Basic Components of Living systems
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
cell functions All living organisms are made of cells, there are several different types of cells, some of them sharing some common features. Human are made up of eukaryotic cells. All eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. A more detailed structure of cells called the ultrastructure can be obtained by using a microscope.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
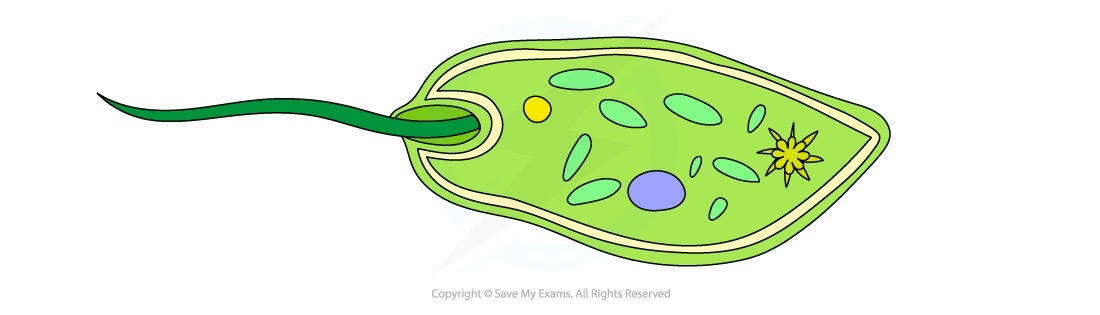
Flagella
a tail-like filament which rotates to move the cell
many bacteria have flagella, as do sperm
Slime Capsule
a protective slimy layer which helps the cell to retain moisture and adhere to surfaces
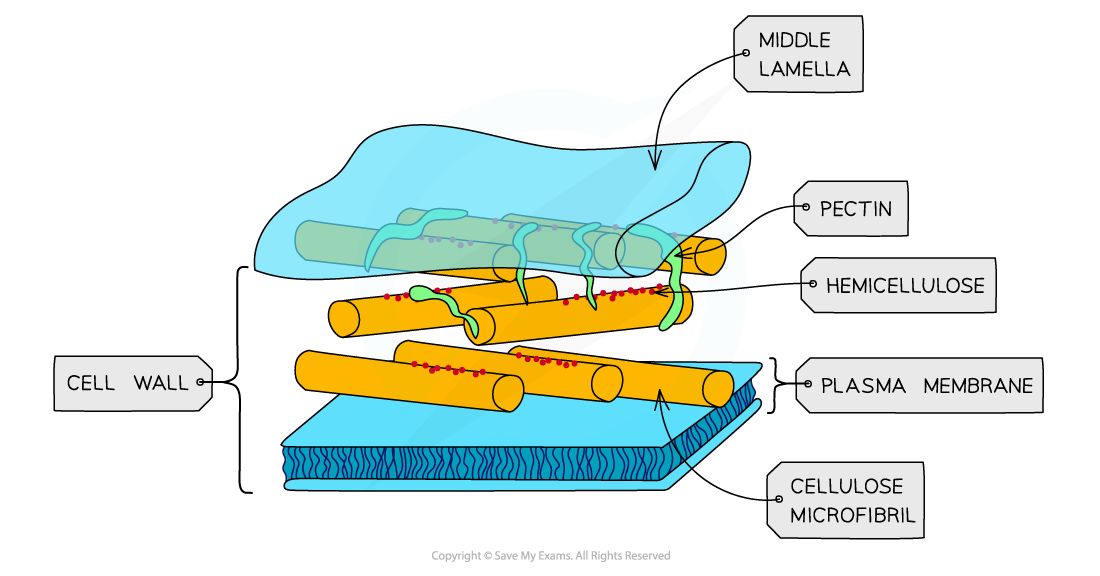
Cell Wall
Made of peptidoglycan rather than cellulose (plants) This is made of sugars and amino acids and forms a mesh. Gram positive bacteria have a much thicker wall – gram staining involves applying crystal violet then iodine which fixes the die. The slide is washed with alcohol and the gram positive bacteria retain the violet stain so show up purple or blue. Gram negative bacteria have thinner walls so lose the stain. The bacteria are then stained with safranin dye (a counterstain) that will adhere to the gram negative bacteria that show up red.
It is a rigid outer covering that adds structure to the cell- this means they stop changing shape.
adds protection
is freely permeable to all soluble substances because of small pores
Plasmid
circular piece of DNA that replicate independently from the host's chromosomal DNA. They are mainly found in bacteria, but also exist naturally in archaea and eukaryotes such as yeast and plants
Pili
hair-like structures which attach to other bacterial cells they can have a role in movement, but are more often involved in adherence to surfaces, which facilitates infection
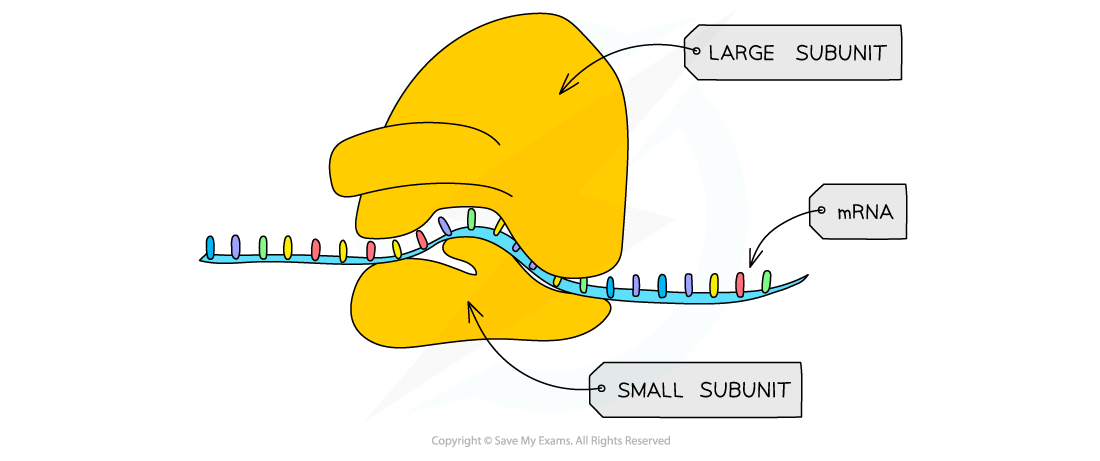
Ribosomes
small organelles that are either free in the cytoplasm (of all cells) or are attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (only in eukaryotic cells) Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis (where proteins are made) They 'read' RNA to make polypeptides (proteins) in a process known as translation.
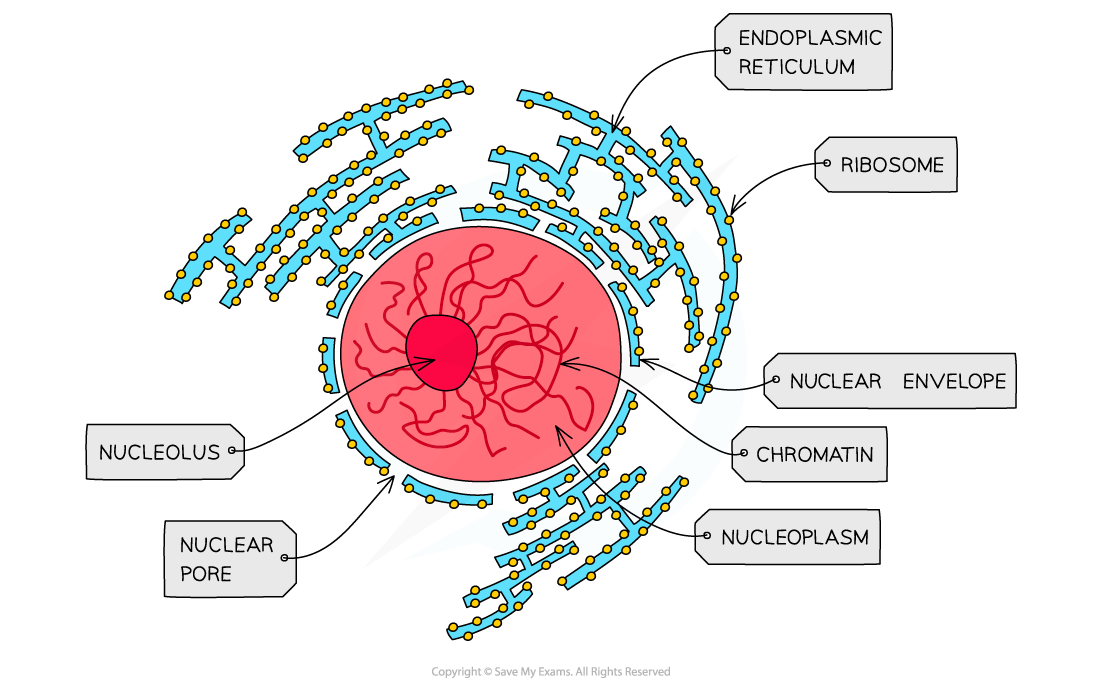
Nucleus
-the central control center of the eukaryotic cell and is responsible for managing the cell's genetic material. The nucleus contains the cell's DNA, which is organized into chromosomes, and is responsible for controlling the cell's growth and division.
Nuclear envelope
-The double membrane of the nucleus is called the nuclear envelope. It surrounds the nucleus and protects genetic material from mixing with the cytoplasm. Nothing can enter or leave the nucleus without passing through this envelope.
Nuclear pores
-nuclear pores are important channels for allowing mRNA and ribosomes to travel out of the nucleus, as well as allowing enzymes (eg. DNA polymerases) and signalling molecules to travel in
Nucleolus
-a spherical structure found in the cell's nucleus whose primary function is to produce and assemble the cell's ribosomes. The nucleolus is also where ribosomal RNA genes are transcribed.
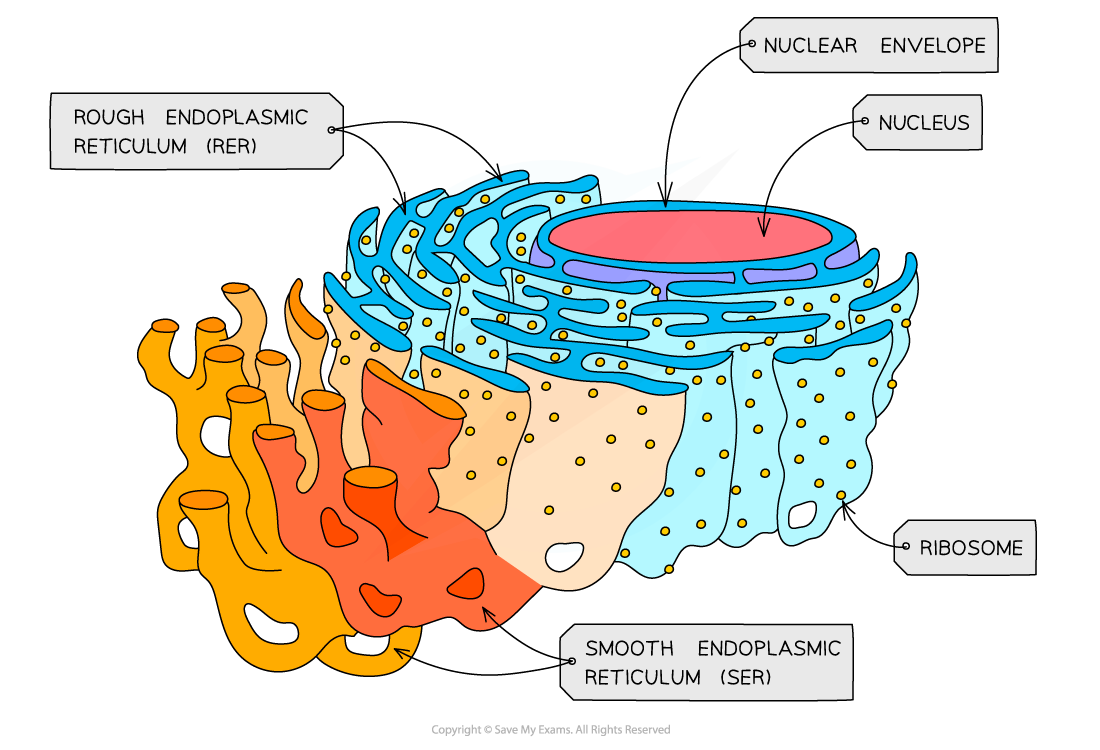
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
The RER contains stacked, fluid-filled membranes. The RER is a membrane bound organelle located near the nucleus. It is structurally very similar to the Golgi Apparatus. It is made up of thin, fluid filled membranes that are stacked together.
The surface of the RER is covered in ribosomes. This is why we call it the rough endoplasmic reticulum, because it looks bumpy under a microscope. The ribosomes attached to the RER are the ribosomes that are responsible for making proteins that are meant to exported outside of the cell or to the cell surface membrane.
The RER folds and packages proteins and sends them to the Golgi Apparatus. Proteins meant for export are made by the ribosomes and then released into the RER, which folds them and packages them and then sends them to the Golgi Apparatus. Proteins that are meant for use inside of the cell are primarily made at ribosomes that are free floating in the cytoplasm.
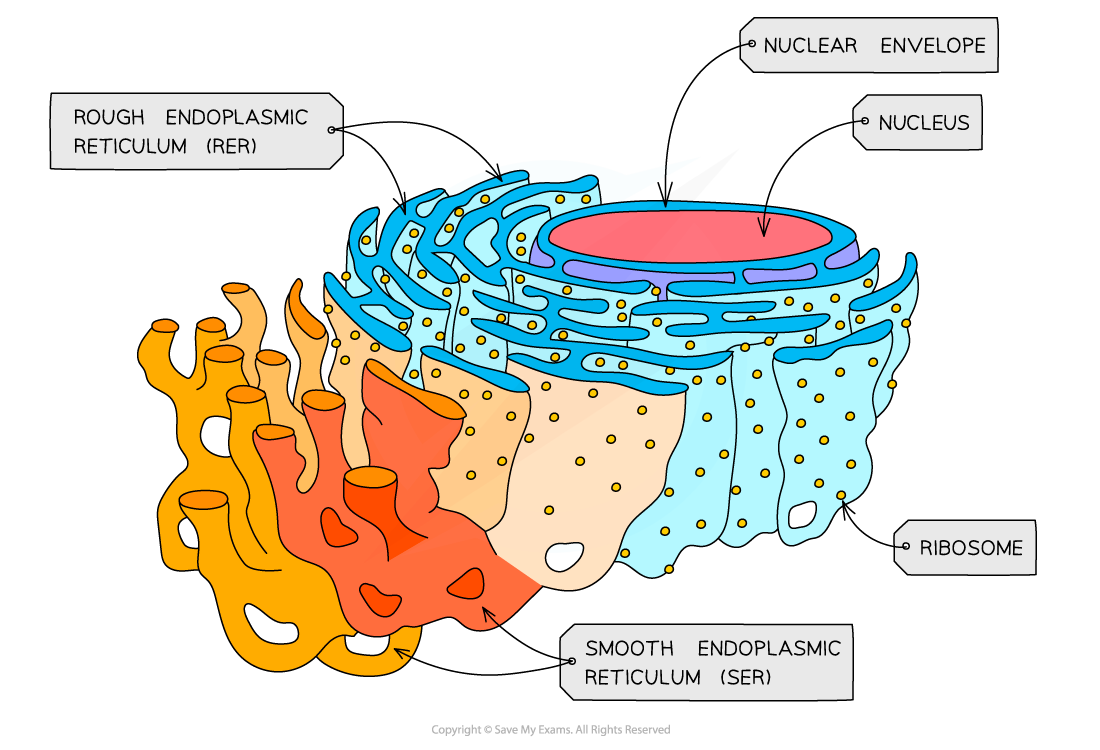
Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum
The SER does not have ribosomes. The SER is structurally similar to the RER. Except its smooth because it has no ribosomes on its surface.
Its main function is to synthesise lipids. The SER synthesises many lipids such as cholesterol, and other molecules such as steroids and hormones for use inside the cell and for export outside of the cell. When exporting these molecules, the SER packages them and sends them to the Golgi Apparatus.
The SER is also involved in detoxification. The SER plays a crucial role in detoxification of toxins that are either consumed by the cell, such as alcohol, or toxins produced as metabolic byproducts of metabolism.
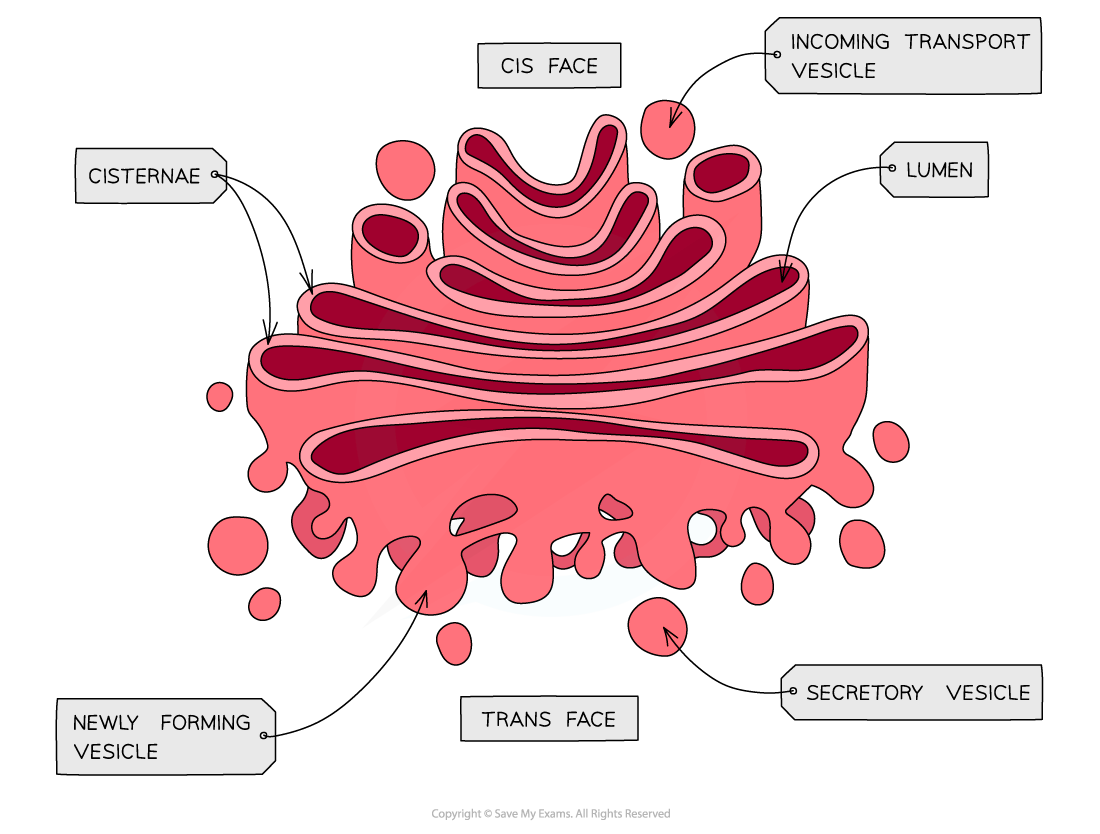
Golgi apparatus
Golgi apparatus are a series of flat membrane-bound sacs. The numbers of Golgi apparatus differ according to the cell’s secretion activity. Golgi apparatus are specialized for receiving the molecules of substances secreted by the endoplasmic reticulum across a group of transporting vesicles. Then, it classifies and modifies these vesicles and distributes them into the places where they are used in the cell. Golgi apparatus may also pack the molecules inside secreting vesicles called lysosomes, which move forward to the cell membrane as the cell dismisses them outside as secretory products.
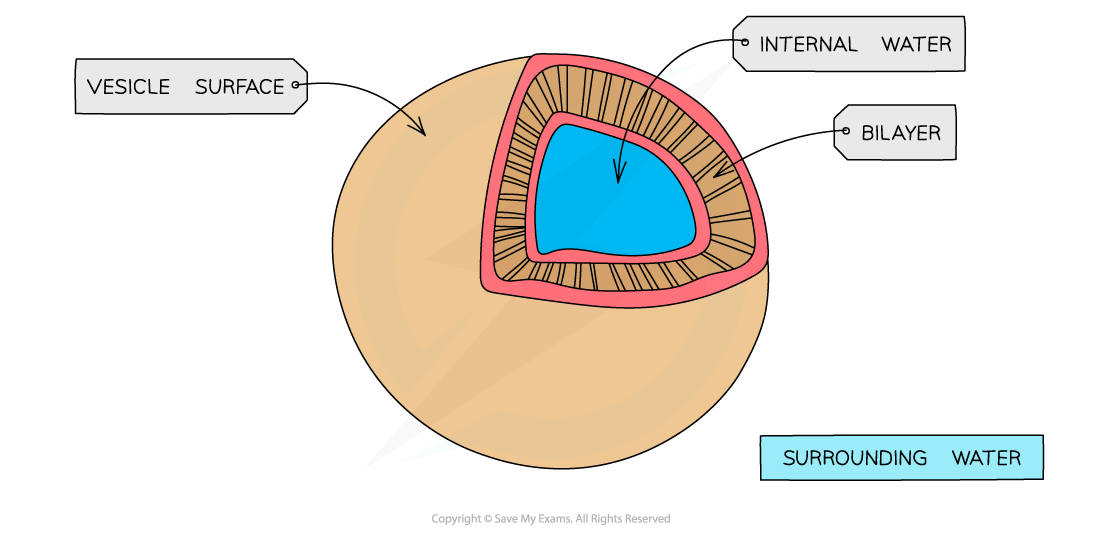
Vesicle
It is a small, spherical compartment that is separated from the cytosol by at least one lipid bilayer.
Many vesicles are made in the Golgi apparatus and the endoplasmic reticulum or are made from parts of the cell membrane by endocytosis.
Because vesicles are made of phospholipids, they can break off of and fuse with other membranous material. This allows them to serve as small transport containers, moving substances around the cell and to the cell membrane.
Examples of vesicles include secretory vesicles, transport vesicles, synaptic vesicles, lysosomes etc.
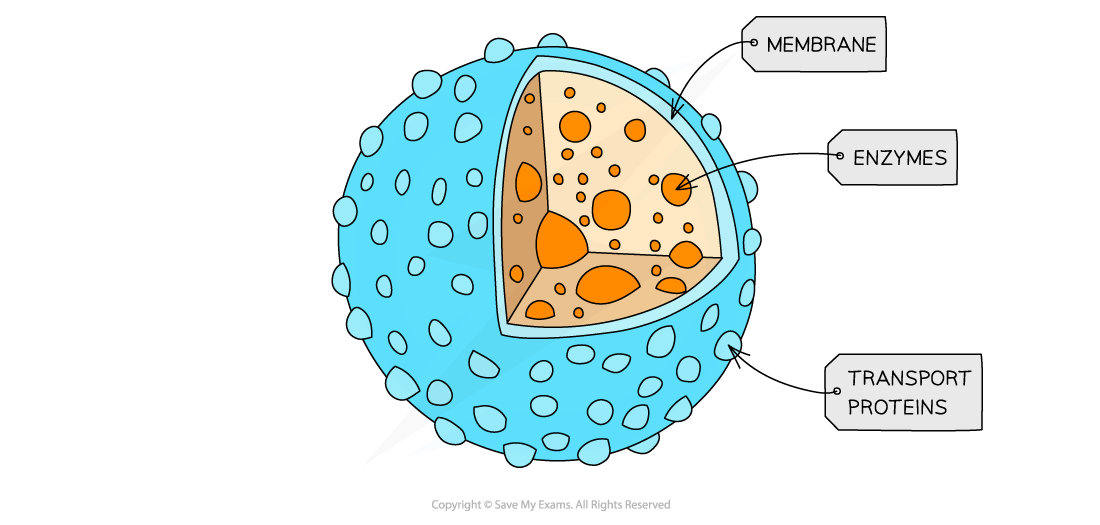
Lysosome
responsible for breaking down waste material in cells eg old organelles
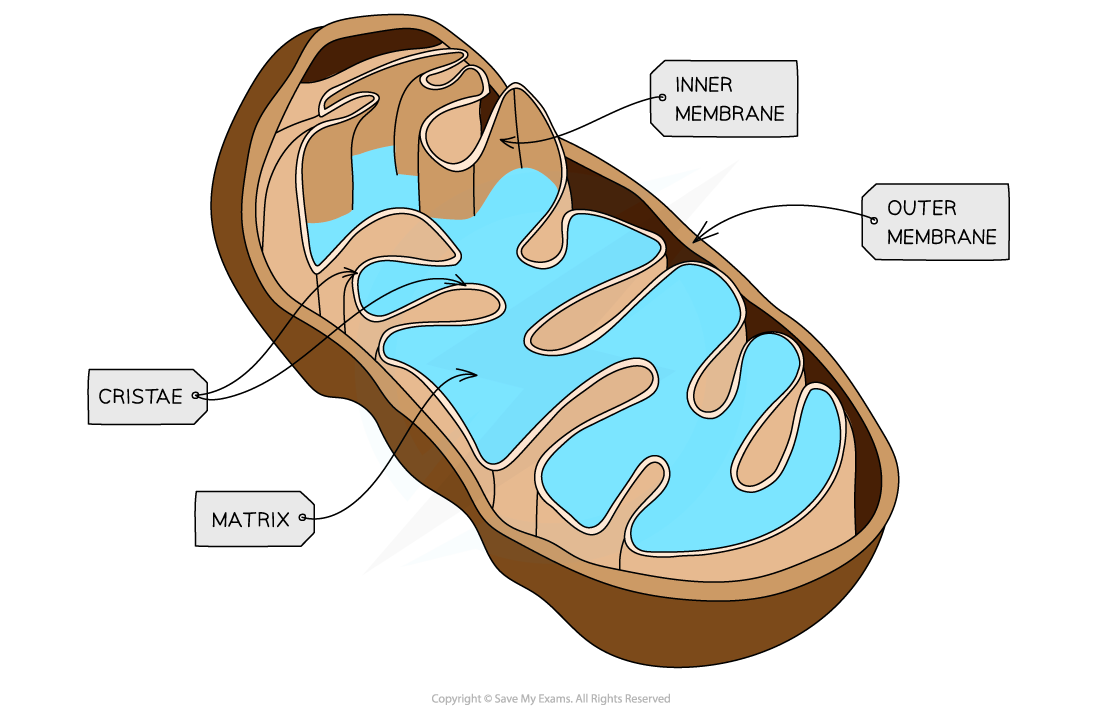
Mitochondria
site of aerobic respiration within all eukaryotic cells
- site of final stages of cellular respiration, where the energy is stored in the bonds of complex, organic molecules are made available for the cell to use by the production of the molecule ATP
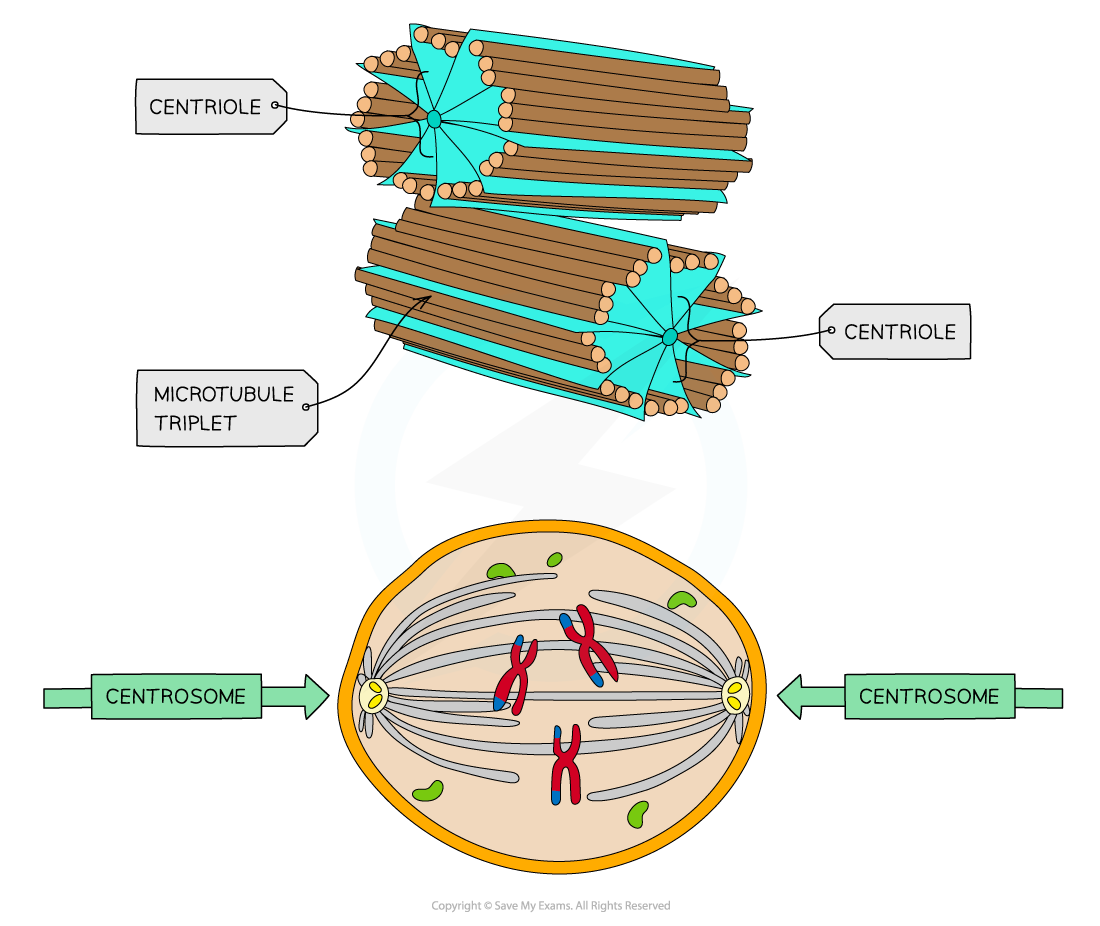
Centrioles
-located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope. Centrioles play a role in organizing microtubules that serve as the cell's skeletal system. They help determine the locations of the nucleus and other organelles within the cell.
they play a vital role in facilitating the reproduction of cells.
They engage in the arrangement of mitotic spindles during cell division.
It aids in cytokinesis.
It organises the microtubules in the cytoplasm.
They regulate the position of the nucleus and other organelles in the cell.
A centrosome comprises two microtubule rings known as centrioles. Its main function is to organize the microtubules and provide a structure to the cell. It also pulls the chromatids apart during cell division.
Cytoskeleton
-the cytoskeleton is a network of protein filaments. The cytoskeleton is made up of protein filaments which form a mesh-like network in the cytoplasm of the cell. They are present in all cells, including bacteria.
It provides mechanical strength as well as aiding transport within cells and enabling cell movement.
Cytoplasm
-a fluid-like substance present between the cell membrane and nucleus. It is mainly composed of water, as well as some organic and inorganic substances. The cytoplasm contains a network of threads and microtubules that help the cell to maintain its shape and form.
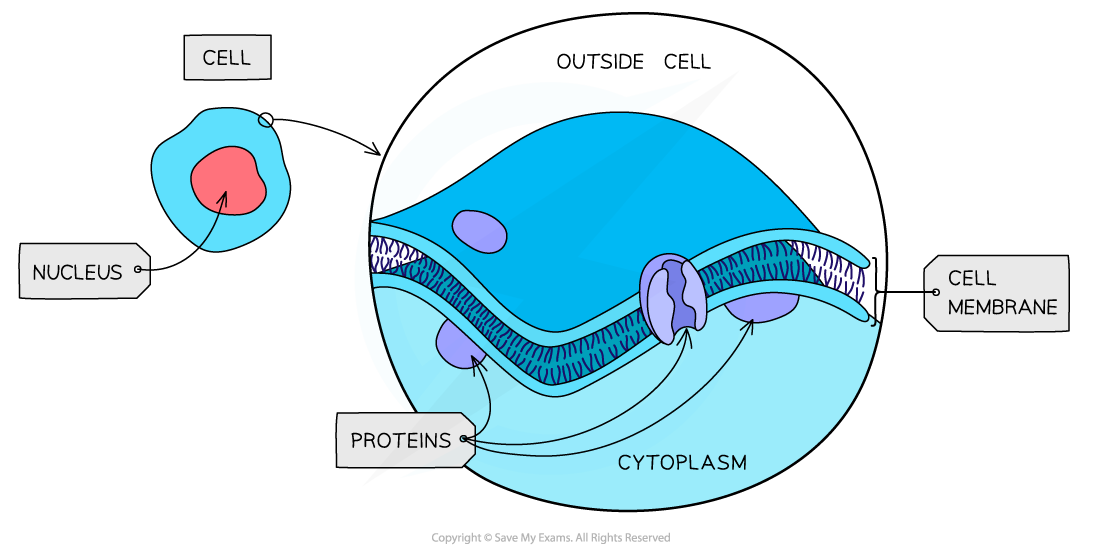
plasma cell membrane
-found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The cell membrane regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
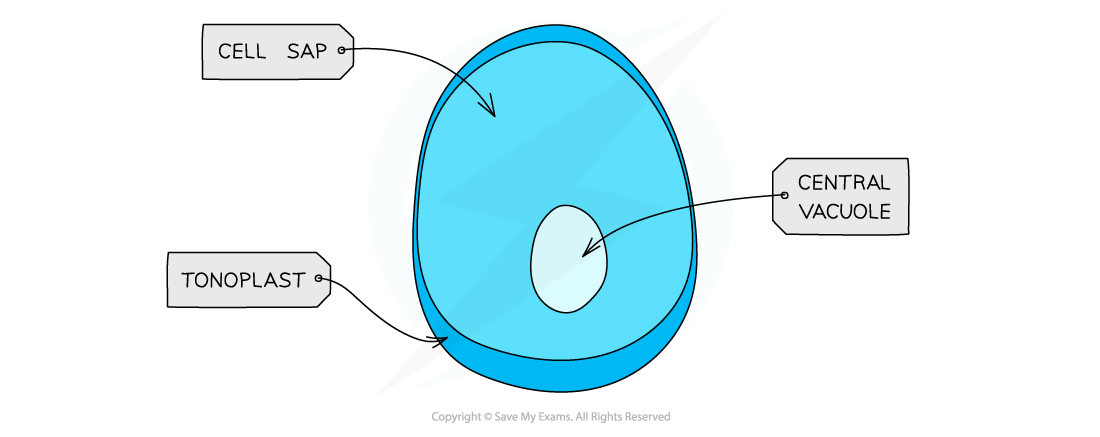
vacuoles
membranous sacs (similar to bubbles filled with a liquid). They store water, nutrients, and the waste materials of the cell until it gets rid of them. The vacuoles are small and large in number in animal cells, while they are collected in one big vacuole (or more) in plant cells.
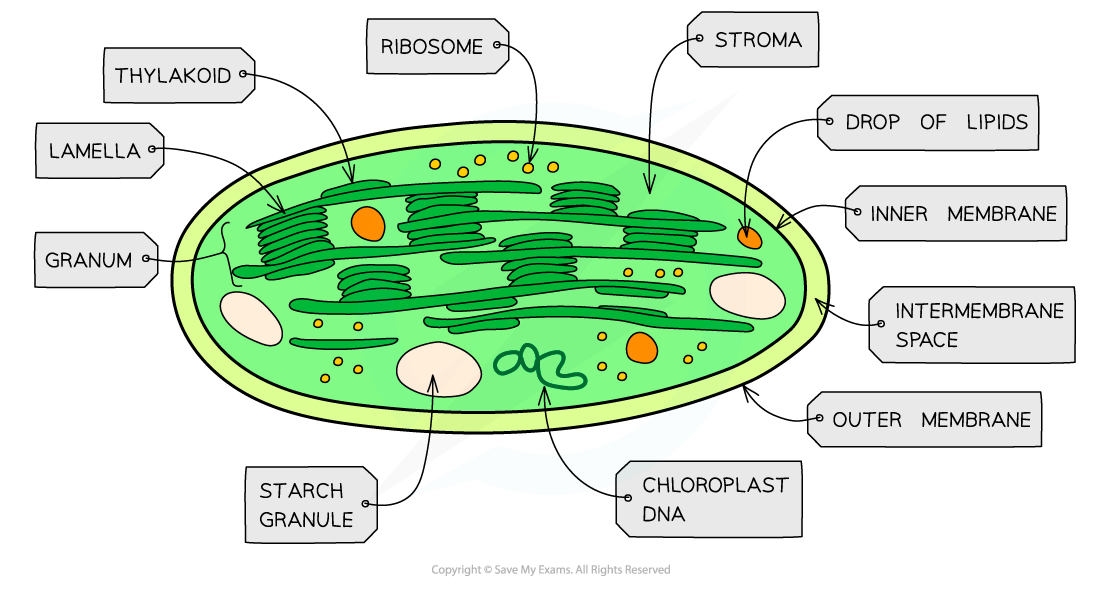
chloroplast
Chloroplasts are unique to plant cells and are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy stored in organic compounds such as sugars.
Each chloroplast is surrounded by a double-membrane envelope
Each of the envelope membranes is a phospholipid bilayer
Chloroplasts are filled with a fluid known as the stroma
The stroma is the site of the light-independent stageof photosynthesis
cilia
Cilia are hair-like structures on surface membranes. Some animal cells have cilia, which are tiny hair-like structures that protrude from the surface membrane.
There are motile and non-motile cilia. Motile cilia can move due to the activity of the microtubules inside it. This type of cilia help substances to move along the surface of cell membranes e.g. respiratory cilia help waft mucus along the respiratory tract. Non-motile cilia do not move and are typically found in sensory organs e.g. some photoreceptor cells in the eye have non-motile cilia as a part of its structure.
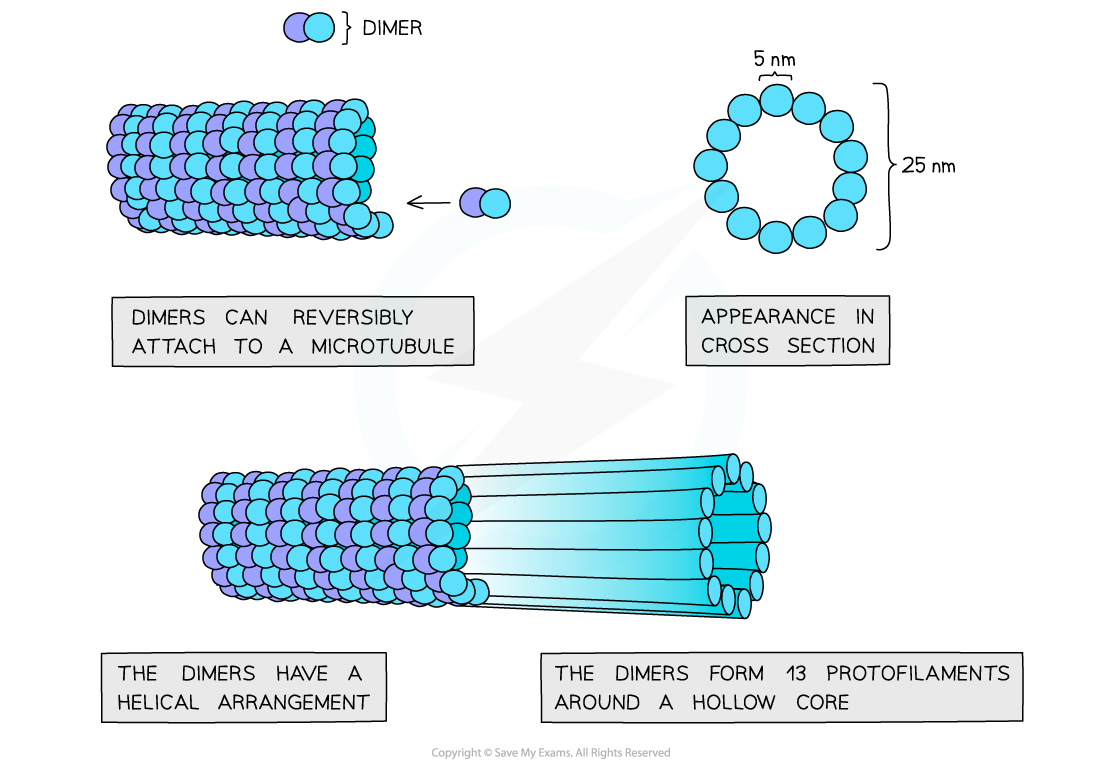
microtubule
- These are made of the protein tubulin which joins together to form tubes (18 - 30nm in diameter)
The filaments change length by adding/removing monomer subunits i.e. they are dynamic
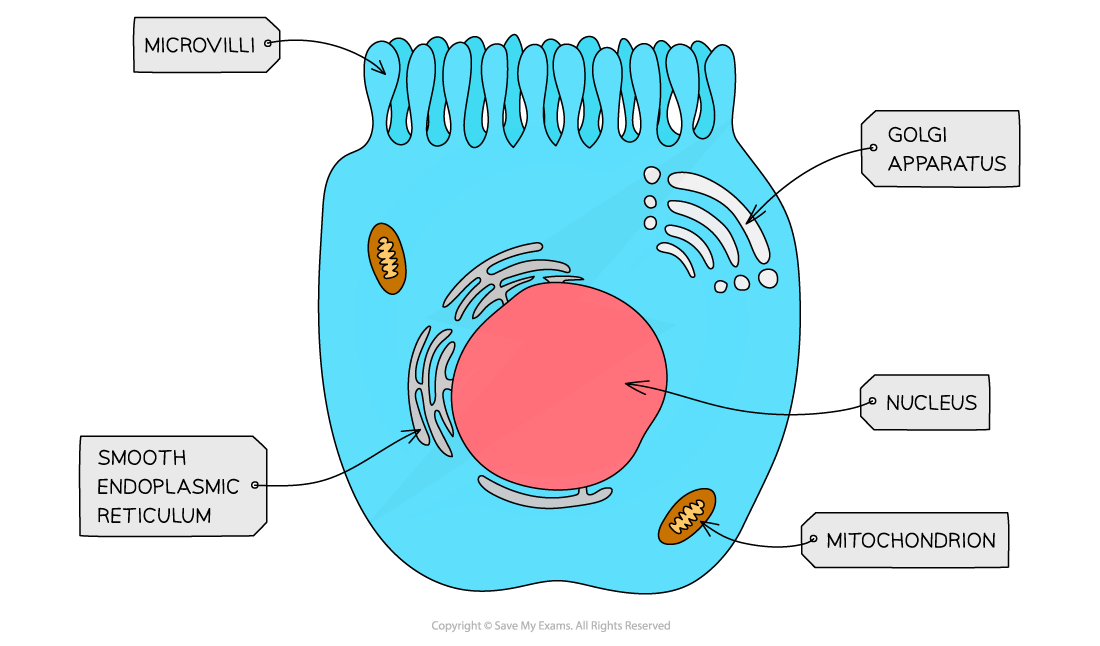
microvilli
mall finger-like projections found on cells within the body that help the cells to get nutrition. Microvilli are membrane protuberances that arise from epithelial cells. They are usually about 0.1µm in diameter and up to 2 µm long
intermediate filaments
intermediate filaments are composed of a variety of proteins.
- They give mechanical strength to cells and help maintain their integrity
microfilaments
Responsible for cell movement e.g. in phagocytes, sperm cells, or an amoeba trying to capture it's food, and cell contraction during cytokinesis.