of Attitudinal Change
This theory suggests that when individuals experience inconsistency between their beliefs and behaviors, they feel discomfort (dissonance) and are motivated to reduce it
Theory of Cognitive Dissonance
Models of Behavioral Change
Health-related behavior is influenced by personal beliefs or perceptions about a
disease and the strategies available to decrease its occurrence.
Health Belief Model
the desire to avoid illness, or conversely get well if already ill.
the belief that a specific health action will prevent, or cure, illness.
Models of Behavioral Change
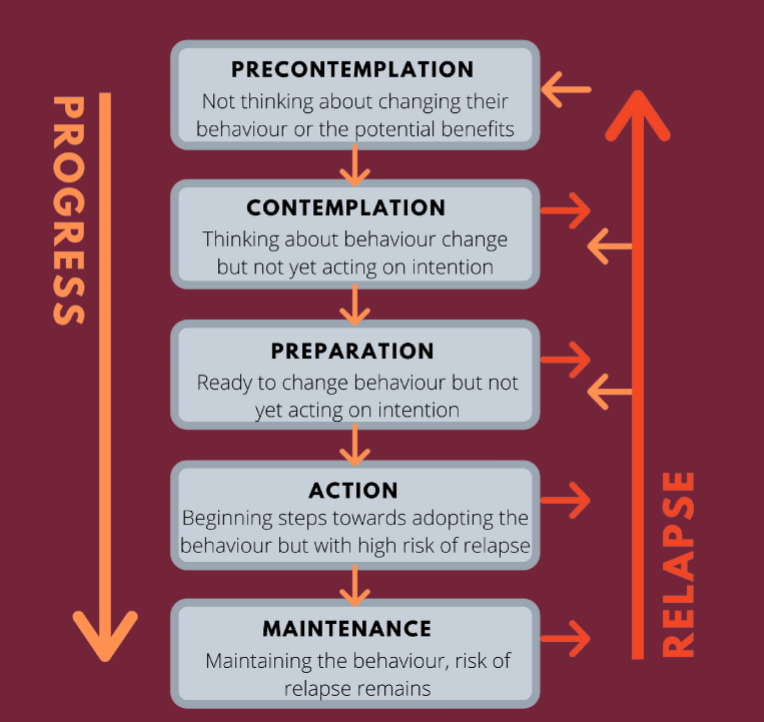
Describes behavior change as a process that occurs through a series of stages, from initial awareness to sustained behavior change.
Transtheoretical Model
General Social Change Strategies
These strategies are based on the idea that people will change their behavior
when they are provided with empirical evidence that demonstrates the benefits
of the change.
Empirical-Rational Strategies
provide info is da goal
General Social Change Strategies
These strategies focus on changing attitudes, norms, and values through education and social influence.
Normative/Re-educative Strategies
General Social Change Strategies
These strategies rely on authority, power, and sometimes coercion to enforce
change.
Power/Coercive Strategies
rewards or punishments