meiosis quiz
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
another name for meiosis
reduction division
meiosis occurs in
gamete cells
gamete cells
testes or ovaries
mitosis happens in all _________ cells
somatic
meiosis
cell division where the number of chromosomes is halved to produce sex cells
meiosis produces
4 haploid cells
genes
sections of DNA that control a specific trait
how many divisions does meiosis have?
2
diploid human cell has
46 chromosomes
haploid human cell has
23 chromosomes
diploid
the total number of chromosomes which consists of 2 sets
haploid
half the number of chromosomes, only one set
homologous chromosomes
chromosomes that have the same length and centromere position
homologous chromosomes have the same _______ in the same __________
genes, location
alleles
alternative forms of genes
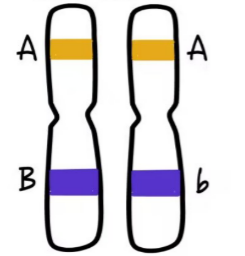
genes in homologous chromosomes are same but have
different alleles
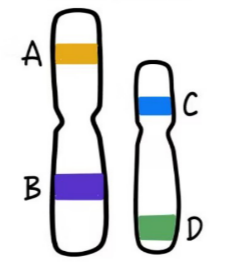
non-homologous chromosomes have
different genes
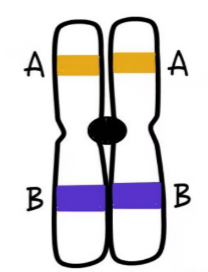
sister chromatids
same genes and alleles, held together at centromere
autosomal chromosomes
chromosomes that don’t determine sex, humans have 22 pairs
female sex chromosomes
xx
male sex chromosome
xy
2 main parts of meiosis
Meiosis 1 and Meiosis 2
Interphase occurs in _____ but not in _______
meiosis 1, meiosis 2
T/F: There are 92 chromosomes after DNA replicates in S-phase.
false, only 46 with sister chromatids
what separates in meiosis 1?
homologous chromosomes
after meiosis 1 and 2, cells have
haploid chromosomes
in meiosis 2, what separates?
sister chromatids
sperm and egg each contain
23 chromosomes
duplication happens before/after meiosis
before
which meiosis is similar to mitosis?
meiosis 2
what happens in prophase 1
crossing over
crossing over
non sister chromatids exchange genetic material
when non sister chromatids cross over,
they make a chiasma
result of crossing over
increase genetic diversity, chromatids no longer identical
after crossing over, chromosomes pull apart and
recombinant chromatids form
independent assortment
after metaphase 1, homologous chromosomes separate independently and randomly
metaphase 1
homo chromos lined up on metaphase plate
how many possible combos for one person?
223
fertilization increases
genetic variation
anaphase 1
homologous chromosomes pulled apart, sister chromatids remain attached
Telophase
cleavage furrow develops and cell separates
there is no interphase after
meiosis 1
at the beginning or meiosis 2, cells are
haploid, cells contain sister chromatids
Prophase 2 does not have
crossing over
end of cytokinesis
4 haploid daughter cells with unique DNA
benefits of meiosis
cells are genetically different and don’t have to rely on mutations alone to evolve
2 causes of genetic variation
crossing over and independent assortment
benefits of genetic variation
better chance for species to survive and evolutionary advantage
each sperm cell can produce
4 sperms
zygote
diploid cell formed by fertilization of an egg
out of 4 mature haploid eggs,
3 are smaller polar bodies
in ovaries, after meiosis 1
1 of the 2 cells get smaller in size and produces 2 polar bodies
after meiosis 2, the larger cell
produces 1 polar body and 1 egg
how many sperms can enter an egg
1
sperm have enzymes on head of body that
break down the outer membrane of egg
after one sperm fertilizes the egg
the egg releases chemicals that inhibit sperm
karyotype
visual display of chromosomes arranged by shape, size and banding pattern
band on chromosomes show
genes
non-disjunction
failure of chromosomes to separate
result of nondisjunction
gain or loss of chromosomes
which phase does nondisjunction occur during?
anaphase
aneuploidy
change in chromosome number (higher or lower)
euploidy
avg number of chromosomes in a species (46 for humans)
types of aneuploidy
trisomy or monosomy
which is worse trisomy or monosomy?
monosomy, bc genes are missing
nondisjunction is worse if it happens in
meiosis 1 bc more daughter cells are affected
monosomy
missing one homologous chromosome in a homologous pair
trisomy
extra chromosome in a homologous pair
how many trisomys are viable beyond birth?
three
which trisomys are viable beyond birth?
trisomy 13, 18 and 21
trisomy 13 name
patau syndrome
effects of trisomy 13
major circulatory, eye and brain defects, children rarely live more than a few months
trisomy 18 name
edward’s syndrome
trisomy 18 effects
small heart, all organs effected
trisomy 21 name
Down syndrome
what is the most common type of trisomy
21, down syndrome
trisomy 21 effects
slight mental handicaps, short, flat face, heart problems
prevalence of down syndrom increases with
mother’s age
XO name
turner’s syndrome
XO effects
short, wide neck, ovaries don’t develop correctly, infertile, small breasts, low hairline, short life expectancy
XXY name
kleinfelter’s syndrome
XXY effects
less muscle, body hair, small d, big breasts, infertile, insufficient puberty
XXX syndrome
female
XXX effects
tall, low IQ, anxiety, motor skill issues, delayed speech, fertile
XYY syndrome
male
XYY effects
tall, mental handicap, acne, feminine physique, fertile
SRY gene
stimulates growth of the male reproductive system