1 prenatal development
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
what are the three stages of prenatal development
germinal, embryonic and foetal
when does the germinal period occur
weeks 1-2
what is the germinal period
fertilisation and formation of the zygote, implantation into uterine lining and development of nourishing and protective structures such as the amnion, chorion, yolk sac, placenta and umbilical cord
when does the embryonic period occur
weeks 3-8
what is the embryonic period
central nervous system, internal organs, muscles and skeleton begin to form, heart begins pumping blood, neurons develop rapidly, external features begin to form such as eyes, ears, nose and limbs
when does the foetal period occur
week 9 to the end of pregnancy
when is the first trimester
weeks 1-12
what happens in the first trimester
organs, muscles and nervous system begin to organise, lungs begin to expand and contract, sex of foetus detectable with ultrasound
when is the second trimester
weeks 13-26
what happens in the second trimester
fetus is active, mother can feel movement, neurons rapidly form synapses, sensitivity to light and sound emerges
when is the third trimester
weeks 27-40
what happens in the third trimester
age of viability: 22-26 weeks
substantial growth and weight gain, rapid gains in neural connectivity and organisation, expanding sensory and behavioural capacities, signs of developing temperament
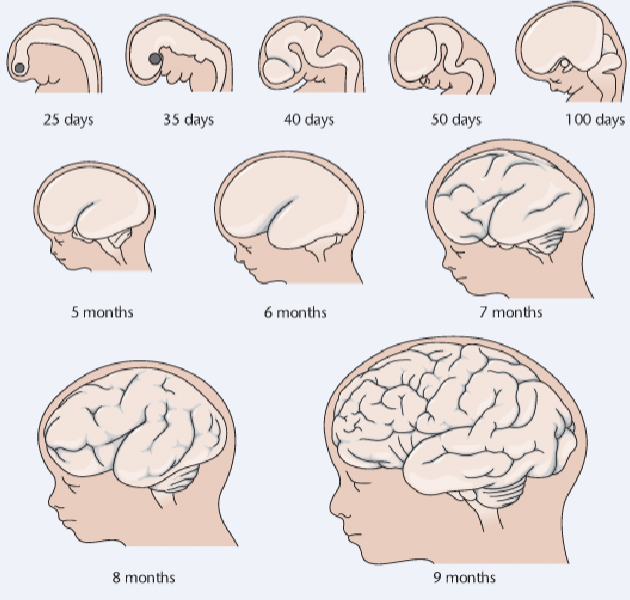
describe the formation of the brain during prenatal development
during the first month the neural tube forms, during the 6th month most of the brains neurons are in place and synaptogenesis begins, associated with new behavioural capacities, during the last trimester the cerebral cortex enlarges
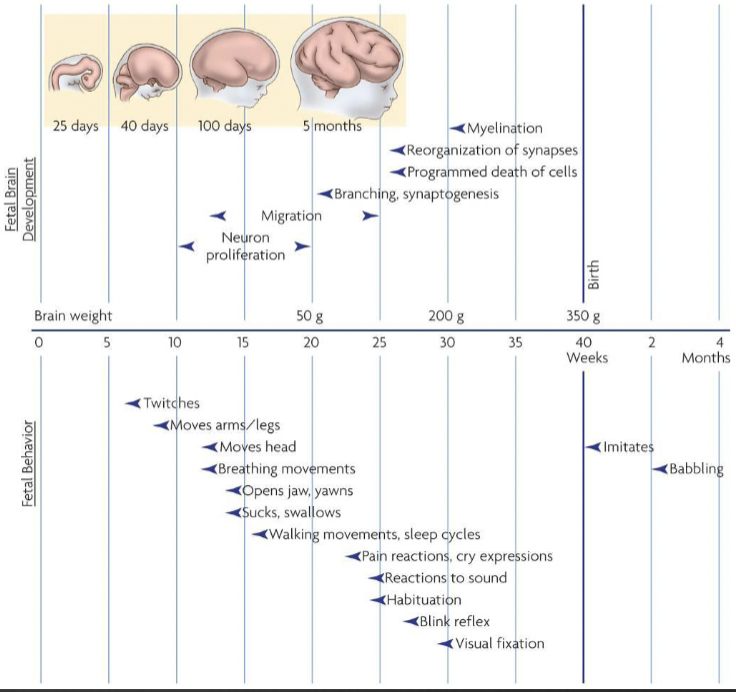
describe fatal movement progression during prenatal development
fetal movement from week 8 onwards, felt by mother at 18-20 weeks (variable), behaviour becomes progressively more organised with gestational age
describe prenatal learning
foetuses respond to sound during the third trimester, can discriminate between familiar and novel auditory stimuli from the 32nd week
is prenatal learning retained after birth
hell yeah (DeCasper & Spence, 1986)
how many chromosomes do humans have and what are they made up of
23 pairs of chromosomes, each made up of multiple genes
what is a gene and what is the point
a small section of dna that codes for a specific protein, they are how characteristics are inherited from our parents
how many chromosome pairs are sex related
22 pairs are matching autosomes and the 23rd pair are sex chromosomes (xx female xy male)
what are alleles
different possible forms of a gene
describe the difference between homozygous chromosomes and heterozygous chromosomes
homozygous - the same allele was inherited from both parents
heterozygous - different alleles were inherited from each parent
explain the idea of dominant vs recessive alleles in genetic inheritance
dominant alleles always express their characteristics
both recessive alleles must be present to express their characteristics (recessive alleles can be passed to children even if not expressed in the parent)
homozygous inheritance of certain recessive alleles can cause serious disabilities and diseases
explain what polygenic means in terms of genetic inheritance
many genes contribute to a single trait, resulting in a combined trait or one that is intermediate between the two, eg. hair colour, height, skin colour
explain multiple alleles in terms of genetic inheritance
more than two alleles for a gene, affecting a single trait, resulting in codominance or incomplete dominance
explain what is meant by a mutation in terms of genetic inheritance
sudden, permanent change in a dna segment, can occur spontaneously or be caused by hazardous environmental agents
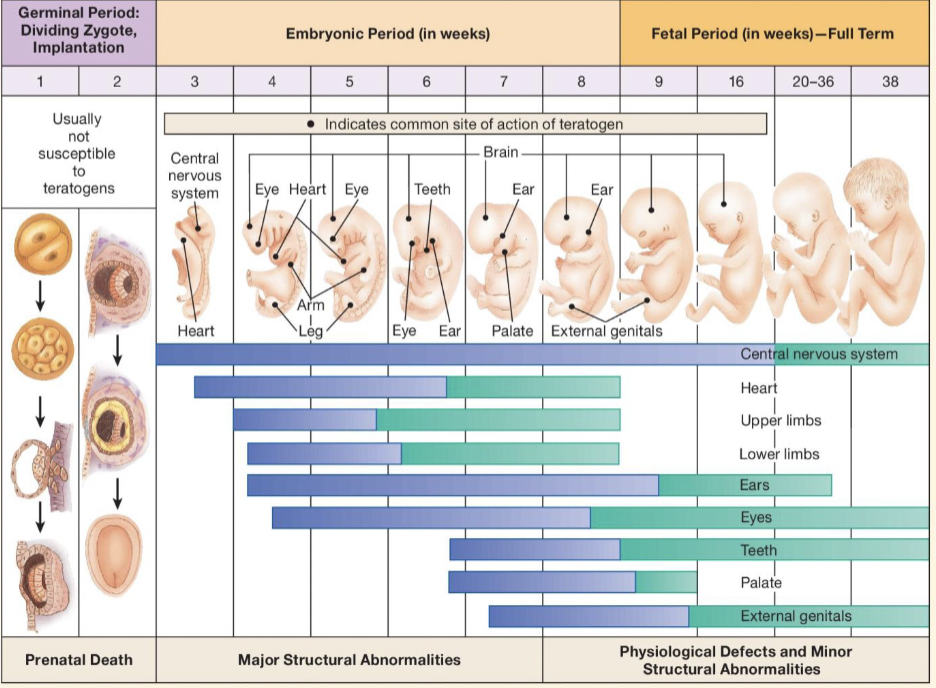
what are teratogens
environmental agents causing damage during the prenatal period
what are examples of teratogens
smoking, alcohol, drugs, environmental toxins
what effects can smoking have when done during the prenatal period
low birth weight, prematurity, impaired heart rate and breathing rate, infant death, asthma in later childhood, ADHD
what effects can alcohol have when consumed in the prenatal period
physical abnormalities, learning difficulties, hyperactivity, anxiety, fetal alcohol syndrome
what effects can drugs have when taken during the prenatal period
poor blood flow to placenta, babies born with signs of addiction
what effects can environmental toxins have if exposed during the prenatal period
mercury - cerebral palsy and cognitive impairments
arsenic - low birth weight and cognitive impairments
what effects can maternal diseases have if contracted during the prenatal period
rubella, hiv, gestational diabetes, zika
which maternal factors can impact the baby
diet, age, emotional state, poverty
sensitive periods?
what is a gene-environment interaction
genetic characteristics mediate responsiveness to environment
define epigenetics
factors modulating the expression of a gene
outline Radtke et al. (2011) study and findings
recruited women who had and hadn't experiences domestic violence during pregnancy
they measured dna for cortisol receptors (associated with a number of physical and behavioural problems)
in mothers there was no difference associated with their experience of domestic violence however when the children were aged 10-19 there was a significant difference in those who’s mothers had experienced violence during preganancy
the stress from experiencing domestic violence affected gene expression in the developing, unborn child that last through to adolescence