OB-Chpater 11 decision making
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
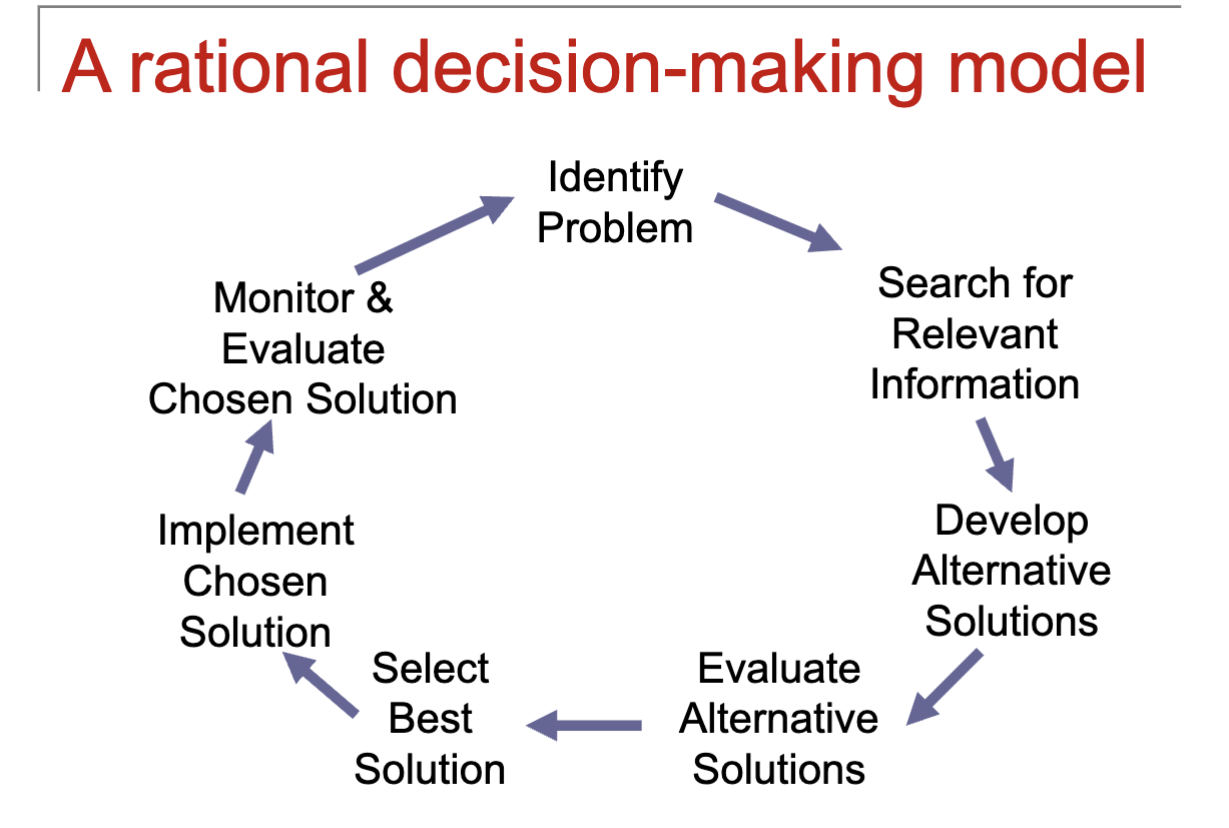
Well-structured problem (IIASE)
Identifying the problem
Information search
Too little versus too much informationDevelop, evaluate & select best alternative
Maximization
SatisficingSolution implementation
Factors to consider: Motivation & KSAsEvaluating solution
Escalation to a failing course of action
Preventing escalation
Hindsight
Perfect rationality
decision-making approach that is fully informed, perfectly logical, and focused entirely on maximizing economic gain.
ex. Choosing the cheapest supplier after comparing all options.
bounded rationality
decision-making approach that uses limited information and takes into account time limits and political factors, leading to a satisficing rather than an optimal solution.
ex. Picking the first good supplier you find due to time pressure
Framing
How information about a problem is presented, which influences decision makers’ perceptions and choice ex. Presenting a surgery as having a 90% survival rate instead of a 10% death rate to influence patient choice
Cognitive biases (ARIN)
Availability heuristic: Making decisions based on information that is easiest to recall.
Representative heuristic: Judging the probability of something based on how much it resembles a typical case.
Ignoring the base rate: Overlooking general statistical information when making judgments about specific cases.
Not-invented-here bias: The tendency to dismiss or reject ideas and solutions that come from outside one’s own organization or team.
Anchoring effect
When people rely too heavily on an initial number or piece of information (the “anchor”) and don’t adjust enough when making later estimates or decisions.
ex. Starting negotiations at $100,000 and sticking too close to that number.
Satisficing
Choosing the first solution that meets an acceptable standard instead of searching for the perfect one
ex. Buying the first laptop that meets your basic needs instead of comparing every model.
Sunk costs
Resources already spent that cannot be recovered.
Ex. Continuing a movie you dislike because you already paid for the ticket.
Escalation of commitment:
Investing more resources into a failing project hoping to turn it around.
Example: Pouring more money into a failing startup instead of cutting losses.
Hindsight
The tendency to look back on a decision and believe you knew the outcome all along, judging it as obvious after the fact.
ex. Saying “I knew that would happen” after a project fails.
Groupthink
When the desire for group harmony leads members to suppress doubts and ignore alternatives, harming decision quality.
ex. team agrees quickly on a risky plan without raising concerns to avoid conflict.
Isolated
Highly cohesive
Strong leader
High stress
Important
prevent group think
avoid exerting pressure towards decision
outcome
Establish norms that reinforce constructive
dissent and/or appoint a devil’s advocate
Develop & follow a rational decision-making
strategy
Bring in experts to challenge group opinions
pros of decision-making ( 4 )
pooling of resources
cspecializatin of labour
decision acceptance
creativity
cons of decision-making
waste time
group conflict
group think
intimidation by group leaders
shift
Risky Shift
Groups choose riskier options than individuals would alone.
Example: Team agrees to invest heavily in a high-risk startup.
Conservative Shift
Groups make safer, less risky decisions than individuals might.
Example: Committee opts for a low-risk, steady investment instead of a bold venture
Crowdsourcing
Delegating parts of a decision-making process to a large group of people, often through an open call or online platform.