Project Management Final
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
For the project manager, leadership is:
A) The process by which she influences the project team.
B) The process of assembling a group of individuals.
C) The process of building skills among all team members.
D) The process of maintaining control of the budget.
A
2) The idea that all members of a project team have the ability to offer a contrary position in order to achieve true partnership between the project manager and the team is called:
A) Exchange of purpose.
B) A right to say no.
C) Joint accountability.
D) Absolute honesty
B
3) In a partnership, each member of the project team is responsible for the project's outcomes and the current situation, whether it is positive or shows evidence of project problems. The term that BEST describes this responsibility is:
A) Exchange of purpose.
B) A right to say no.
C) Joint accountability.
D) Absolute honesty
C
4) The authentic atmosphere of straightforwardness that is vital for project manager and team to function in can be described as:
A) Exchange of purpose.
B) A right to say no.
C) Joint accountability.
D) Absolute honesty.
D
5) Comment on the project profiles Aziza Chaouni and Her Project to Save a River and Dr. Elattuvalapil Sreedharan, India's Project Management Rock Star. What evidence is offered of project leadership skills in these vignettes?
The Aziza Chaouni profile speaks to the leadership skills of creating vision, taking a long-term (20 years for this project) view, and working with a diverse group of stakeholders. The success of Dr. Elattuvalapil Sreedharan is attributed in large part to his ability to create and articulate a clear vision, to hold team members accountable for both financial and temporal resources. He demonstrates transparency with all stakeholders, holds frequent communication meetings, and stresses punctuality, integrity, and professional competence as basic qualities for success.
The facet of partnership that describes the requirement that every worker be responsible for defining the project's vision and goals is called:
A) Exchange of purpose.
B) A right to say no.
C) Joint accountability.
D) Absolute honesty.
A
Which statement regarding the duties of leaders and managers is BEST? A) Leaders embrace the status quo while managers support change. B) A manager's title is bestowed by the organization. C) Leaders aim for efficiency. D) Managers aim for effectiveness.
B
Which statement regarding the duties of leaders and managers is BEST? A) Leaders embrace change while managers support the status quo. B) Management is more about interpersonal relationships than leadership is. C) Leaders aim for efficiency. D) Managers aim for effectiveness.
A
Which of these lists of duties is more reflective of managerial tasks? A) Creating vision and strategies B) Problem solving C) Long-term risk taking D) Communication by word and deed
B
Which of these duties is more reflective of a leader's tasks? A) Efficiency of operations B) Delegation and maintaining C) Motivation and inspiration D) Marshalling resources
C
Which of these is more characteristic of a manager? A) Develop new processes B) Originate C) State their position D) Focus on people
C
Which of these is more characteristic of a leader? A) Strive for control B) Do things right C) Demand respect D) Inspire trust
D
A more apt title for a project manager is: A) Controller. B) Comptroller. C) Project director. D) Project leader.
D
Projects are often underfunded in the concept stage because: A) The project requirements were deliberately understated. B) There is complete trust in project managers by top management so more resources can be asked for at any time. C) The project's goals are too clearly defined. D) The project's top management sponsor is too influential.
A
A common tactic project managers use when they realize their project is underfunded is to rely on: A) Intimidation. B) Political tactics. C) Asking for forgiveness rather than permission. D) The kindness of strangers.
B
Project team motivation comes primarily from: A) The project manager. B) The project champion. C) Within each team member. D) The project client's acceptance.
C
It is most important that a project manager: A) Focuses on meeting daily challenges head on. B) Focuses on meetings. C) Remembers the overall picture, or goals, that define the project. D) Operates on the boundary between strategy and tactics.
D
The project management pearl of wisdom that declares, "If they know nothing of what you are doing, they assume you are doing nothing," means that: A) Stakeholders must be communicated with on a continual basis throughout the project's development. B) The duration of most projects is sufficiently long as to contain many days when no actual progress is being made. C) The more complex a project is, the more likely that the client who will ultimately receive the project has no idea how it is being executed. D) A project manager that holds lengthy progress meetings with his team will generally complete projects more successfully.
A
Task-oriented leadership behavior is characterized by: A) Showing trust in project team members. B) Acting friendly and supportive towards project team members. C) Contributing to the completion of project assignments. D) Recognizing the accomplishments of team members.
C
Which of these behaviors is task-oriented? A) Every Friday is ice-cream day at the job site; everyone gets a double dip of their favorite flavor. B) The employee of the month plaque is updated monthly and placed in a prominent position near the checkout stand. C) The dean reached into his pocket, extracted his money clip and peeled off $3,000, saying, "Why don't you pick out some window treatments for the office? Something nice." D) When my computer broke, the project manager had it replaced immediately.
D
Project management people skills include: A) Team building. B) Scheduling. C) Budgeting. D) Project evaluation.
A
The first step in assembling a project team is to: A) Talk to potential team members. B) Identify the required skills. C) Negotiate with the functional supervisor. D) Notify top management.
B
Which two steps of project team building are out of sequence? A) You always identify skills before you identify people. B) You always negotiate with the functional supervisor before you negotiate with top management. C) You always negotiate with the functional supervisor before you talk to potential team members. D) You always identify personnel before you talk to potential team members.
C
A project manager can identify the skills needed for the project from the: A) Departmental personnel listings. B) Project budget. C) Stakeholder meeting. D) Work breakdown structure.
D
Most project resources are negotiated with: A) Project managers. B) Potential team members. C) Top management. D) External stakeholders.
A
Stacey noted that the client was a cantankerous old man and that her current project team lacked the requisite skills to work with him. Time was running short, so the BEST approach to making sure the project team had the necessary skills was to: A) Locate a new client for this project. B) Identify a suitable training program and implement it. C) Hire a contractor for the life of the project. D) Modify the skill set to something that her current team possessed
C
If a functional manager will NOT release the resources you need as project manager, your best course of action is to: A) Complete the project as best you can and inform management and the client that you predicted this outcome. B) Use social media to voice your concerns. C) Notify top management of the consequences. D) Update your resume.
C
With a failure to secure personnel releases from functional managers, a project manager should: A) Proceed as originally planned. B) Abandon the project. C) Adjust schedules and scope documents. D) Relinquish project leader status.
C
Team building and conflict management skills are two of the most important people skills that project managers can cultivate.
True
The first step in assembling a project team is to talk to potential team members.
False
If preferred project team members are not available, the project manager should notify top management of the consequences.
True
What are the steps in assembling a project team? Which is most critical? Why?
1) The first step in building a project team is to examine the work breakdown structure and identify the skills required to perform the assignments.
2) The second step is to identify the personnel that have these skills and talk to them about the project. The project manager must then negotiate with the functional supervisor about the availability of the skilled personnel. If this is successful, the team can be assembled and the project moves into the next phase of role clarification and responsibility determination.
If the desired people are not available, the project manager should renegotiate with top management and if successful, then assembles the team.
If negotiations with top management are unsuccessful, then the project manager should turn to a fallback position. Answers will vary as to which step is most critical.
You have been tapped as project manager for your dream project and find yourself initially rebuffed by functional managers that are reluctant to release members of your "dream team" to help you work on the project. What are three alternatives you might choose from and which is most attractive?
The three alternatives that are available to a manager constitute fallback positions in the project life cycle. One alternative is to negotiate for partial assistance; if a full-time assignment is sought, perhaps the manager will relinquish the employee at one-quarter time. The advantage of this approach is that it secures an inroad into the employee's time that may be increased later. Another alternative is to adjust the project schedule and priorities accordingly. If the employee is not available full time, then it must be accepted that the project cannot proceed at the desired pace, or perhaps can be completed within the allotted time frame in some limited scope. The third alternative is to report the situation to top management and ask for their intervention or inform them of the dire consequences of this lack of skilled personnel.
A key determinant of project success is a: A) Rapidly assembled team. B) Slowly assembled team. C) Project leader voted on by the team. D) Clear project mission.
D
The number one predictor of project success is: A) The absence of conflict among project team members. B) Documentation that clearly articulates the consequences of failing to achieve the objectives. C) A mission that is understood and accepted by all team members. D) A well-prepared fallback position in case the project cannot be executed as imagined.
D
The BEST source of troubleshooting for problems is the: A) Project team. B) Project manager. C) Project customer. D) Project champion.
A
Productive interdependencies hinge upon: A) The project manager's role as the hub of the team with all team members as spokes. B) The degree of knowledge the team members have and the importance they attach to interrelatedness of efforts. C) The cohesiveness of the project team's supply chain and the degree of assistance they render the project team. D) The support the key stakeholders offer to the overall project success.
B
The study group that Philip had formed in his first MBA class had gotten him through his management science course; of that there could be no question. Now as he neared the end of his MBA he reflected on how team members had chosen courses together each semester, keeping the study group intact and keeping themselves one step ahead of their classmates. His MBA project team had: A) Trust coming out of their ears. B) Cohesiveness in spades. C) An overabundance of enthusiasm. D) A plethora of results orientation.
B
Trust based on a person's competence would be summarized by this team member's affectionate statement towards another team member: A) "I trust you to honor your commitments." B) "Does it feel right to allow you to make this decision?" C) "I trust you to be able to accomplish this task." D) "I trust you to do the right thing."
C
The key to creating the energy and spirit that drives effective project efforts is: A) Results orientation. B) Trust. C) Cohesiveness. D) Enthusiasm.
D
The difference between projects that fail and those that are ultimately successful has to do with: A) The plans that have been made to deal with problems as they arise. B) The fact that a successful project doesn't encounter problems. C) Whether the project is for an internal or external customer. D) Whether the problem is time- or budget-related.
A
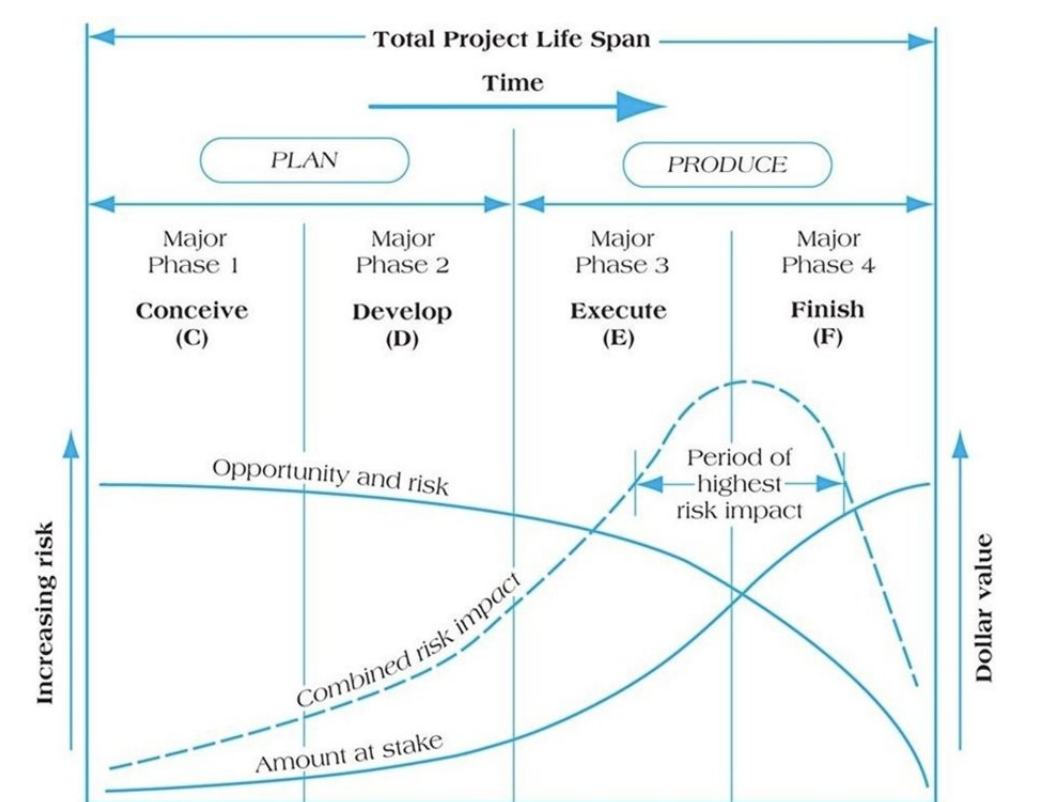
Project risk is highest during the: A) Finish phase of the project life cycle. B) Conceive phase of the project life cycle. C) Execute phase of the project life cycle. D) Develop phase of the project life cycle.
B
Project risk is lowest during the: A) Conceive phase of the project life cycle. B) Execute phase of the project life cycle. C) Finish phase of the project life cycle. D) Develop phase of the project life cycle.
C
The period of highest risk impact for a project risk exists primarily in the: A) Develop phase of the project life cycle. B) Conceive phase of the project life cycle. C) Execute phase of the project life cycle. D) Execute and Finish phases of the project life cycle.
D
The greatest project risk occurs when: A) The probability of the event is high and the consequences of the event are high. B) The probability of the event is high and the consequences of the event are low. C) The probability of the event is low and the consequences of the event are high. D) The probability of the event is low and the consequences of the event are low.
A
The greatest project opportunity occurs when: A) The project is in the conceive phase. B) The project is in the develop phase. C) The project is in the execute phase. D) The project is in the finish phase.
A
The amount a company has at stake in a project rises above the dollar value of opportunity in the: A) Execute phase. B) Develop phase. C) Conceive phase. D) Finish phase.
D
Risk and opportunity: A) Both increase throughout the project life cycle. B) Vary inversely throughout the project life cycle. C) Both decrease throughout the project life cycle. D) Do not vary throughout the project life cycle.
C
To protect his poultry from meteorites, the gentleman farmer made hard hats for each bird and installed a meteor detection system that opened umbrellas throughout the yard if a meteor were detected. The safety of his flock thus assured, the farmer was surprised when he read his latest issue of Risk Management Magazine and discovered that this event was: A) High in consequence and high in probability. B) Low in consequence and low in probability. C) Low in probability and high in consequence. D) High in probability and low in consequence.
C
Jim knew instinctively that his professor wouldn't appreciate it if he brought his single scoop of vanilla ice cream into the lecture hall with him. He could almost hear the inevitable question, "Did you bring enough for everyone?" To avert such an embarrassment, he practically inhaled his frozen confection as he raced down the hall. He had eaten ice cream in this fashion before and knew he would soon have an ice cream headache, which could be described as: A) High in consequence and high in probability. B) Low in consequence and low in probability. C) Low in probability and high in consequence. D) High in probability and low in consequence.
D
While thrilling, there is a chance that you would have an accident if you elected to drive on the wrong side of a divided highway in Woodward, an outcome that could be described as: A) High in consequence and high in probability. B) Low in consequence and low in probability. C) Low in probability and high in consequence. D) High in probability and low in consequence.
A
The risk is highest in the earliest phase of the project life cycle.
True
Opportunity emerges from favorable project circumstances and risk from unfavorable events
True
As risk decreases in the project life cycle, opportunity increases.
False
Risks can be quantified by multiplying the likelihood a failure will occur by the severity of the failure.
True
How does risk level vary with project life cycle stages? Where is the period of highest risk impact? Why?
Risk is at its highest during a project's concept phase, falling off gradually during development phase and reduces dramatically during execution and termination phases. At project completion, risk is at its nadir. Risk is highest at the start of a project because uncertainty is high; what may be a clear vision in the customer's and project leader's minds is far from realization. Questions are answered and uncertainties resolved as the project progresses, but the amount at stake, as measured in man hours of labor, materials, and other expenses, rises. The period of highest risk impact is late in a project's life (during the execute and finish phases of the project); while risk itself is lower, the amount at stake is much higher, and until the project is finished and accepted there is potential for a poor finish. Since one important criterion of project success is customer acceptance, the risk impact remains high to the end.
Sketch the risk level and opportunity curves as a function of the project life cycle stage. Provide an example of a project from the recent business literature or your personal experience that exhibits these characteristics. Cite specific instances where the levels of opportunity, risk, and stake fluctuated
Risk management is a: A) Three-stage process. B) Four-stage process. C) Five-stage process. D) Six-stage process.
B
The construction foreman posted a large sign requiring all work site visitors to don a hard hat and safety glasses. He also purchased copious quantities of both items and made them readily available at the entrance. The foreman is engaged in:
B
The residents of Enumclaw, Washington, live in the shadow of majestic Mount Rainier and its 26 glaciers. The Cascades form a ring of fire around the Pacific Northwest and erupt with surprising regularity, although Mount Rainier hasn't erupted on a major scale since about a thousand years ago. When it does erupt, the pyroclastic flow (a massive cloud of superheated ash and rock up to 1500 degrees Fahrenheit that can travel at speeds up to 300 miles per hour) will make Enumclaw a less pleasant place to live. City leaders have completed the:
A) Control and documentation phase of risk management. B) Risk identification phase of risk management. C) Analysis of probability and consequences phase of risk management. D) Risk mitigation strategies phase of risk management.
C
Traditional, highly structured approaches to planning and managing projects are recognized as being less effective for ________ than Agile Project Management. A) construction projects B) software development C) wedding planning D) university baccalaureate degrees
B
Which adjective is most appropriate for Agile Project Management? A) Iterative B) Sequential C) Linear D) Hirsute
A
Agile Project Management is well-suited for instances where: A) Customer needs are well-defined. B) Time constraints exist. C) Customer needs are evolving. D) Budget constraints exist.
A
The waterfall project development process is well-suited for instances where: A) Requirements are allowed to float throughout the duration of the project. B) Customer needs change quickly. C) Time constraints exist. D) Resources are limited.
C
The sprint portion of the Agile Project Management process is targeted to last: A) 10 plus or minus 2 weeks. B) 7 plus or minus 1.5 weeks. C) 5 plus or minus 1.5 weeks. D) 2.5 plus or minus 1.5 weeks.
D
The customers articulate the necessary features of a software project through: A) Stories. B) Tasks. C) Requests for proposal. D) Bid rigging.
A
In Agile Project Management, the term "scrum" refers to: A) A period of enforced chaos. B) A meeting. C) The time when code is actually being written. D) Disagreements between the customer and the project team
B
In Agile Project Management, a sprint backlog is essentially a: A) Period of time. B) Punch list. C) Forecast. D) Meeting.
B
Which of these numerical (quantity) comparisons is CORRECT? A) Scrum meeting > Sprint B) Scrum master > Development team C) Sprint time box > Project duration D) Daily scrum duration < Development work duration
C
Agile project management features a logical series of steps that occur sequentially, each one is begun only when its predecessor is complete.
False
Agile project management is well-suited for the case where requirements change in the middle of project development.
True
What is the waterfall planning process and when is it the ideal approach to project development?
The waterfall process is the traditional process used for the software development process; it emphasizes completion of each step in the cycle, investing significant effort in planning the entire project before moving out of the planning stage into system design, system implementation, and the following steps. This process was to a great extent dictated by the nature of the programming languages available (procedural) and the ease with which programs could be modified once the coding had been done. The steps of the waterfall model are: Gather requirements, Design system, Implement system, Test system, Full deployment, and Maintenance. The waterfall paradigm works like an actual waterfall in that just as water doesn't flow uphill, once a level is complete, the developers can't go back and re-do something that was poorly implemented. The waterfall development process works well when the customer requirements are very well understood and fixed, the product definition is stable and not subject to changes, the technology is understood, there are ample resources with required expertise, and the project is relatively short.
What is Agile PM and what makes it ideal for many software development projects?
Agile project management reflects a new era in project planning that places a premium on flexibility and evolving customer requirements throughout the development process. Agile PM recognizes the importance of these evolving customer needs and allows for an incremental, iterative planning process—one that stays connected to clients across the project life cycle. Agile PM is usually referred to as Scrum, which recognizes it is a mistake that once the initial conceptualization and planning have been completed, the project can simply be executed. Agile PM turns development into a series of short development cycles known as the sprint that fit with a predetermined time box of one to four weeks in duration. This process is well-suited for deployment during software development projects, which are prone to constant change.
What takes place in the Scrum process?
In Agile PM, Scrum refers to the development strategy agreed to by all key members of the project. Scrum meetings involve assessing the current status of the project, evaluating the results of the previous Sprint, and setting the goals and time-box for the next iteration. The Scrum process involves a set of meetings that manage the project development process through 1) Sprint Planning, 2) Daily Scrums, 3) the Development Work, 4) Sprint Review, and 5) Sprint Retrospective. During the Sprint three guidelines shape the process: a) no changes are made that would endanger or modify the sprint goal, b)quality goals to not decrease, and c) scope may be clarified and renegotiated between the project owner and the development team as more is learned. The work to be performed in the Sprint is identified during the Sprint Planning session. This plan is created by the collaborative work of the entire Scrum team. The Daily Scrum is a short (15 minutes) event that allows the development team an opportunity to synchronize their activities and create a plan for the next 24-hour time window. During the meeting, members of the development team explain what they accomplished in the past 24 hours to meet the Sprint goal, what they intend to work on during the current day, and identify any problems that might prevent the development team from completing the next Sprint goal.
Compose a haiku using three or more of the key terms in Agile PM.
Development team.
Product backlog, burndown chart,
Product owner, scrum.
I am Scrum Master.
Where is the product owner?
Time box is closing.
Development team.
Listen to user stories,
Then make something great
What are the key elements of extreme programming?
Extreme Programming (XP) is a more aggressive form of Scrum and is a software development methodology intended to improve software quality and responsiveness to changing customer requirements. XP emphasizes keeping the programming code simple, reviewing it frequently, testing it early and often, and working normal business hours. Two of the guiding features of XP are the process of refactoring and pair programming. In order to speed software development, functional testing of all requirements is done before coding begins and automated testing of the code is performed continuously throughout the project. Refactoring is the continuous process of streamlining the design and improving code, not waiting until final testing to edit and fix code. Pair programming demands that all code is written by teams of two programmers that literally work side by side on the same machine doing the coding.
What is the motivation for programming in pairs using one terminal? How can this approach be more productive than having each of the two programmers at his own terminal?
Pair programming demands that all code is written by teams of two programmers that literally work side by side on the same machine doing the coding. Pair programming can help programmers resolve issues and clarify interpretations of user stories that drive the requirements. While engaged in pair programming, the writer of the code, called the driver, receives assistance from the navigator (sometimes called the observer or pointer) who reviews the line of code and considers the strategic direction of the work. While pairs tend to spend 15% more time writing code, the resulting code has 15% fewer defects. In addition, coders learn from each other and surface more possibilities for solving problems than if just one person coded in isolation.
What are some arguments against the XP technique of pair programming?
Pair programming demands that all code is written by teams of two programmers that literally work side by side on the same machine doing the coding. Just as in any team environment, disengagement, such as when one coder is not hands on with the keyboard decides to use his tablet or smartphone to check email or update his Facebook page, negates any advantage pair programming might offer. Some pairings of programmers are less successful than others—if one coder is far more skilled, then a "watch and learn" approach may relegate the other coder to literally watching without offering any opinions. Also, if the coders do not fit together well for reasons of personality or approach to the task at hand, then the clash of personalities or work ethic may make them significantly less productive.
All of these happen during the sprint phase EXCEPT: A) Technical issues are forwarded to the product owner. B) Scope clarification. C) Sprint goal modification. D) Scope renegotiation.
C
A product backlog: A) Shows remaining work in the sprint backlog. B) Is controlled by the customer. C) Shows what has been ordered to complete the project but not yet received from suppliers. D) Is a constantly evolving list.
D