Alternating Current [INCOMPLETE]
1/20
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What are the two conditions required for a current to be an alternating current?
Amplitude is constant
Alternate half cycle is positive and negative
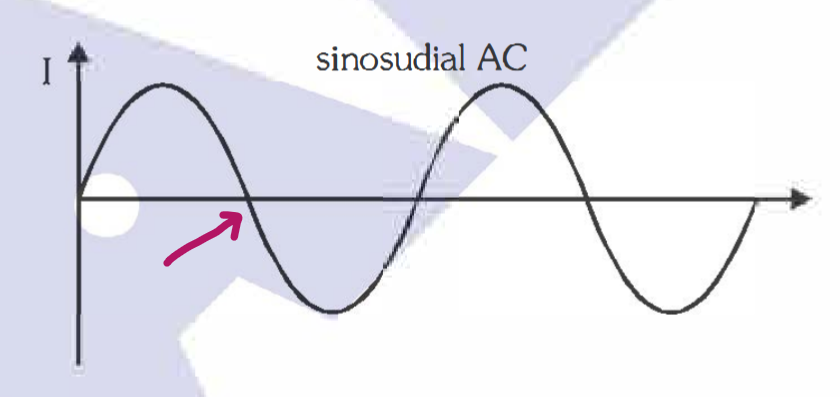
If I=I_0\sin(\omega t ) then what is the value of the x axis at this point?
\dfrac{\pi}{\omega}
What is average emf for 1 time period?
0
What is the formula for average emf in half a time period? (there are 3)
\varepsilon_{\text{avg}}=\dfrac{\text{area under}\ \varepsilon\text{-}t\ \text{curve}}{\Delta t}=\dfrac{\int \varepsilon\ dt}{\int dt}=\dfrac{2\varepsilon_0}{\pi}
where \varepsilon_0 is the peak voltage.
What is the formula for average current in half a time period? (there are 3)
I_{\text{avg}}=\dfrac{\text{area under}\ I\text{-}t\ \text{curve}}{\Delta t}=\dfrac{\int I\ dt}{\int dt}=\dfrac{2I_0}{\pi}
where I_0 is the peak current.
What is the formula for rms value of current?
I_{rms}=\sqrt{<I²>}=\sqrt{\dfrac{\int I^2\ dt}{\int dt}}=\dfrac{I_0}{\sqrt{2}} (the last one is for sinusodial current)
for two currents:
I_{rms}=\sqrt{<(I_1+I_2)²>}=\dfrac{\sqrt{\text{sum of squares of peaks}}}{\sqrt{2}}
What is the formula for peak value of current when there are multiple currents for which you know the peaks?
I_{\text{peak}}=\sqrt{\text{sum of squares of peaks}}
What is the formula for rms value of voltage?
V_{rms}=\sqrt{<V²>}=\sqrt{\dfrac{\int V^2\ dt}{\int dt}}=\dfrac{V_0}{\sqrt{2}} last one is for sinusodial emf)
AC-measuring instruments always measure ____ (peak, rms) value of current/voltage. Why?
AC-measuring instruments always measure rms value of current/voltage, because they measure the heating effects of it.
In a purely resistive circuit, what is the phase difference between current and voltage? Which one leads the other?
0, neither leads.
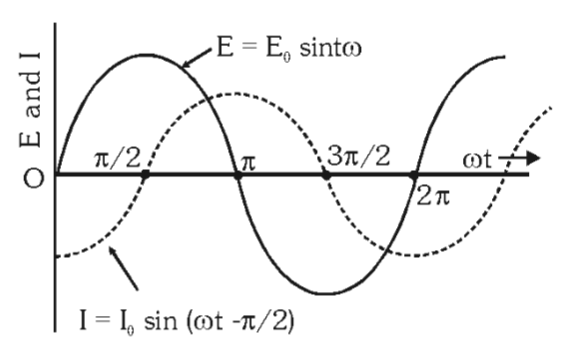
In a purely inductive circuit, what is the phase difference between current and voltage? Which one leads the other?
phase difference is \frac{\pi}2 and voltage leads current.
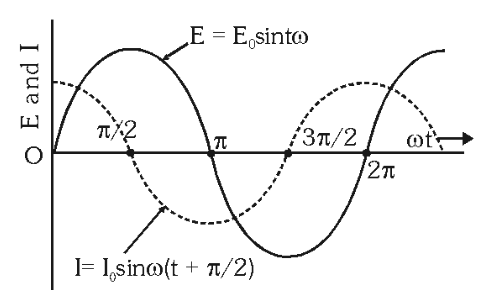
In a purely capacitive circuit, what is the phase difference between current and voltage? Which one leads the other?
phase difference is \frac{\pi}2 and current leads voltage.
What is the formula for capacitive reactance?
X_C=\dfrac{1}{\omega C}
What is the formula for inductive reactance?
X_L=\omega L
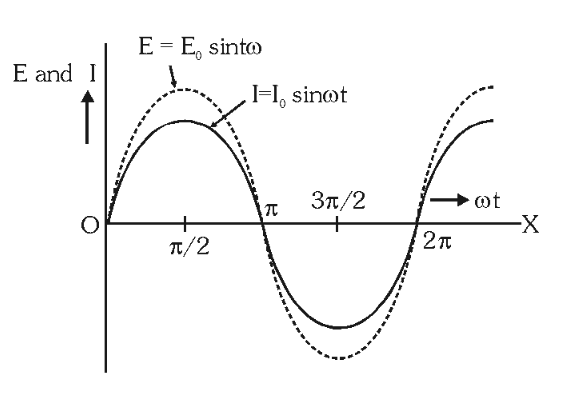
What does the graph look like for \varepsilon,I by t in a purely resistive circuit?
What does the graph look like for \varepsilon,I by t in a purely inductive circuit?
What does the graph look like for \varepsilon,I by t in a purely capacitive circuit?
When AC flows through a circuit, what is the emf induced in an inductor? Explain why it is positive or negative sign.
\varepsilon=-L\dfrac{dI}{dt}
it is negative because the emf induced is in opposite polarity to the emf applied.
What is the unit of reactive inductance and reactive capacitance?
Ohm
Which of the following is true:
X_L\propto f
X_L \propto \dfrac{1}{f}
X_L\propto f