Chapter 1 - Principles of Government
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
State (Nation, Nation-State)
An independent political unity characterized by population, territory, government and sovereignty.
Sovereignty
A characteristic of a legitimate state; A state's right to rule itself

Government
A characteristic of a legitimate state; The people and institutions with the authority to establish and enforce laws and public policies
Public Policy
Any course of government action directed toward achieving a national goal

Divine Right
The belief that royalty's right to rule comes from God

Social Contract
An agreement among members of a society to create a state and obey its government

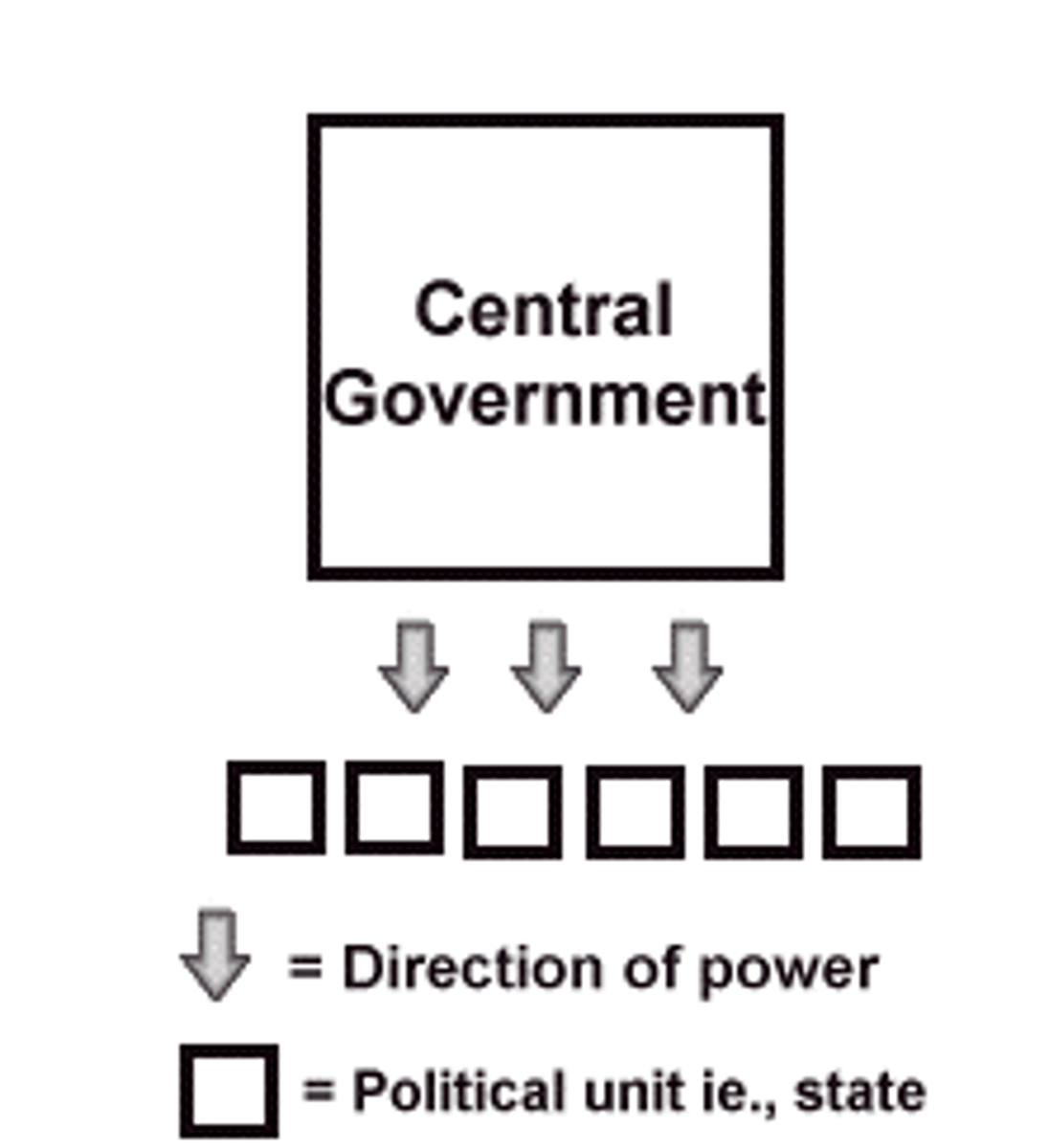
Unitary Government
A form of government in which the central government has authority over all political subdivisions
Confederation
A form of government in which two or more independent states join together to achieve a common goal, but retain their individual sovereignty in other matters

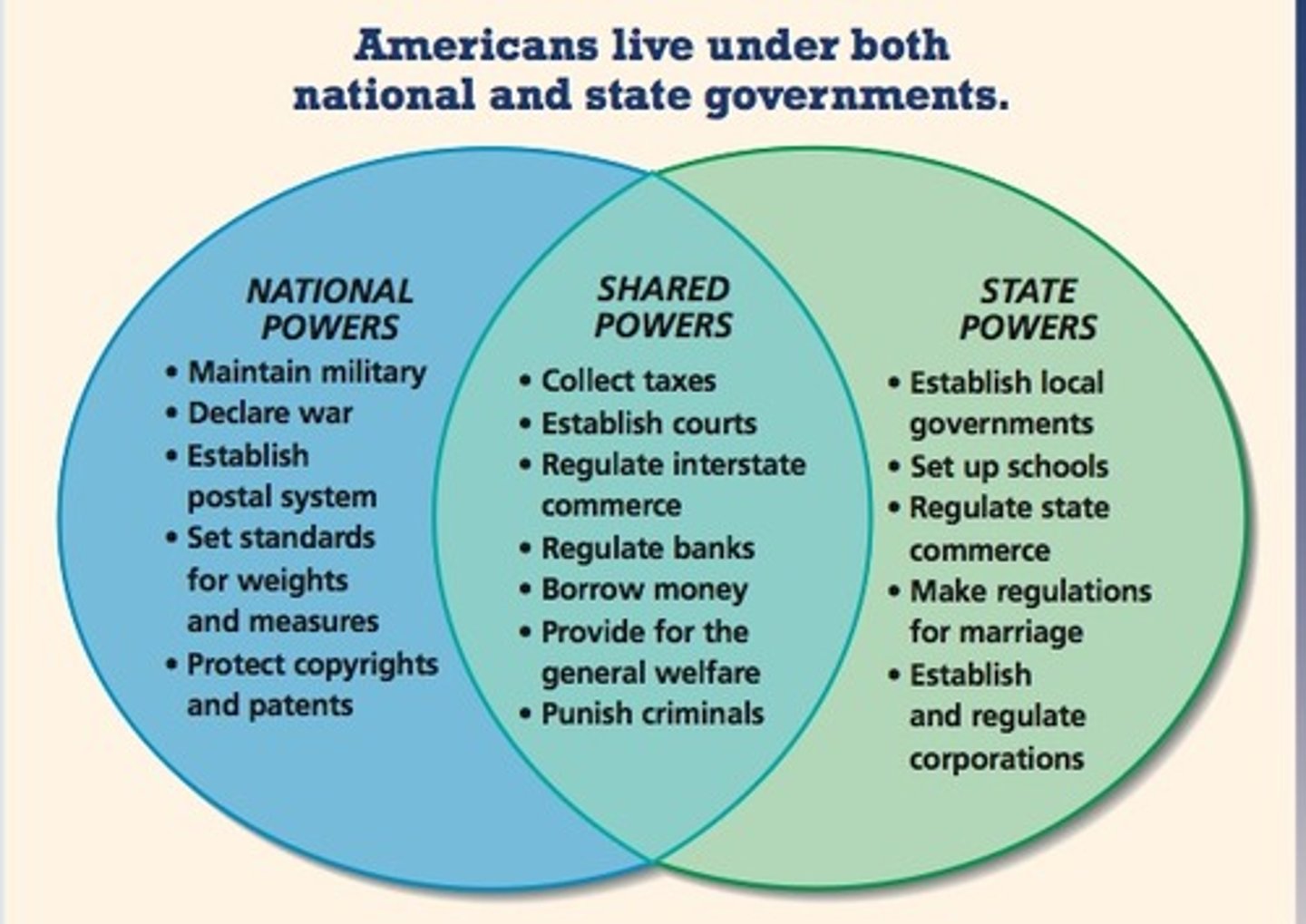
Federal System
A political system in which authority is divided between a national government and its political subdivisions
Autocracy
Rule by one person

Oligarchy
Rule by a small group

Democracy
Rule by the people

Monarchy
A form of autocracy in which the ruler acquires position through inheritance or family
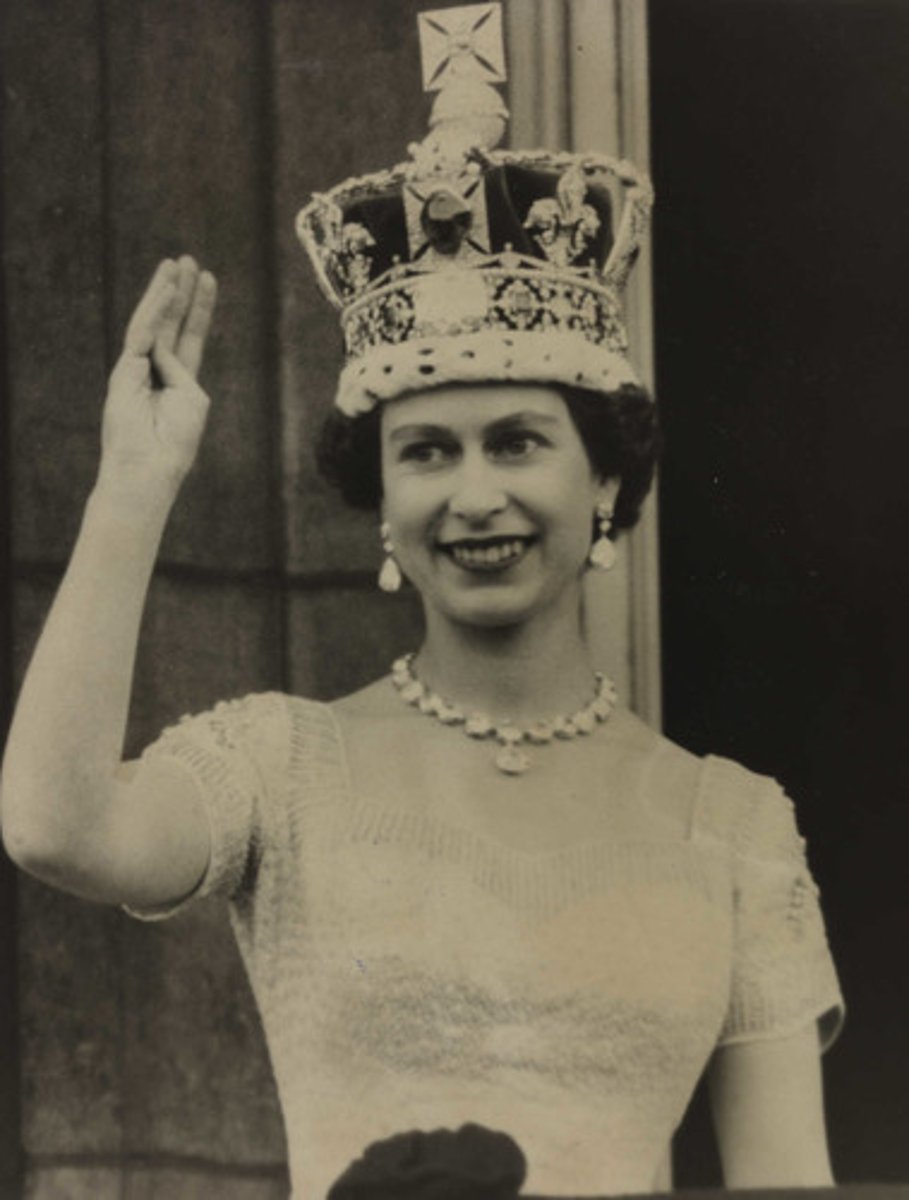

Constitutional Monarchy
A form of government in which the monarch is mainly a ceremonial head of state and shares authority with an elected legislature

Dictatorship
A form of autocracy in which a ruler acquires and maintains leadership through fear and force

Direct Democracy
A form of government in which all citizens have a chance to participate on a first-hand basis

Indirect/Representative Democracy
A form of government in which people elect a group of citizens to represent them in making laws and establishing public policies

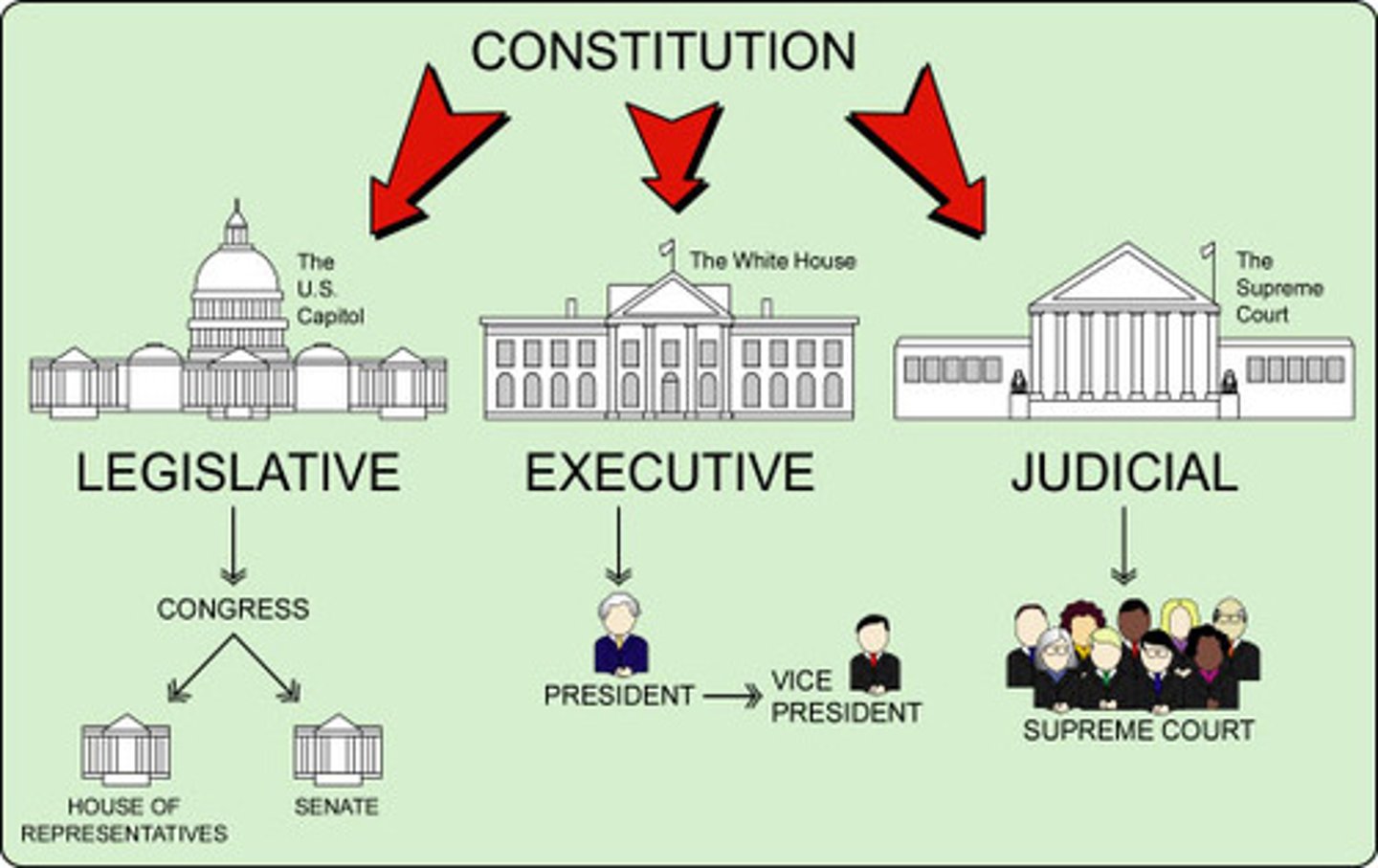
Legislative Power
The power to make and frame public policies
Executive Power
The power to execute, enforce, and administer the law
Judicial Power
The power to interpret the laws, determine the meaning, and to settle disputes that arise within the society
Constitution
A body of fundamental laws setting out the principles, structures, and processes of a government.
Population
A characteristic of a legitimate state; the number does not determine statehood; China is the largest state when considering this characteristic
Territory
A characteristic of a legitimate state; the size does not determine statehood; Russia is the largest state when considering this characteristic
Force
The idea that one person or a small group claimed control over an area and forced all within it to submit to that person's or group's rule.
Evolutionary
The belief that the state evolved from the primitive family. As family members reproduced, the family turned to a clan, then tribe and then government.
Form a More Perfect Union
Purpose of Government - to make everything in our
country as perfect as
possible
Establish Justice
Purpose of Government - create fairness for all
Insure Domestic Tranquility
Purpose of Government - promise that everything in
our country will be peaceful
Provide for the Common Defense
Purpose of Government - care for those in need and protect our nation from invasion and/or war
Promote the General Welfare
Purpose of Government - care for all those citizens who may be in need
Secure the Blessings of Liberty
Purpose of Government - make sure freedom and
fairness continues for ourselves and all our children
Presidential Government
Features a separation of powers between the executive and legislative branches; chief executive is elected independently of the legislature.
Parliamentary Government
The executive branch is made up of a Prime Minister and their cabinet; the legislature (Parliament) is elected by the people and the Prime Minister is chosen by and from the legislature.
Nation
Refers to the nationality of an organized group of people
Country
Refers to the geographic location of an organized group of people