PLPA 30003 final exam study guide
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
_______ cells divide primarily by mitosis
Eukaryotic
A relationship between organisms where one benefits and the other is harmed
Parasitism
________ is a directional growth as a mechanosensory response to touch
Thigmotropism
Necrosis is a _______ of disease
Symptom
Gram-positive bacteria stain ______ during gram staining
Purple
______ plants cannot be infected by the pathogen
Immune
_________ is a gram-negative bacterium and a significant disease of apple and pear causing die-back
Erwinia amylovora
________ is a genetically-determined increase in stress tolerance as a result of natural selection over generations
Adaptation
An _______ is a specialized cell that fungi produce to penetrate the plant cuticle
Appressorium
Name the three components of the disease triangle
Environment, host, pathogen
Which of the following is true of high-throughput sequencing methods for plant pathogen diagnostics compared to traditional methods
They can comprehensively detect a broad range of pathogens, including unknown ones
What plant pathogen was responsible for the Irish potato famine in the mid-1800s
Phytophthora infestans
Horizontal gene transfer in bacteria is a key driver of microbial evolution and adaptation. Which method of horizontal gene transfer is most common between bacteria
Conjugation
Which best describes an organism that can extract nutrients from dead tissue?
Saprophyte
Describe a non-host plant
Lacks a critical component of pathogen growth, or completely inhibits the pathogen
Which of the following best describes the difference between frost and freeze injury in plants
Frost forms ice outside the plant and is generally less damaging than freeze injury
Bacterial plant pathogens typically enter plants trhough:
Natural openings or wounds
Which of the following is most commonly associated with interveinal chlorosis, or yellowing of leaf tissue between the green veins
Viruses or abiotic deficiencies
Describe downy mildew
Oomycete, has signs on the underside of the leaf, requires high humidity, and is a biotroph
Which of the following best distinguishes a xylem-limited disease from a phloem limited disease
Xylem-limited pathogens disrupt one-way flow and cause wilt, while phloem-limited pathogens interfere with sugar transport and lead to yellowing and stunting
Which of the following best distinguishes a polycyclic disease from a monocyclic one?
Polycyclic diseases produce secondary inoculum, allowing multiple infection cycles within a single season

Produces several toxins
Epiphytes and plant pathogens
Causes angular leaf spots
Can cause galls or wilts
When grown on low-iron media, produces a fluorescent pigment
Pseudomonas

Few species
Gram positive
Causes important wilts, blights, and cankers
Clavibacter

Related to rhizobium
Commonly found on pome, stone fruits, grapes
Soft and rhizosphere inhabitant
Cause growth regulator abnormalities
Agrobacterium

Symptoms are angular leaf spot and chlorotic halo
Colonies are yellow due to the production of a yellow pigment
Most species are plant pathogens
Few cause blights and cankers
Xanthomonas

Fastidious
Lives exclusively in xylem tissue and inside mouthparts of vector
Causes scorch diseases
Causal agent of Pierces Disease
Xylellum

Common pathogen of plants in Rosaceae
Native to North America. Most destructive disease of pear
Kills flowers, twigs, may girdle trunks
Erwinia amylovora
Describe the fundamental steps of basic PCR and the essential components. Then explain how it aids in plant disease diagnostics
The fundamental steps of basic PCR are denaturation, annealing and extension. This is achieved with the use of primers and enzymes. Primers isolate the target DNA. During denaturation, the DNA is heated and separated into single strands. Annealing, cooling and primers bind to their complementary sequences on the single-stranded template. Extension, heated again and polymers extend and multiply the DNA. PCR aids in plant disease diagnostics as it is sensitive to pathogen presence, quick, and not reliant on unreliable ID techniques such as morphology. PCR is very accurate and allows diagnosticians to make effective recommendations for disease control
What are Koch’s postulates for establishing proof of pathogenicity? Why is it not sufficient to simply isolate an organism from infected tissue and assert that it is the pathogen?
Association, isolation, inoculation, re-isolation
It is not sufficient to simply isolate an organism from infected tissue and assert that it is the pathogen as it is possible to isolate an epiphytic organism that is simply living on the plant and not causing disease.
Koch originally stated three postulates the fourth was added later. Why do you think it was added
The fourth postulate (re-isolation) was added later as different pathogens can cause similar symptoms. Re-isolation rules out contamination or coincidence
Explain why insecticides are sometimes used to protect high-value crops from infection by phytoplasmas, but are not used for fire blights
Insecticides are used to protect high-value crops from infection by phytoplasmas because these diseases are vectored by non-beneficial insects such as leaf hoppers or other hemipterans. Phytoplamas are able to live in the mouthparts of these insects and are transmitted to vascular tissue when the insect feeds. Fire blight on the other hand can be spread by wind-blown rain events when bacterial ooze is present. Therefore, solely using insecticides is not effective at controlling the disease. Furthermore, fire blight is transmitted via pollinators. An important organism in fruit production of apples and pears
Which feature distinguishes Oomycetes from true fungi
Diploid vegetative hyphae
What role do haustoria play in Oomycetes like Phytophthora infestans
Extract nutrients while the host cell remains alive
Which mycotoxin is also known as vomitoxin
Deoxynivalenol
The Bordeaux mixture was first developed to control
Downy mildew of grape
Magnaporthe oryzae, the Rice Blast pathogen, possess G-protein coupled receptors which sense environmental cues to know when and where to form appressoria. Which of the following is not a cue sensed by these receptors
The presence of stomata
Which genus produces both antibiotics and mycotoxins, depending on species
Penicillium
What is the significance of chasmothecia in powdery mildew?
They are survival structures producing ascospores
Plant pathogens that cause powdery mildew are classified as
Ascomycota
Which of the following describes a critical difference between rust fungi and smut fungi in terms of their life cycles?
Rust fungi have multiple spore-producing stages, while smut fungi typically have fewer
Which of the following is a distinguishing feature of a plant disease caused by oomycetes compared to fungal pathogens?
Oomycetes produce motile zoospores that aid in the spread of the disease in wet conditions
________ are produced inside sac - like fungi
Ascospores
_______ _______ produces aflatoxins, which are potent liver carcinogens
Aspergillus flavus
Teleomorph is a term for ascomycetes used to describe the _______ stage or _____ reproduction cycle
perfect, sexual
Mycotoxins are ______ metabolites of fungi
Secondary
________ ________ causes Sudden Oak Death and can also infect ornamentals like rhododendron
Phytophthora ramorum
Conidia are asexual spores produced by ________
Ascomycetes
______ Rust fungi require one host to complete their life cycle
Autoecious.
Heteroecious rust fungi require multiple hosts to complete their life cycle
_______ are the only true fungi that produce flagellated spores
Chytrids
__________ lack a true mycelium and reproduce by budding, like yeasts
Chytridiomycota
Peach leaf curl is caused by the fungus ______ _______
Taphrina deformans
Oomycete sexual spore
Oospore
Oomycete asexual spore
Sporangia/Zoospores
Oomycete overwintering structure
Oospore
Oomycete ploidy (nuclear condition of hyphae)
Diploid (2N)
Two examples of Oomycota pathogens
Phytophthora infestans and Pythium spp.
Ascomycota sexual spore
Ascospore
Ascomycota asexual spore
Conidium/conidia
Ascomycota example of overwintering structure
Cleistothecia
Ascomycota ploidy (nuclear condition of hyphae)
Haploid (n)
Two examples of ascomycota pathogens
Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici and Venturia inaequalis
Basidiomycota sexual spores
Basidiospores
Basidiomycota asexual spore
Uredospore
Basidiomycota overwintering structure
Teliospores
Basidiomycota ploidy (nuclear condition of hyphae)
Dikaryotic (n + n)
Two examples of Basidiomycota pathogens
Puccinia graminis and Ustilago maydis

Haploid cells (1N)
Plasmogamy
Fusion of two parent cells without the nuclei merging. Produces a Dikaryotic cell
Dikaryotic cell
Karyogamy
Fusion of two haploid nuclei to form a single diploid nucleus. Forms diploid 2N cell

Diploid (2N) cell
Meiosis
Cell division that forms 1N haploid cells
List 3 differences between Oomycetes and true fungi. Use correct terminology
Oomycetes have a cell wall that is made of glucans/cellulose. True fungi cell wall is composed of chitin
Oomycetes produce flagellated zoospores that are motile in free water. Fungal spores are not flagellated
Oomycetes have coenocytic or non-septate hyphae. Fungi have septate hyphae
List 3 examples of non-pathogenic basidiomycetes
Jelly fungi, stinkhorns, puff balls
Mycotoxins create both health and economic risks. List one major mycotoxin, the primary crop it’s associated with, and one key health effect. Next, explain two ecological or environmental factors that influence mycotoxin production by fungi in the field. Propose two cultural/management practices a grower could take to reduce this risk, for each action explain the biological reason why it works.
One major mycotoxin is Deoxynivalenol or DON. DON is primarily associated with grain crops. One key health effect is that is causes vomiting and feed refusal in pigs and other livestock. Two ecological or environmental factors that influence mycotoxin production by fungi are drought and hotter than usual climates associated with global warming/climate change. Two cultural/management practices that a grower can take to reduce the risk of mycotoxins are 1. monitoring and spraying fungicides. Fungicides work by targeting the chitin present in fungal cell walls. Spraying fungicides allow for crops to have limited or no presence of fungal pathogens. Another cultural/management strategy is to burn plant material if mycotoxins are present in a field. While it is a costly process, most crops affected by mycotoxins are not useable. Burning fields inhibits the spread of mycotoxin producing fungi and prevents the fungi from overwintering
Explain the workflow of how spore traps and qPCR are used to monitor downy mildews
Spore traps are used in agricultural systems to capture downy mildew sporangia. The traps works by sucking up particulate matter in the surrounding air. qPCR or real time/qualitative PCR is then used on the contents collected in the spore traps. If spores from the downy mildew are detected then the farmer then knows that it is time to use a fungicide that targets the oomytcete
Basidiomycete spore types in order
Basidiospores, Pycnidiospores, Aescospores, Urediniospores, Teliospores
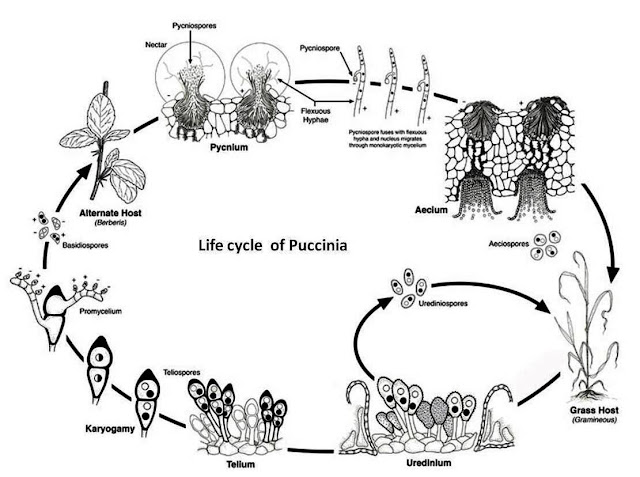
Puccinia graminis disease cycle. Urediniospores are repeating.
Teliospores produces
Basidium/basidiospores
Horizontal resistance differs from vertical resistance because it
Involves many genes and is more durable
ELISA tests for viruses rely on
Antibody sequencing
Cultural control strategies are effective because they:
Modify environmental conditions to be unfavorable for disease
Which nematode lacks sexual dimorphism, where both males and females remain veniform?
Root lesion nematode
RNA viruses defy the central dogma because they:
Use RNA as genetic material and replicate it directly
Golden rice was engineered to produce
Vitamin A (B-carotene)
Disease incidence measures
The proportion of plants infected
The four components of IPM include
Monitoring, survey, prevention, control
The three major plant parasitic nematodes include
Root-knot, Cyst, and Lesion nematodes
Which of the following is true of viroids compared to viruses
Viroids are naked RNA molecules
Antibiosis in biocontrol refers to
Production of antimicrobial compounds
________ genes are essential for disease and contribute to virulence
Pathogenicity
The ______ stage of many nematodes is the infective stage
second-stage juvenile (J2)
_____ codes categorize fungicides based on their chemical structure and mode of action
FRAC
_______ _______ can involve antagonistic microbes that compete for nutrients or produce antibiotics
Biological control
A _______ disease progress curve describes multiple infection cycles that occur in a growing season
Polycyclic
Monocyclic diseases typically show ________ increase in disease progress curves
Linear
Agrobacterium tumefaciens uses a ____ __ secretion system to deliver T-DNA into plant cells
Type IV
Plant viruses can move through plasmodesmata as _______ proteins modify the channel
Movement
______ nematodes form permanent feeding structures known as giant cells
Root-knot
______ plant defenses include structures like the cuticle, waxes, and preformed antimicrobial compounds
Passive