Stomach Disorders: Hiatal Hernia and Gastritis
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
stomach, diaphragm, aging
Hiatal Hernia: Background
-Protrusion (herniation) of the upper part of the _______ through the ___________ into the thorax
-Risk Factors → obesity, _____, and weakening of musculofascial structures. Really anything that causes a loss of elasticity
GE, above, short, vagal, muscles, supine, down, pressure, reflux, LES
Type 1: Sliding Hernia (MC)
-__ junction slides _____ diaphragm with some of the stomach
-Could be due to a congenitally _____ esophagus, fibrosis or excessive _____ nerve stimulation, or weakening of the diaphragmatic ________ at the GEJ contributes
-______ position causes hernia to slide up and standing causes it to slide ______
-Exacerbated by increased intraabdominal ___________ secondary to coughing, bending, tight clothing, obesity, etc.
-Associated with ______ (diminishes resting pressure of ___)
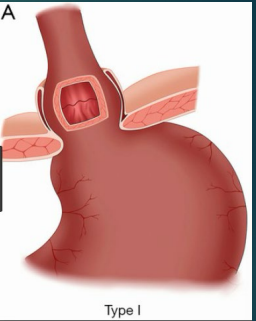
rolling, fundus, esophagus, below, reflux, ulcer, ischemia
Type II: Paraesophageal Hernia (________ hernia)
-Herniation of the gastric ______ alongside the ___________, with the GEJ remaining _____ the diaphragm
-______ is uncommon because the sphincter mechanism is intact
-Can cause congestion of mucosal blood flow leading to gastritis and ______
-Strangulation can occur, causing __________ and necrosis
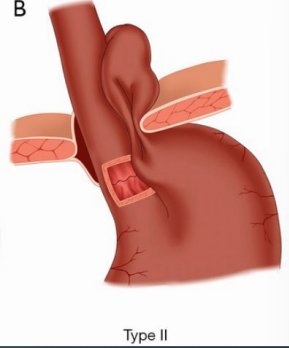
GERD, III, viscera
Hiatal Hernia: Type III and IV
-Type III → Mixed Hernia
Combo of type I and II
Occur in conjunction with other diseases like ____, peptic ulcer, cholecystitis
-Type IV
Aggravated form of Type ___
Includes herniation of other abdominal ________ (intestine, pancreas, spleen)
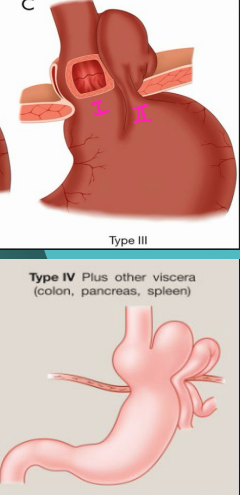
asymptomatic, heartburn, pain, fullness, bleeding
Hiatal Hernia Symptoms
-MC in Type I and III:
Often ____________
________
Regurgitation
Dysphagia
-MC in Type II-IV:
Epigastric or substernal ____
Postprandial ___________
N/V
-Strangulation Symptoms → acute, severe chest/epigastric pain, N/V, GI ________
thorax, swallow, hernia, GE
Hiatal Hernia: Diagnosis
-CXR → see protrusion of stomach into the ______, often found incidentally
-Barium ________ → determine anatomy and size of ______, orientation of stomach, location of GE junction
-Upper endoscopy
-Manometry → shows location of __ junction
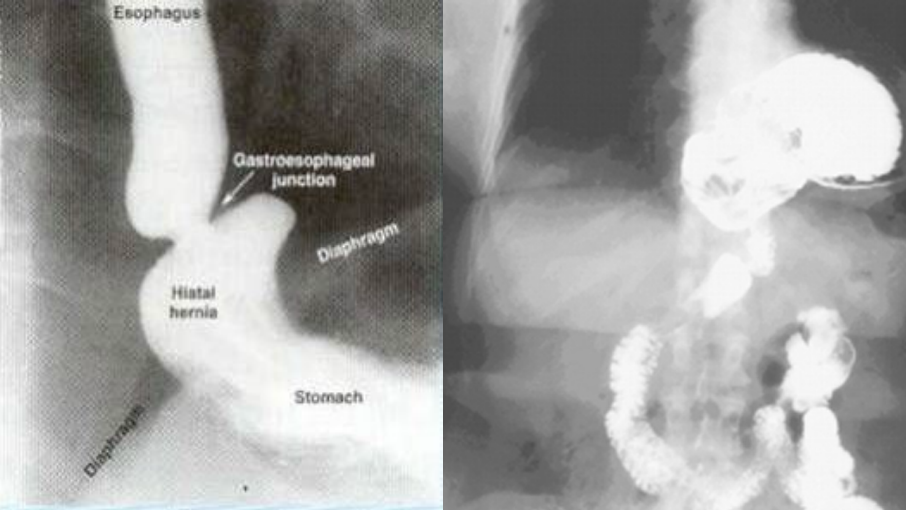
GERD, prophylactic, repair, below, fundoplication
Hiatal Hernia: Treatment
-Type I
Asymptomatic → nothing
Symptomatic → manage ____ (PPI, weight loss if needed)
-Type II-IV
Asymptomatic → controversial, most are against ____________ surgical intervention
Symptomatic → surgical _____. Return herniated stomach _______ diaphragm, repair enlarged esophageal hiatus, and then ____________
inflammatory, mucosa, NSAIDs, shock, H. pylori, autoimmune
Gastritis: Background
-Acute or chronic ____________ disorder of the gastric ______
-Subtypes:
Erosive → _______ or ETOH, MC cause of acute gastritis
Reflux
Hemorrhagic → reaction to hemodynamic disorder (_____)
Infectious → _._____ or viruses
Atrophic → _____________, environmental, and H.pylori can cause too
protective, NSAIDs, prostaglandin, hypermotility, ETOH, erosions
Acute Gastritis: Background
-Injury of the ____________ mucosal barrier (drugs, chemicals)
-_______ inhibit action of COX-1 → inhibit ___________ synthesis
-NSAIDs (not ASA) cause gastric ____________ → mucosal compression and injury
-_____, metabolic disorders (uremia) can contribute
-Superficial or deep ________ with or without hemorrhage
epigastric, bleeding, spontaneously
Acute Gastritis Symptoms
-Abdominal discomfort
-N/V
-__________ tenderness
-Gastric mucosal _________
-Heals ____________ within a few days
atrophy, metaplasia, fundal, antral, pangastritis
Chronic Gastritis: Background
-Chronic inflammation, mucosal _______, epithelial ___________ progressing over years
-Type A (immune, ______, associated with rheumatoid arthritis and T1D), Type B (nonimmune, _______, associated with H.pylori), Type AB (__________), and Type C
severe, T-cell, autoantibodies, parietal, mucosa, anemia, B12, autoimmune
Type A-Immune (Fundal) Gastritis
-Rare but most ______ form
-Associated with loss of _-____ tolerance and development of _____________ against _______ cells or intrinsic factor or both
-Gastric ______ degenerates significantly in body and fundus leading to atrophy
-Can lead to pernicious _______ (decreased vitamin ____ absorption)
-Associated with other _____________ disorders (RA, T1D)
H.pylori, mimicry, fundus, ETOH, NSAIDs
Type B-nonimmune (Antral) Gastritis
-More common
-Associated with _.______ infection
May trigger immune response through molecular ________ or cause mucosal injury
Can progress to autoimmune atrophic gastritis and involve ______ (Type AB)
-Chronic use of ____, tobacco, and _______ may contribute
anorexia, bleeding
Chronic Gastritis: Symptoms
-__________ → maybe associated weight loss
-Fullness
-N/V
-Epigastric pain
-Gastric mucosal ___________
negative, fecal-oral, asymptomatic, PUD, adenocarcinoma, increased, decreased
Helicobacter Pylori: Background
-Gram-________ rod with flagellum
-Transmitted by _____-____ or oral-oral route, usually acquired in childhood
-____________ in 70% of cases
-Gene-environment interaction and different strains increase risk of developing disease/symptoms
-Common cause of chronic/acute gastritis, ___, gastric _____________, gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)
Causes inflammation, __________ gastric secretion in antral gastritis and _________ gastric secretion in fundal gastritis, pain, N/V
urease, ammonia, neutralizes, protective, penetration, epithelium, adhesion, cytokines, apoptosis
H.pylori: Pathogenic/Virulence Factors
-Bacterial ______ hydrolyzes gastric luminal urea to form ________, which __________ gastric acid and forms __________ cloud around organism. This enables ____________ of gastric mucus layer
-Spiral shape, flagella, and mucolytic enzymes produced facilitate passage through mucus layer to gastric __________
Attaches to gastric epithelial cells by specific receptor mediated ________
-Release ___________ and chemokines, which promotes gastric epithelial cell ____________
Results in atrophy, ulcers, cell proliferation/dysplasia/cancer
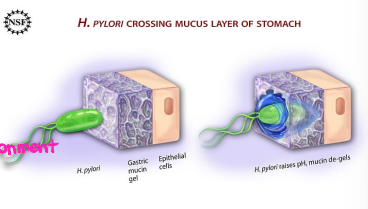
60, NSAIDs, iron, peptic
H.pylori: Indications for Testing
-Pts with dyspepsia < __ y/o who do not have alarm symptoms
-Prior to chronic treatment with ________
-Unexplained _____ deficiency
-Adults with immune thrombocytopenia
-MALT
-Active or PMH of _______ ulcer
-Early gastric cancer
endoscopy, urease, breath, CO2, stool
H.pylori: Diagnosis
-Upper ___________ (gold standard) → biopsy ______ test, tissue histology, C&S of biopsied specimens
Rapid urease test is positive when there is a change in the pH and color of test material. Taking antacid therapy within a wk before testing can give false negatives
-Urea _____ test → based on hydrolysis of urea by H. pylori to produce ___ and ammonia
-______ antigen assay → detect bacterial antigens
-Serologic Testing → IgG/IgM are the least sensitive tests (elevated within 2mo or 3-4 wks of infection), used to support diagnosis
metronidazole, tetracycline, PPI, amoxicillin, confirm, after
H. pylori: Treatment
-Quadruple therapy (1st line) → bismuth subsalicylate + ____________ + __________ + ___
Given for 10-14 days
-Triple therapy (old 1st line) → PPI + ___________ + clarithromycin
Given for 14 days
-_______ eradication (4+ weeks after treatment) → urea breath test, stool antigen test, or endoscopy
stop, H2, PPI, H.pylori
Gastritis: Treatment
-____ offending drug/chemical (NSAIDs or ETOH)
-Antacids
-__ receptor antagonists
-___ x 8-12 weeks
-Treat _._____ if present