Organic 1 + 2 Mechanisms for ACS final
1/121
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ACS final stuff you need to know :) NOTE WHEN I SAY FORMS ENANTIOMERS, THIS IS ONLY THE CASE IF PRODUCT ISN'T ACHIRAL. If it had a chiral center before, it forms diastereomers. Also ensure it's not meso!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
Radical halogenation
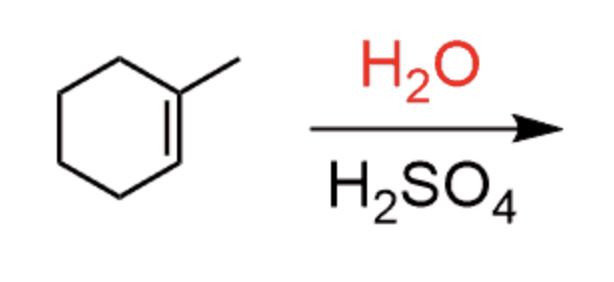
Hydration of alkenes
H3O+ or H2O/H2SO4… CH3OH also works, but results in OCH3 being added instead of OH
- results in OH on most sub. carbon
- Markovnikov
- not stereoselective
- 1,2 hydride shifts and carbocation rearrangements can occur
- produces enantiomer (carbocation formation)
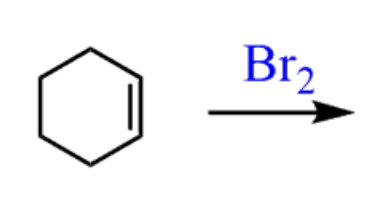
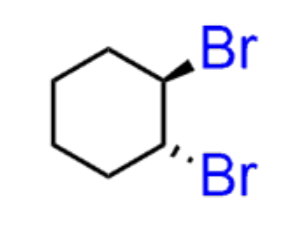
Halogenation of alkenes
Br2 or Cl2 (not I2)
- results in 2 halogens being added anti.
- no regiochem
- Anti addition
- produces enantiomers
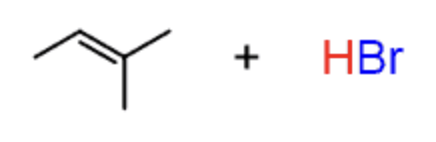
Hydrohalogenation
HBr or HCl
- results in halogen being added on most sub. carbon
- Markovnikov
- not stereoselective
- 1,2 hydride shifts and carbocation rearrangements can occur
- produces enantiomers
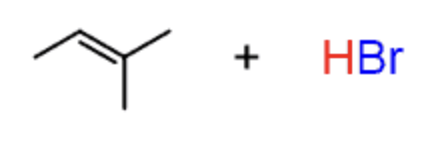
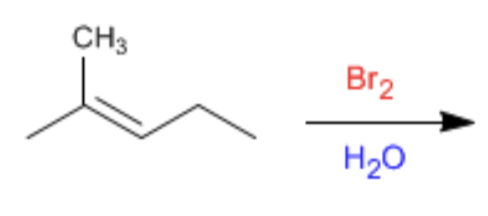
Halohydrin
Br2 or Cl2 and H2O or CH3OH as solvent
- results in halogen being added anti to OH or OCH3, OH or OCH3 being added to most sub carbon.
- markovnikov
- anti addition
- produces enantiomers
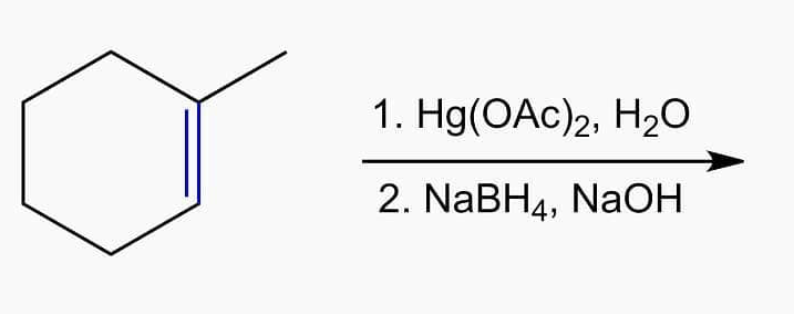
Oxymercuration demercuration
1) Hg(OAc)2, H2O 2) NaBH4
- results in an OH on most sub carbon and H on other.
- Markovnikov
- anti additon ONLY FOR OXYMERCURATION PART, which results in anti OH and HgOAc. Demurcuration is NOT stereospecific, so you can have syn or anti.
- results in enantiomers
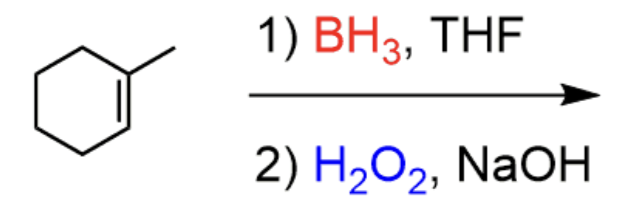
Hydroboration Oxidation
1) BH3 THF 2) H2O2, NaOH
- results in OH on least sub carbon, H on most, OH and H on same side
- anti-markovnikov
- syn addition
- results in enantiomers
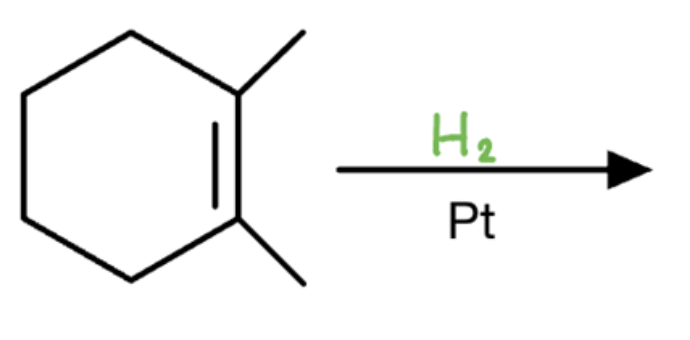
Catalytic hydrogenation
H2/Pt or H2/Ni or H2/PdC
- results in alkane with 2 H added to same side
- no regiochem
- syn addition
- results in enantiomers
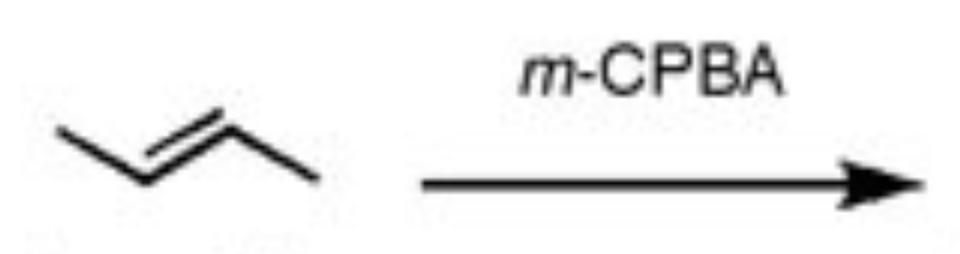
Peroxy acid expoxidation
m-CPBA
- results in epoxide that is trans or cis
- No regiochem
- Keeps trans/cis shape. Aka a trans alkene will produce a trans epoxide, and vice versa
- Syn addition
- trans alkenes and unsymmetrical cis alkenes will produce enantiomers, but symmetrical cis alkenes will produce meso compounds
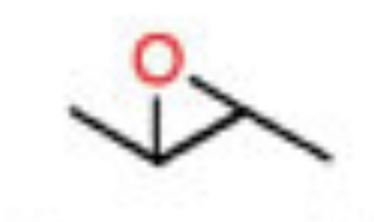
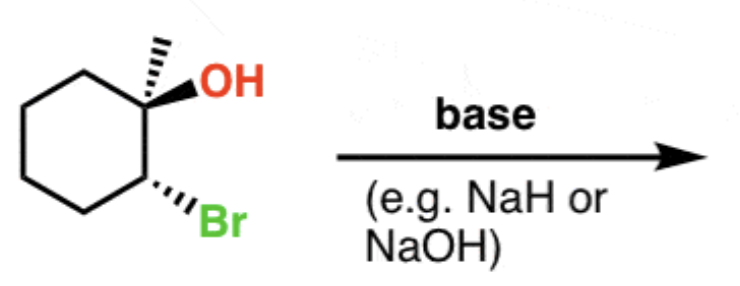
Epoxide formation from halohydrins
Base (NaOH, NaH, etc.)
- results in epoxide that lacks halogen
- occurs via SN2 rxn!
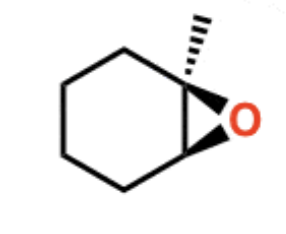
Epoxide opening under acidic conditions
Epoxide opening under basic conditions
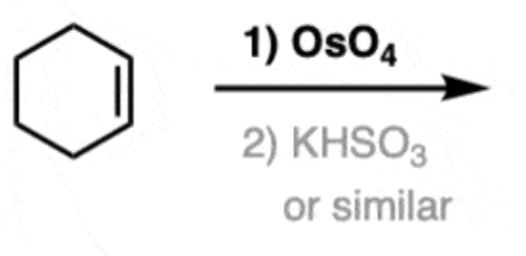
Osmium tetraoxide
1) OsO4
- results in 2 OHs being added to the same side
- no regioselectivity
- syn addition
- produces enantiomers
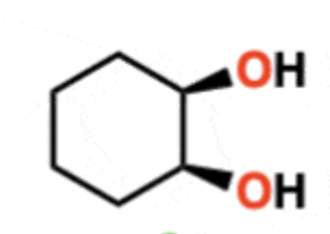
Oxidative cleavage
Carbene formation
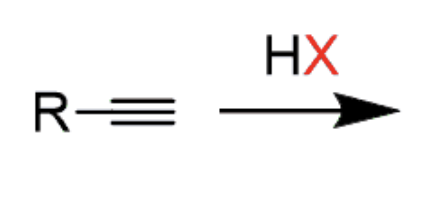
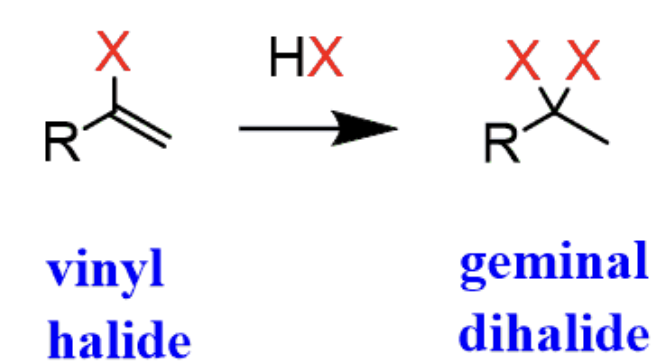
Hydrohalogenation of an Alkyne
HCl or HBr
First addition results in vinyl halide, second addition results in geminal halide
- first addition is anti addition and maokovnikov
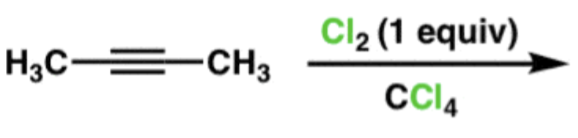
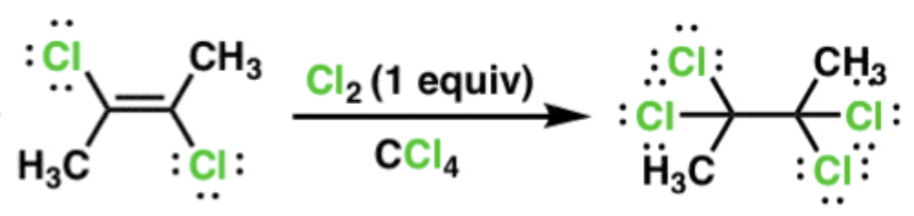
Halogenation of an Alkyne
Cl2 or Br2
1st addition results in trans alkene (anti addition), second addition results in a product with 4 halogens
Acid catalyzation of an Alkyne?
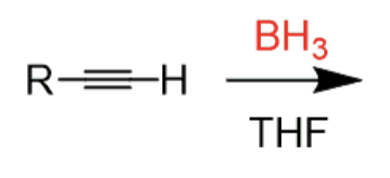
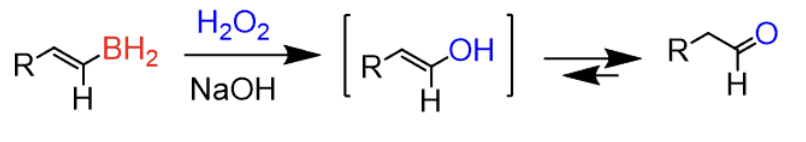
Hydroboration of an Alkyne
1) BH3/THF 2) H2O2, NaOH
forms enol (OH bound to an alkene) → tautomerizes to aldehyde (terminal alkyne)
- anti-markovnikov
Catalytic hydrogenation of an Alkyne
2 H2/Pt or Pd/C
- full reduction to alkane
- syn addition
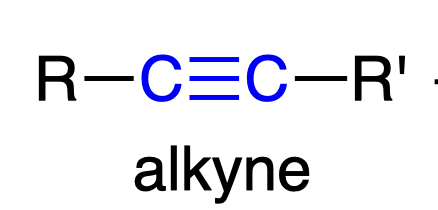
Lindlars Cat.
H2/Lindlars catalyst
- partial reduction aka reduces to cis-alkene
- syn addition
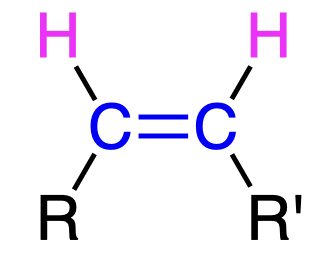

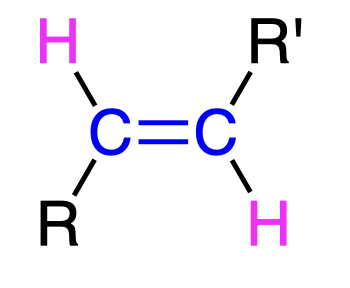
Dissolving metal reduction
Na/NH3
- partial reduction aka reduces alkyne to trans-alkene
- anti addition
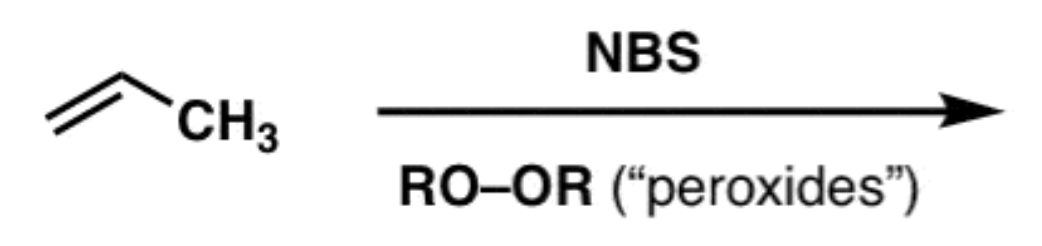
Allylic bromination
NBS/Peroxide
- bromine adds to allylic position carbon (next to double bond)
- radical mechanism
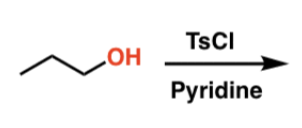
Tosylate formation
TsCl, pyridine
- converts OH to OTs (good leaving group)
- retains stereochemistry
Grignard reagents as bases
SN2 rxns
- backside attack
- 1° or 2° alkyl halides best
- inversion of stereochem
- no carbocation rearrangement
- polar aprotic solvent
SN1 rxns
- carbocation intermediate
- 3° or 2° alkyl halides
- racemic mixture (if chiral)
- rearrangements possible
- polar protic solvent
E2 rxns
- strong base
- no rearrangement
- Zaitsev product (more substituted alkene favored)
E1 rxns
- weak base, heat
- carbocation intermediate
- Zaitsev product
- rearrangements possible
Diels Alder
- diene + dienophile
- concerted [4+2] cycloaddition
- dashed =
- wedge =
- syn addition (endo preference)
- diene must be in
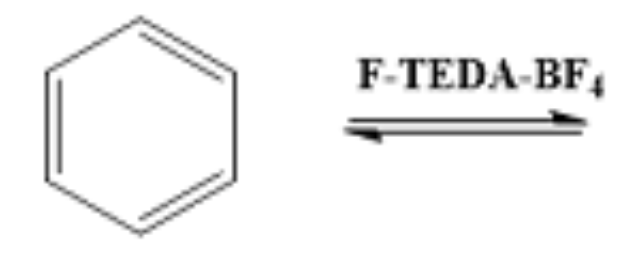
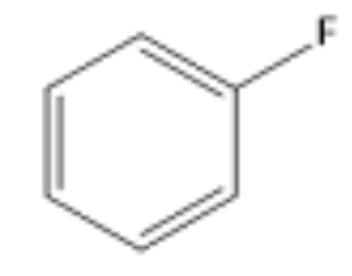
EAS Fluorine
F-TEDA
- Fluorine added to ring.
- ortho/para-directing, deactivating
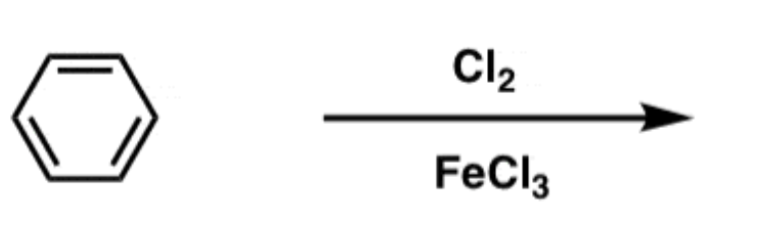
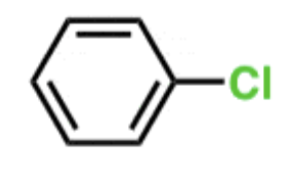
EAS Chlorine
Cl2/FeCl3
- Adds Cl to ring.
- ortho/para-directing, deactivating
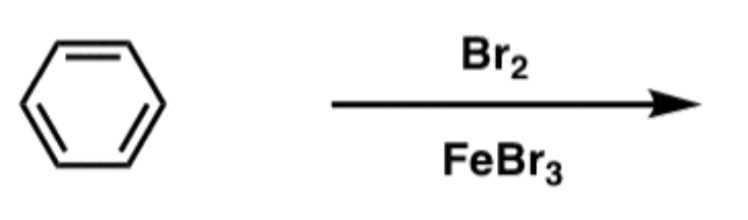
EAS Bromine
Br2/FeBr3
- Adds Br to ring
- ortho/para-directing, deactivating
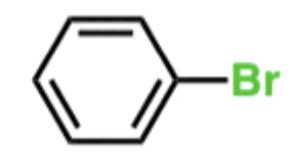
EAS Iodine
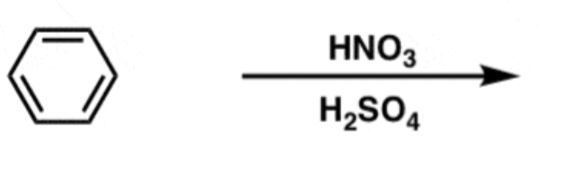
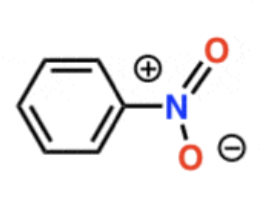
Aromatic Nitration
HNO3 + H2SO4
- adds NO2
- meta-directing, deactivating
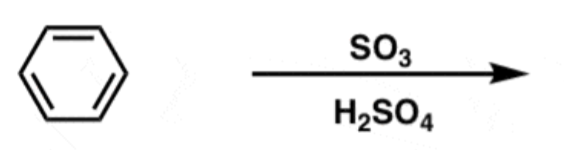
Aromatic Sulfonation
SO3 + H2SO4
- Adds adds SO3H
- meta-directing, deactivating
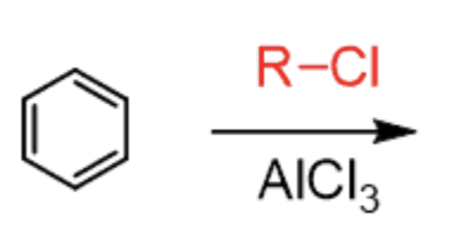
Friedel Crafts Alkylation
R–X + AlCl3
- adds R group
- carbocation rearrangement possible
- ortho/para-directing
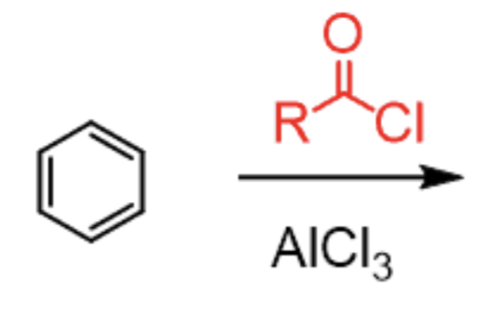
Friedel Crafts Acylation
RCOCl + AlCl3
- adds RCO group
- no rearrangement
- ortho/para-directing
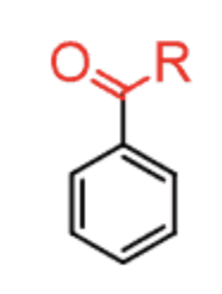
Benzylic oxidation
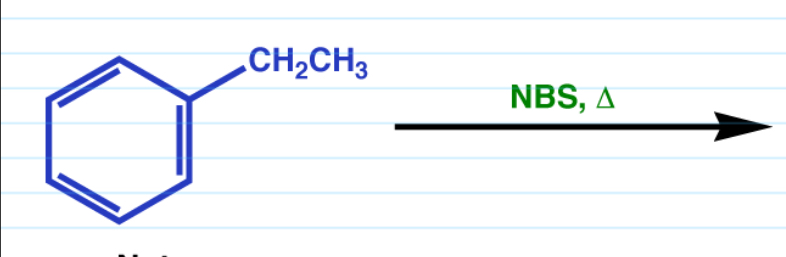
Benzylic Bromination
Substitutes benzylic hydrogens only.
reduction???
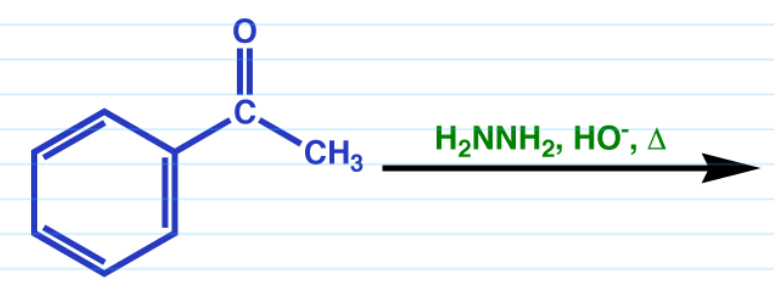
Wolff-Kishner
Basic conditions.
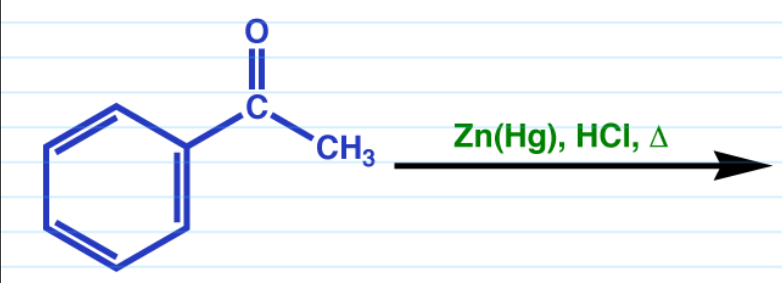
Clemmsen reduction
Works on aldehyde and ketones (same result for both)
Acidic conditions.
Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution
Addition—Elimination
Meisenheimer complex
Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution
Elimination—Addition
Benzyne
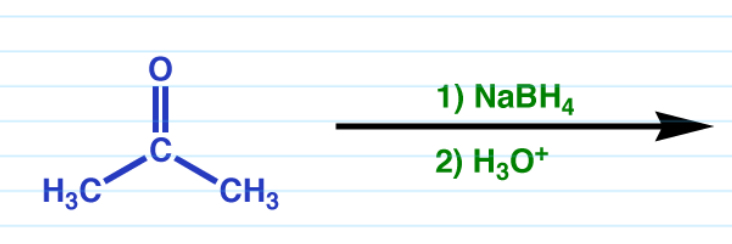
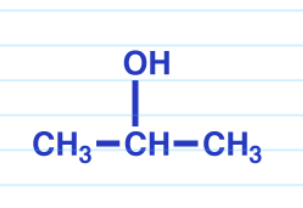
Reduction via NaBH4
Reduction via LiAlH4
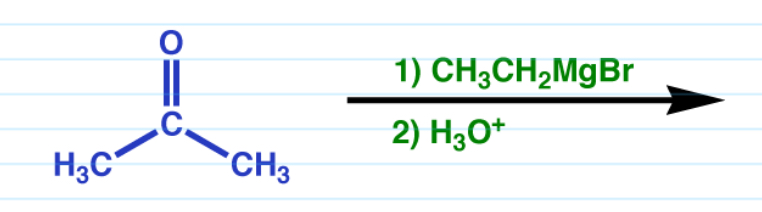
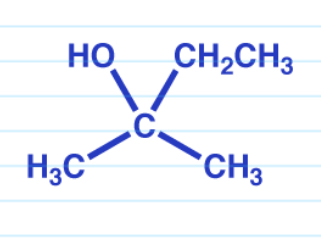
Reduction via Grignard
Works with both aldehydes and ketones.
Ketones turn into a tertiary alcohol
Aldehyde turns into a secondary alcohol.
TMS protection
Hydride additon
Hydration of aldehyde
Hydration of ketone
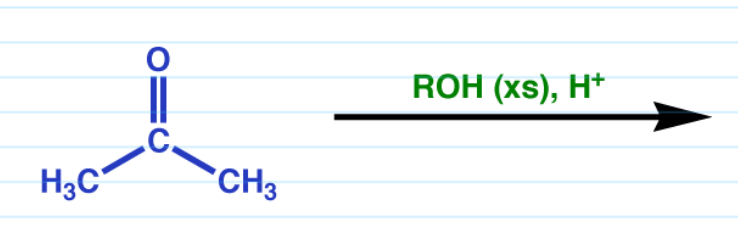
Acetal formation
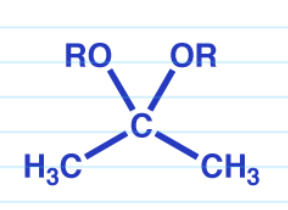
Base nucleophilic addition rxn
Acid catalyzed nucleophilic addition rxn
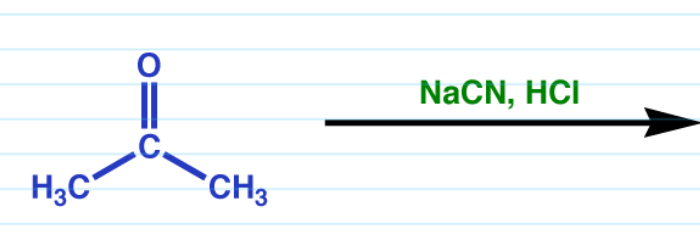
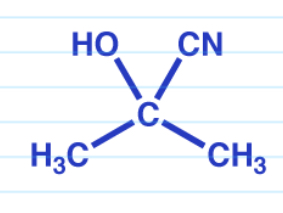
Cyanohydrin
DB O becomes OH and a CN is added
Cyclic acetals as protecting groups
Thiol formation
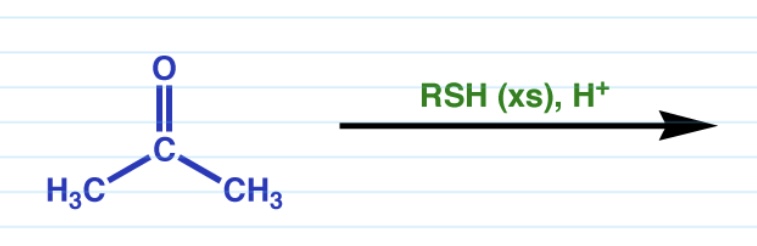
Thiolacetals
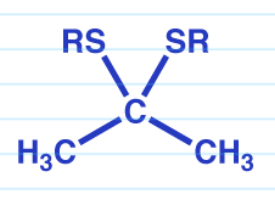
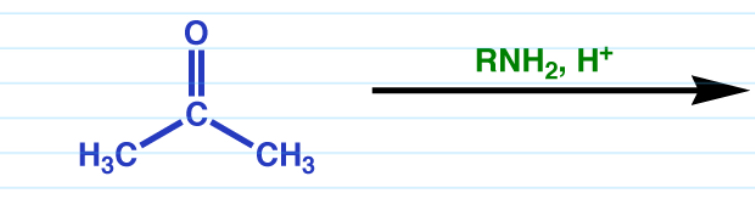
Imines
Requires a 1* amine
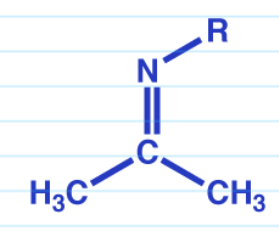
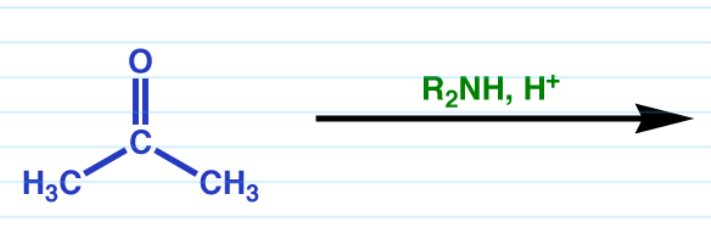
Enamines
Works for both aldehydes and ketones
Requires a 2* amine.
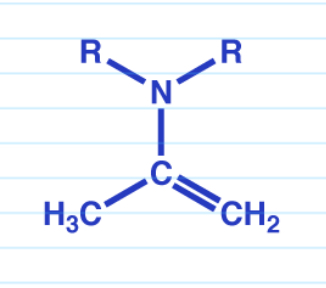
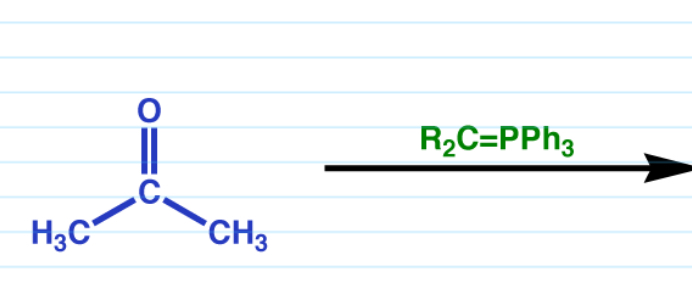
Witting rxn
Cyanide addition
Additions to alpha and beta unsaturated ketones/aldehydes
Nitrile formation SOCl2 and 1 amine
Nitrile formation SN2
Nitrile reduction w/ LiAlH4
Nitrile with Grignard
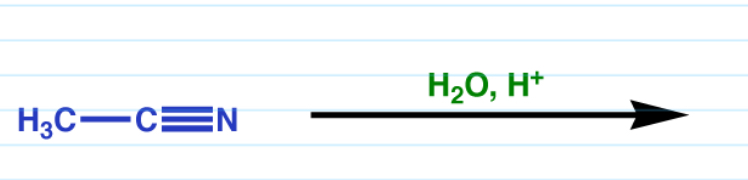
Nitrile hydrolysis acidic conditions
Nitrile hydrolysis basic conditions
Carboxylic acid formation w/ CO2 + Grignard
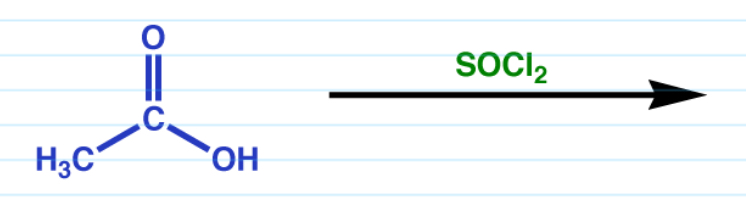
Carboxylic acid to acid chloride w/ SOCl2
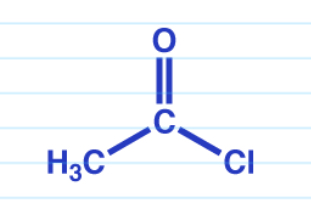
Carboxylic acid to anhydride w// heat
Carboxylic acid to ester via SN2

Carboxylic acid to ester Fischer esterification
Fancy name for “Add ester with acid”.
Must have an excess of alcohol.
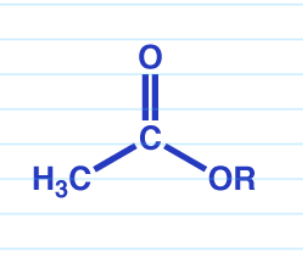
Carboxylic acid to amide via heat
Carboxylic acid to amide peptide synthesis
DCC activation
Carboxylic acid to amide peptide synthesis
Coupling
Carboxylic acid to amide peptide synthesis
Boc protection
Carboxylic acid to amide peptide synthesis
Boc deprotection
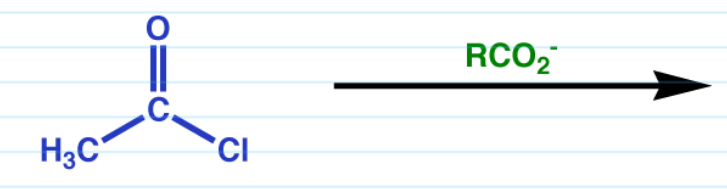
Acid halide to anhydride w/ carboxylate
Cl is ejected and CO2- takes over.

Acid halide to ester w/ alcohol and base
Acid halide to ester w/ alkoxide
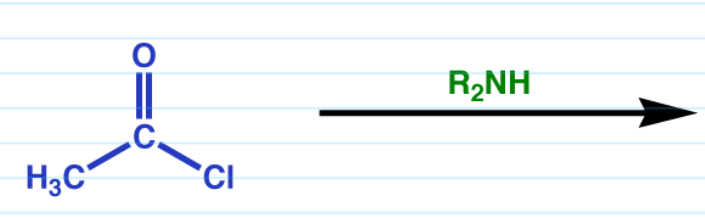
Acid halide to amide
+ Ammonia —> 1 amide
+ RNH2 —> 2 amide
+ R2NH —> 3 amide
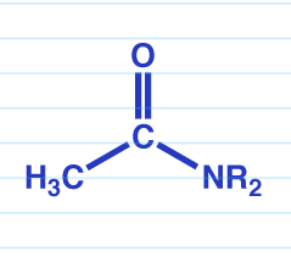
Acid halide reduction w/ LiAlH4
Acid halide reaction w/ excess grignard
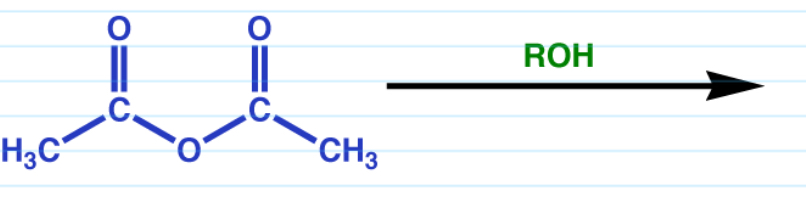
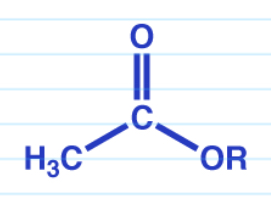
Acid anhydride to ester w/ alcohol
Acid anhydride to ester w/ alkoxide

Acid anhydride to carboxylic acid acid catalyzed
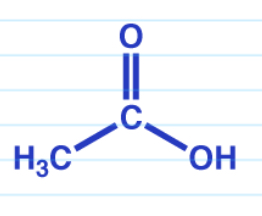
Acid anhydride to carboxylic acid in base
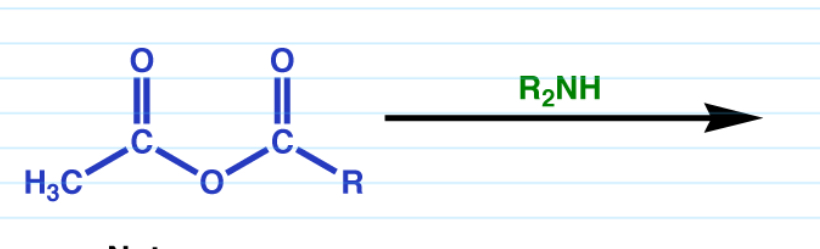
Acid anhydride to amide
R-NH2
Works with ammonia, 1 and 2 amines
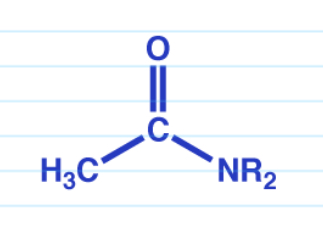
Acid anhydride reduction w/ LiAlH4
Acid anhydride reaction w/ excess grignard
Transesterification acid catalyzed
Transesterification base catalyzed
Ester hydrolysis to carboxylic acid acid catalyzed
Ester hydrolysis to carboxylic acid in base
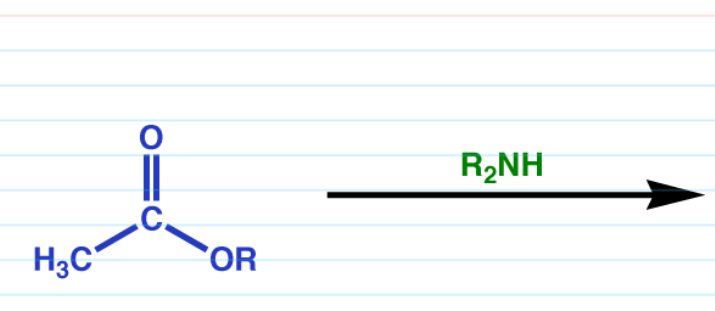
Ester to amide
+ Ammonia —> 1 amide
+ RNH2 —> 2 amide
+ R2NH —> 3 amide
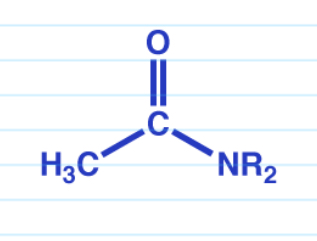
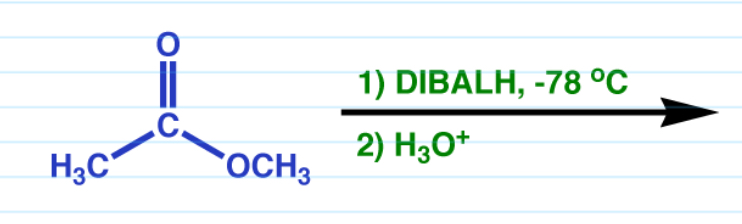
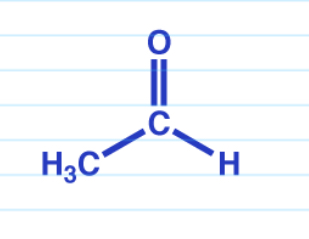
DIBAL reduction
- converts esters into aldehydes
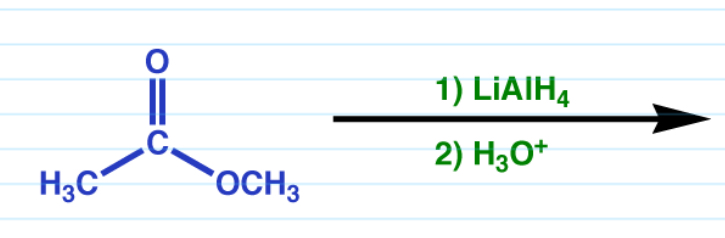
Ester reduction w/ LiAlH4
Removes db O, replaces ester with OH.