AP Physics II - Unit 9 - A
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
The temperature in Kelvin of an ideal gas is directly proportional to…
the average kinetic energy of the gas’ particles
T = …
(2/3)(avg kinetic energy/Boltzmann’s constant)
For an ideal gas, thermal energy is directly proportional to…
temperature
What does N mean?
The number of particles in the sample
What does n mean?
The number of moles in a sample
What does NA mean?
Avogadro’s number or 6.02 * 1023 or the number of particles in 1 mole
What does T mean?
The temperature of the sample in Kelvins
What does kb mean?
Boltzmann’s constant or 1.38 * 10-23 J/K or the relation of temperature to energy
What does R mean?
Rydberg constant or gas constant or 8.31J/mol K
What is the formula for n?
N/NA
What is a gas?
A system in which each particle moves freely through space until it collides with another particle or a wall
What is a liquid?
A system in which weak bonds permit motion while keeping particles close together
What is a solid?
A system in which bonds hold particles in a definite shape that can be compressed only slightly
What is the SI unit of volume?
m3
Convert 1 m3 to liters.
1 Liter
Convert 1 cm3 to m3
10-6 m3
Write the definition of pressure in a gas
p = F/A
What is the SI unit of pressure?
1 pascal or 1 Pa or 1 N/m2
From where is the standard atmosphere or kPa measured?
Sea level
What does psi stand for?
pounds per square inch
What is a vacuum?
An enclosed space with p << 1 atm (NOTE that removing every molecule from a container to make a perfect vacuum is impossible, p = 0 Pa)
When is a net pressure force exerted with a container of gas?
When there is a pressure difference between the two sides of a surface
What is gage pressure, pg?
The difference between actual pressure and atmospheric pressure
What is pressure in relation to gas temperature?
Directly proportional
What is pressure in relation to container volume?
Inversely proportional
What is pressure in relation to the number of gas particles?
Directly Proportional
What is the ideal gas law?
pV = NkbT or pV = nRT
List the properties Ideal-gas processes have.
The quantity of gas is fixed (n is constant), the initial state is defined, and the final state is defined
What is the relation between the initial and final state of an ideal-gas process?
(pfVf)/Tf = (piVi)/Ti
What is a trajectory?
An ideal-gas process that changes the state of the gas
Name the ideal-gas process where the volume of the system stays constant.
isochoric
Name the ideal-gas process where the pressure of the system stays constant.
isobaric
Name the ideal-gas process where the temperature of the system stays the same.
isothermal
What is an example of an isochoric process?
Warming a gas in a closed container
What kind of line does an isochoric process appear as on a pV diagram?
A vertical line
What is an example of an isobaric process?
A container with a movable piston that keeps the system in equilibrium
What is an example of an isothermal process?
A container in a larger container with a constant temperature that changes its volume slowly so the sample can transfer heat to a larger container
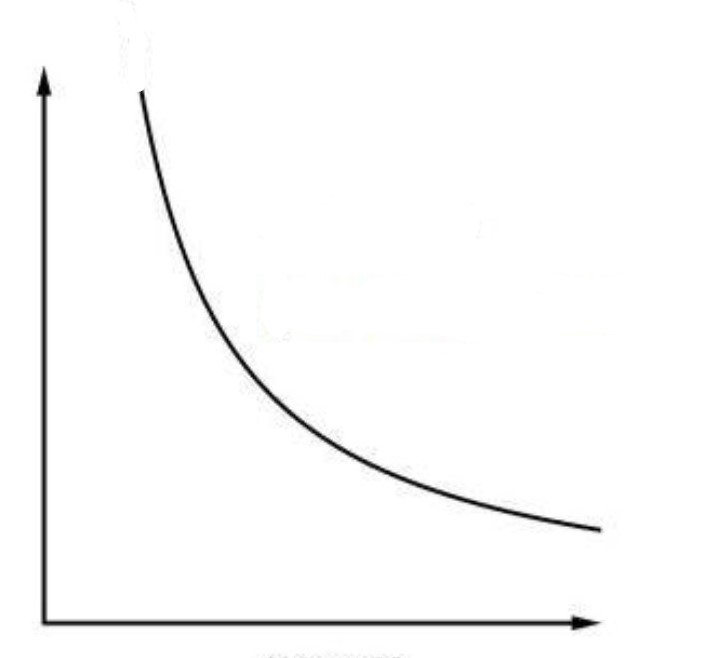
What is the graph of an isothermal process?
A hyperbola
What is an isotherm?
A graph of an isothermal process
How do you convert Fahrenheit to Celsius?
(5/9)(Tf - 32)
How do you convert Celsius to Fahrenheit?
(9/5)Tc + 32
How do you convert Celsius to Kelvin?
Tc + 273
What are the freezing and boiling points of Celsius?
0 and 100
What are the freezing and boiling points of Fahrenheit?
32 and 212
What does 0K mean?
The average kinetic energy of atoms is zero, and the particles are not moving
Define thermal energy
The total of all kinetic and potential energy of the atoms in an object
Kavg = …
3/2kbT
Eth = …
3/2NkbT
delta Eth= …
3/2nR(deltaT)
What is volume in relation to temperature?
Directly proportional
What is volume in relation to the number of particles?
Directly proportional
What is the root mean square velocity?
The average velocity of a particle in a gas
Vrms = …
sqrt((3kbT)/m)
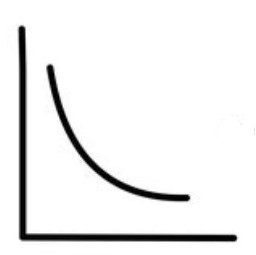
What relationship is this a graph of?
the relationship between pressure and volume
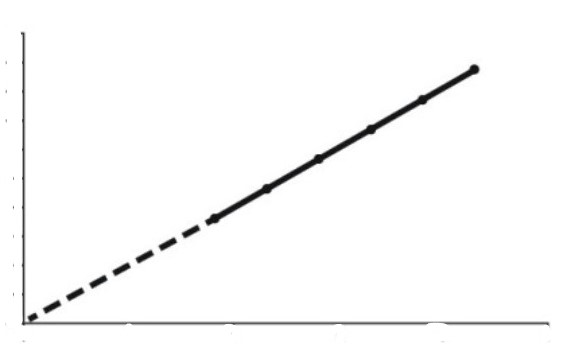
What relationship is this a graph of?
the relationship between pressure and temperature
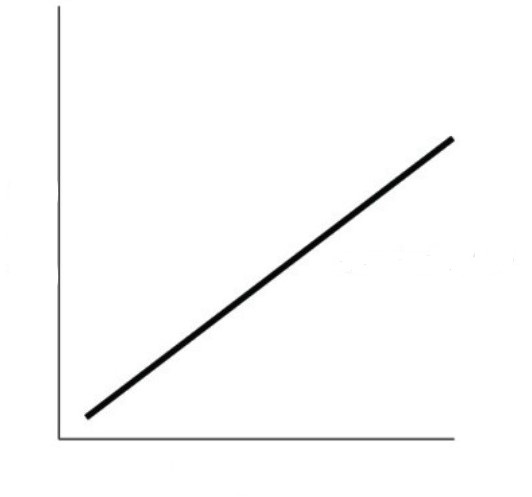
What relationship is this a graph of?
the relationship between temperature and volume
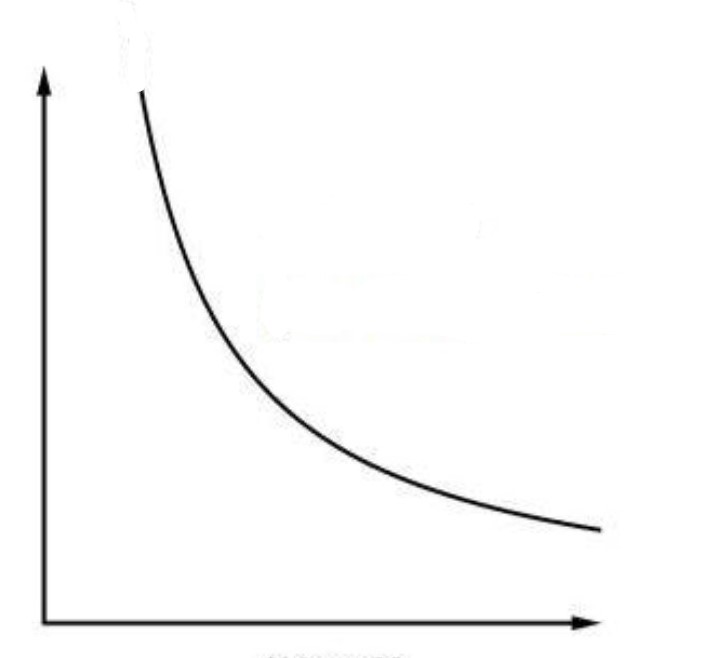
What type of process is this PV diagram showing?
an isothermal process
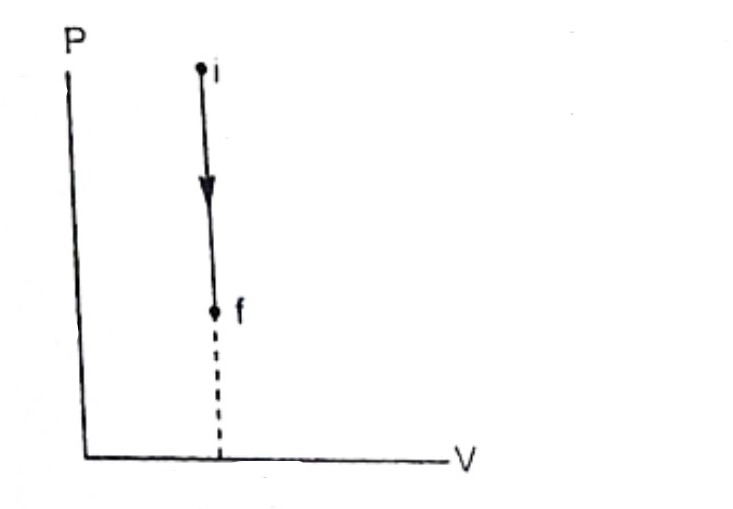
What is the change in T or U, Q, and W? (0, negative, positive, or another value)
0, positive, negative (Q = -W)
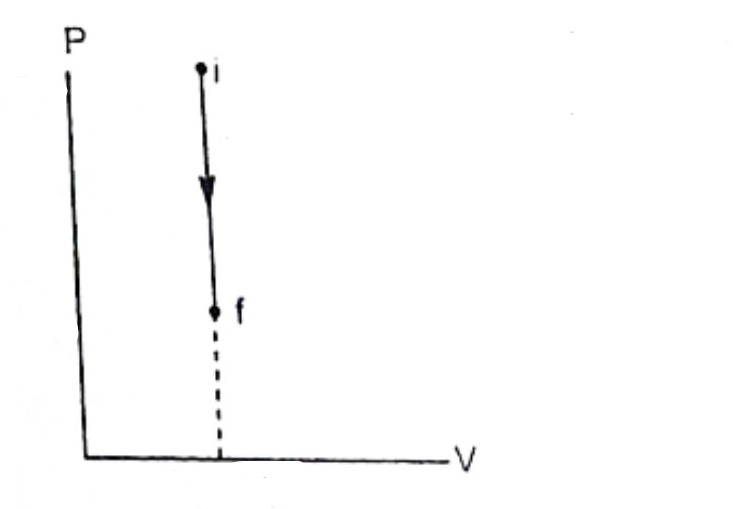
What type of process is this PV diagram showing?
an isovolumetric or isochoric process
What is the change in T or U, Q, and W equal to? (0, positive, negative)
positive, positive, 0 (deltaT = Q)
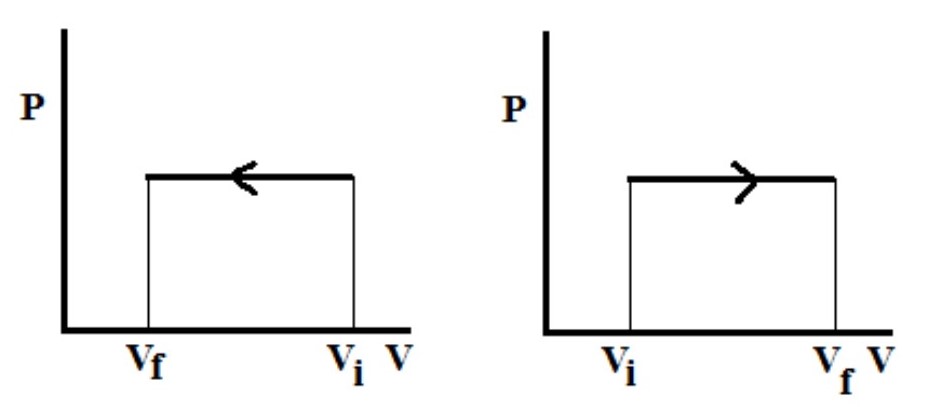
What type of process is this PV diagram showing?
an isobaric process
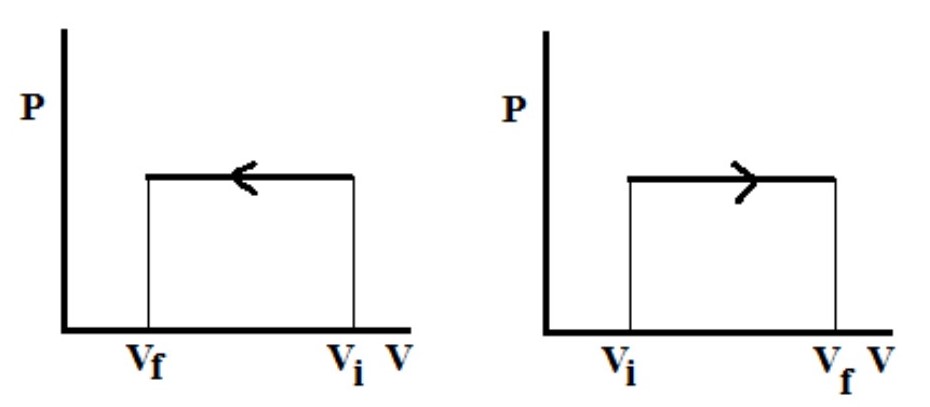
What is the change in T or U, Q, and W equal to? (0, positive, or negative)
positive, positive, positive (deltaU = Q + PdeltaV)
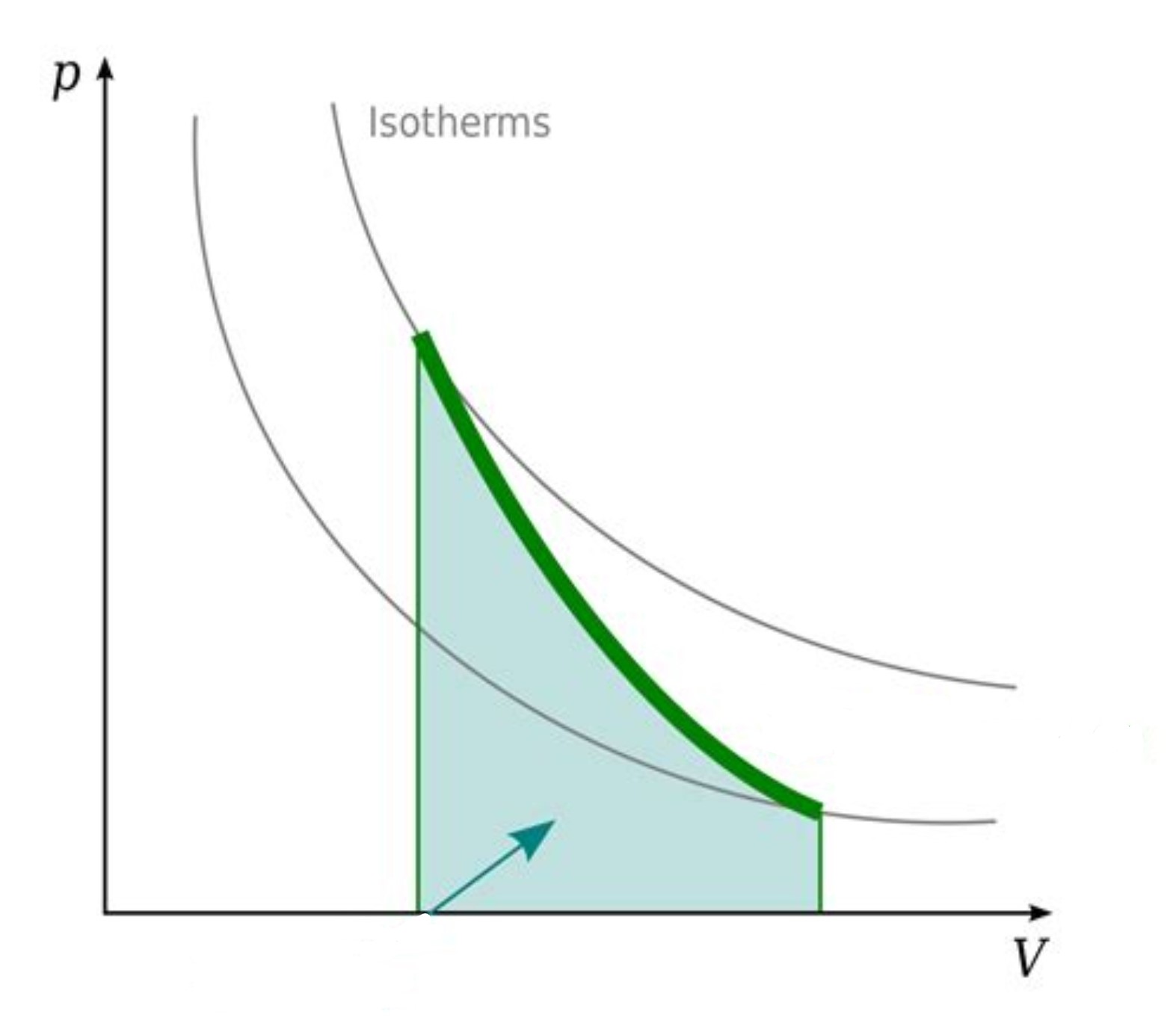
What type of process is this PV diagram showing?
an adiabatic process
What is the change in T or U, Q, and W equal to? (0, positive, or negative)
positive, 0, positive (adiabats have no heat transfer, deltaU = W)
In a full cycle of a thermodynamic processes, what is the change in T or U, Q, and W equal to? (0, positive, or negative)
0, positive, negative (if V increases then decreases, and vice-versa)
Why can PiVi/Ti = PfVf/Tf?
Because R is a constant and when n is constant, the gas law formula can be written as PV/T = nR. Therefore PV/T has to be constant, and the initial and final values are equal.
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
When thermal energy (Q) is transferred to a system the internal energy (U) increases or the system does work (like pushing on a piston to expand). Work is only done if the volume changes W = P(deltaV)
How can you calculate work by looking at a PV diagram?
Find the area of the space below the curve.
When work is done on a system, W is … and the gas typically…
positive, compresses
When a system does work, W is … and the gas typically…
negative, expands
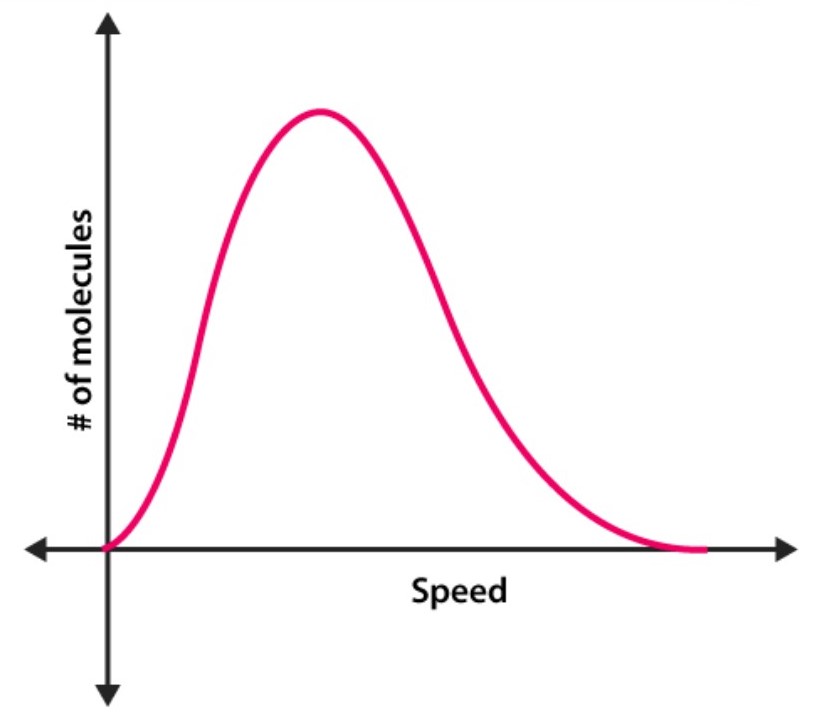
What is this a graph of?
A Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution
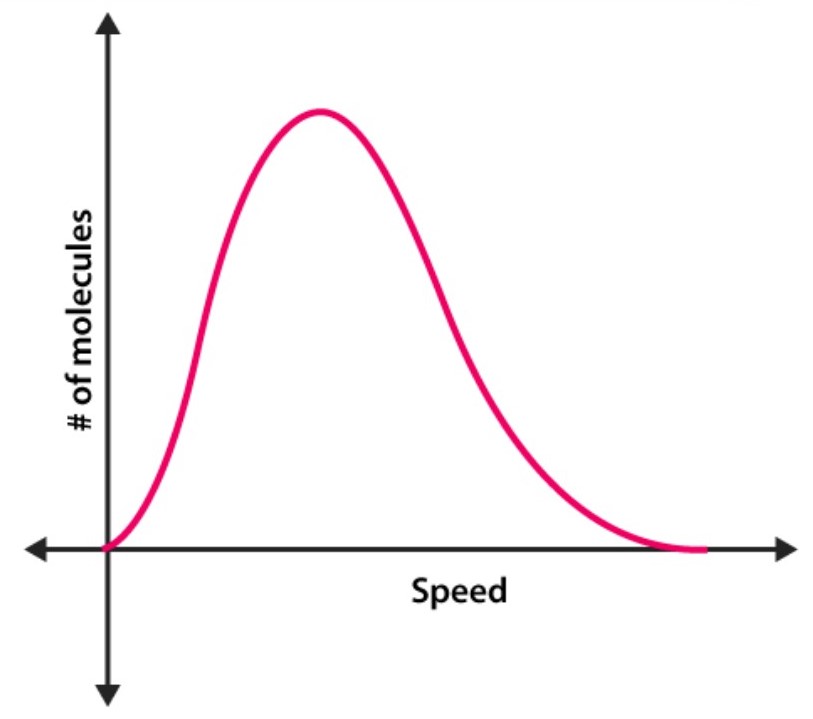
What does the highest point on the graph represent?
the most probable speed of all the molecules in that system
The pressure of an ideal gas in a closed container…
is equal throughout