Syphilis Serology (Exam 3)
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Syphilis can be spread ______ or can be ______.
sexually, congenital
What are the 4 stages of untreated syphilis?
- Primary
- Secondary
- Latent
- Tertiary
Primary syphilis can be recognized by the presence of a ______.
chancre
Secondary syphilis is characterized by generalized lymphadenopathy, fever, and ______.
rash (hands and feet)
Latent syphilis usually has no ______.
S/Sx
Latent syphilis is noninfectious except ______.
congenitally
Tertiary syphilis can cause ...
- Gummatous syphilis
- CVD
- Neurosyphilis
Tertiary syphilis occurs ______ years post-infection.
10-30
What are the most common/effective treatments of syphilis?
- Penicillin
- Tetracycline or erythromycin
Direct detection via dark field microscopy examines samples taken from the patient's ______.
lesion
Inspection uses a microscopy with a ______ condenser.
dark-field
A positive dark field microscopy direct test indicates the presence of ______ on the black background
motile spirochetes
Direct dark field microscopy may be positive before ______ tests.
serological
Direct detection via fluorescent Ab uses fluorescent-conjugated ______ Ab.
anti-Treponema pallidum
This type of test detects T. pallidum in ______ from the lesion site.
fixed smears
Fluorescent Ab direct detection has better ______ and reduced ______ than dark field microscopy.
sensitivity/specificity, infection risk
Treponemal serological tests detect _______ against T. pallidum or specific ______ associated with it.
Abs, antigens
Treponemal serological tests are usually positive before ______ tests.
non-treponemal
Serological tests are close to 100% reactive if the patient is in ______ or ______ phase.
secondary, latent
What tests are serological?
- TP-PA
- FTA-ABS
- EIA/CLIA
Fluorescent Treponemal Antibody Absorption (FTA-ABS) tests are ______ (direct/indirect).
indirect
FTA-ABS combines ______ with ______.
heat-inactivated patient serum, nonpathogenic treponemes
These two are then ______.
incubated
What is added to the mixture after incubation?
Fluorescent-conjugated secondary Ab
The ______ is then read.
fluorescence (0-4+)
FTA-ABS is very sensitive and specific except for ______ cases.
congenital
Particle Agglutination Tests include ______.
T. pallidum particle agglutination (TP-PA)
TP-PA is very sensitive in detecting what stages of syphilis?
secondary, tertiary, latent
TP-PA tests incubate patient serum in microtiter plates with ______, coated with ______.
gel particles, T. pallidum antigen
A positive (agglutinated) TP-PA results in gel particles ______ in the well, creating a cloudy appearance.
"dissolving"
A negative TP-PA shows particles on the ______.
bottom of the well
Immunoassays are used for ______ and ______ syphilis.
screening (IgG/IgM), congenital (IgM)
What are the types of immunoassays used for syphilis detection?
- Non-competitive ELISA
- Competitive ELISA
- Chemiluminescent immunoassays (CLIA)
Immunoassays are very ______ when it comes to detection of syphilis.
sensitive/specific
Non-treponemal serological tests detect patient IgM and IgG against ______.
cardiolipin
Non-treponemal serological tests are used for ______ and to monitor ______.
screening, therapy
What are the two types of non-treponemal serological tests?
RPR and VDRL
RPR and VDRL are ______ rections.
flocculation
Non-treponemal titers ______ with effective therapy.
decrease
Non-treponemal titers ______ with recent infection, reinfection, or relapse.
increase
Treponemal tests for Abs will always stay _______ once infected with syphilis once.
high
Non-treponemal Ab tests (RDR, VDRL) will _______ after initial syphilis exposure and cessation.
decrease
Non-treponemal tests (RPR, VDRL) will be positive ______ weeks after appearance of ______.
1-4, chancres
In Rapid Plasma Reagin (RPR), the antigen is ______.
cardiolipin as well
In an RPR, very fine particles will show ______ when Ab is present.
clumping
______ is added to RPR to enhance visibility.
Charcoal
RPR is used to monitor patient _______ to therapy after diagnosis.
reaction
RPR is more sensitive than VDRL in the ______ syphilis stage.
primary
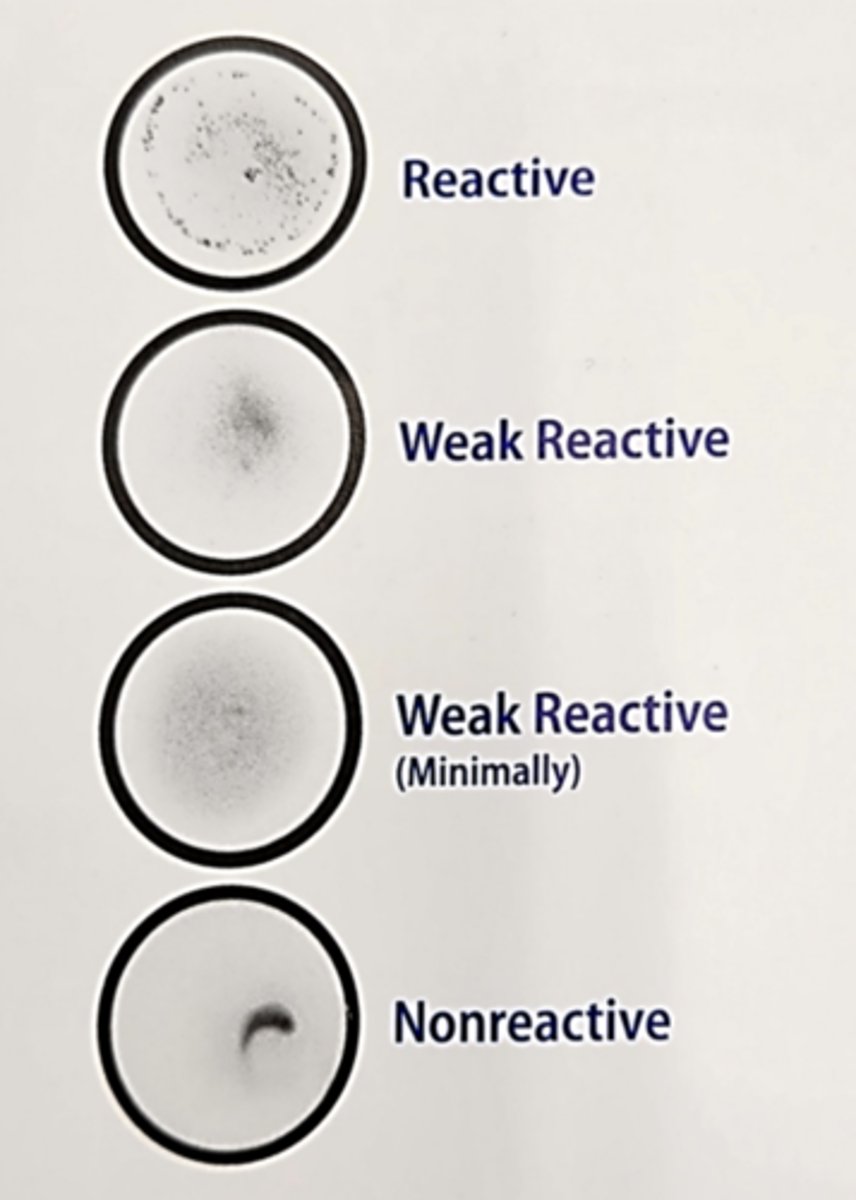
RPR Results
The antigen in VDRL is ______.
cardiolipin too
VDRL is performed on ______ and heat-inactivated ______.
CSF, serum (inactivates complement)
VDRL is used more for potential ______.
neurosyphilis
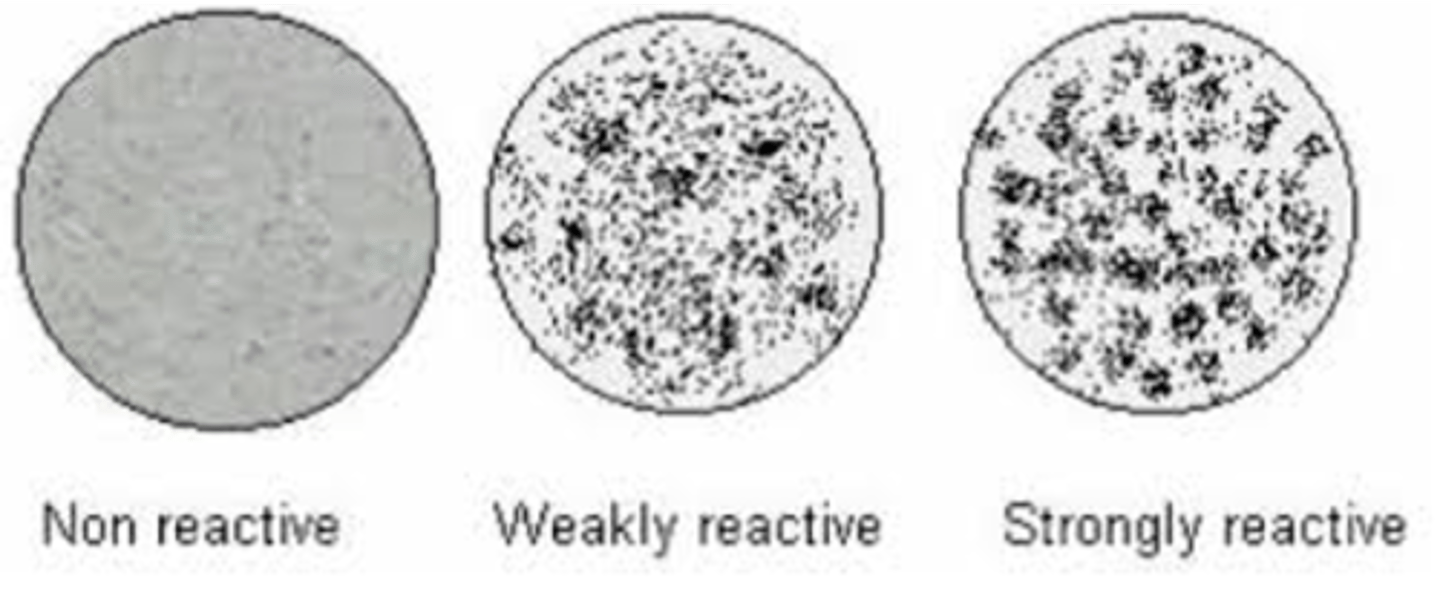
VDRL Results
A ______ can occur with non-treponemal tests, indicating a large amount of Ab in the secondary syphilis stage.
prozone
When a prozone occurs, you should ______ the serum and retest it.
dilute
Biological false positives can occur with additional _______.
viral infections
Biological false positives can also occur due to ______.
chronic disease
Biological false negatives can occur due to ...
- Prozone
- Testing too early
- Latent stage
- Immunodeficient patient
In the lab, false positives/negatives can occur due to ...
- Dried serum on card before antigen is added
- Rotated too long (common!!)
- Not humidified during rotation
- Hot reagents or room
What components are important in daily quality control when in comes to syphilis diagnosis?
- Controlled room temperature
- Rotator speed
- Antigen needle drop size
- Reactive, non-reactive, minimally-reactive controls
What tests are usually done first when it comes to syphilis detection?
EIA/CIA or TP-PA
TP-PA can also be done ______.
last/third
What test is usually done second?
RPR or VDRL
RPR is ______ for positive results.
confirmatory
TP-PA can be done on samples with ______ results.
discrepant
Congenital syphilis is done via ______ followed by ______ or ______.
IgM EIA, Western Blot or PCR
This is because the infant ______ must be detected.
antibodies
VDRL and ELISA only routinely use ______ samples.
CSF
These two are very specific and diagnostic if positive, but lack ______.
sensitivity