Week 16: Antimicrobial drugs
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Bactercidial
kills susceptible bacteria
Ex: penicillin — disrupts cell wall
Bacteriostatic
inhibits bacterial growth or replication and then the immune system kills the bacteria
Ex: inhibits synthesis and slows down replication
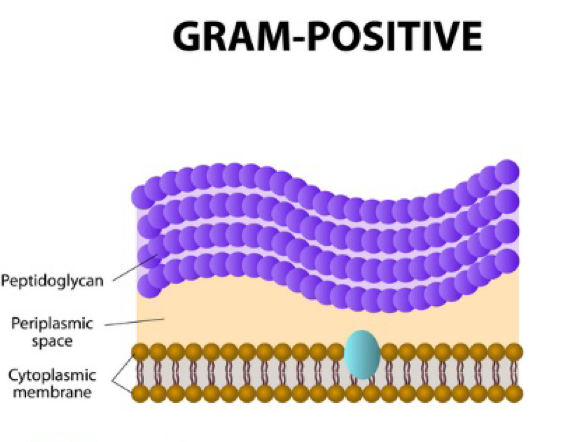
Gram positive bacteria
Thick peptidoglycan layer
Ex: strep
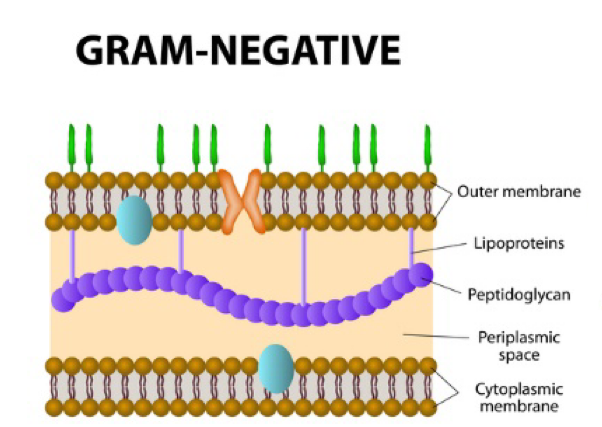
Gram negative bacteria
has an outer membrane and a thin pepdidoglycan layer in the periplasmic space
Ex: E. coli
Empiric antibiotic therapy
the use of abx before the identification of a microorganism that is causing an infection, or before knowing how that microorganism ill respond to abx
Broad spectrum antibiotic
Active against a wider number of bacterial types and may be used to treat a variety of infectious diseases
especially useful when infecting agents is unknown
Also kills good bacteria
Ex: if someone comes in with sepsis and they don’t know what the cause is so they give the patient a strong broad spectrum bacteria
Narrow spectrum antibiotic
active against a select group of bacterial types — must know the exact bacteria to ensure that we know what is causing the illness
Kills fewer good bacteria
Beta lactam
Antibiotics that share a beta lactam ring structure e.g. penicillins, carbapenems, and cephalosporin
Beta lactamase
An enzyme produced by some bacteria that cleaves beta lactam thereby inactivating the antibiotic.
Vancomycin Resistant Enterococci (VRE)
Very hardy bacteria — very hard to treat
Intrinsically resistant to many antibiotics
Vancomycin usually the treatment of choice
However acquired resistance has made strains resistant
Not a problem for healthy people but can cause wound, urinary, and septicemia in very young, old, frail
Healthy people without enterococci disease can be carriers
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)
infection is caused by a strain of staph bacteria that's become resistant to the antibiotics commonly used to treat ordinary staph infections
Methicillin is a penicillin derivative
Clostridium Difficile Infection (CDI)
Resistant to antibiotics and they start to take over. They produce a toxin that is harmful to the GI lining, which causes the symptoms.
Diarrhea!
Antibiotics that inhibit cell wall synthesis
Penicillin
Cephalosporins: cephalexin
Carbapenems: imipenem
Vancomycin
Antibiotic that blocks bacterial Nucleic acid replication
Fluoroquinolones: ciprofloxacin
Antibiotics that block protein synthesis
• Aminoglycosides: gentamicin
• Tetracyclines: doxycyclin
• Macrolides: azithromycin
Antibiotics that inhibit synthesis of bacterial metabolites
Sulfonamide/trimethoprim
Abx drug resistance mechanisms (make more flashcards for this — this one has too much on it)
They are not mutagenic and do not cause genetic changes that lead to drug resistance
Mutations in bacteria arise through spontaneous mutation and conjugation and these events occur naturally and in the absence of antibiotics
Antibiotics just produce favorable conditions for drug resistant organisms to emerge
All antibiotics can promote the growth of drug-resistance organisms. Broad spectrum antibiotics are better at this because they kill off more competing organisms than narrow spectrum drugs.
Adverse effects of antibiotics in general
Hypersensitivity rxns
GI effects
Superinfection
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Hypersensitivity reactions assessment findings
Rash
Pruritus
Urticaria
Systemic anaphylaxis
GI effects assessment findings
Nausea
Abdominal pain
Diarrhea
Superinfection
any infection that occurs d/t antibiotic therapy
Ex: yeast infection developing d/t healthy bacteria dying — yeast isn’t “in check”
Superinfection assessment findings
Sore or furry throat
Vaginal itching or discharge
Rectal itching
Foul-smelling feces
Superinfection by C.diff assessment findings
Fever
Abdominal pain/cramps
Large volume of diarrhea with blood and mucous
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome assessment findings
Fever
Rash
Blisters on skin
Sloughing of skin
Possible heath d/t infection from loss of skin integrity
Beta Lactam antibiotics that inhibit bacterial CW synthesis (3)
Penicillins: penicillin G
Cephalosporins: cephalexin
Carbapenems: imipenem
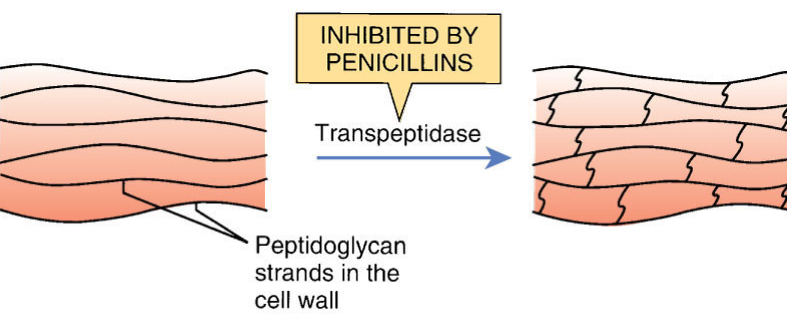
Penicillin MOA
Penicillin blocks transpeptidase using its beta-lactam ring, activating autolysins that break down the cell wall → bactericidal (mainly gram+)
Penicillin G uses via IM and IV administration
Streptococcal species: pneumonia and meningitis
Mainly gram + but some gram – bacteria
Acid labile so administered IM or IV
Excreted unchanged by the kidney
Penicillin G adverse effects
Least toxic of all antibiotics and safest of all medications
Penicillin ALLERGY
Pain at IM injection site, nausea, vomiting.
Renal abnormalities with large doses
Neurotoxicities (seizures, confusion, hallucinations) if blood concentration too high
How long should you monitor penicillin after giving?
20 minutes
If you have a sensitivity to _____, you should not take penicillin because…
cephalosporins
it is another beta-lactam antibiotic — rxn to abx is d/t the beta-lactam structure
can be given if the patient only has a mild rash, but if they have anaphylaxis they need to avoid it
Bacterial resistance to penicillin
Some bacteria can produce beta-lactamase (penicillinase)
Cleaves the beta-lactam ring of penicillin rendering it inactive
Cephalosporin prototype name
Cephalexin
Cephalosporins MOA
Beta-lactam abx
Bactercidial
Benefits of later generations of cephalosporins
can get into the CSF easier
can treat meningococcal infections bc it gets into CSF
Cephalosporin adverse effects
GI: Abdominal pain, N/V
Suprainfections: C. diff
Alcohol intolerance
IV and IM: abscess formation
Nephrotoxicity
Cephalosporin monitoring
RF
Thrombophlebitis — rotate injection sites
Cross allergy with penicillin
What should you do if cephalosporin is causing GI upset?
take with food
Carbapenems prototype name
Imipenem
Carbapenems MOA
Carbapenems indications
Very broad spectrum, gram + and gram – organisms.
Treating mixed and serious infections, including CNS infections*
Administration of Imipenem (Carbapenems)
IM and IV
Imipenem is only given IV or IM
Carbapenems adverse effects
Generally well tolerated
Hypersensitivity reactions
Superinfections
Seizures with renal dysfunction (rare) — bc excreted by kidneys
Carbapenems drug interactions
Penicillin
Cephalosporins
Valproic acid
Vancomycin MOA
disrupts CW by binding to peptidoglycan precursors
no Beta lactam ring
Vancomycin uses
Serious infections only with gram+ bacteria
C.diff. and MRSA
Vancomycin adverse effects
Major toxicity is renal failure.
Otoxicity (rare, and reversible)
Vancomycin Infusion Syndrome
Thrombophlebitis
Immune-mediated thrombocytopenia (rare)
What do you do when you get Vancomycin Infusion Syndrome?
A reaction does NOT mean that you stop vancomycin — you need to slow down the administration and administer antihistamines
To monitor during vancomycin administration
kidney and auditory function
Aminoglycosides prototype name
Gentamicin
IV and IM
Where do Aminoglycosides accumulate?
Kidney and inner ear
contributes to adverse effects
Aminoglycocides dose age
varies between patient — need to monitor each patient’s peak and troughs
Aminoglycosides adverse effects
Nephrotoxicity: usually reversible.
Irreversible ototoxicity (high trough levels for long periods)
Vestibular effects: impaired balance, headache
Neuromuscular blockade: flaccid paralysis, resp. depression
GI: Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
Primary indicator of aminoglycoside toxicity
elevated TROUGH
How long after aminoglycoside administration should you check the peak?
30 mins after med given
Things to monitor when administering Aminoglycosides
check 8th cranial nerve function (hearing and balance)
Report tinnitus
Vertigo
Nystagmus
Ataxia
HA
Check RF (BUN, creatinine, CrCl)
Encourage fluids
Tetracycline prototype name
doxycycline
Tetracycline adverse effects
Gastrointestinal irritation
Effect on bone and teeth- don’t give to pregnant, or breastfeeding women or children younger than 8y/o
Superinfection
Hepatotoxicity
Renal toxicity
Photosensitivity
Remembering adverse effects for tetracycline
“Terrible for teeth and tongue, tough on the tummy, toxic to liver and kidneys, teratogenic, and take sunscreen wherever you go!”
Interactions with Tetracyclines
Chelation?: iron, vitamin C, milk products, Mg containing laxatives, most antacids, anything with metal causes chelation
Affects absorption of tetracycline
Take on empty stomach — 1 hr before meals or 2 hrs after meals and a full glass of water (NEVER with vitamins or milk)
Oral contraceptive efficacy can be decreased by tetracycline
Macrolides prototype name
Azithromycin
Macrolides type of med
Broad spectrum
similar to penicillin, so it’s often used as a replacement for people with penicillin allergy
Macrolides adverse effects
Generally tolerable
GI
QT prolongs action and sudden cardiac death if given with CYP3A4 inhibitors
Superinfection
Hepatotoxicity
Hearing loss in elderly
Macrolides drug interactions
Major inhibitor of CYP3A4
Other QT prolonging drugs — increases risk
Macrolides patient education (break this up)
TRY to take oral med 1 h before or 2-3 h after meals with full glass of water; if GI upset can take with food
Monitor liver function AST(SGOT, ALT (SGPT)
Can be used in patients with compromised renal function because it is primarily excreted in the bile
Monitor EKG in pt’s with known prolonged QT
Prototype name for drugs that block folic acid synthesis
Trimethoprium / sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim)
Where is Trimethoprium / sulfamethoxazole metabolized and excreted?
Metabolized by liver
Excreted by kidneys
Trimethoprium / sulfamethoxazole interactions
Cross hypersensitivity with other sulfur-based drugs
Thiazide and loop diuretics
Sulfonylureas used to treat diabetes – use of both can intensify effect of sulfonylureas and promote hypoglycemia
Trimethoprium / sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim) adverse effects
Kernicterus — brain damage in newborns d/t extremely high bilirubin
Blood dyscrasias, including hemolytic anemia (immune mediated)
Hepatotoxicity
Hyperkalemia
Hypoglycemia
Hyponatremia
Class of drug that blocks bacterial nucleic synthesis
fluoroquinolone
Prototype name of fluoroquinolone
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro)
Fluoroquinolone adverse effects*
Tendon rupture – especially Achilles tendon- Black box warning
Phototoxicity – severe sunburn
GI symptoms
Azoles use
broad spectrum antifungal that can be used for many fungal infections
Azole prototype name
Fluconazole (Diflucan)
Fluconazole Administration methods
Oral
IV
Topical
Fluconazole MOA
Inhibits synthesis of ergosterol, a component of the fungal cytoplasmic membrane, leading to increased membrane permeability and leakage of cellular components
Fluconazole adverse effects (typically for systemic administration — IV)
GI
HA
Cardiac suppression — decrease in ventricular EF
Liver injury
Fluconazole drug interactions
Cytochrome p450 inhibitor
Drugs that reduce gastric acidity — take 1 hour before or 2 hours after Fluconazole
NO PPIs d/t long duration of action
Antiviral therapy
Antivirals are limited because viruses rely on host cell machinery, making it hard to stop replication without harming the host; drugs work by targeting viral-specific reproductive processes.
Acyclovir (Zovirax) use
Only active against members of the herpes family
Herpes simplex virus
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV)
Acyclovir (Zovirax) MOA
Inhibits viral replication of herpes virus
Acyclovir (Zovirax) side effects
GI: N/V and diarrhea
HA/vertigo
Neuraminidase inhibitors prototype name
Oseltamivir (Tamiflu)
Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) use
Treatment fir influenza A and B — within 2 days of symptom onset
Flu prophylaxis — within 48 hours of exposure
Patients >1 y/o
Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) adverse effects
HA
N/V