Quiz 3 Animal Nutrition UCM
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
lipids, carbs, protein
What nutrient rank provides the most energy?
top one has 2.25 times more energy compared to carbohydrates and protein on a per weight basis
carbs, protein, lipids
What nutrient classes are the main source of energy in farm animal diets?
lipids are used in small amounts to still provide energy, but also prevent the feed to go rancid during storage since they easily break down feed
If lipids (i.e. fats and oils) are so high in energy, why aren’t lipids used as the primary energy source in farm animal diets?
oils are polyunsaturated fatty acids while animal fats are saturated
Difference between fats and oils
polyunsaturated have 2 carbons with dbl bonds while saturated doesnt have any
Polyunsaturated fatty acids have what compared to saturated fatty acids?
Fats = solid, oil = liquid
The difference between fats and oils is their physical state at room temperature (i.e. approximately 68-77°F) ?
long chain of carbons (4-28)
What is a fatty acid?
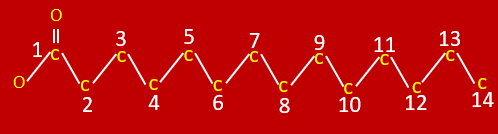
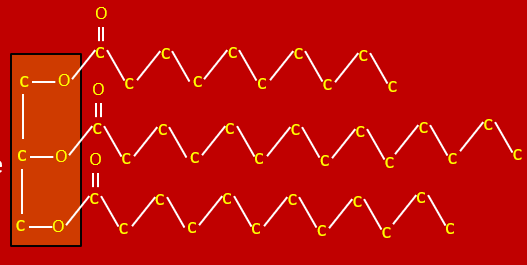
three fatty acids connected to a glycerol backbone
What is a triglyceride?
essential fatty acids are lipids that animals must consume in diet
What are EFAs?
because the body require them to live as a source of energy. since the body cant make them, they must be consumed
Why are EFAs essential?
linoleic, linolenic, arachidonic acid
What are three EFAs that are typically found in most plants making it easier for livestock producers?
carbs are formed from a combo of CO2, water, and sunlight during photosynthesis
How are carbohydrates (CHO) formed?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
What are carbohydrates made of?
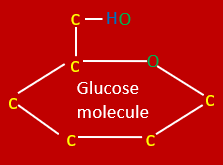
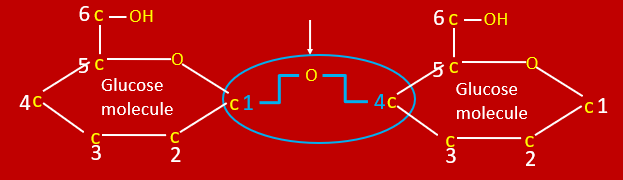
draw
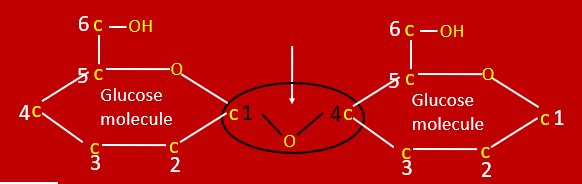
Draw glucose molecule and label C
one CHO molecule
What is a monosaccharide made of?
two CHO molecule
What is a disaccharide made of?
more than two CHO molecule
What is a polysaccharide made of?
glucose
Example of monosaccharide
maltose
Example of disaccharide
starch
Example of polysaccharide
polysaccharide chain of glucose molecules used as energy by the plants
What is starch?
as glucose stored in the plant primarily in the seed for a highly digestible energy source
Where do we find starch?
blood sugar
What is glucose also referred too?
6 carbons, 1 oxygen, 1 OH
How many carbons does glucose have?
Through alpha 1, 4 bond
Where in starch does the glucose molecules connect?
polysaccharide chains that contain glucose that are lowly digestible carbs
What are cellulose and hemicellulose?
in stems and leaves of plants (structural carbs) where they are consumed and used as energy
Where are cellulose and hemicellulose found?
straight chain of glucose molecules
What does cellulose look like in conformation?
randomly branched chain of different CHO molecules
What does hemicellulose look like in conformation?
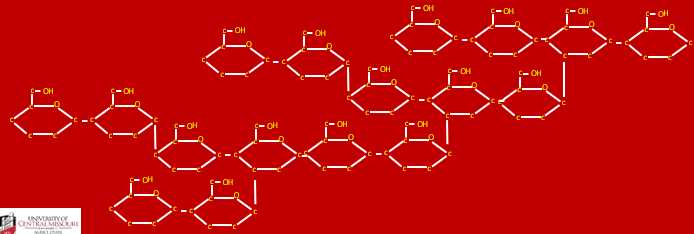
they provide the plant’s stems and leaves structural integrity so they can grow vertically
What purpose does the different conformations of hemicellulose and cellulose serve?
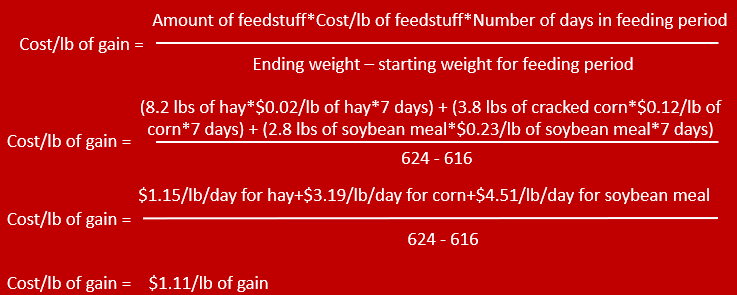
(amount of feedstuff * cost per pound * number of days in feeding period) / (ending weight - starting weight)
cost of the diet per pound of weight gain equation
FE = amount of feed fed for the feeding period / difference in weight for the feeding period
feed efficiency equation
ADG = ending weight - beginning weight / number of days in the time period
average daily gain equation
used by livestock producers to evaluate different feed diets for livestock to determine how that diet affected the weight gain of an animal
What is ADG used for in animal nutrition?
used to determine how many pounds of feed were needed to produce one pound of weight gain for one animal
Describe feed efficiency
(amount of hay* cost per pound * number of days in feeding period)+(amount of corn* cost per pound * number of days in feeding period) / (ending weight - starting weight)
Example of cost of diet per 1 lb of weight gain with multiple feedstuffs
it means the animal lost weight
What does a negative number mean when calculating FE or cost per 1 lb of weight gain?
beta 1, 4 bond (horizontal)
Where in cellulose does the glucose molecules connect?
beta 1, 4 or 1, 3 bonds
Where in hemicellulose does the glucose molecules connect?

vertical
Which way to do beta 1, 3 bonds form?
different types of bonds allow for branching structure in hemicellulose
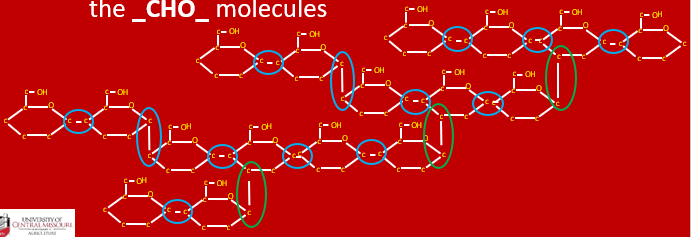
Alpha bonds can only be broken by the enzyme amylase, which is primarily produced in the pancreas of the animal and by the microbes
Why are the bonds between the carbohydrate molecules in starch, cellulose and hemicellulose so important to understand regarding alpha bonds?
Beta bonds can only be broken by the enzyme cellulase which is only produced by the microbes during microbial digestion in the rumen and/or in the cecum
Why are the bonds between the carbohydrate molecules in starch, cellulose and hemicellulose so important to understand regarding beta bonds?
It shows why ruminant and HGF animal can benefit from forages compared to monogastrics (microbial digestion)
What can we understand through understanding bonds between the carbohydrate molecules in starch, cellulose and hemicellulose?
mechanical digestion, enzymatic digestion through amylase in saliva
How is starch digested in the mouth?
mechanical digestion, chemical digestion from HCl, no enzymatic digestion
How is starch digested in the stomach?
Through amylase, enzyme released from pancreas, which breaks starch into maltose
How is starch digested in the small intestine → duodenum?
Maltose is broken into 2 glucose molecules by maltase, sucrose is broken into glucose/fructose by sucrase, lactose is broken into glucose/galactose by lactase. individual glucose molecules can be absorbed
How is starch digested in the small intestine → duodenum on the surface of the villi?
only absorption of monosaccharides happens here into the blood stream since water soluble
How is starch digested in the small intestine → jejunum and ileum?
glucose, fructose, galactose
What monosaccharides (since they are water soluble nutrients) are mainly absorbed into the bloodstream then the liver?
As glucose enters the blood stream, the pancreas is triggered to release insulin. Insulin allows the cell to absorb glucose (like a key) without glucose can’t enter
How is glucose absorbed into the cell?
When glucose gets too low in the bloodstream, the hormone glucagon is released by the pancreas to stimulate the liver to release glucose from glucose reserves (glycogen)
How is glucose maintained in the bloodstream?
cellular metabolism of glucose is how the cell gets energy. The source of energy in the cell is adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
How is glucose metabolized by the cell to make energy?
temporary storage in long chains called glycogen, long term storage as fat
How is glucose metabolized by the cell for storage?
RNA and DNA backbone
How is glucose metabolized by the cell to make other cellular products?
Stage 1: glycolysis → Acetyl-CoA, Stage 2: Kreb’s cycle → NADH, FADH2 (reduced e- carriers), Stage 3: oxidative phosphorylation → ATP
Metabolism of glucose in the cell to produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
36-38
What is the total amount of ATP produced from one glucose molecule during the stages of cellular metabolism?
mechanical digestion, enzymatic digestion by the microbes through microbial digestion
How is starch digested in the rumen and cecum?
bacteria, protozoa, fungi
3 types of microbes in the rumen and cecum
hundreds of bacteria populate in anaerobic environment (little to no oxygen)
What has research show regarding bacteria in the rumen?
one that digests cellulose/hemicellulose from forages, and one that digests starch from grains
What are the two basic categories of bacteria?
If majority of diet is forages then mainly forage digesting bacteria will be present. Vice versa for grain
How does the proportion of two different bacteria change depending on diet?
10-14 days to allow for microbial population to adapt
In what period of time should a ruminant diet be changed?
6 to 6.4
What is the normal pH of the rumen?
The pH drops to 6, if drops lower than the forage bacteria will stop functioning but the starch bacteria continues. The starch digesting bacteria produces excess lactic acid which can cause lactic acidosis
What can happen with a ruminant is consuming a grain based diet?
bicarbonate
What helps maintain the pH of the rumen from the saliva?
Always contain some forages even in a high grain diet
What can we do to prevent decline in feed intake from lactic acidosis?
acetate, propionate, butyrate
What are the 3 VFAs produced in the rumen during microbial digestion?
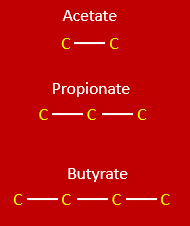
produced from the digestion of starch, cellulose, and hemicellulose
How are VFAs produced?
microbes break apart polysaccharide chains into individual glucose molecules using enzymes amylase and cellulase
What is first happens in microbial digestion regarding polysaccharide chains?
microbes use glucose molecules as energy
What is the second step in microbial digestion glucose?