Speciation and Macroevolution
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Microevolution
changes in gene frequency over generations
changes within a gene pool/population
macroevolution
level of change in organisms that is evident in the fossil record (requires a long period of time)
changes above the species level
creates new species / groups of species
________ bridges microevolution and macroevolution
speciation
species
a group of organisms that maintains a distinctive set of attributes in nature AND can produce FERTILE offspring
______ occurs by accumulation of microevolutionary changes or changes in the genes
macroevolution
biological species concept
groups where the members have the potential to interbreed in nature to produce viable, fertile offspring but their offspring cannot successfully interbreed with members of OTHER species
ring species
members of geographically neighboring populations are related closely that they interbreed (same species) but the members of the populations near the “end” of the spread are incapable of interbreeding (different species)
phylogenetic concept
species are identified by having a unique combination of traits
in the past, physical traits were used - now we identify unique traits by DNA sequences
Evolutionary Concept
a species is derived from a single lineage that is distinct from other lineages and has its own evolutionary tendencies & historical fate
Ecological concepts
each species occupies a unique set of habitat resources that it requires, as well as its influence on the environment and other species
this results in competition, and such competing individuals are likely to be of the same species
reproductive isolating mechanisms
process which keeps two groups separate
prevents gene flow / interbreeding and thus the development of one single species
temporal isolation
prezygotic (before egg fertilized) mechanism
breed at different times
nocturnal v day time
fall v spring
behavioral isolation
PRE-ZYGOTIC
two individuals have different hobbies / behaviors
decorating their nest in two different colors (blue v white bower birds)
Mechanical Isolation
PRE-ZYGOTIC
reproductive parts fit perfectly with corresponding reproductive partner
Gametic Isolation
Pre-Zygotic
gametes of same species are very chemically similar to its own species and will not be fertilized by a different species
Ecological / Habitat Isolation
PRE-ZYGOTIC
two individuals living in different areas
LA v NYC
Describe how Species can be isolated Post-zygotic
a. zygotic (fertilized egg) dies
b. the individual is a hybrid and is sterile
c. the individual is a hybrid and is weak, low fitness (ability to survive) and has a high mortality rate among their offspring ex: liger
How does speciation emerge?
the accumulation of genetic changes that ultimately results in enough differences so that we can determine that the population constitutes a unique species
patterns of speciation
how microevolution (changes within species) results in macroevolution (changes in TYPES of species)
Anagenesis
small, progressive changes in a single species over long period
NO INCREASE IN SPECIES NUMBER - the single species is just changing into another
most common in bacteria

anagenesis
cladogenesis
speciation pattern
cluster of species all derived from one single common ancestor (most common)
Allopatric Speciation
mode of speciation
geographical isolation resulting in an new species - the gene flow between populations slows or stops (most common mode)
two species on different sides of the grand canyon would experience what mode of speciation?
allopatric - separated geographically
geographic separation leads to…
adaptive radiation: one group spreads out into new areas and undergoes new adaptations

allopatric separation (geographically separated & hold different characteristics)
adaptive radiation (spreading out into new areas and undergoes new adaptations
parapatric speciation
reproductive isolation (they don’t reproduce together) evolves in neighboring populations that share small zones of contact (but still have different habitats) and exhibit modest gene exchange (from living near each other)
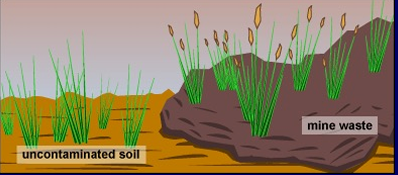
parapatric speciation
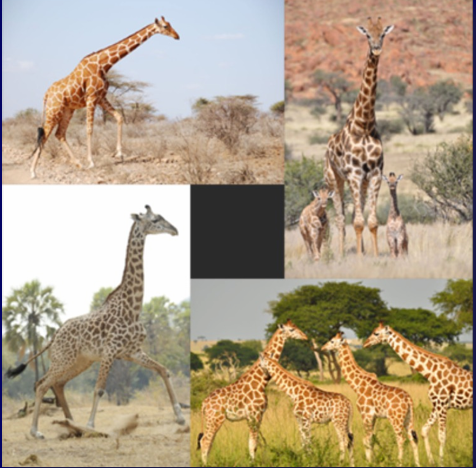

different patterned / colored giraffes is a result of parapatric speciation & how they evolve differently living in neighboring areas
sympatric speciation
new species evolves in same area as parental species (common in plants)
what causes sympatric speciation?
change in chromosome number due to abrupt genetic changes and leads to reproductive isolation
change in ecology - different eating habits, results in different size and in turn effects mating preferences & leads to reproductive isolation

allopatric:
same species
barrier formed
reproductive isolation lead to different species

same species
an environmental niche / habitat change emerged
the niche / change lead to natural selection & reproductive isolation leading to a new species
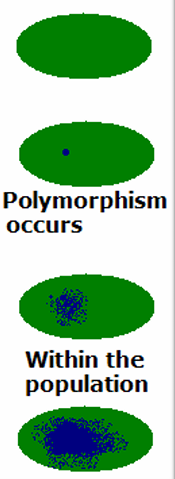
sympatric speciation
parent population
change in genetic appears and leads to reproductive isolation
reproductive isolation leads to emergence of new species
gradualism
early division produces two lines and undergoes gradual transitions with new species emerging from the same common ancestor
punctuated equilibrium
long periods of time with little changes are interrupted by widely spread episodes of speciation and each time results in a new species

gradualism

punctuated equilibrium
a major change occurs and results in a new species