1.1.1 Intro to Microbiology
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
Which of the following pathogens are subcellular biological entities?
A. prions
B. chlamydiae
C. Fungi
D. Rickettsiae
E. viruses
F. Protozoa
G. Helminths
H. Arthropods
I. Mycoplasma
J. Classic Bacteria
A,E
Which of the following pathogens are prokaryotic microorganisms?
A. prions
B. chlamydiae
C. Fungi
D. Rickettsiae
E. viruses
F. Protozoa
G. Helminths
H. Arthropods
I. Mycoplasma
J. Classic Bacteria
B,D,I,J
Which of the following pathogens are eukaryotic microorganisms?
A. prions
B. chlamydiae
C. Fungi
D. Rickettsiae
E. viruses
F. Protozoa
G. Helminths
H. Arthropods
I. Mycoplasma
J. Classic Bacteria
C,F
Which of the following pathogens are animals?
A. prions
B. chlamydiae
C. Fungi
D. Rickettsiae
E. viruses
F. Protozoa
G. Helminths
H. Arthropods
I. Mycoplasma
J. Classic Bacteria
G,H
What is a key feature of prokaryotic microorganisms?
lack of a defined nucleus
What is a key feature of eukaryotic microorganisms?
has a defined nucleus which contains DNA
All prokaryotic microorganisms have a rigid cell wall with the exception of?
A. chlamydiae
B. Rickettsiae
C. Mycoplasma
D. classic bacteria
C. mycoplasma
How do bacteria replicate?
binary fission
How many cells do bacteria have?
single celled
Do bacteria have membrane bound organelles?
no
Virulence factors __________ infectivity?
A. increase
B. decrease
A. increase
bacteria have a rigid cell wall containing _____________.
A. flagella
B. peptidoglycan
C. Lipid A
D. Exotoxins
B. peptidoglycan
What is the first step of the gram staining process after fixing the organism to the slide?
A. Wash off with water and flood with iodine solution. Wait 60 seconds
B. wash off with water then decolorize with 95% alcohol
C. counter stain with safranin. wait 30 seconds and wash off with water
D. Apply crystal violet stain (purple dye) and wait 60 seconds
D. Apply crystal violet stain (purple dye) and wait 60 seconds
How long should you wait after applying the crystal violet stain (purple dye) before continuing
A. 60 seconds
B. 30 seconds
C. 90 seconds
D. you dont have to wait
A. 60 seconds
What is the second step of the gram staining process?
A. Apply crystal violet stain and wait 60 seconds
B. Wash off with water and flood with iodine solution. Wait 60 seconds
C. wash off with water then decolorize with 95% alcohol
D. counter stain with safranin. wait 30 seconds and wash off with water
B. Wash off with water and flood with iodine solution. Wait 60 seconds
Iodine is a mordant. What does this mean?
It will trap crystal violet in the cell wall if it is present
What is the third step in the gram staining process?
A. Wash off with water and flood with iodine solution. Wait 60 seconds
B. wash off with water then decolorize with 95% alcohol
C. counter stain with safranin. wait 30 seconds and wash off with water
D. Apply crystal violet stain (purple dye) and wait 60 seconds
B. wash off with water then decolorize with 95% alcohol
What is the last step of the gram staining process?
A. Wash off with water and flood with iodine solution. Wait 60 seconds
B. wash off with water then decolorize with 95% alcohol
C. counter stain with safranin (red dye). wait 30 seconds and wash off with water
D. Apply crystal violet stain (purple dye) and wait 60 seconds
C. counter stain with safranin (red dye). wait 30 seconds and wash off with water
What color will appear if your gram stain is positive?
blue or purple
what color will appear if your gram stain is negative?
red or pink
What does having a positive gram stain mean?
The organism has a thicker cell wall
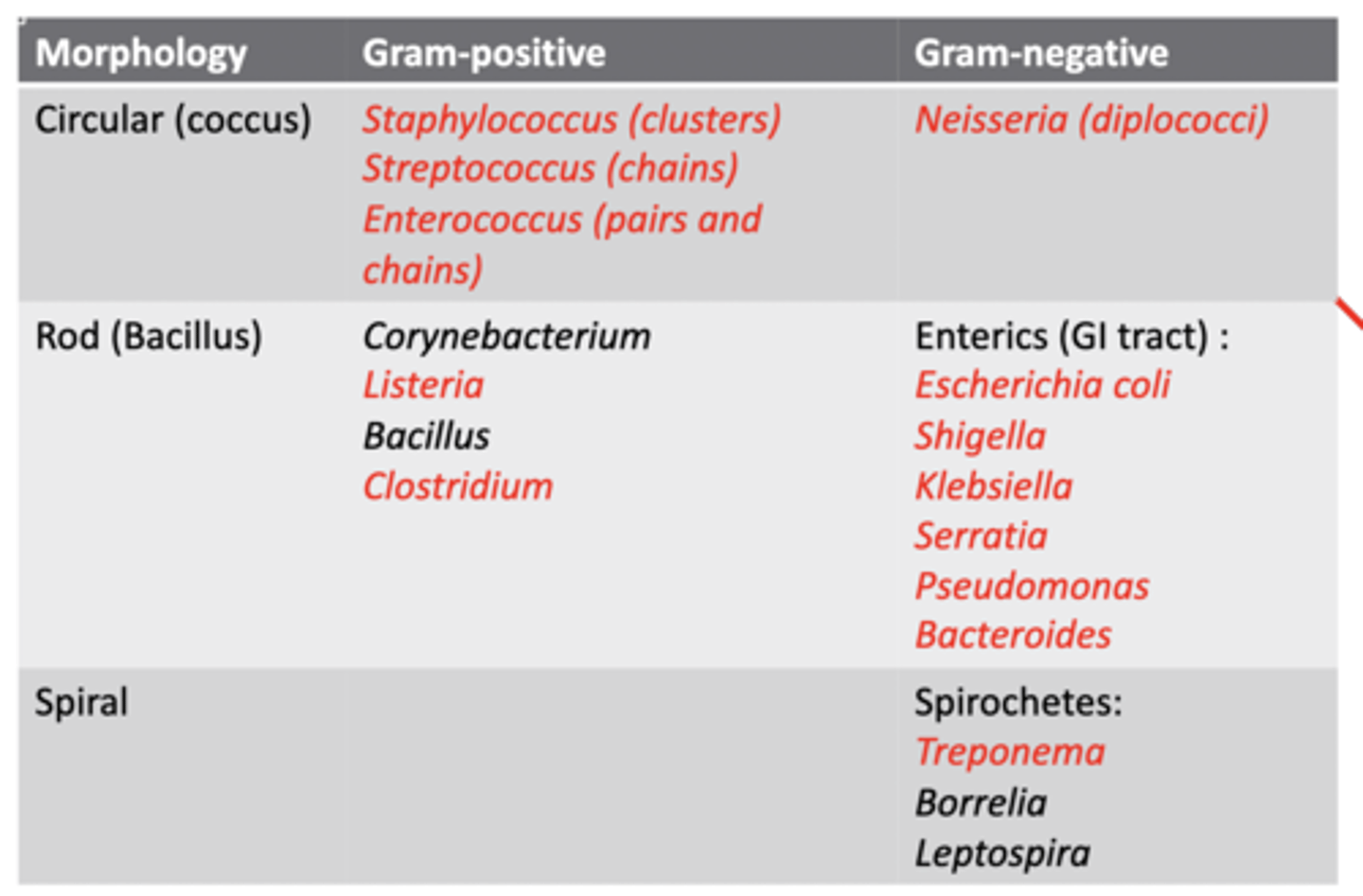
What is the morphology of cocci bacteria?
A. rod-shaped
B. spiral
C. spherical
C. spherical
What is the morphology of bacilli bacteria?
A. rod-shaped
B. spiral
C. spherical
A. rod-shaped
What is the morphology of spirochete bacteria?
A. rod-shaped
B. spiral
C. spherical
B. spiral
Categorize the following bacteria with the correct morphology: Staphylococcus
A. coccus (spherical)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
C. spirochete (spiral)
A. coccus (spherical)
Categorize the following bacteria with the correct morphology: streptococcus
A. coccus (spherical)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
C. spirochete (spiral)
A. coccus (spherical)
Categorize the following bacteria with the correct morphology: enterococcus
A. coccus (spherical)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
C. spirochete (spiral)
A. coccus (spherical)
Categorize the following bacteria with the correct morphology: neisseria
A. coccus (spherical)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
C. spirochete (spiral)
A. coccus (spherical)
Categorize the following bacteria with the correct morphology: listeria
A. coccus (spherical)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
C. spirochete (spiral)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
Categorize the following bacteria with the correct morphology: clostridium
A. coccus (spherical)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
C. spirochete (spiral)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
Categorize the following bacteria with the correct morphology: E. coli
A. coccus (spherical)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
C. spirochete (spiral)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
Categorize the following bacteria with the correct morphology: shigella
A. coccus (spherical)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
C. spirochete (spiral)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
Categorize the following bacteria with the correct morphology: klebsiella
A. coccus (spherical)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
C. spirochete (spiral)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
Categorize the following bacteria with the correct morphology: serratia
A. coccus (spherical)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
C. spirochete (spiral)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
Categorize the following bacteria with the correct morphology: pseudomonas
A. coccus (spherical)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
C. spirochete (spiral)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
Categorize the following bacteria with the correct morphology: Bacteroides
A. coccus (spherical)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
C. spirochete (spiral)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
Categorize the following bacteria with the correct morphology: Treponema
A. coccus (spherical)
B. bacillus (rod-shaped)
C. spirochete (spiral)
C. spirochete (spiral)
Categorize the following bacteria as gram positive or gram negative: Staphylococcus
gram positive
Categorize the following bacteria as gram positive or gram negative: streptococcus
gram positive
Categorize the following bacteria as gram positive or gram negative: enterococcus
gram positive
Categorize the following bacteria as gram positive or gram negative: listeria
gram positive
Categorize the following bacteria as gram positive or gram negative: costridium
gram positive
Categorize the following bacteria as gram positive or gram negative: neisseria
gram negative
Categorize the following bacteria as gram positive or gram negative: E. coli
gram negative
Categorize the following bacteria as gram positive or gram negative: shigella
gram negative
Categorize the following bacteria as gram positive or gram negative: klebsiella
gram negative
Categorize the following bacteria as gram positive or gram negative: serratia
gram negative
Categorize the following bacteria as gram positive or gram negative: pseudomonas
gram negative
Categorize the following bacteria as gram positive or gram negative: bacteroides
gram negative
Categorize the following bacteria as gram positive or gram negative: treponema
gram negative
how are staphylococcus arranged?
A. chains
B. pairs and chains
C. clusters
C. clusters
How are streptococcus arranged?
A. chains
B. pairs and chains
C. clusters
A. chains
How are enterococcus arranged?
A. chains
B. pairs and chains
C. clusters
B. pairs and chains
What are normal flora?
microbes that are typically found at a specific anatomic site
Where are bacteroides normally found?
colon, throat, vagina
where are clostridium normally found?
colon
where are enterococcus normally found?
colon
where are E. coli normally found?
colon, vagina, genitourinary tract
where are propionibacterium acnes normally found?
skin
where are staphylococcus aureus normally found?
nose, skin
where are staphylococcus epidermidis normally found?
skin, nose, mouth, vagina, urethra
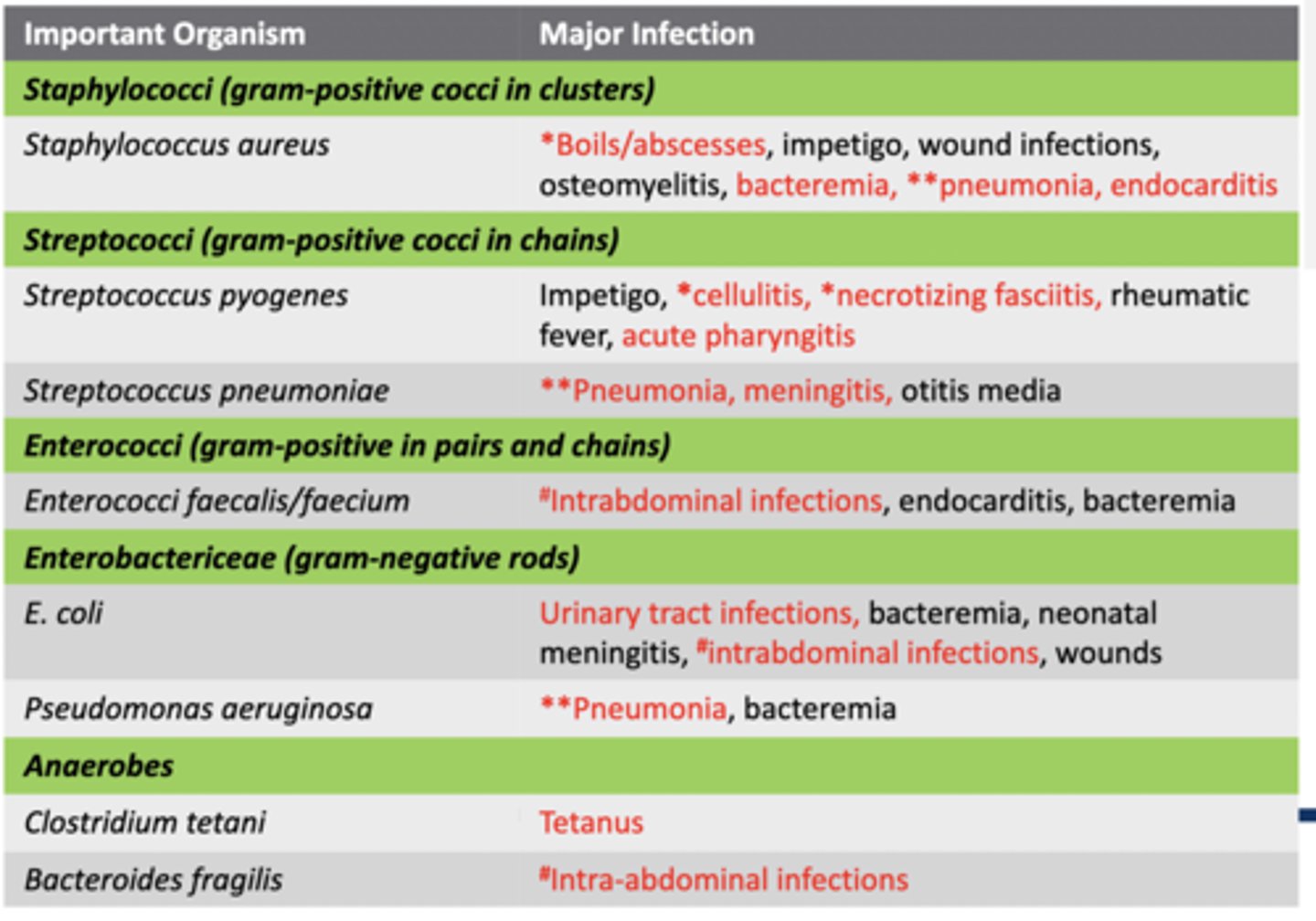
What organism is gram-positive cocci in clusters and can cause boils/abcesses?
A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
B. E. coli
C. staphylococcus aureus
D. enterococci faecalis
C. staphylococcus aureus
What organism is gram-positive cocci in clusters and can cause bacteremia?
A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
B. E. coli
C. staphylococcus aureus
D. enterococci faecalis
C. staphylococcus aureus
What organism is gram-positive cocci in clusters and can cause pneumonia?
A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
B. E. coli
C. staphylococcus aureus
D. enterococci faecalis
C. staphylococcus aureus
What organism is gram-positive cocci in clusters and can cause endocarditis?
A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
B. E. coli
C. staphylococcus aureus
D. enterococci faecalis
C. staphylococcus aureus
What organism is gram-positive cocci in chains and can cause cellulitis?
A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
B. streptococcus pyogenes
C. staphylococcus aureus
D. enterococci faecalis
B. streptococcus pyogenes
What organism is gram-positive cocci in chains and can cause necrotizing fasciitis?
A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
B. streptococcus pyogenes
C. staphylococcus aureus
D. enterococci faecalis
B. streptococcus pyogenes
What organism is gram-positive cocci in chains and can cause acute pharyngitis?
A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
B. streptococcus pyogenes
C. staphylococcus aureus
D. enterococci faecalis
B. streptococcus pyogenes
What organism is gram-positive cocci in chains and can cause pneumonia?
A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
B. streptococcus pyogenes
C. staphylococcus aureus
D. enterococci faecalis
A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
What organism is gram-positive cocci in chains and can cause meningitis?
A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
B. streptococcus pyogenes
C. staphylococcus aureus
D. enterococci faecalis
A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
What organism is gram-positive cocci in pairs and chains and can cause intraabdominal infections ?
A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
B. streptococcus pyogenes
C. staphylococcus aureus
D. enterococci faecalis
D. enterococci faecalis
What organism is gram negative rod shaped and can cause urinary tract infections?
A. Clostridium tetani
B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
C. E. coli
D. bacteroides fragilis
C. E. coli
What organism is gram negative rod shaped and can cause intraabdominal infections?
A. Clostridium tetani
B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
C. E. coli
D. bacteroides fragilis
C. E. coli
What organism is gram negative rod shaped and can cause pneumonia?
A. Clostridium tetani
B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
C. E. coli
D. bacteroides fragilis
B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Which organism is an anaerobe that causes tetanus?
A. Clostridium tetani
B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
C. E. coli
D. bacteroides fragilis
A. Clostridium tetani
Which organism is an anaerobe that causes intraabdominal infections
A. Clostridium tetani
B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
C. E. coli
D. bacteroides fragilis
D. bacteroides fragilis
KNOW SLIDE
KNOW SLIDE
Gives rigid support, protects against osmotic pressure, is the site of action for antibiotics
A. teichoic acids
B. Peptidoglycan
C. Lipopolysaccharide
D. Porin Channel
B. Peptidoglycan
gives cell structure, protects against antibiotic attack, cell division, surface antigen
A. teichoic acids
B. Peptidoglycan
C. Lipopolysaccharide
D. Porin Channel
A. teichoic acids
barrier against antibiotics, modulates response by the host immune system
A. teichoic acids
B. Peptidoglycan
C. Lipopolysaccharide
D. Porin Channel
C. Lipopolysaccharide
passage on nutrients, antibiotics, site for development of antibiotic resistance
A. teichoic acids
B. Peptidoglycan
C. Lipopolysaccharide
D. Porin Channel
D. Porin Channel
What type of Bacterial cells have peptidoglycan?
A. gram negative
B. gram positive
C. both
C. BOTH gram negative and gram positive
What type of Bacterial cells have teichoic acids?
A. gram negative
B. gram positive
C. both
B. gram positive
What type of Bacterial cells have lipopolysaccharide?
A. gram negative
B. gram positive
C. both
A. gram negative
What type of Bacterial cells have porin channels?
A. gram negative
B. gram positive
C. both
A. gram negative
What type of Bacterial cells has a higher lipid content?
A. gram negative
B. gram positive
C. both
A. gram negative
What type of Bacterial cells has a lower lipid content?
A. gram negative
B. gram positive
C. both
B. gram positive
What type of Bacterial cells is more susceptible to antibiotics?
A. gram negative
B. gram positive
C. both
B. gram positive
What type of Bacterial cells is more resistant to antibiotics?
A. gram negative
B. gram positive
C. both
A. gram negative
Where is peptidoglycan found?
only in cell wall
what cross links D and L amino acids?
A. transpeptidase
B. glycosyltransferase
C. Crosslinktidase
D. aminoacidlinkerase
A. transpeptidase
In peptidoglycan what carbohydrates are alternating?
N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) and N-acetylglucosamine (NAG)
When is lipid A released?
A. When the bacteria replicates
B. when the bacteria undergoes lysis
C. when the bacteria is shocked
D. when the bacteria joins plasmid
B. when the bacteria undergoes lysis
What is the cause of fever and shock secondary to infection?
A. LPS
B. peptidoglycan
C. lipid A
D. porin channel
C. lipid A
not a protein that is excreted from the cell but rather a normal component of the cell
A. endocytosis
B. endotoxin
C. exocytosis
D. exotoxin
B. endotoxin
Lipid A is an _______________
A. endocytosis
B. endotoxin
C. exocytosis
D. exotoxin
B. endotoxin
proteins are released by both gram negative and gram positive bacteria
A. endocytosis
B. endotoxin
C. exocytosis
D. exotoxin
D. exotoxin
neurotoxin and enterotoxin are _______________
A. endocytosis
B. endotoxin
C. exocytosis
D. exotoxin
D. exotoxin
Which of the following are virulence factors for adherence?
A. Capsule
B. flagella
C. spores
D. glycoclayx
E. pili
F. biofilm
A. Capsule
D. glycoclayx
E. pili