Physiology of oropharynx and esophagus
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What two things occur in the oral cavity?
mechanical digestion (mastication) and enzymatic digestion (via saliva)
digestion of ___ and ____ starts in the oral cavity
starch (carbohydrates) and lipids
saliva contains ____ (what enzyme)
salivary amylase
what are the 3 salivary glands, which one produces the most saliva, and what type of saliva is produced by each?
parotid: serous
submand: mucous-serous; 70% of saliva production
subling: mucous
Saliva starts out ____ and once it is released it is ____ compared to plasma
starts isotonic and at the end its hypotonic
if the saliva comes out too fast/ production is too fast then what do we see in its makeup?
it is produced too fast for ion exchange → increased Na+ and Cl- in saliva
regulation of salivary secretion: what are 4 things that have a positive affect on the nucleii salvatorii to increase saliva production
chewing, taste, smell, and nausea
regulation of salivary secretion: what are 4 things that have a negative affect on the nucleii salvatorii to decrease saliva production
sleep, fatigue, dehydration, and atropine
What cranial nerves are involved with saliva production?
CN VII and CN IX
What are the 3 protective functions of saliva?
bicarb to neutralize acid
cooling hot food
lubrication that provides oral hygiene
what are the 3 digestive functions of saliva?
alpha-amylase: digest starches/carbs
lingual lipase: lipid digestion
lubrication of food for swallowing
what are the two enzymes in saliva and what do they initiate the digestion of?
alpha-amylase: starches/carbs
lingual lipase: lipids
saliva is always ___ to plasma
hypotonic
What is the function of the R proteins in saliva?
binds to vit B12 (cobalamin) to protect it from acid degradation in the stomach
deglutition (swallowing): describe the oral stage (include voluntary or involuntary)
mouth to oropharynx, bolus is formed, voluntary process
deglutition (swallowing): describe the pharyngeal stage (include voluntary or involuntary)
involuntary process/reflex, the soft palate acts as a valve
deglutition (swallowing): describe the esophageal stage (include voluntary or involuntary)
involuntary phase that transports food to the stomach
the medulla oblongata control the ___ stage of deglutition (swallowing)
esophageal stage
swallowing innervation: impulses are transmitted through the sensory portions of ___ and ___ nerves to the swallowing center in the _____
trigeminal (CN V) and glossopharyngeal (CN IX) → medulla oblongata
the UES and LES are normally in a ____ state, and initiation of swallow ____ both sphincters
normally contracted, swallowing relaxes them
what are the 5 layers of the enteric nervous system from internal to external?
mucosa → submucosal plexus (Meissner plexus) → circular muscle → myenteric plexus (Auerbach’s plexus) → longitudinal muscle
relaxation of the LES is mediated by what two neurotransmitters?
vasoactive intestinal peptide and NO
contraction of the LES is mediated by what two neurotransmitters?
acetylcholine and substance P
What causes difficulty swallowing mainly solid food, regurgitation, weight loss, bad breath, choking, and coughing?
Zenker’s diverticulum
true vs pseudo/false diverticulum:
has all layers of the gut wall
give example
true diverticulum → Meckel’s diverticulum
true vs pseudo/false diverticulum:
lacks the muscularis layer
give example
pseudodiverticulum → Zenker’s diverticulum
what results from failure of LES to function as a sphincter
GERD (reflux esophagitis)
what lacks in newborns and is decreased in pregnancy
LES tone lacks → increased GERD
portal hypertension can lead to what?
esophageal varices (the veins bulge out) and can lead to bleeding
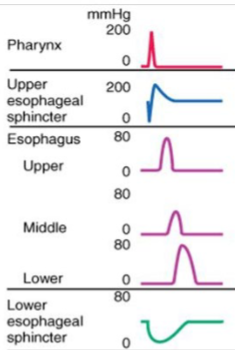
What condition is this pattern from the esophageal manometry showing?
Normal
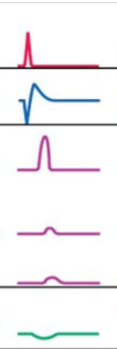
What condition is this pattern from the esophageal manometry showing?
Scleroderma
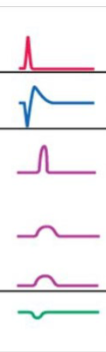
What condition is this pattern from the esophageal manometry showing?
Achalasia

What condition is this pattern from the esophageal manometry showing?
Diffuse esophageal spasm

What condition is this pattern from the esophageal manometry showing?
Pharyngeal paralysis
Failure of relaxation of the upper esophageal sphincter (UES) is most likely due to what muscle?
Cricopharyngeus
During the pharyngeal phase of swallowing, what event prevents aspiration?
Closing of the nasopharynx
A patient with Zenker diverticulum most likely has a dysfunction of what structure?
Cricopharyngeal muscle