embryo lab (3)
1/210
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
211 Terms
stalk of ovary
1
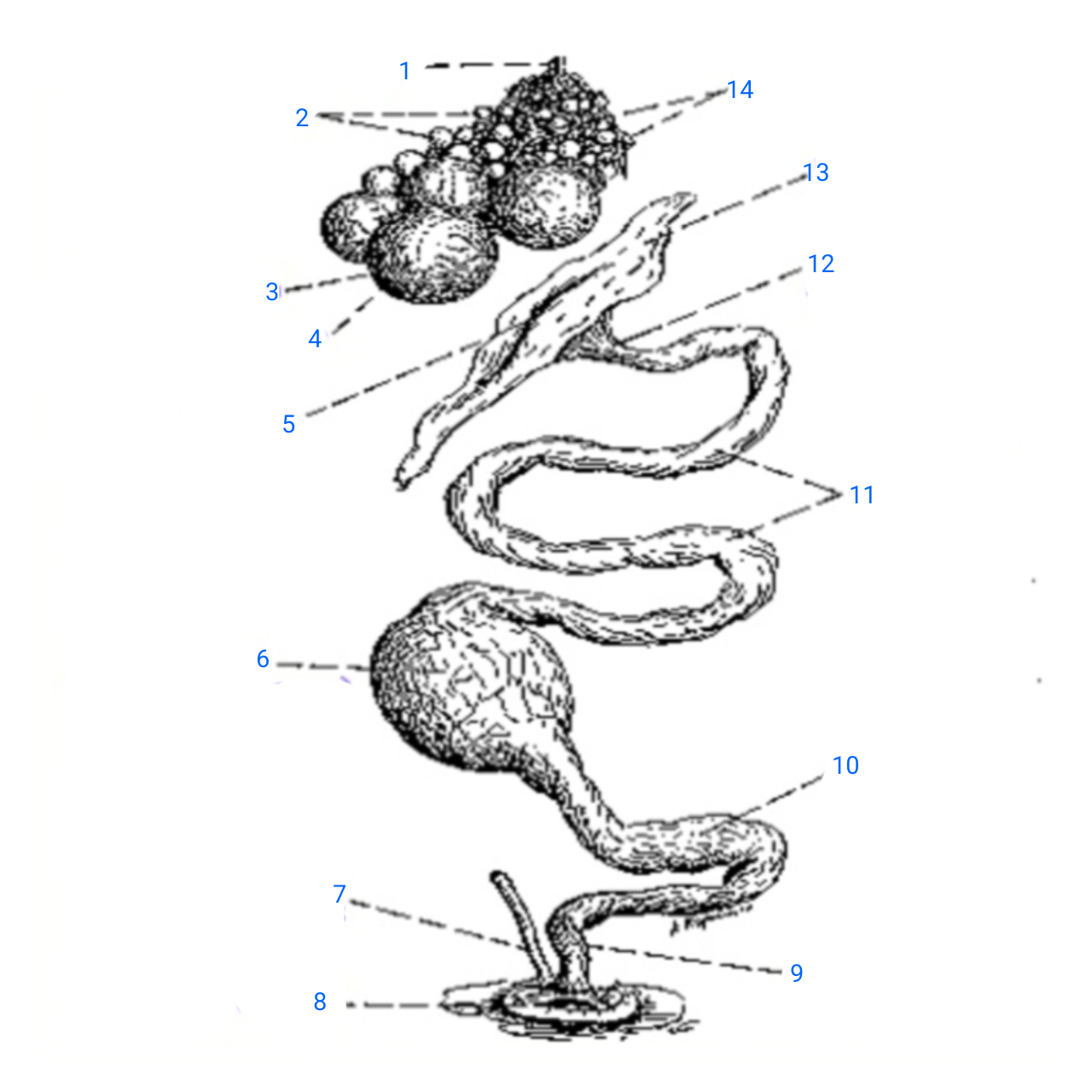
small ova
2
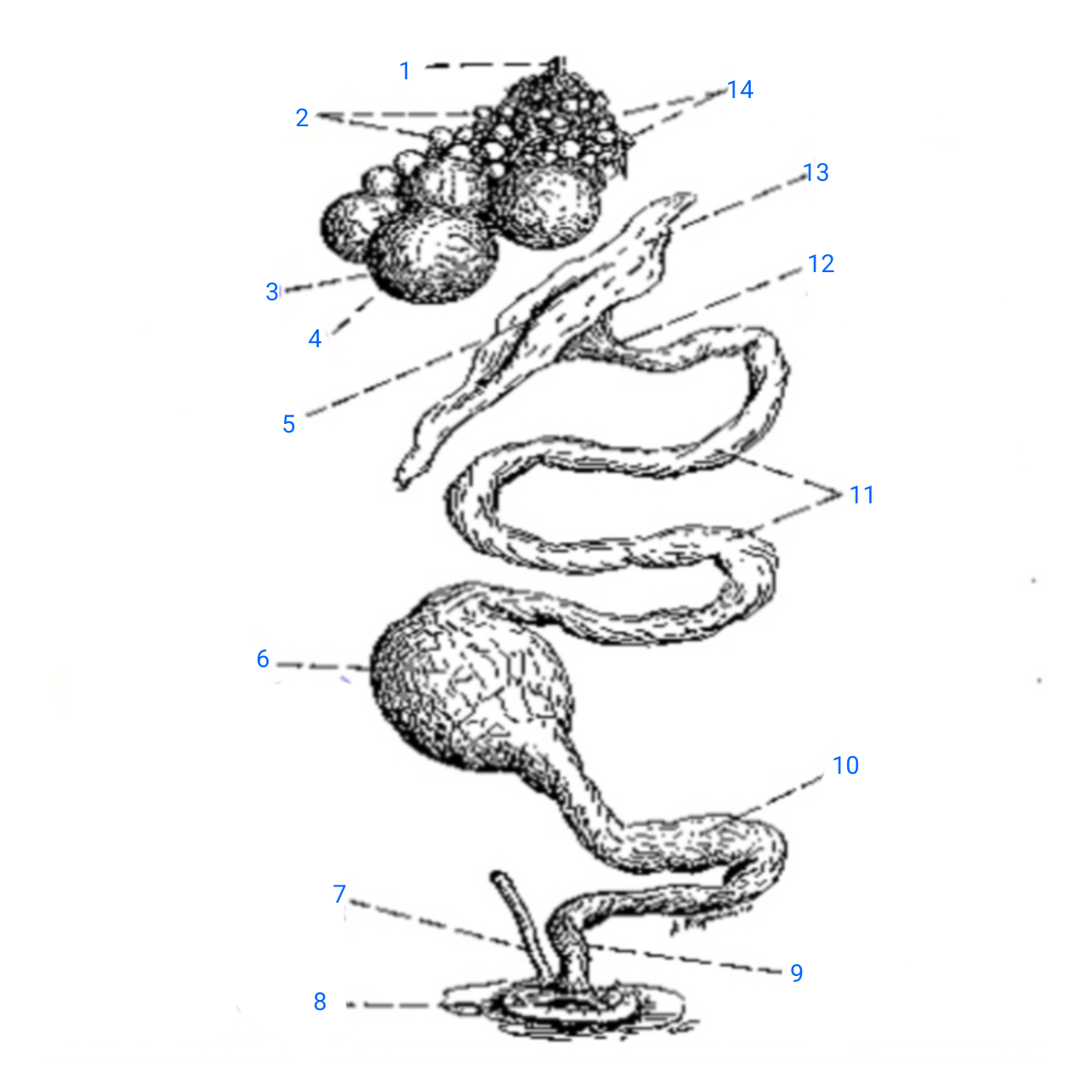
mature ovum
3
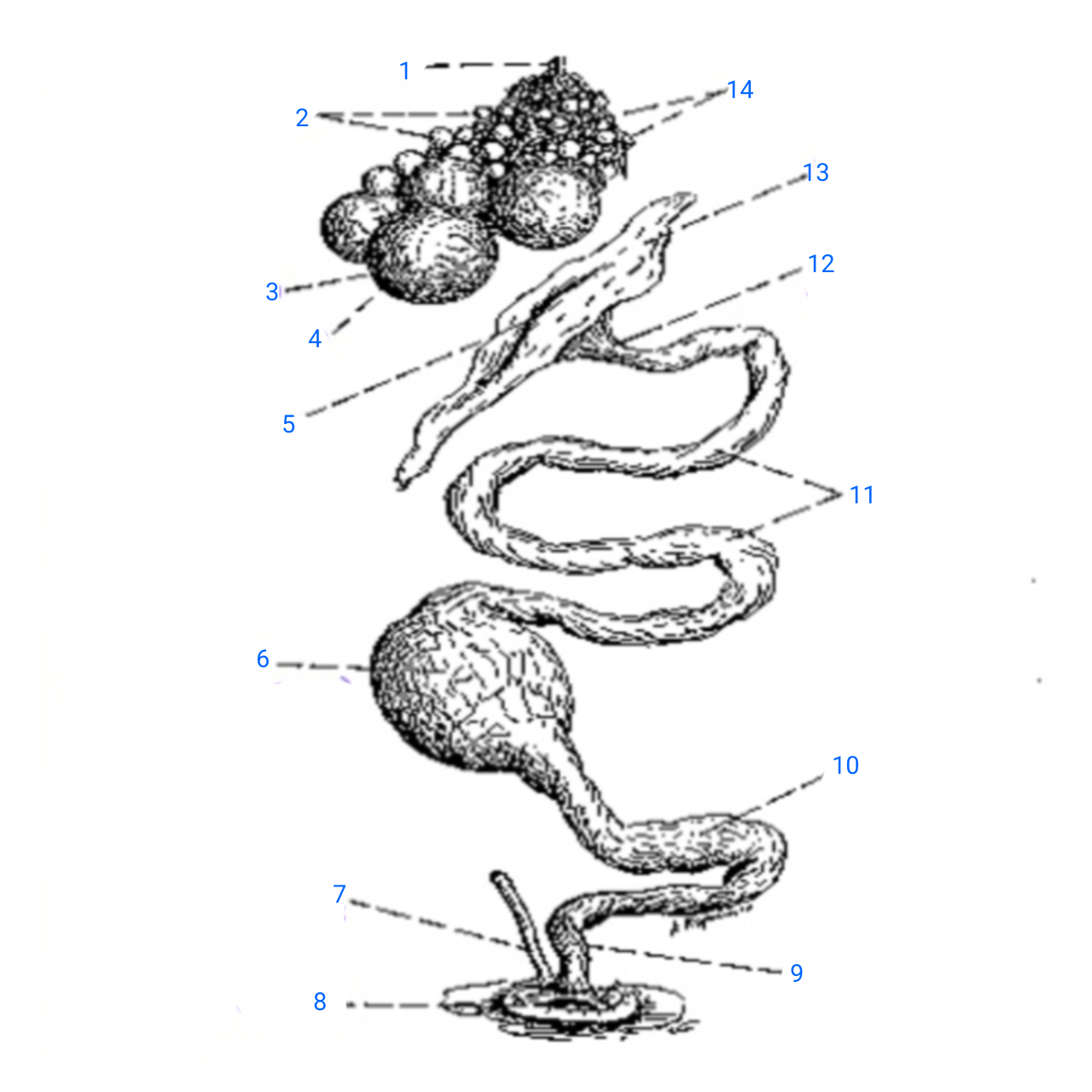
stigma
4
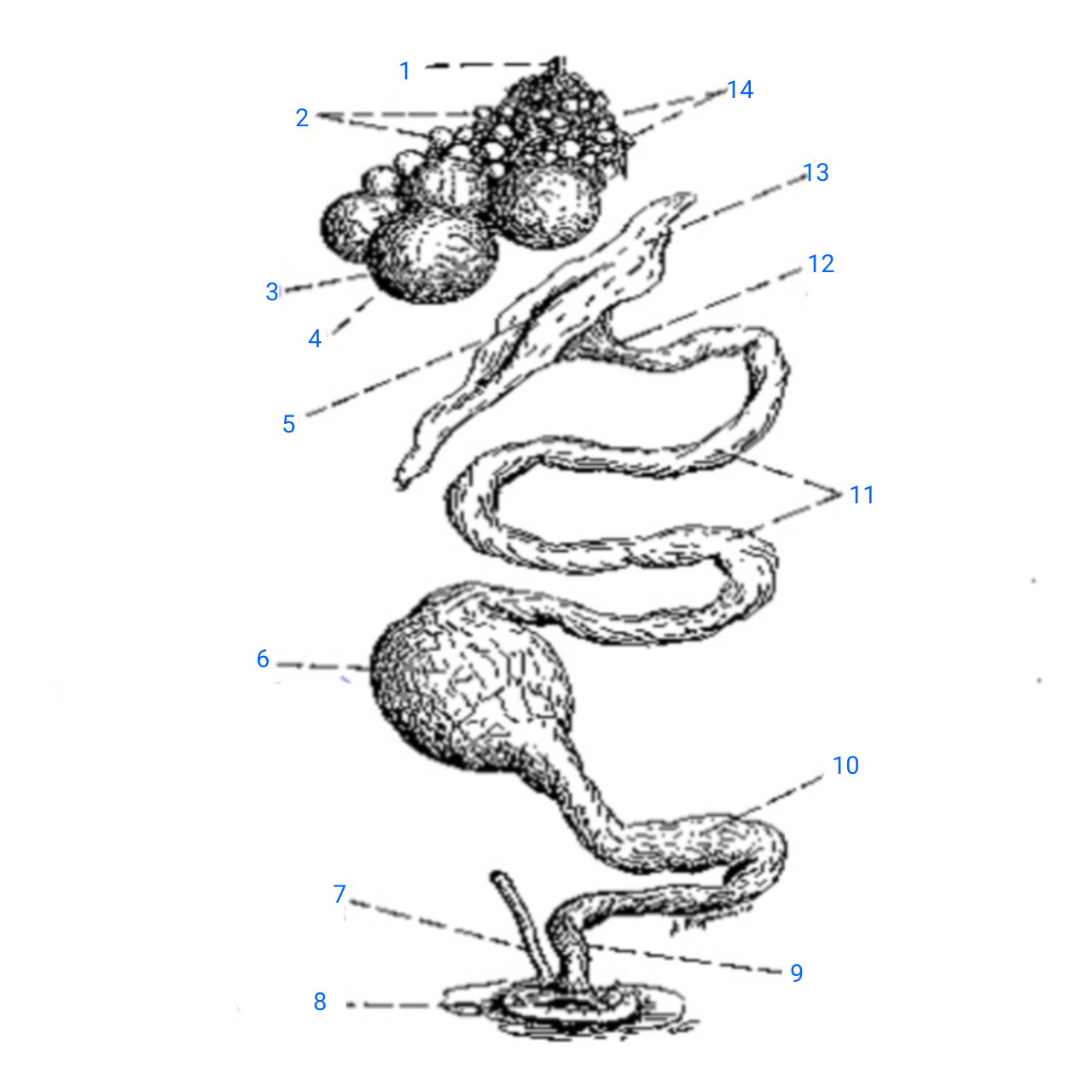
ostium
5
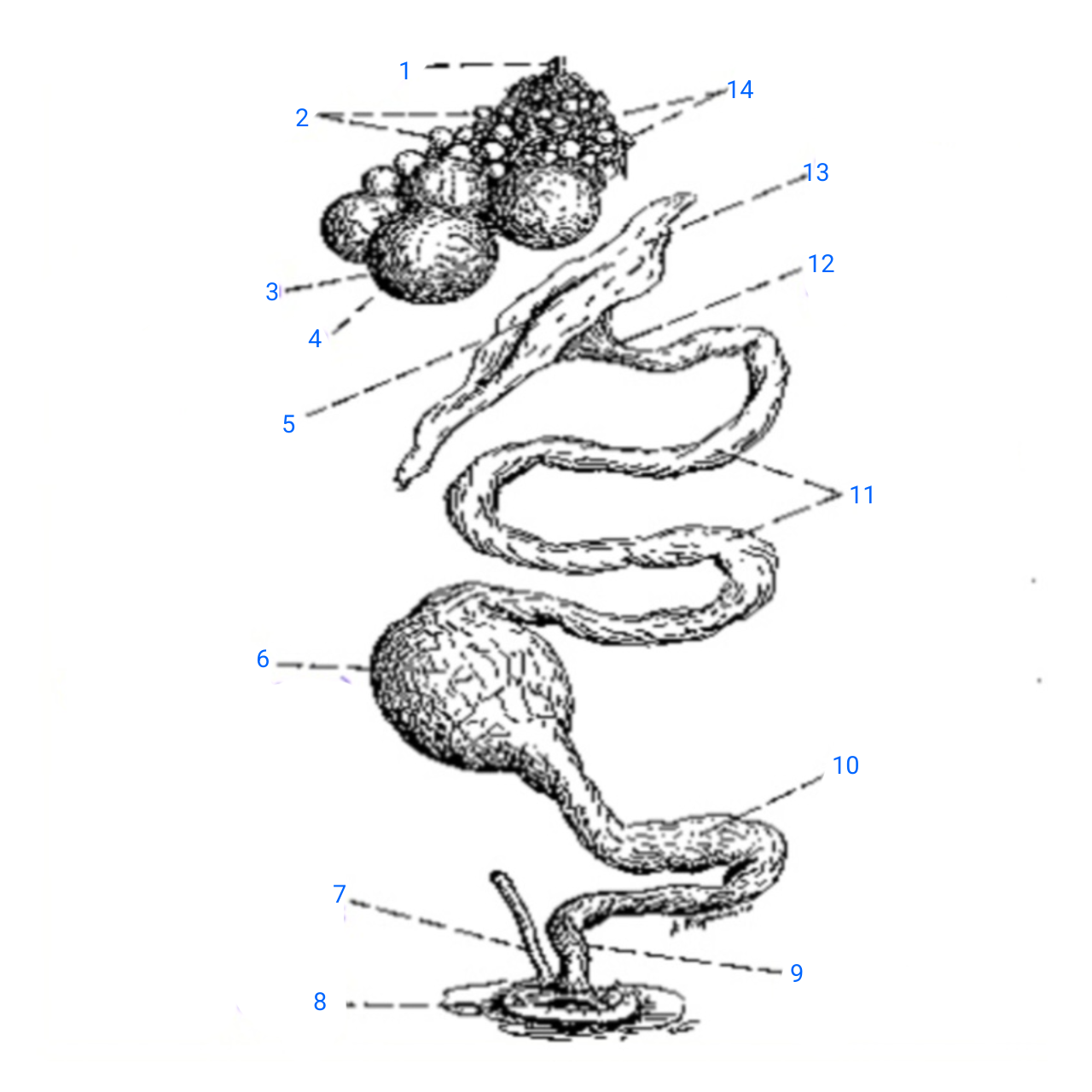
isthmus (with incomplete egg)
6
rudimentary right oviduct
7
cloaca
8
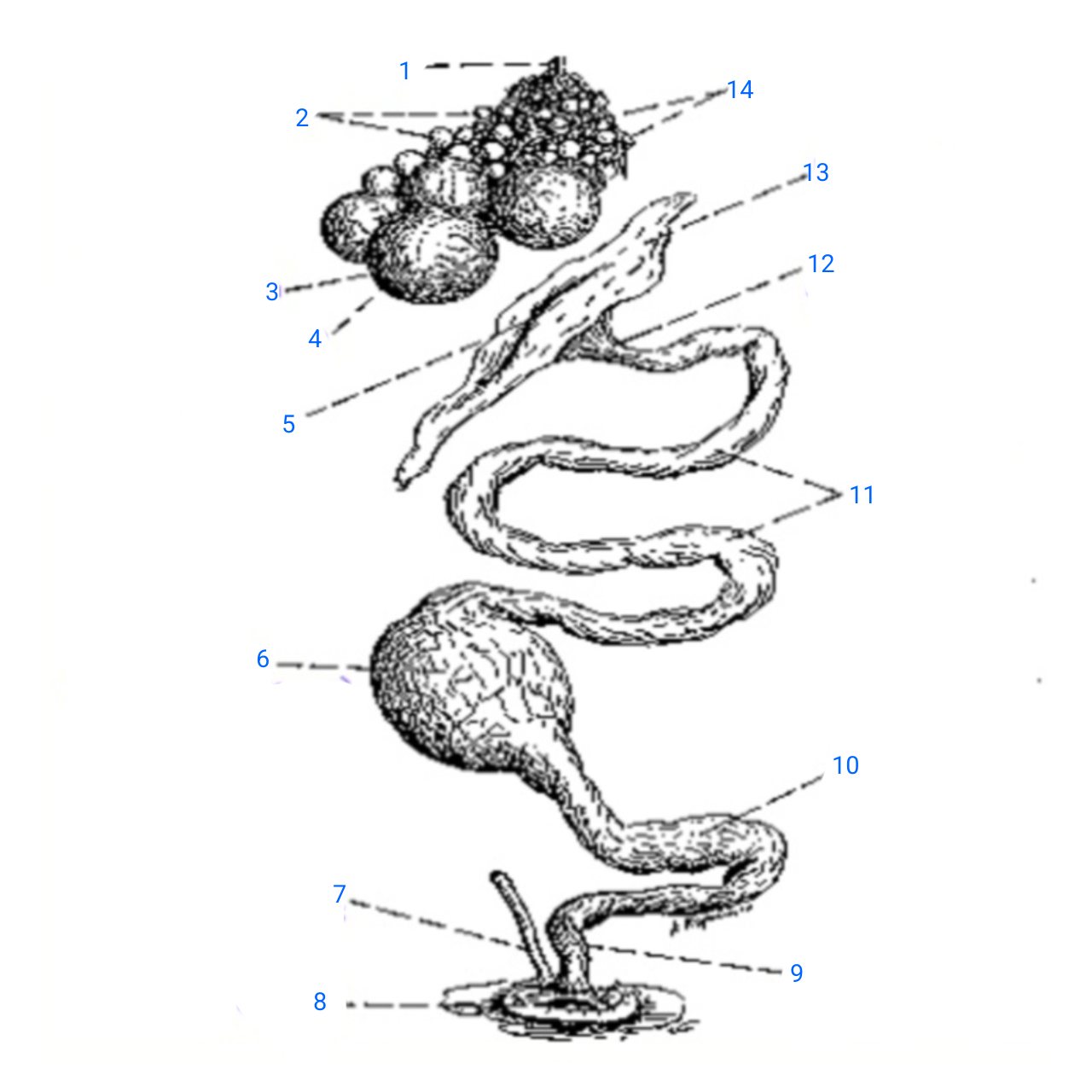
vagina
9
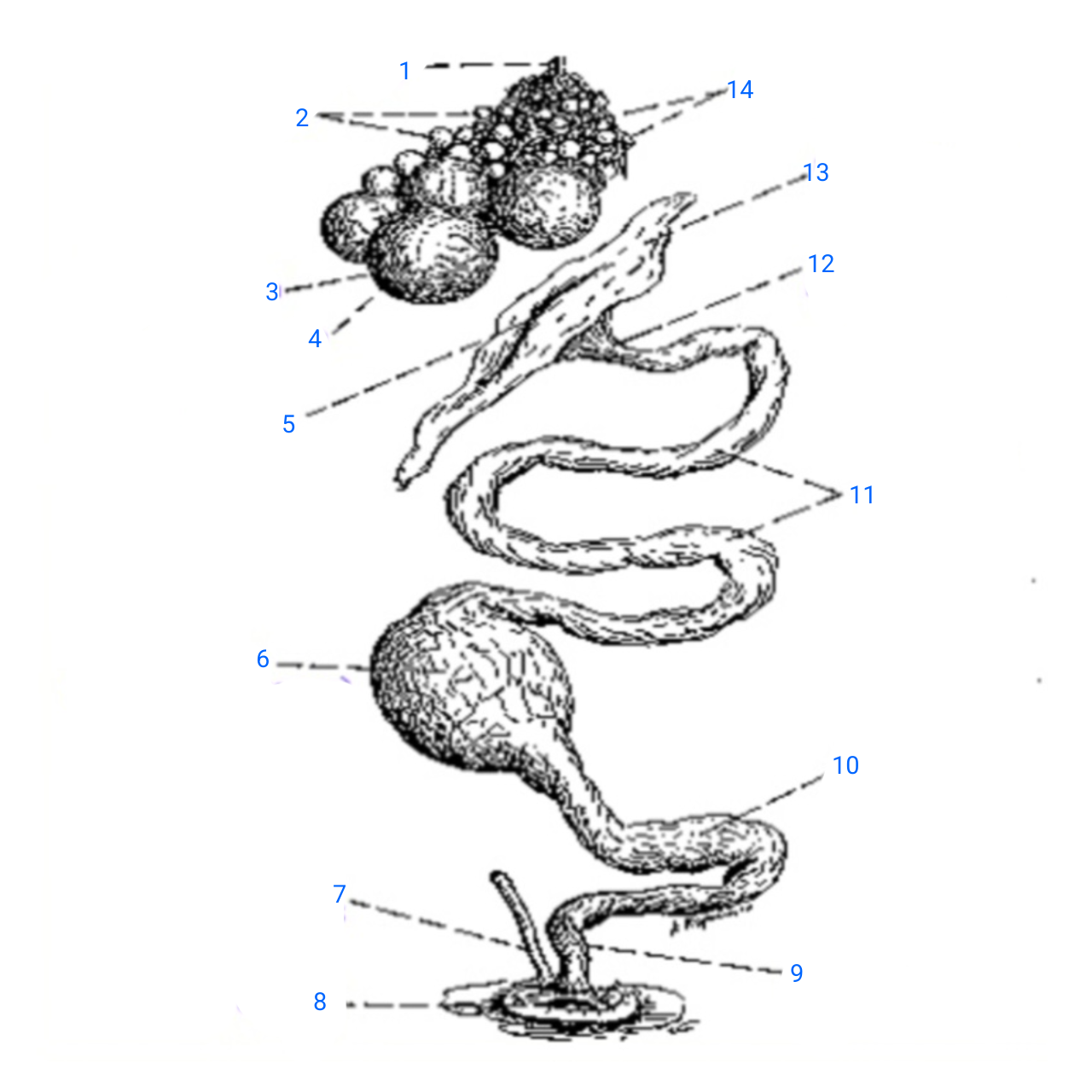
uterus
10
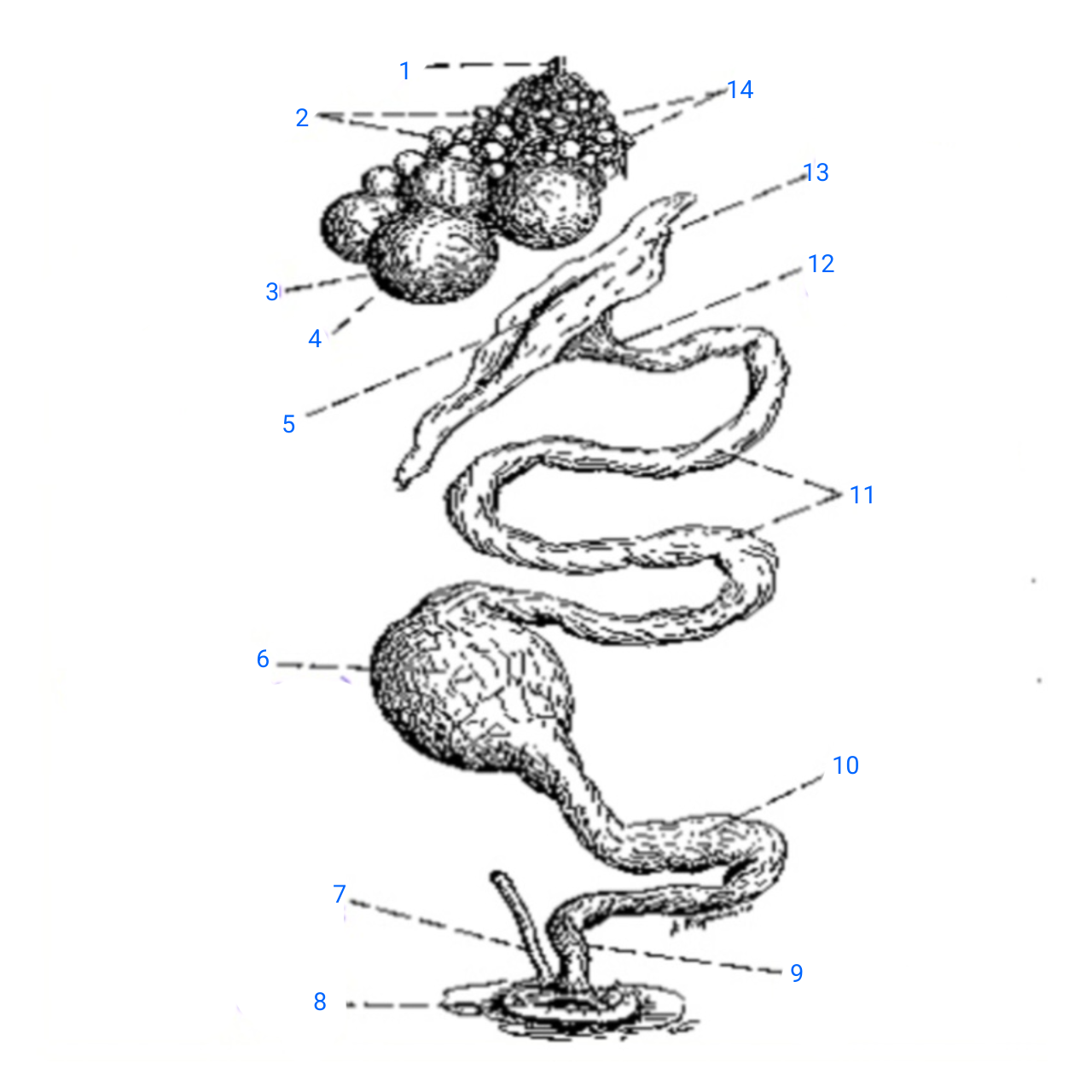
albumen secreting region
11
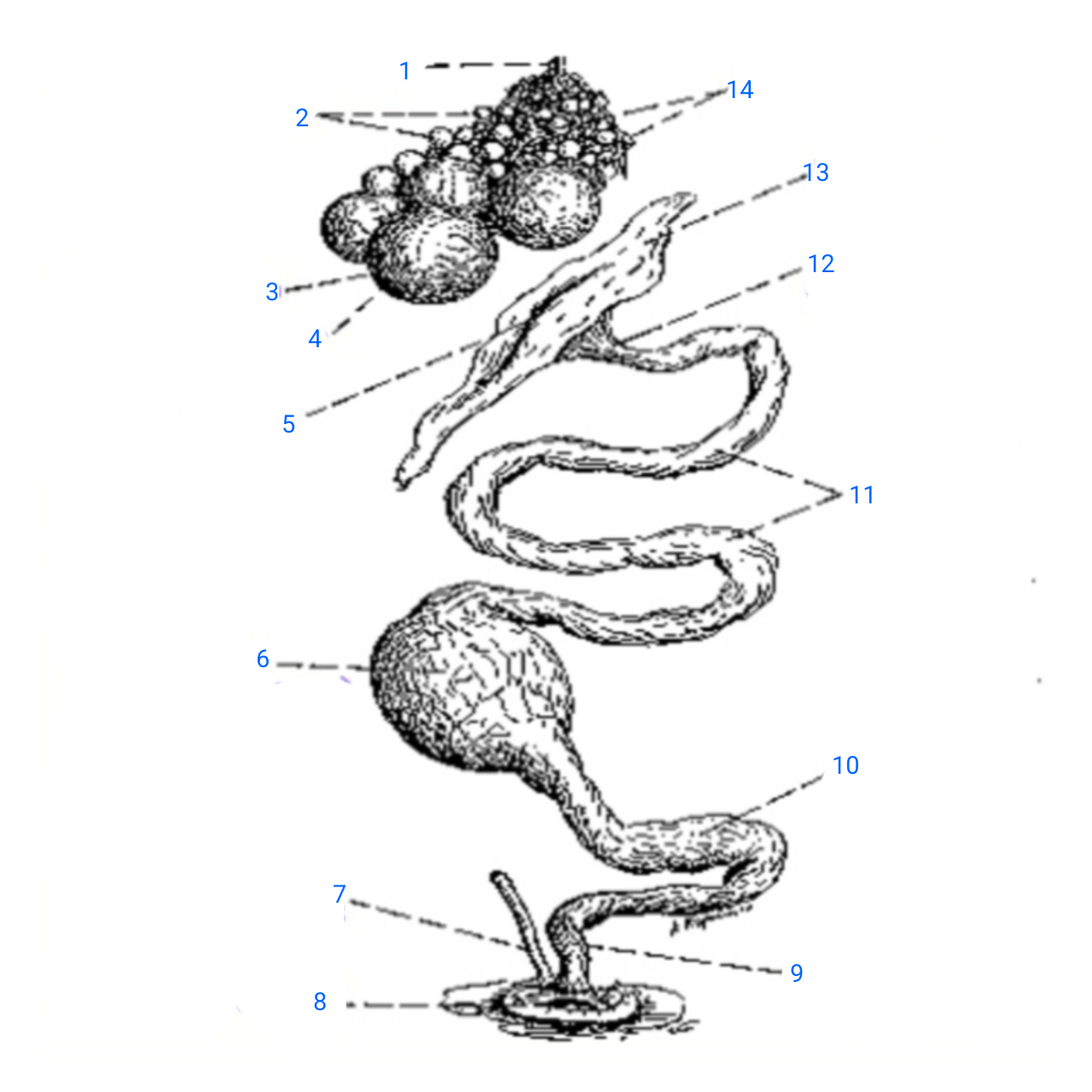
neck of infundibulum
12
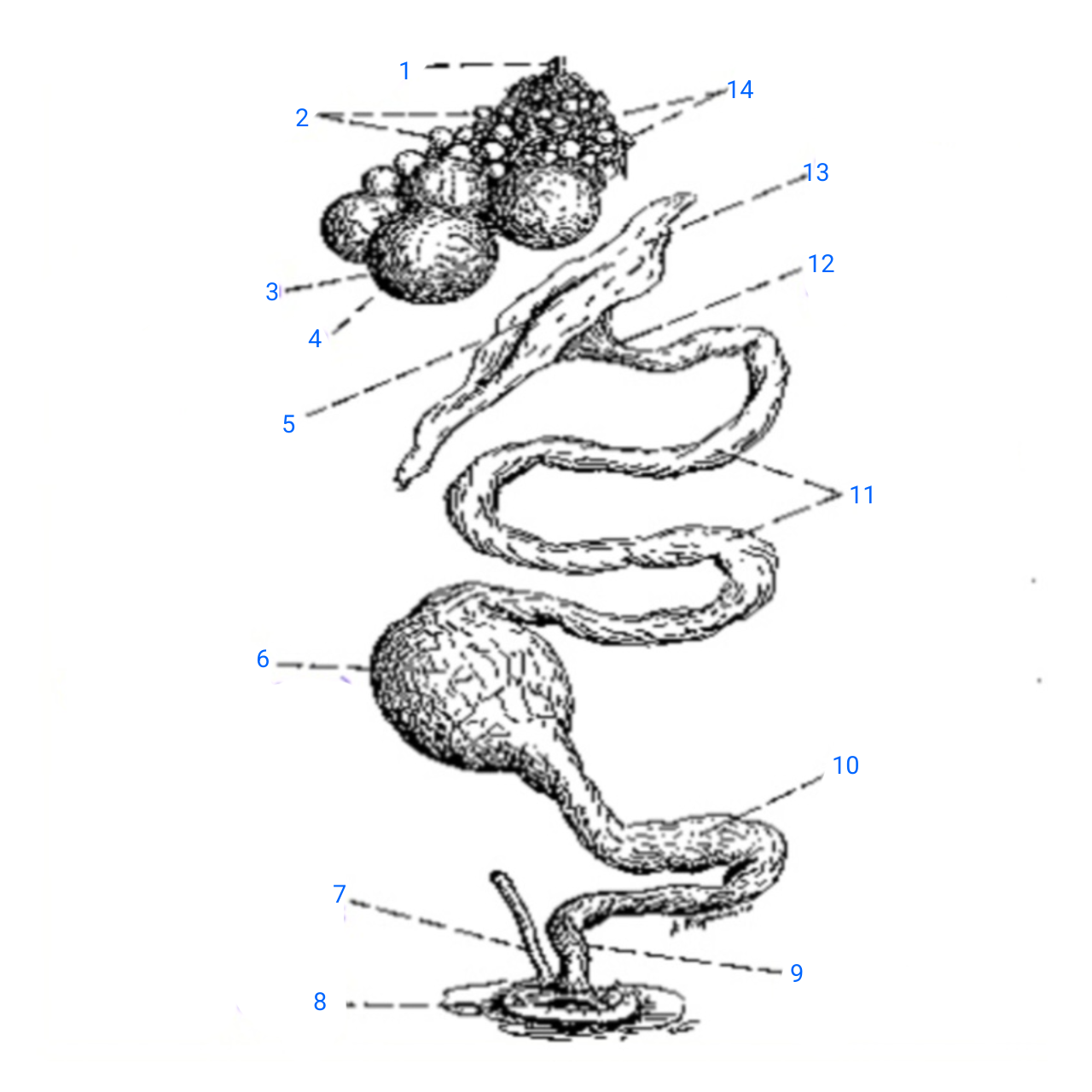
infundibulum
13
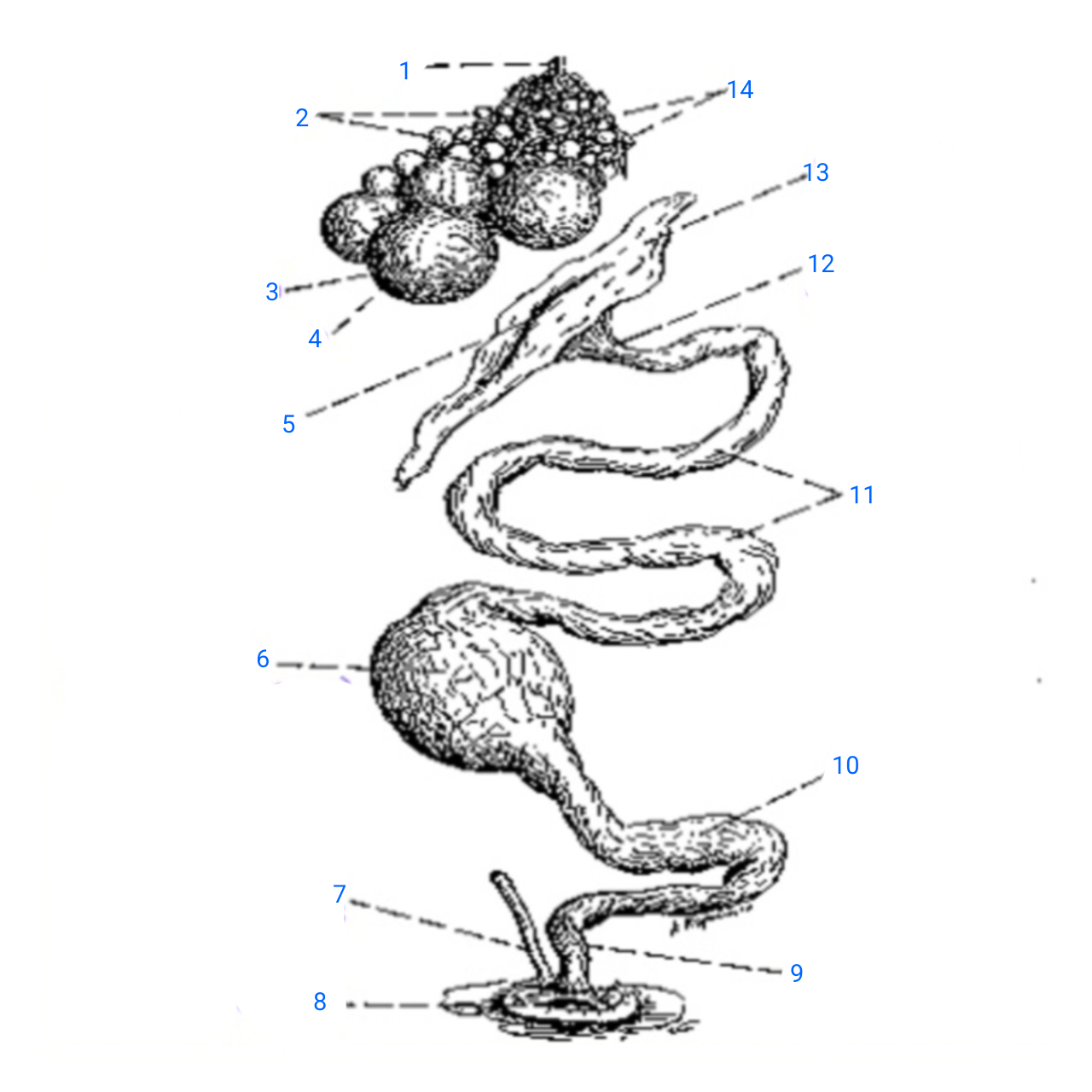
empty follicles
14
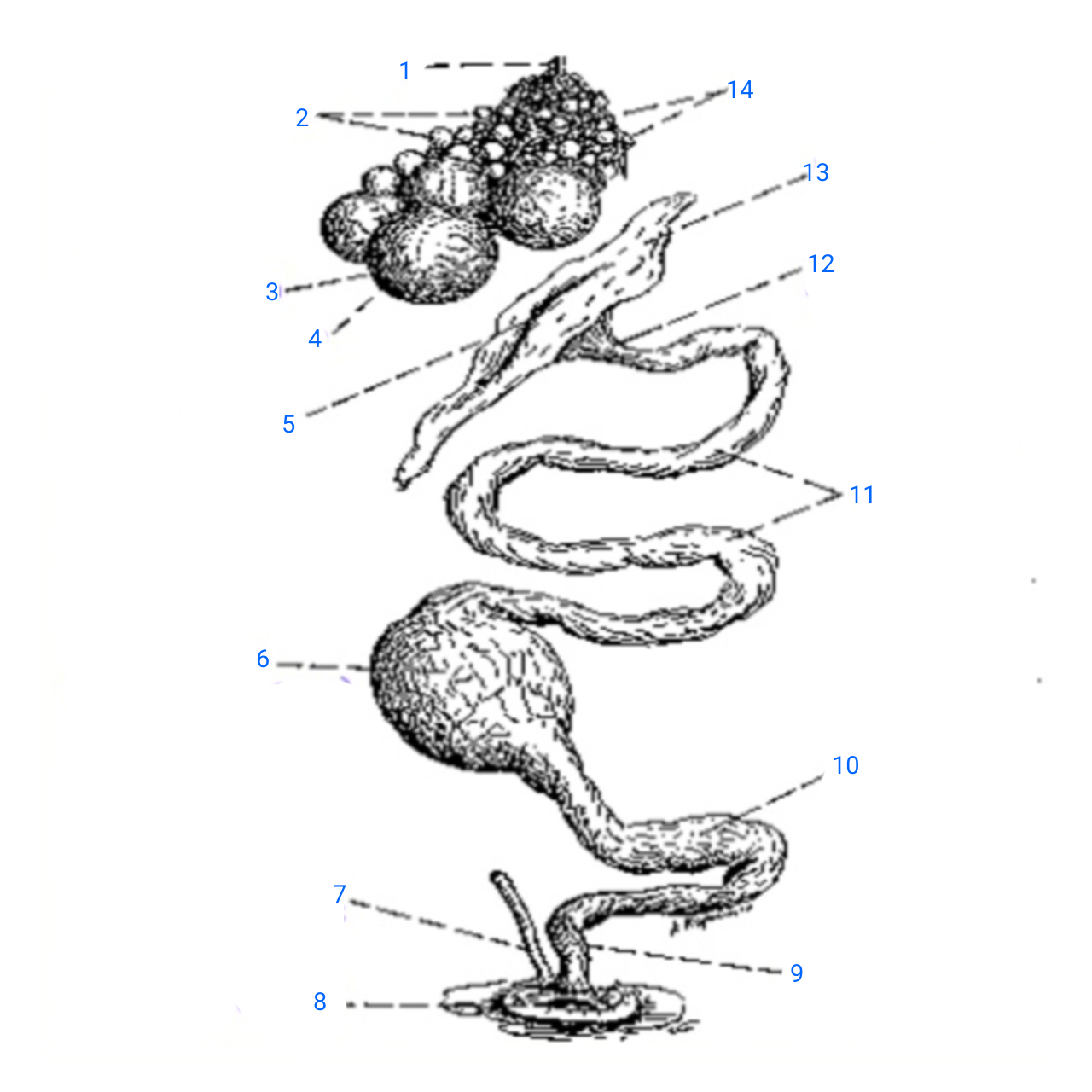
left pair (ovary and oviduct)
develops and functional in all species of birds
kiwis
both the left and right ovaries develop and only the left oviduct develops
left ovary
contains follicles of various sizes and developmental stages
quiescent primordial follicles
pre-hierarchical growing follicles
large yolk filled follicles
developmental stages in the left ovary includes
3 days
growth of the ovary takes how many days to get from 3 to 5 mm
2 days
growth of the ovary takes how many days to get from 5 to8 mm
engulfs yolk
reservoir for spermatozoa
fertilization
function of the infundibulum
9 cm
length of infundibulum
18 mins
time spent in the infundibulum
albumen
function of magnum
40%
percentage of albumen added by the magnum
2 hrs and 54 mins
time spent in the magnum
33 cm
length of the magnum
10 cm
lenght of isthmus
1hr and 15 mins
time spent in the isthmus
inner and outer shell membrane
function of isthmus
10-12 cm
uterus lenght
20 hrs and 40 mins
time spent in the uterus
shell (CaCo3)
function of uterus
47%
percentage of calcium from the chicken's bone
12 cm
length of the vagina
cuticle
function of the vagina
74 cm
total length of the poultry reproductive system
25-26 hrs
total hours spent in the poultry reproductive system
primary follicle
1
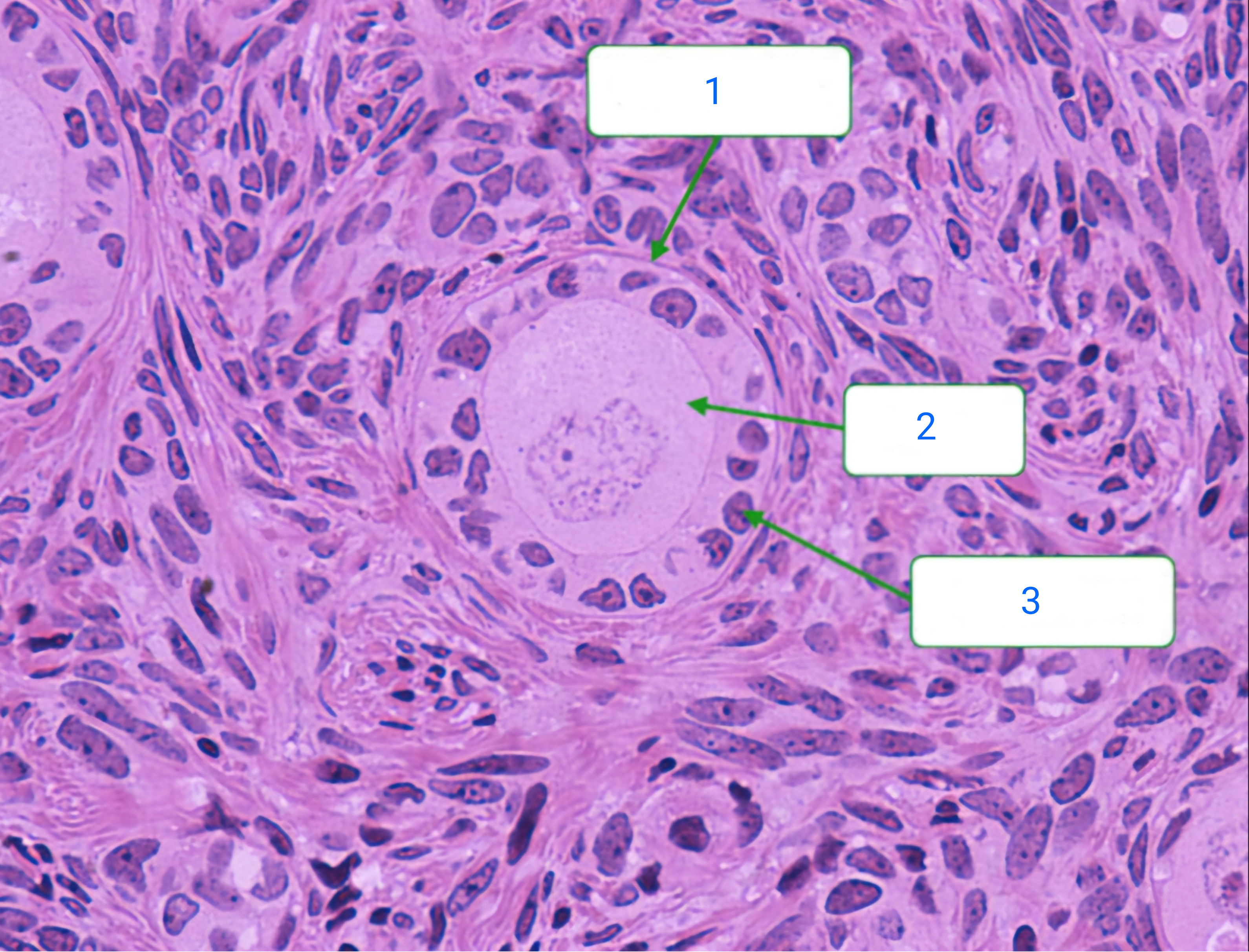
oocyte
2
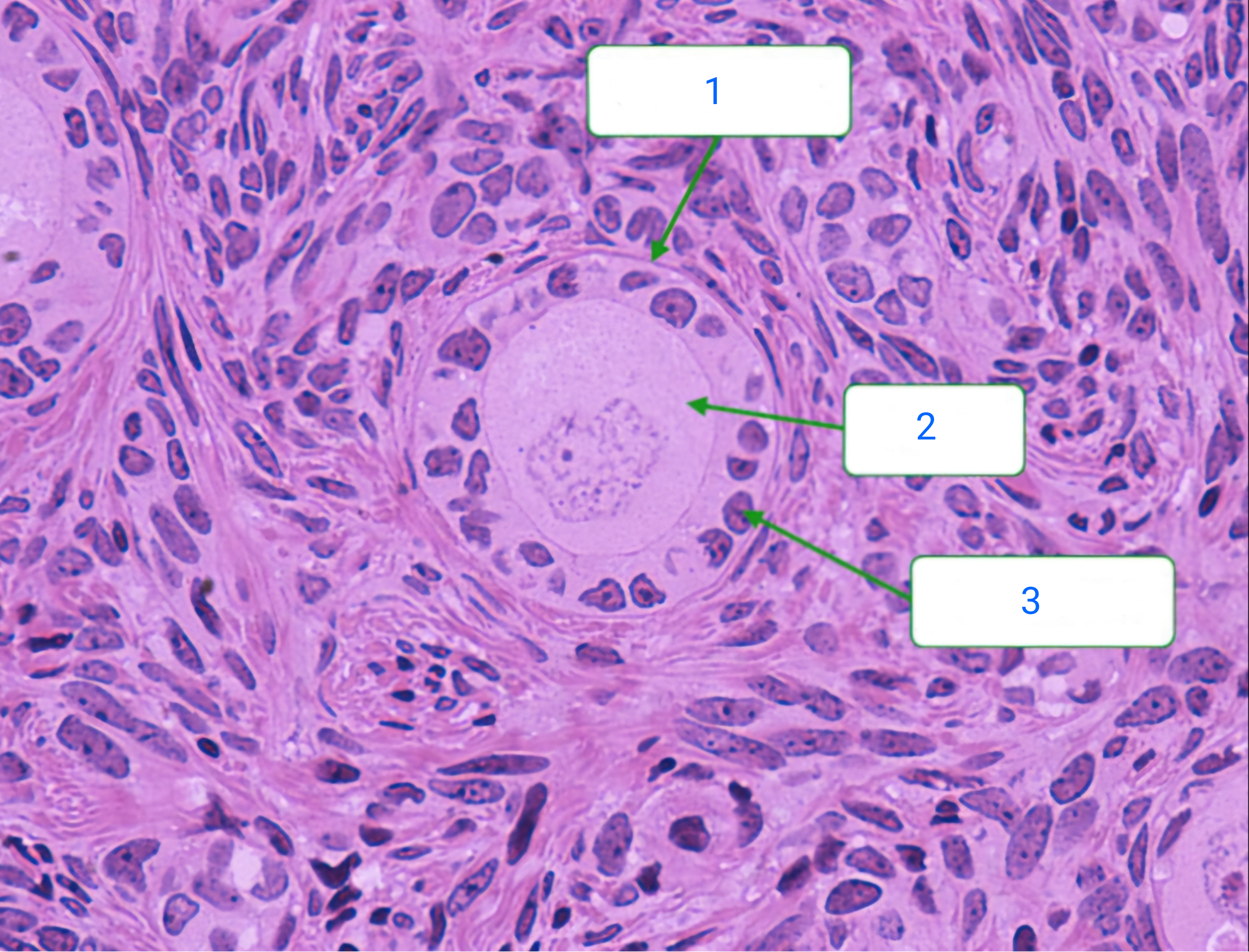
follicular cell
3
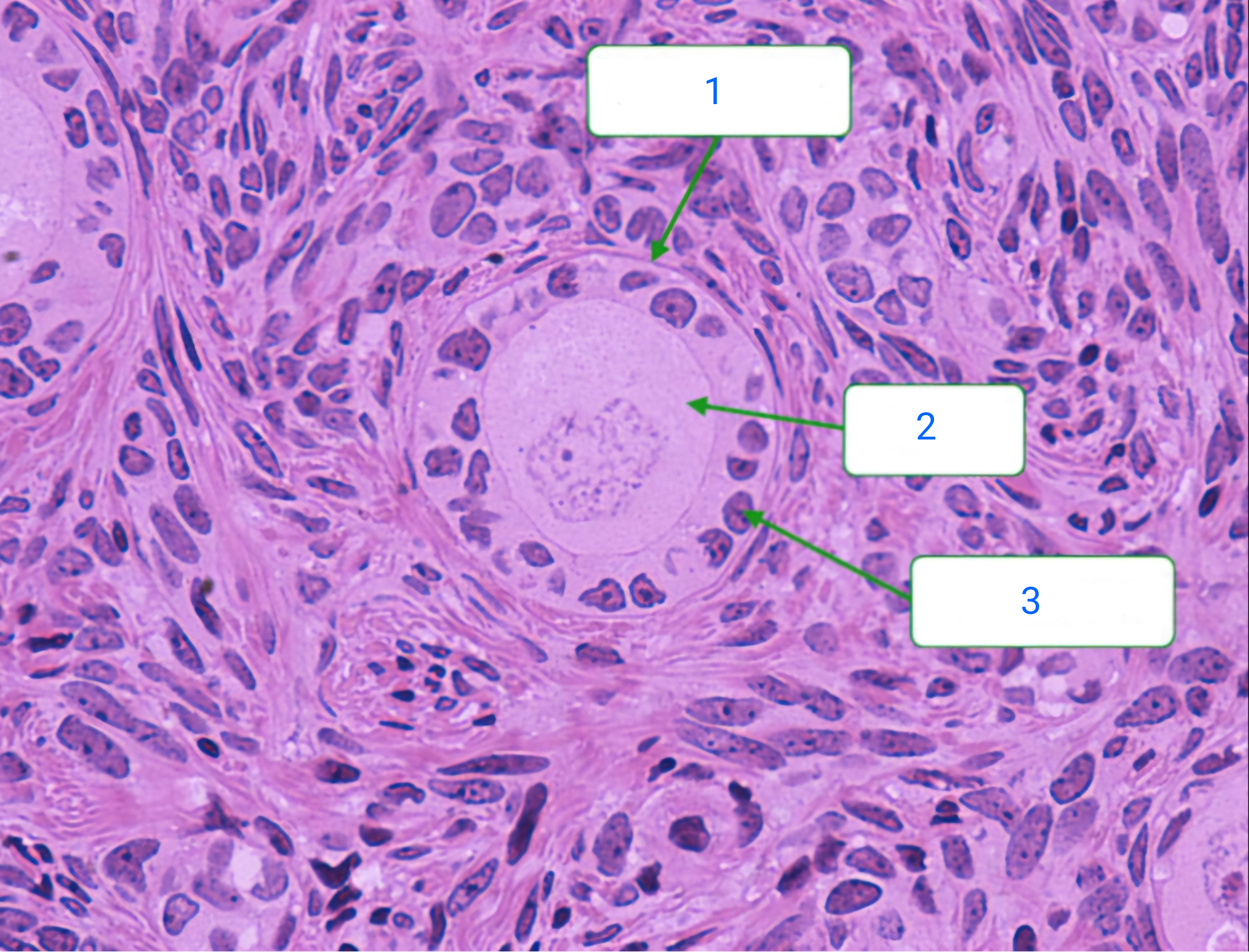
primordial follicle
These follicles consist of oocytes surrounded by a single layer of squamous follicular cells. The follicles remain in the process of the first meiotic division.
early primary follicle
first apparent histological stage, consists of a central oocyte surrounded by a single layer of follicular cells which have become cuboidal. The zona pellucida is a thin band of glycoproteins that separates the oocyte and follicular cells.
late primary follicle
the follicular cells proliferate into a stratified epithelium known as the zona granulosa
oocyte
1
antrum
2
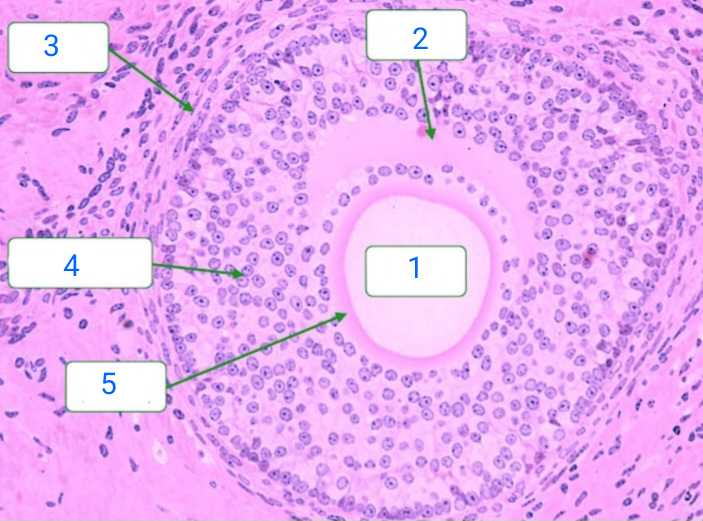
theca interna
3
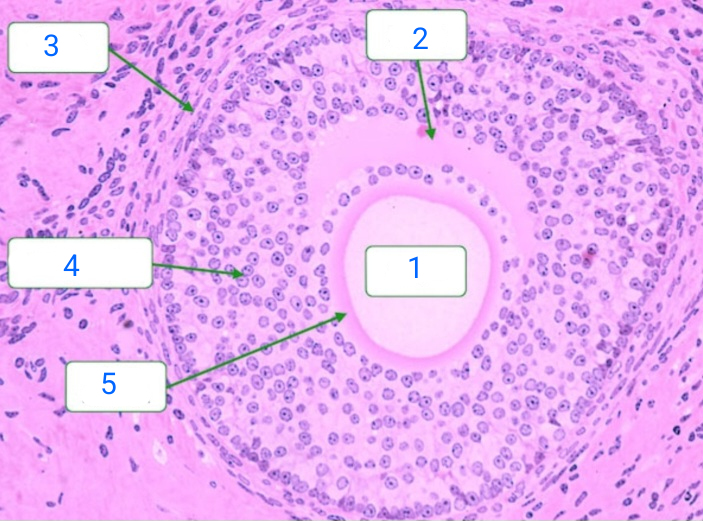
zona granulosa
4
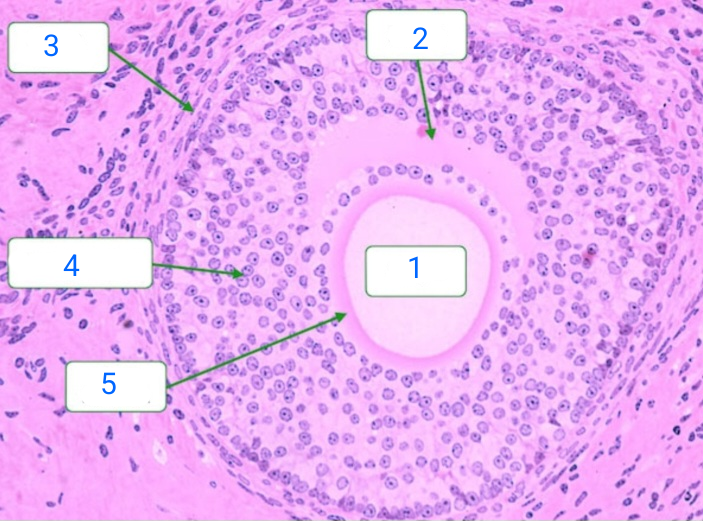
zona pellucida
5
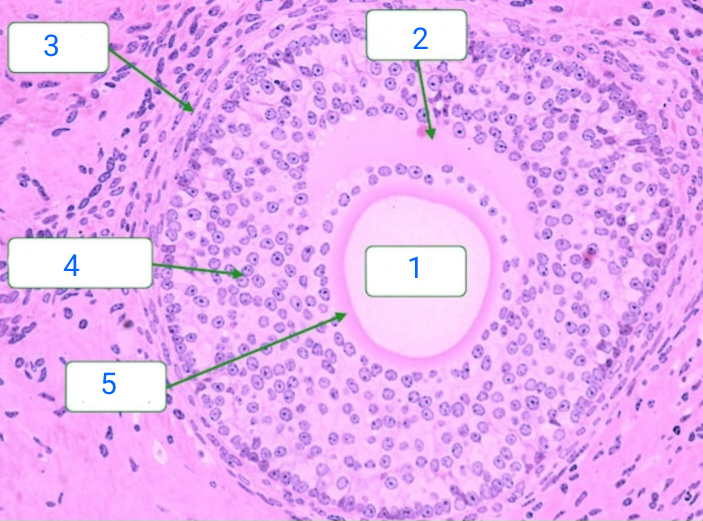
secondary follicle
has appearance of a follicular antrum within the granulosa layer, and the antrum contains fluid which is rich in hyaluronan and proteoglycans.
graafian follicle
after the first meiotic division has completed but before ovulation. The oocyte is now a 2N haploid. The follicle is characterized by a large follicular antrum that makes up most of the follicle.
The secondary oocyte, having undergone the first meiotic division, is located eccentrically. It is surrounded by the zona pellucida and a layer of several cells known as the corona radiata.
oocyte
enveloped by zona pellucida and corona radiata at ovulation
oogonia
gives rise to primary oocytes by mitosis within the mpembryo
spermatozoa
propelled from vagina to uterine tube by contraction of female gential tract
spermatozoa
gives rise to primary spermatocytes by mitosis repetitively following ouberty
meiosis 1 - secondary spermatocytes
primary spermatocytes undergo ___ to produce ____
meiosis 2 - spermatids - spermatozoa
secondary spermatocytes complete ____ producing ____ that undergo transformation intro ____
capacitation
removal of surface protein that would impede contact with an oocyte
capacitation
sperm cell’s need to uncover receptors that may recognize the chemicals in the female reproductive tract that in turn initiate changes in both motility in the form of hyperactivation as well as the morphological changes
hyperactivation and morphological
Capacitation is the sperm cell’s need to uncover receptors that may recognize the chemicals in the female reproductive tract that in turn initiate changes in both motility in the form of _____ as well as the ______ changes
fertilization
union of a haploid oocyte and a haploid spermatozoon producing a diploid zygote
gamete fusion
fertilization begins at what
start of cleavage
fertilization ends with the?
uterine tube
fusion of a spermatozoon and oocyte takes place in the?
glycoprotein
the spermatozoon MUST bind to a specific __
acrosomal reaction
enzyme that denature the zona pellucida, allowing the sperm to penetrate the barrier
12
mitosis begins ___ hrs after sperm fusion
cleavage
a series of cell division which immediately after fertilization, follow upon one another in close succession
yolk (deutoplasm)
cleavage differ in various groups of animals due to varying amount of ______ stored in the egg cells
active protoplasm
cleavage division is carried out by the _____ of the cell
non living and inert
food material in the cytoplasm of an egg cell is
deutoplasm
plays no part in mitosis except it exerts a retarding effect by the mechanical impediment it offers to the process
amphioxus
amount of yolk is meager (small) and fairly distributed throughout the cytoplasm. Undergoes an unhindered mitosis
isolecithal (homolecithal)
undergoes a type of cleavage which is essentially unmodified mitosis
unmodified mitosis
isolecithal egg undergoes a type of cleavage which is essentially ____
telolecithal
in amphibia]ovum contains considerable amount of yolk and accumulation of yolk at one pole has crowded the nucleus and the active cytoplasm of the ovum toward the opposite pole
vegetative pole
region of egg where yolk is accumulated
animal pole
opposite region where nucleus and most of active cytoplasm is located
telolecithal
type of egg that has a yolk is much greater than in amphibian eggs. Cleavage the same as in egg of amphibia but the mass of yolk is so great the yolk is not divided.
discoidal cleavage
The process of segmentation is limited to the small disk of protoplasm lying on the surface of the yolk at the animal pole.
partial meroblastic cleavage
blastomeres
the cells formed in the process of segmentation where they are completely separated or partially separated
holoblastic cleavage
process of segmentation where they are completely separated
meroblastic cleavage
process of segmentation where they are partially separated
fertilization and cleavage
earliest stages of the chick embryo which takes place before the egg is laid
open cells
not completely enclosed by their own cell membrane but are partially continuous with the yolk
large amount of yolk
the presence of ____ has resulted in specific adaptations to development, especially in the young embryo
koller’s sickle
precursor of the primitive streak
cleavage
refers to the initial series of mitotic divisions by which the large zygote is fractionated into numerous “normal size” cells
blastomere
each daughter cell of the cleavage process is termed a
zygote
cleavage begins with a ___
eight blastomeres
the first___ are undifferentiated and have identical potential in mammals
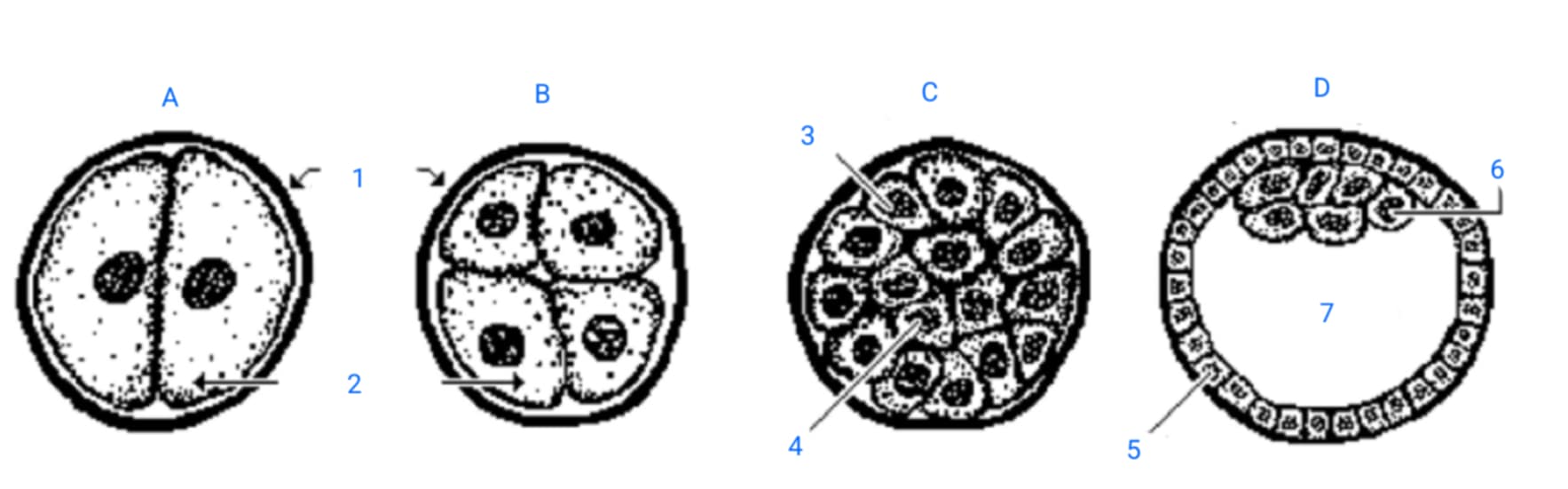
first cleavage division
A

second cleavage division
B
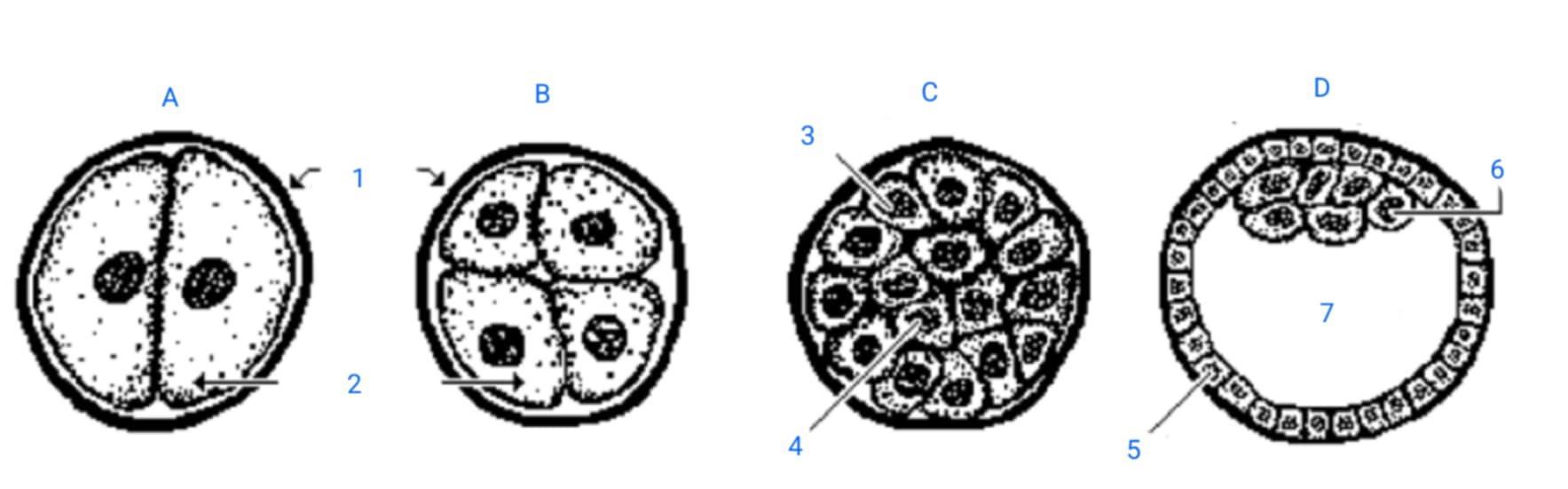
morula
C
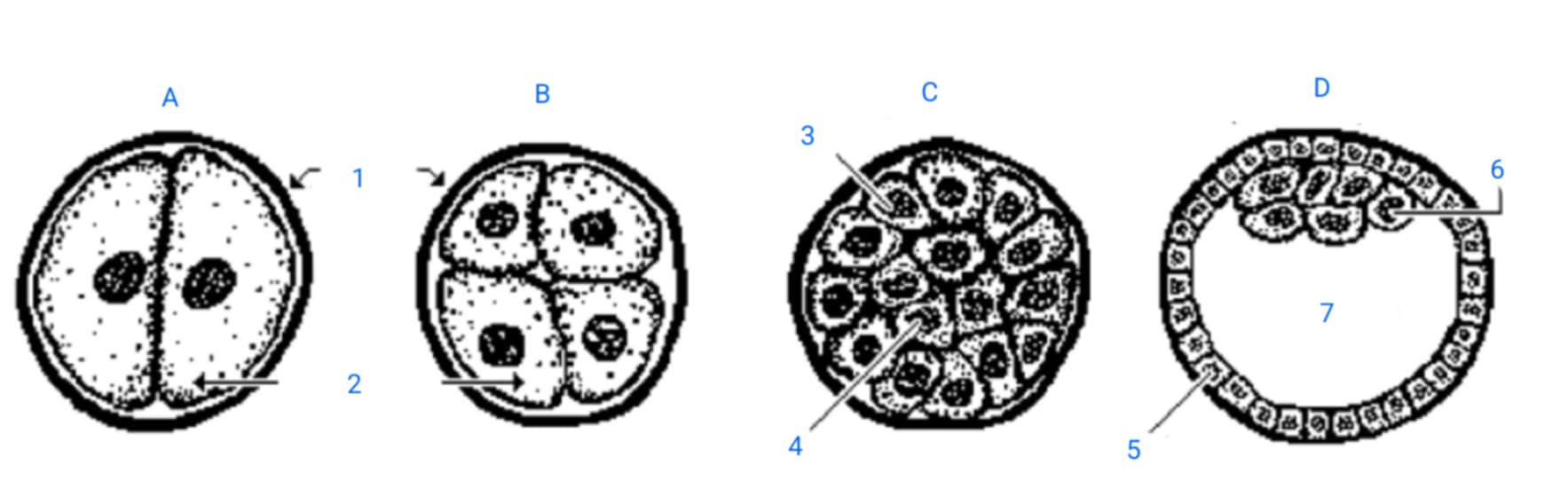
blastula
D
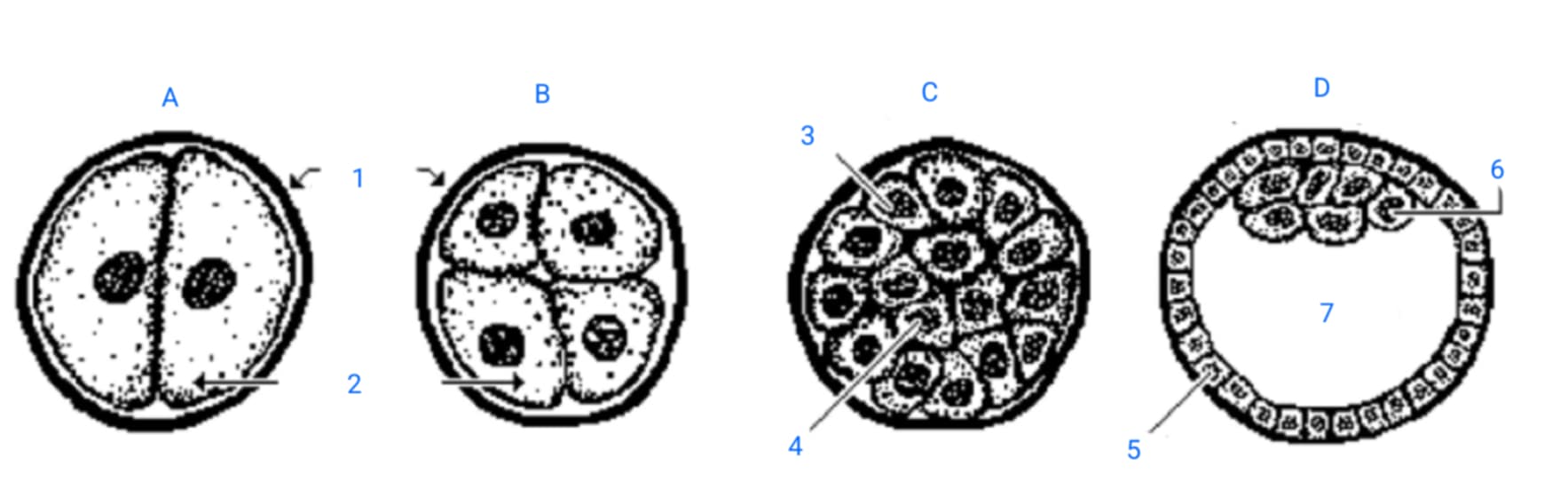
zona pellucida
1
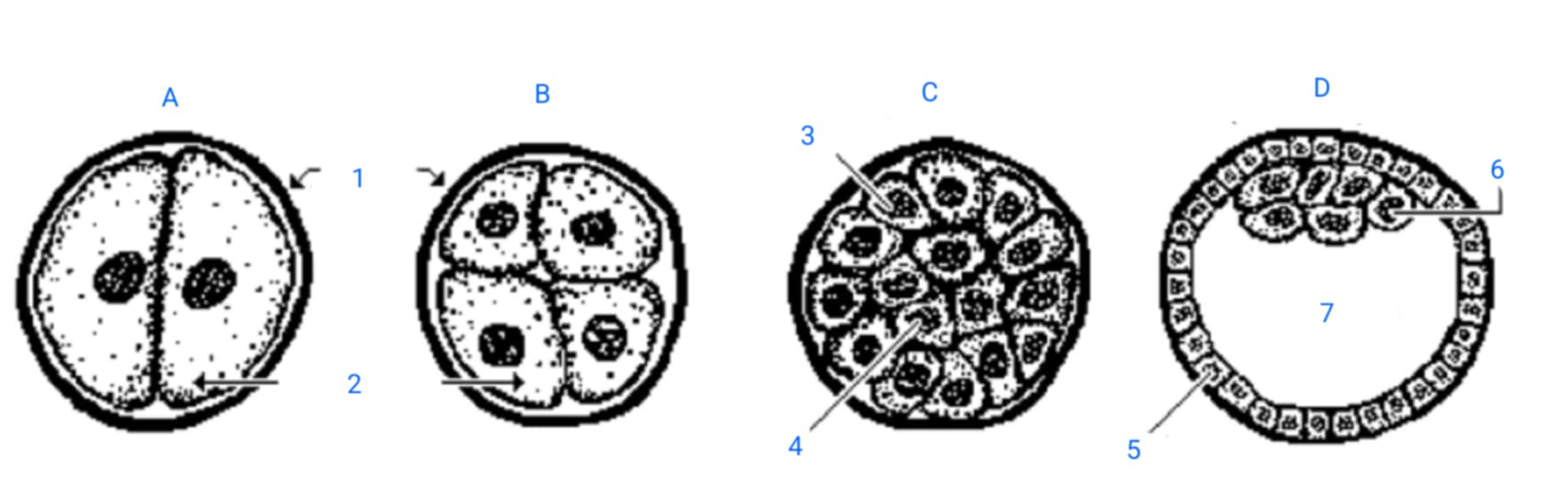
blastomeres
2
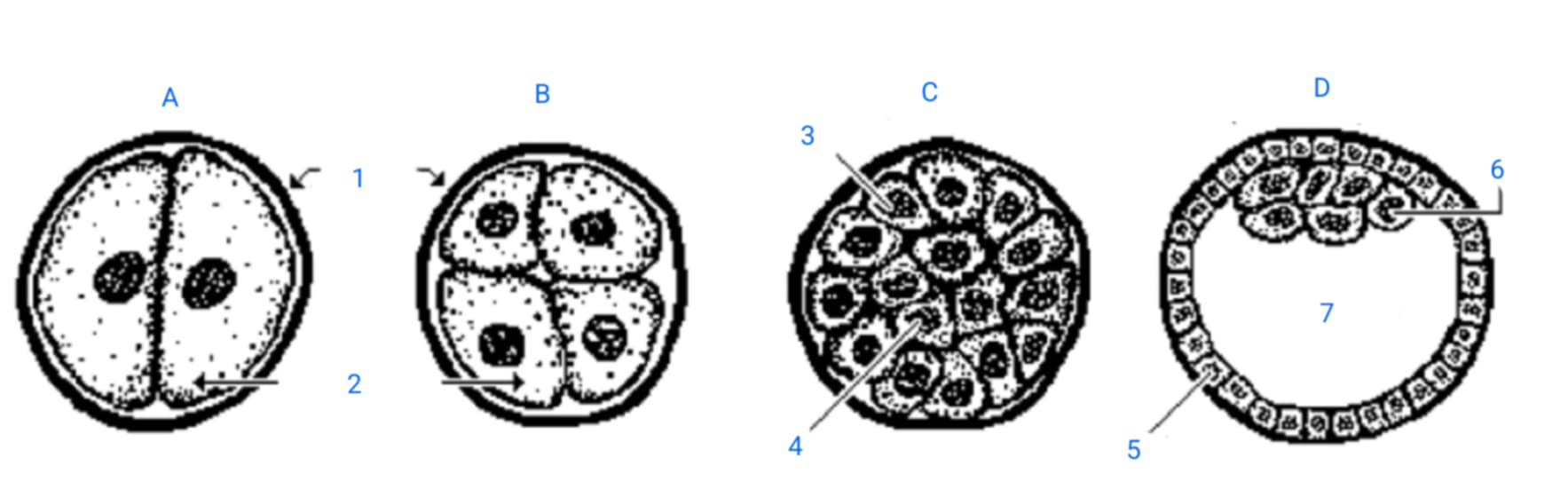
outer blastomeres
3
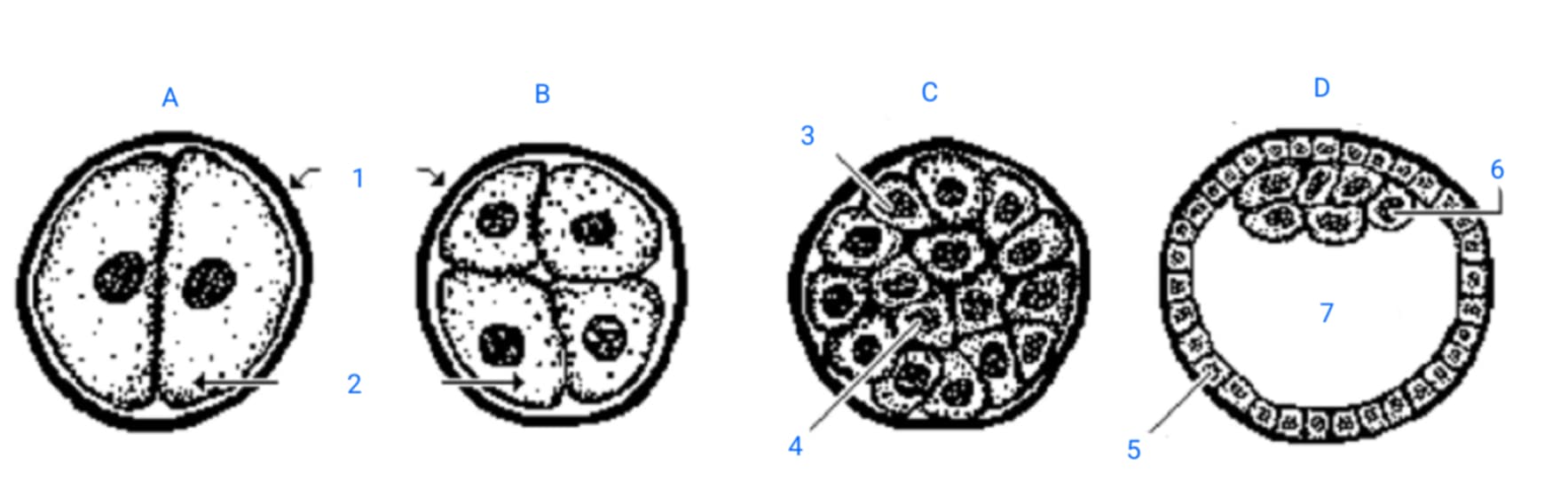
inner blastomeres
4
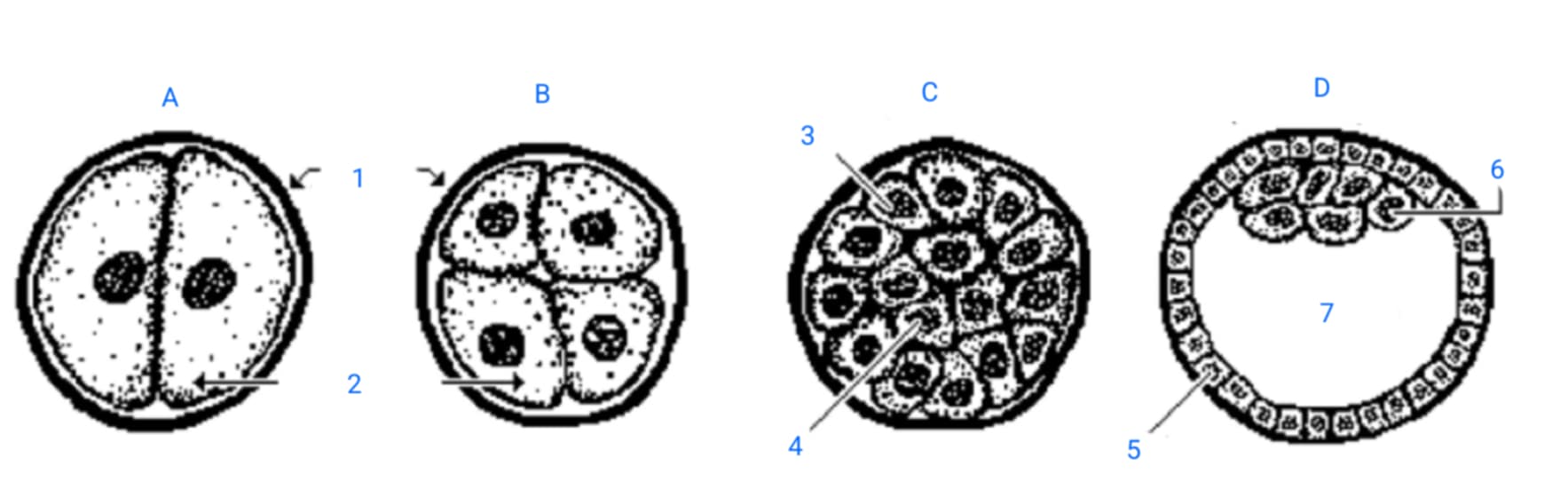
trophoblasts
5