W3, Drugs for Diabetes
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
What are routes to give drugs for diabetes?
SubQ, insulin pump, IV (sometimes, depends on type of insulin)
What are 2 most common ways to monitor daily blood glucose levels?
Blood glucose meter (glucometer), continuous glucose monitor (CGM)
What is a continuous glucose monitor (CGM)?
It’s a wearable medical device that measures blood sugar levels in real time throughout the day and night, and uses a small sensor under skin to track glucose in interstitial fluid, sending data to a phone or receive
What is a blood glucose meter (glucometer)?
It’s a handheld meter with test strips that helps patient measure how much glucose is in a small sample of blood
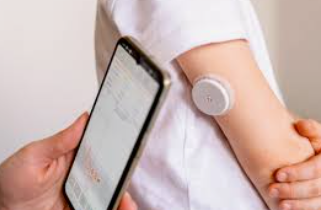
What is this?
Continuous glucose monitor (CGM)
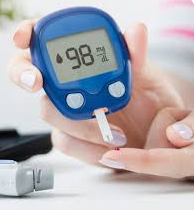
What is this?
Blood glucose meter (glucometer)
What is treatment goal for A1C levels in Type 1 and Type 2 diabetics?
To have A1C be less than 7%
What is A1C test, also called glycated hemoglobin test?
Blood test that measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2–3 months, and shows how well blood sugar is managed, with higher percentages reflecting higher average glucose levels
What are overall treatment goals in Type 1 diabetics?
To improve diet, exercise, give insulin (adjusted based on diet and exercise), and control BP and lipids (think syndrome X)
What would cause insulin dosage to be adjusted for someone with Type 1 diabetes?
Due to changes in diet, exercise, illness, stress, hormonal fluctuations, or weight changes
What are overall treatment goals in Type 2 diabetics?
To improve diet, exercise, lifestyle, give oral medications for diabetes and insulin if needed (if the oral medications are not working), and control BP and lipids (think syndrome X)
Are Type 2 diabetics given insulin right away as treatment?
Usually, Type 2 diabetics are first treated with lifestyle modifications and oral medications. Insulin may be added later if blood glucose is not well controlled or if levels are very high at diagnosis
True/False: Type 2 diabetics are given insulin right away as treatment
False; Type 2 diabetics are usually first treated with lifestyle modifications and oral medications. Insulin may be added later if blood glucose is not well controlled or if levels are very high at diagnosis
Why do Type 1 diabetics get insulin right away as treatment but Type 2 diabetics typically start off with lifestyle modifications and oral medications as treatment?
Type 1 diabetics need insulin immediately as treatment because body makes little to no insulin, whereas Type 2 diabetics usually still produce insulin but their body doesn’t use it effectively (insulin resistance)
Why do both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetics need to control their BP and lipids?
Controlling BP and lipids in diabetics relates to metabolic syndrome (syndrome X) because these conditions cluster together and significantly increase the risk of heart disease and stroke, especially in Type 2 diabetes
True/False: Controlling BP and lipids in diabetics relates to metabolic syndrome (syndrome X) because these conditions cluster together and significantly increase the risk of heart disease and stroke, especially in Type 2 diabetes
True
Where is insulin produced?
In pancreas by beta cells
What is function of insulin?
Facilitates glucose uptake (in cells) and storage
True/False: Insulin is required for most tissues (except CNS)
True
What does insulin deficiency lead to?
Leads to catabolic state, increased glycogenolysis, increased gluconeogenesis, decreased glucose utilization leading to hyperglycemia, potential production of ketones in body
What is glycogenolysis?
Rapidly breaks down stored glycogen into glucose
What is gluconeogenesis?
Creates "new" glucose from non-carbohydrate sources like lactate and amino acids
What is a catabolic state?
Metabolic condition where body breaks down complex molecules, such as muscle tissue and fat, into smaller units to release energy
True/False: Insulin deficiency leads to anabolic state
False; insulin deficiency leads to catabolic state, increased glycogenolysis, increased gluconeogenesis, decreased glucose utilization leading to hyperglycemia, potential production of ketones in body
What are 4 types of insulin?
Short duration rapid-acting, short duration slower-acting (regular), intermediate duration, long duration
What is therapeutic use of all 4 types of insulin?
To manage blood glucose levels in patients with Type 1 diabetes and in patients with Type 2 diabetes when insulin therapy is required
What is adverse effect of all 4 types of insulin?
Hypoglycemia
What is generic name of short duration rapid-acting insulin?
Insulin Lispro, Insulin Aspart
What are 2 short duration rapid-acting insulin drugs?
Insulin Lispro, Insulin Aspart
What is brand name of Insulin Lispro?
Humalog
What is brand name of Insulin Aspart?
NovoLog
What is classification of Insulin Lispro (HumaLog) and Insulin Aspart (NovoLog)?
Short duration rapid-acting
What is onset of HumaLog and NovoLog?
15 to 30 minutes
What is duration of HumaLog and NovoLog?
3 to 6 hours
How is HumaLog and NovoLog administered?
Inject 5 to 10 minutes before meals subcutaneously or via insulin pump
When does HumaLog and NovoLog reach peak effect?
1 hour after injection
What is insulin pump?
Small, wearable, computerized device for diabetes management that delivers rapid-acting insulin 24/7 through a tiny tube (catheter) inserted under the skin, replacing daily injections. It mimics a healthy pancreas by providing a continuous, programmed "basal" rate and "bolus" doses for meals (can program the pump to deliver a quick surge of insulin ("bolus") to cover carbohydrates consumed)
True/False: HumaLog and NovoLog should be administered 30 minutes before meals
False; inject HumaLog and NovoLog 5 to 10 minutes before meals subcutaneously or via insulin pump because patient is at risk for hypoglycemia if patient doesn’t eat within 15 minutes of receiving medication (because medication has such quick onset)
Why does HumaLog and NovoLog need to be injected 5 to 10 minutes before meals?
Patient is at risk for hypoglycemia if patient doesn’t eat within 15 minutes of receiving medication (because medication has such quick onset)
What is therapeutic use of HumaLog and NovoLog?
To manage blood glucose levels in patients with Type 1 diabetes and in patients with Type 2 diabetes when insulin therapy is required
What is adverse effect of HumaLog and NovoLog?
Hypoglycemia
What is mnemonic for onset, peak, and duration of HumaLog and NovoLog?
15-1-3
Why is 15-1-3 mnemonic for onset, peak, and duration of HumaLog and NovoLog?
15 minutes is onset, peak effect is 1 hour after injection, duration is 3 hours of Insulin Lispro and Insulin Aspart
What should nurse check for prior to administering HumaLog and NovoLog?
Nurse should check for room tray, because if room tray is not there nurse should wait to administer HumaLog and NovoLog because patient is at risk for hypoglycemia if patient doesn’t eat within 15 minutes of receiving HumaLog and NovoLog
What are 2 short duration slower-acting (regular) insulin drugs?
Humulin R, Novolin R
What are 2 brand names for insulin regular, the 2 short duration slower-acting (regular) insulin drugs?
Humulin R, Novolin R
What is generic name for short duration slower-acting (regular) insulin drugs, Humulin R and Novolin R (2 brand names)?
Insulin regular
What is onset of Humulin R and Novolin R?
30 to 60 minutes
What is classification of Humulin R and Novolin R?
Short acting slower-duration (regular)
What is duration of Humulin R and Novolin R?
10 hours
When does peak effect happen after injecting Humulin R and Novolin R?
1 to 5 hours
What are routes of administration of Humulin R and Novolin R?
SubQ, IV (for emergencies)
What is appearance of Humulin R and Novolin R?
Clear in color
When would Humulin R and Novolin R be given via IV?
In emergencies like acute, severe hyperglycemia or in specific, critical care situations
Who would be receiving Humulin R and Novolin R?
Type 1 diabetics, Type 2 diabetics if oral medications are not working, those who are NPO
What is therapeutic use of Humulin R and Novolin R?
To manage blood glucose levels in patients with Type 1 diabetes and in patients with Type 2 diabetes when insulin therapy is required
What is adverse effect of Humulin R and Novolin R?
Hypoglycemia
What is mnemonic for onset, peak, and duration of Humulin R and Novolin R?
1-5-10
Why is 1-5-10 mnemonic for onset, peak, and duration of Humulin R and Novolin R?
Onset is 1 hour, peak effect occurs at 5 hours, and duration is 10 hours
What are 2 brand names for intermediate duration type of insulin?
Humulin N, Novolin N
What is generic name for intermediate duration insulin?
Insulin NPH
What are brand names of NPH, intermediate duration insulin?
Humulin N, Novolin N
What is classification of Humulin N and Novolin N?
Intermediate duration insulin
How is Humulin N and Novolin N administered?
Given BID/TID for control between meals and at night by subcutaneous injection
True/False: Humulin R and Novolin R are given BID/TID for control between meals and at night by subcutaneous injection
False; Humulin N and Novolin N are given BID/TID for control between meals and at night by subcutaneous injection
What is onset of Humulin N and Novolin N?
1 to 3 hours
When does peak effect of Humulin N and Novolin N occur?
At 8 hours
What is duration of Humulin N and Novolin N?
12 to 16 hours, but about 12 hours
What are routes of administration of Humulin N and Novolin N?
Only subQ, NEVER IV
True/False: Humulin N and Novolin N can only be given via IV
False; Humulin N and Novolin N can only be given subQ, NEVER IV
What is appearance of Humulin N and Novolin N?
Cloudy, so must roll to mix
When preparing Humulin N and Novolin N, what should nurse remember before administration?
Roll to mix medication and NEVER shake it
True/False: Nurse should shake Humulin N and Novolin N before administration to mix it properly
False; nurse should ROLL Humulin N and Novolin N before administration to mix it properly, and NEVER shake it (would ruin medication)
True/False: Nurse should roll Humulin R and Novolin R before administration to mix it properly
False; nurse should roll Humulin N and Novolin N before administration to mix it properly, whereas nurse doesn’t have to do anything before administration of Humulin R and Novolin R
What is only type of insulin that can be mixed with short duration types of insulin?
Intermediate duration insulin is only type that can be mixed with short duration types of insulin
True/False: Only intermediate (NPH) duration insulin can be mixed with short-acting insulin; all other types should be given alone
True!
What is therapeutic use of Humulin N and Novolin N?
To manage blood glucose levels in patients with Type 1 diabetes and in patients with Type 2 diabetes when insulin therapy is required
What is adverse effect of Humulin N and Novolin N?
Hypoglycemia
What is generic name of long duration insulin?
Glargine
What is brand name of long duration insulin, glargine (generic name)?
Lantus
What is classification of Lantus?
Long duration insulin
What is duration of Lantus?
Up to 24 hours
What is therapeutic use of Lantus?
To manage blood glucose levels in patients with Type 1 diabetes and in patients with Type 2 diabetes when insulin therapy is required
What is adverse effect of Lantus?
Hypoglycemia
When does peak effect of Lantus occur?
Has no peak effect because medication works at steady rate
True/False: Peak effect of Lantus occurs at 8 hours
False; Lantus has no peak effect because medication works at steady rate
How is Lantus administered?
Dosed once subcutaneously usually at bedtime
Why is Lantus administered at bedtime?
To provide steady overnight insulin and reduce daytime low blood sugar
True/False: Lantus provides steady basal control of blood sugar for 24 hours
True
What is appearance of Lantus?
Clear solution
How should unopened vials of all 4 types of insulin be stored?
In fridge
How should opened vials of all 4 types of insulin be stored?
At room temperature for 1 month
True/False: Unopened vials of all 4 types of insulin should be stored at room temperature, whereas opened vials should be stored in the fridge
False; unopened vials of all 4 types of insulin should be stored in fridge, whereas opened vials should be stored at room temperature for a month
What should nurse remember when administering any type of insulin as subQ injection?
To rotate injection sites to prevent lipodystrophy (hard nodules form under skin)
True/False: Nurse can administer any type of insulin in same spot for a few days
False; nurse must remember to rotate injection sites to prevent lipodystrophy (hard nodules form under skin)
Why should nurse not administer subQ injection of insulin (any type) in same spot every time?
Hard nodules could form under skin (lipodystrophy) if insulin is given in same spot every time
If nurse is just starting shift, should nurse just guess where to inject next dose of insulin for patient?
No, look at documentation
What should nurse do after administering insulin subcutaneously (any type)?
Document location as well as everything else (plus monitor patient)
What is important for nurse to teach patient with diabetes?
Teach self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG)
How are intermediate duration insulin and short duration insulin mixed together?
First gently roll intermediate duration (NPH) vial to resuspend insulin, then inject air into cloudy vial (NPH) first, followed by clear vial (short duration), and withdraw clear insulin before cloudy insulin (“clear before cloudy”)