SCIOLY - by someone better
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
get out
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
what is the big bang theory?
Is the theory that the universe started at a singular dense and hot point that started rapidly expanding, and when it cooled down it started creating atoms, elements, and finally celestial bodies that make up the universe.
what is the history of the big bang theory?
A belgian physict called Lemaitre first suggested this theory. Fred Hoyle then came up with the name “big bang theory.” Edwin Hubble was the first to come with evidence to support this theory, including red shift and universe expansion.
Evidence 1: Universe Expansion (Big bang theory)
Hubble discovered that everything was moving away from each other in different directions thru observations.
Evidence 2: Red shift (Big bang theory)
The farther things are farther the waves are percieved causing us to percieve them at a lower frequency. This is called the doppler shift. For evidence it was used on light waves. If light were stretched when reaching us (moving farther) they seem red while if light waves are compressed (closer together) when reaching us (moving closer) they seem blue. The universes seem red.
Evidence 3: Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (Big bang theory)
In the atmosphere, CMB’s microwave static was found scattered evenly around the universe and cold. This matches the exact characteristics of what the big bang remnant should be like.
Evidence 4: Hydrogen and Helium (Big bang theory)
The universe mainly contains hydrogen and helium which are both the lightest elements in the periodic table. These elements were found within the microwave energy remnants. The big bang theory was only able to create light elements because of fast it expanded and cooled.
Evidence 5: Oldest star age (Big bang theory)
The universe is old enough to form really old stars which are consistent of the BBT because of how old it is.
How was the Solar System specifically formed?
SUN: (solar nebula) clouds of dust/gas collapsed while the matter within it began to move in a giant circle
Smaller clumps of dust/gas collapsed to form planets, minor planets, moons, comets, and asteroids
How was the Milky Way galaxy formed?
The Big Bang Theory (dense clouds of gas/dust either collapsed or stuck together)
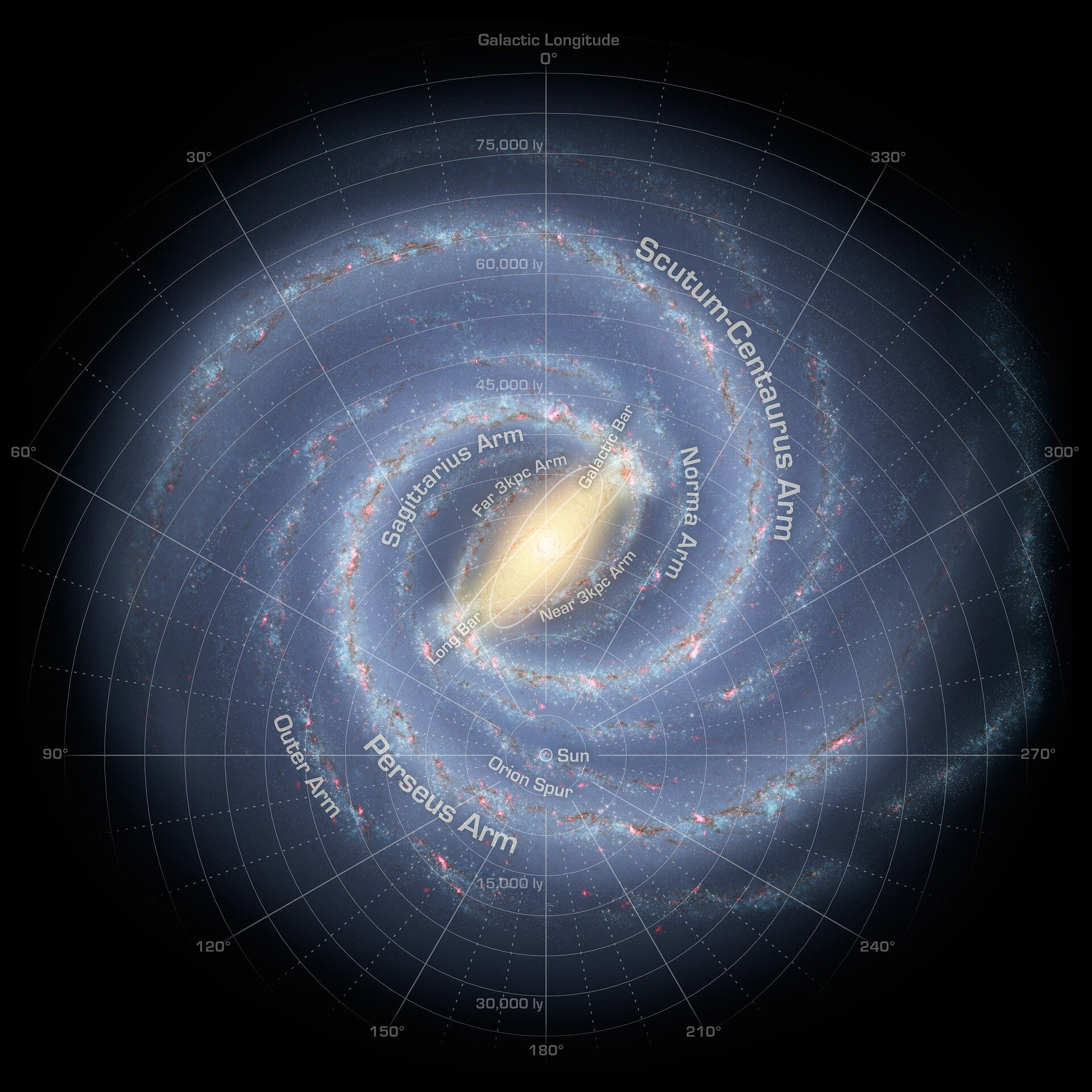
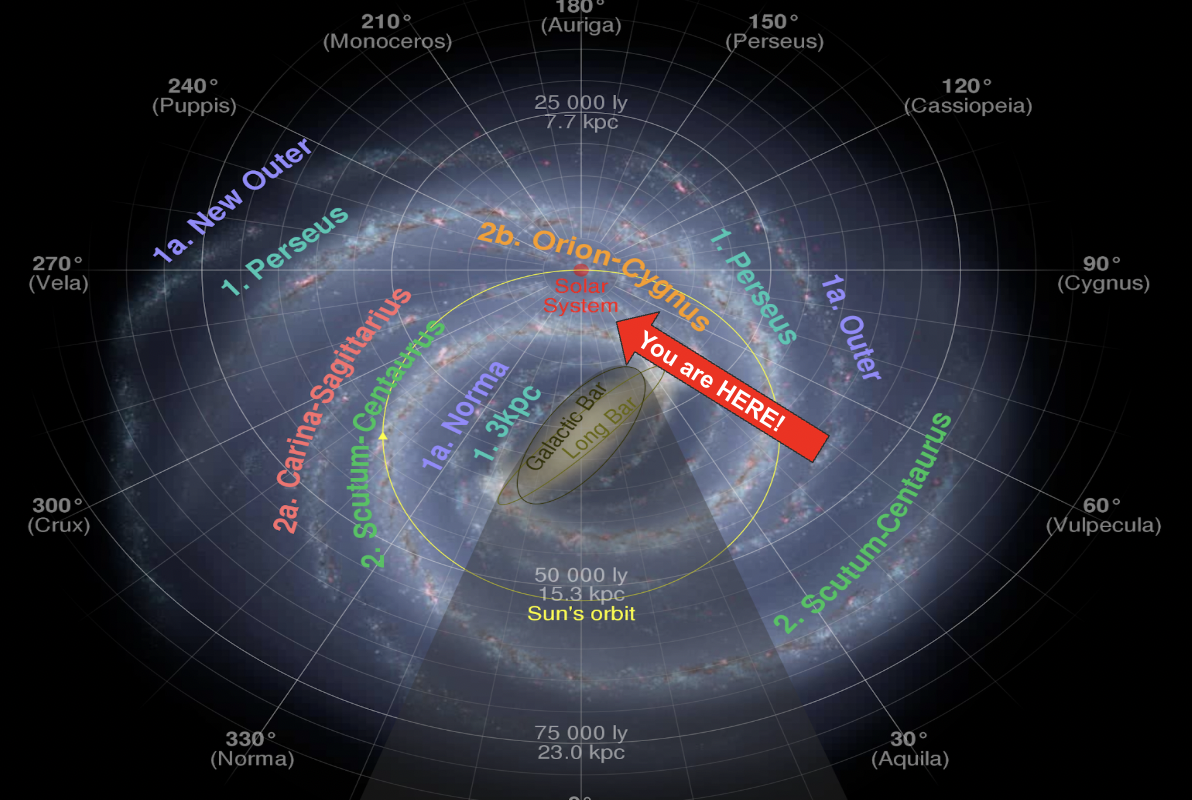
Where is the solar system located in the milky way galaxy?
(yellow circle) the solar system is located on the outer arm of the galaxy around the galactic bar
What is the structure of the milky way galaxy?
The milky way galaxy is a long spiral shaped galaxy. In the center it has a bulge containing disk stars. It has long spiral arms and it has an overall haze appearance (where name came from). It also contains double stars, gases, and dust.
What is the order of the planets in the solar system?
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune (My Very Educated Mother Just Served Nachos/Nectarines/Whatever)
What did Sir Isaac Newton discover?
The three law’s of motion and the universal law of gravitation
Newton’s First Law of Inertia
An object at rest tends to stays at rest while an object in motion tends to stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
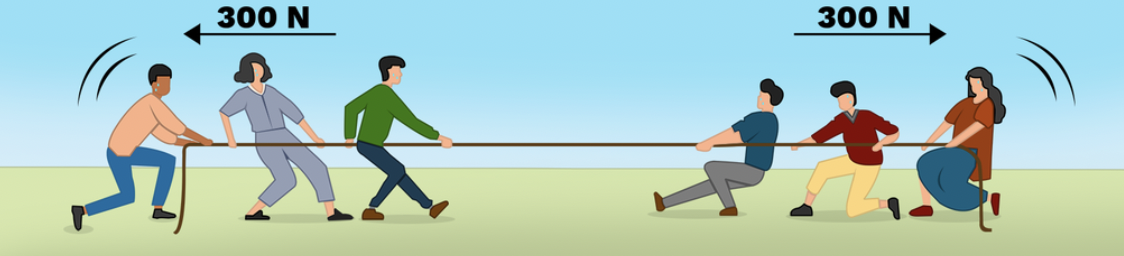
Balanced forces
Forces that are equal and opposite.
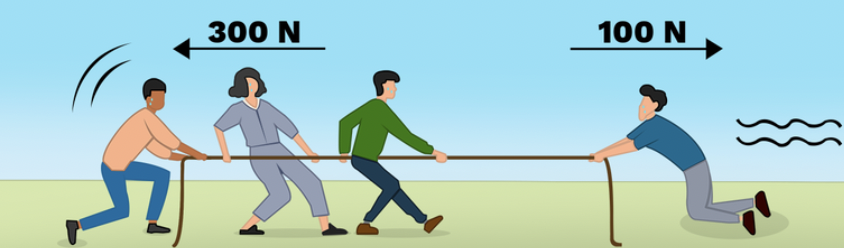
Unbalanced Forces
Forces that are NOT equal and/or opposite. It causes the motion of an object to change.
Newton’s Second Law of Force and Acceleration
Force is directly proportional to Acceleration, while mass is inversely proportional to acceleration. (Force = Mass x Acceleration)
Force
Push or pulll
Acceleration
A change in velocity per unit of time.
Mass
How much matter an object takes.
Newton’s 3rd Law of Action-Reaction
For every action there’s an equal and opposite reaction.
Action
Movement of an object
Reaction
reponse to an action
Gravity
Universal force of attraction acting between all matter.
What are the 3 major concepts of gravity?
1) Gravity attracts all objects towards each other 2) If mass increases force increases 3) If distance increases force decreases
What is the 1st concept of gravity all about?
The first concept is all about how gravity pulls all objects towards it source. Thats the reason planets are round, in there core thats where the planets mass and gravity is. All objects with mass are pulled toward the source.
What is the second concept of gravity about?
The second concept of gravity is about if mass increases force also increases. Objects with a higher mass have a higher gravitational force . Objects with lower mass have a lower gravitational force.
What is the third concept of gravity about?
The third concept states if distance increases force decreases. This means the father a planet is away from the sun the less pull (force) it has towards the sun similarly the closer a plant is to the sun the more pull (force) there is gonna be.
What is Keplers 1st law of Ellipses?
This 1st law is all about elliptical orbits. Other planets circle the sun, moving in elliptical orbits with the sun as the primary focus of the ellipse.
What is Keplers 2nd law of Equal Areas about?
This 2nd law is all about how to sun interacts with other planets. Scientists imagine a line sweeps out from the sun across the orbit surface and it sections the orbit into equal parts in equal times, this means that planets move faster when they are closer to the sun and slower when they are father away from the sun.
What is Keplers 3rd law of Harmonies about?
This 3rd law is all about the time and distance it takes planets to orbit around the sun. For planets it takes a long time for them to orbit around the sun the time of there orbit is called orbital period and it is related to the planets distance away from the sun. So in all the planets distance for the sun adds time to its orbit around the sun.