Functions and Chemistry of Amino Acids
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Defensins
Small proteins with antimicrobial properties.
which amino acids in transmembrane domains
leucine
isoleucine
valine
alanine
phenylalanine
HYDROPHOBIC
polar but non charged amino acids
serine
threonine
tyrosine
cysteine
asparagine
glutamine
D- or L- amino acid?
L if the amino acid is pointing to the left
D if the amino acid is pointing to the right
this is an L amino acid
which way is rthe amino acid sequence read?
the sequence reads from the N-terminus → C-terminus
the N-terminus is that with a free amino group
the C-terminus is that with a free carboxylate group
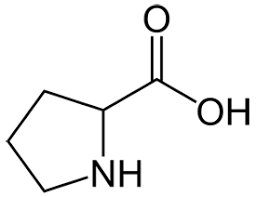
proline
does not fit in any category
much less hydrophobic than aliphatic
rotation around n-c alpha bond is restricted
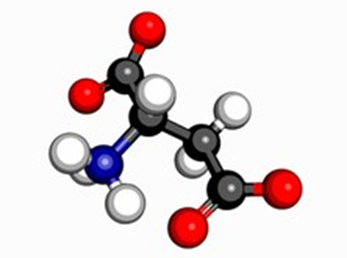
Zwitterion
Molecule with both positive and negative charges.
Chiral centre
Carbon atom bonded to four different groups.
Stereoisomers
Molecules with the same formula but different arrangements.
Enantiomers
Stereoisomers that are mirror images.
Aliphatic amino acids
Amino acids with non-aromatic hydrocarbon side chains
glycine
alanine
valine
leucine
isoleucine
Hydrophobicity of the aliphatic amino acids
alanine, valine, leucine and isoleucine have increasing hydrophobicity
Branched chain amino acids in the aliphatics
valine
leucine
isoleucine
most hydrophobic aliphatic and advantage
isoleucine
protein folding
Aromatic amino acids
phenylalanine
tyrosine
tryptophan
histidine
which aromatic amino acids can make hydrogen bonds
histidine, tyrosine, tryptophan
Hydroxyl amino acids
tyrosine
serine
threonine
ALL POLAR
polarity in hydroxyl amino acids
serine and threonine are more polar than tyrosine
form hydrohen bonds
and phosphate esters - signalling
Sulfur containing amino acids
cysteine
methionine
Disulfide bonds
Covalent bonds formed between cysteine residues.
cysteine characteristics
weak hydrogen bonds
stronger amino acid than serine
ionisable
forms disulfide bonds
Acidic amino acids
aspartate
glutamate
acidic amino acids characteristics
form salt bridges and polar interactions with water
hydrogen bonds
negative charge due to extra carboxyl group on side chain
amides of acidic amino acids
asparagine
glutamine
characteristics of amides of amino acids
not ionisable
highly polar
strong hydrogen donor and acceptor
Basic amino acids
lysine
arginine
have positively charged side chain
Guanidino group
Functional group in arginine contributing to basicity.
strongest basic amino acid
arginine
due to guanidino group