Bio unit trois
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/131
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
1
New cards
4 major macromolecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
carbon containing
carbon containing
2
New cards
Almost all molecules are composed of ______ atoms bonded to eachother and other atoms of different elements
carbon
3
New cards
Organic compounds
carbon based molecules
containing hydrogen atoms in addition to carbon
containing hydrogen atoms in addition to carbon
4
New cards
Why is carbon special?
Very good in forming large and complex molecules
These molecules build structures and carry out functions required for life
These molecules build structures and carry out functions required for life
5
New cards
carbon has ___ electrons in a valence shell which holds 8
4 - it shares electrons with other atoms in 4 covalent bonds
6
New cards
when carbon atoms form hydrogen bonds...
different shapes occur
7
New cards
Molecules shape
function
8
New cards
Carbon chains form the
backbone of most organic molecules
9
New cards
4 different ways in which carbon skeletons can vary
differ in length
be straight
branched
arranged in rings
vary in double bond placement
spatial arrangements
be straight
branched
arranged in rings
vary in double bond placement
spatial arrangements
10
New cards
Isomers
Compounds with the same formula but different structures.
the different shape of isomers add to the diversity of organic molecules and their properties
the different shape of isomers add to the diversity of organic molecules and their properties
11
New cards
Hydrocarbon
molecule consisting of only carbon and hydrogen
major components of petroleum
provide much of the worlds energy
rare in living organisms
major components of petroleum
provide much of the worlds energy
rare in living organisms
12
New cards
carbon atom is most likely to form
covalent bonds
13
New cards
functional group
The first five important chemical groups
affect a molecule's function by chemically reacting
POLAR and hydrophilic so soluble in water
affect a molecule's function by chemically reacting
POLAR and hydrophilic so soluble in water
14
New cards
methyl group
6th group
nonpolar and reactive
affects molecular shape and function
nonpolar and reactive
affects molecular shape and function
15
New cards
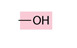
Hydroxyl group
hydrogen atom bonded to an oxygen atom
organic compounds containing hydroxyl groups are called alcohols
no carbon
organic compounds containing hydroxyl groups are called alcohols
no carbon
16
New cards
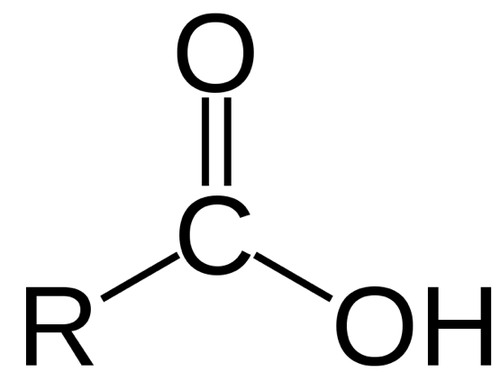
Carboxyl group
Carbon double bonded to an oxygen atom and bonded to a hydroxyl group
The carboxyl group can act as an acid
contributes H+ to a solution becoming ionized
Compounds with this group are called carboxylic acids
The carboxyl group can act as an acid
contributes H+ to a solution becoming ionized
Compounds with this group are called carboxylic acids
17
New cards
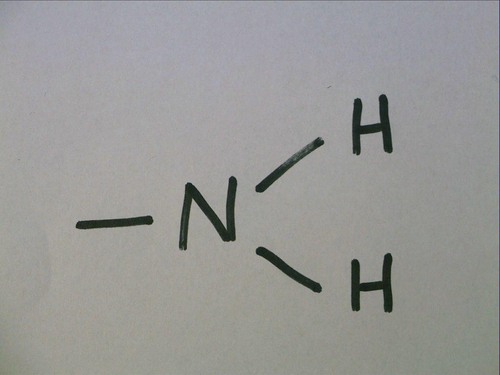
Amino Group
Nitrogen bonded to two hydrogens
act as a base by picking up an H+ solution and becoming ionized
Organic compounds with an amino group are called amines. amino acids contain amino group and carboxyl group
no carbon
act as a base by picking up an H+ solution and becoming ionized
Organic compounds with an amino group are called amines. amino acids contain amino group and carboxyl group
no carbon
18
New cards
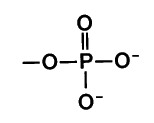
Phosphate group
Consists of a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms
usually ionized
compounds with phosphate groups = organic phosphates (Involved in energy transfers)
no carbon
usually ionized
compounds with phosphate groups = organic phosphates (Involved in energy transfers)
no carbon
19
New cards
Methyl group
Carbon bonded to three hydrogen atoms
methylated compound in the table affects the expression of genes
methylated compound in the table affects the expression of genes
20
New cards
Macromolecules
Gigantic molecule (polysaccharides protein or nucleic acid)
formed by joining smaller molecules usually by dehydration
formed by joining smaller molecules usually by dehydration
21
New cards
Polymer
long molecule consisting of many identical or similar monomers linked by covalent bonds
Make up macro molecules
Make up macro molecules
22
New cards
Monomers
Polymers are made of monomers
23
New cards
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules become covalently bonded to each other with the removal of a water molecule
each monomer contributes part of the water molecule released during the reaction.
reactions are the same regardless of the specific monomers and type of polymer produced
each monomer contributes part of the water molecule released during the reaction.
reactions are the same regardless of the specific monomers and type of polymer produced
24
New cards
Hydrolysis
A chemical reaction the breaks bonds between two molecules by the addition of water a process by which polymers and broken down and an essential part of digestion
bond between monomers is broken by the addition of a water molecule
bond between monomers is broken by the addition of a water molecule
25
New cards
Enzymes
A macromolecule usually a protein that serves as a catalyst changing the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by the reaction.
26
New cards
Diversity of Polymers
Key to diversity: arrangement in order of monomers
monomers are essentially universal
small molecules common to all organisms are ordered into large ones varying from species to species
monomers are essentially universal
small molecules common to all organisms are ordered into large ones varying from species to species
27
New cards
Carbohydrates
range from small sugar molecules (monomers) to large polysaccharides
28
New cards
Monosaccharides
simple sugars
monomers of carbohydrates
simplest carbohydrate
generally have a formula of CH2 O
monomers of carbohydrates
simplest carbohydrate
generally have a formula of CH2 O
29
New cards
Glucose formula
C6H12O6
30
New cards
Two trade marks of a sugar
a number of hydroxyl groups (-OH)
carbonyl group C = O
carbonyl group C = O
31
New cards
What makes fructose sweeter than glucose?
they have the same formula C6H12O6
the arrangement of their atoms make them isomers
the shape of molecules are very important because minor differences give isomers vastly different properties
the arrangement of their atoms make them isomers
the shape of molecules are very important because minor differences give isomers vastly different properties
32
New cards
Shape of molecules
the shape of molecules are very important because minor differences give isomers vastly different properties
33
New cards
Carbon Skeletons
The chain of carbon atoms in an organic molecule, forms the backbone of any molecule.
34
New cards
carbon skeletons of glucose and fructose
6 carbons long
other monosaccharides may have 3-7 carbons
other monosaccharides may have 3-7 carbons
35
New cards
most common sugars are
pentose (5 carbon sugar) and hexose (6 carbon sugar)
36
New cards
-ose
sugars
37
New cards
-ase
enzymes
38
New cards
representation of sugars
ring shape
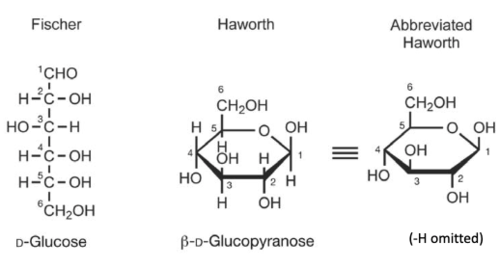
39
New cards
how is sugars ring shape formed
carbon 5 attached to oxygen bonds with carbon 1
carbon 6 extends above ring
carbon 6 extends above ring
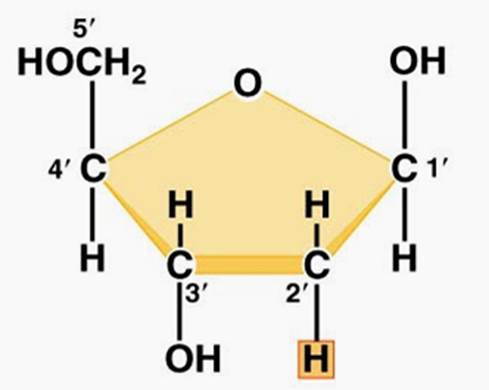
40
New cards
fuel and sugar
monosaccarides (esp glucose) = main fuel molecules for cellular works
41
New cards
when glucose is broken down
cells release energy
42
New cards
dextrose
aqueous solution of glucose
43
New cards
two monosaccharides are linked to form a
disaccaride
44
New cards
disaccaride
sugar molecule consisting of two monosaccharides linked by dehydration reaction
45
New cards
sucrose
most common disaccharide
made of glucose monomer + fructose monomer
made of glucose monomer + fructose monomer
46
New cards
Polysaccharides are long chains of
sugar units
47
New cards
Polysaccaride
large macromolecule formed from monosaccharides
linked by dehydration
function as storage molecules or structural compounds
linked by dehydration
function as storage molecules or structural compounds
48
New cards
starch
A storage polysaccharide in plants consisting entirely of glucose.
consists of long chains of glucose monomers
coils into helical shape
may be branched or unbranched
ex: potato wheat corn rice
consists of long chains of glucose monomers
coils into helical shape
may be branched or unbranched
ex: potato wheat corn rice
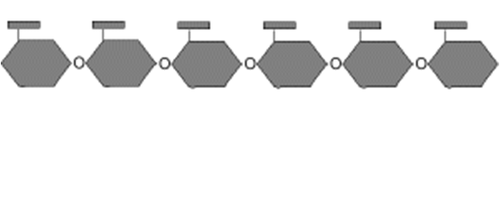
49
New cards
Starch branks
starch granules serve as carbohydrate banks
plant cells can withdraw glucose for energy or building material
plant cells can withdraw glucose for energy or building material
50
New cards
enzyme
humans + most animals have enzymes which can hydrolyze plat starch to glucose
51
New cards
glycogen
An extensively branched glucose storage polysaccharide found in the liver and muscle of animals; the animal equivalent of starch.
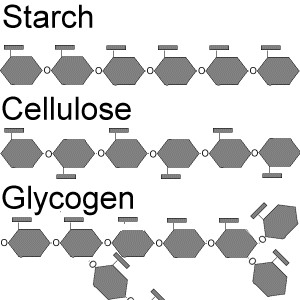
52
New cards
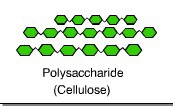
Cellulose
a structural polysaccharide of plant cell walls, consisting of glucose monomers joined by beta glycosidic linkages
most abundant compound
molecules linked by hydrogen bonds
insoluble fiber cellulose that passes through digestive tract remains unchanged
most abundant compound
molecules linked by hydrogen bonds
insoluble fiber cellulose that passes through digestive tract remains unchanged
53
New cards
Chitin
A structural polysaccharide, consisting of amino sugar monomers, found in many fungal cell walls and in the exoskeletons of all arthropods.
54
New cards
Lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
nonpolar
nonpolar
55
New cards
what are lipids mainly contain
carbon and hydrogen atoms
56
New cards
what are lipids linked by
how do lipids react to water
how do lipids react to water
nonpolar covalent bonds
making them hydrophobic
making them hydrophobic
57
New cards
Types of lipids
fats, phospholipids, steroids
58
New cards
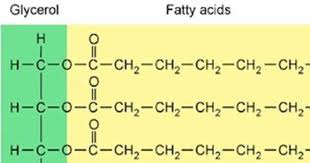
Fats
large lipid made from 2 smaller molecules: glycerol and fatty acids
3 fatty acids to glycerol produces a fat
synonym for fat : triglyceride
3 fatty acids to glycerol produces a fat
synonym for fat : triglyceride
59
New cards
glycerol
3 carbons
each bearing a hydroxyl group (OH)
each bearing a hydroxyl group (OH)
60
New cards
Fatty Acid
consists of a carboxyl group -cOOH
and hydrocarbon chain
fats are hydrophobic because of C-H bond
and hydrocarbon chain
fats are hydrophobic because of C-H bond
61
New cards
Unsaturated fatty acid
fatty acid whos hydrocarbon chain contains one or more double bond
this double bond = one fewer hydrogen atom
which causes kinks in the carbon chain
this double bond = one fewer hydrogen atom
which causes kinks in the carbon chain
62
New cards
saturated fatty acid
maximum number of hydrogen atoms
compact
solidifies at room temp
max number of hydrogen atoms
ex butter meat
compact
solidifies at room temp
max number of hydrogen atoms
ex butter meat
63
New cards
Unsaturated
ex oils
liquids because not packed tightly
double bonds in hydrocarbon skeleton
liquids because not packed tightly
double bonds in hydrocarbon skeleton
64
New cards
Phospholipids
found in all cell membranes
similar to fats mais contain TWO fatty acid instead of three
similar to fats mais contain TWO fatty acid instead of three
65
New cards
what are phospholipds composed of?
glycerol joined to two fatty acids and a phosphate group
66
New cards
phospholipids and water
Non polar Hydrophilic heads and polar hydrophobic tails
67
New cards
4 major macromolecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
carbon containing
carbon containing
68
New cards
Almost all molecules are composed of ______ atoms bonded to eachother and other atoms of different elements
carbon
69
New cards
Organic compounds
carbon based molecules
containing hydrogen atoms in addition to carbon
containing hydrogen atoms in addition to carbon
70
New cards
Why is carbon special?
Very good in forming large and complex molecules
These molecules build structures and carry out functions required for life
These molecules build structures and carry out functions required for life
71
New cards
carbon has ___ electrons in a valence shell which holds 8
4 - it shares electrons with other atoms in 4 covalent bonds
72
New cards
when carbon atoms form hydrogen bonds...
different shapes occur
73
New cards
Molecules shape
function
74
New cards
Carbon chains form the
backbone of most organic molecules
75
New cards
4 different ways in which carbon skeletons can vary
differ in length
be straight
branched
arranged in rings
vary in double bond placement
spatial arrangements
be straight
branched
arranged in rings
vary in double bond placement
spatial arrangements
76
New cards
Isomers
Compounds with the same formula but different structures.
the different shape of isomers add to the diversity of organic molecules and their properties
the different shape of isomers add to the diversity of organic molecules and their properties
77
New cards
Hydrocarbon
molecule consisting of only carbon and hydrogen
major components of petroleum
provide much of the worlds energy
rare in living organisms
major components of petroleum
provide much of the worlds energy
rare in living organisms
78
New cards
carbon atom is most likely to form
covalent bonds
79
New cards
functional group
The first five important chemical groups
affect a molecule's function by chemically reacting
POLAR and hydrophilic so soluble in water
affect a molecule's function by chemically reacting
POLAR and hydrophilic so soluble in water
80
New cards
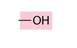
Hydroxyl group
hydrogen atom bonded to an oxygen atom
organic compounds containing hydroxyl groups are called alcohols
no carbon
organic compounds containing hydroxyl groups are called alcohols
no carbon
81
New cards
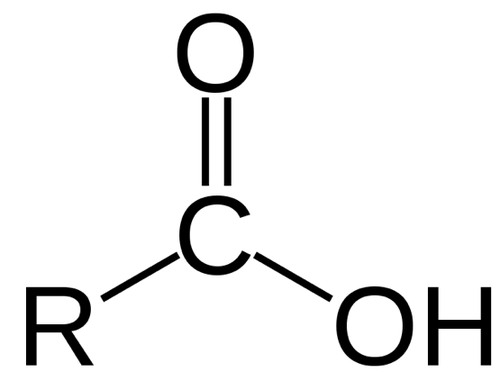
Carboxyl group
Carbon double bonded to an oxygen atom and bonded to a hydroxyl group
The carboxyl group can act as an acid
contributes H+ to a solution becoming ionized
Compounds with this group are called carboxylic acids
-COOH
The carboxyl group can act as an acid
contributes H+ to a solution becoming ionized
Compounds with this group are called carboxylic acids
-COOH
82
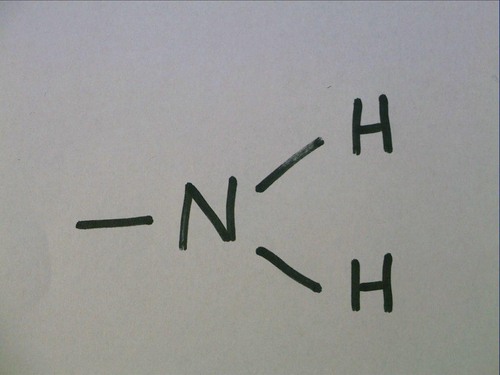
New cards
Amino Group
Nitrogen bonded to two hydrogens
act as a base by picking up an H+ solution and becoming ionized
Organic compounds with an amino group are called amines. amino acids contain amino group and carboxyl group
-NH2
no carbon
act as a base by picking up an H+ solution and becoming ionized
Organic compounds with an amino group are called amines. amino acids contain amino group and carboxyl group
-NH2
no carbon
83
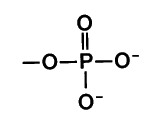
New cards
Phosphate group
Consists of a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms
usually ionized
compounds with phosphate groups = organic phosphates (Involved in energy transfers)
-OPO3 2-
no carbon
usually ionized
compounds with phosphate groups = organic phosphates (Involved in energy transfers)
-OPO3 2-
no carbon
84
New cards
Macromolecules
Gigantic molecule (polysaccharides protein or nucleic acid)
formed by joining smaller molecules usually by dehydration
formed by joining smaller molecules usually by dehydration
85
New cards
Polymer
long molecule consisting of many identical or similar monomers linked by covalent bonds
Make up macro molecules
Make up macro molecules
86
New cards
Monomers
Polymers are made of monomers
87
New cards
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules become covalently bonded to each other with the removal of a water molecule
each monomer contributes part of the water molecule released during the reaction.
reactions are the same regardless of the specific monomers and type of polymer produced
each monomer contributes part of the water molecule released during the reaction.
reactions are the same regardless of the specific monomers and type of polymer produced
88
New cards
Hydrolysis
A chemical reaction the breaks bonds between two molecules by the addition of water a process by which polymers and broken down and an essential part of digestion
bond between monomers is broken by the addition of a water molecule
bond between monomers is broken by the addition of a water molecule
89
New cards
Enzymes
A macromolecule usually a protein that serves as a catalyst changing the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by the reaction.
90
New cards
Diversity of Polymers
Key to diversity: arrangement in order of monomers
monomers are essentially universal
small molecules common to all organisms are ordered into large ones varying from species to species
monomers are essentially universal
small molecules common to all organisms are ordered into large ones varying from species to species
91
New cards
Carbohydrates
range from small sugar molecules (monomers) to large polysaccharides
92
New cards
Monosaccharides
simple sugars
monomers of carbohydrates
simplest carbohydrate
generally have a formula of CH2 O
monomers of carbohydrates
simplest carbohydrate
generally have a formula of CH2 O
93
New cards
Glucose formula
C6H12O6
94
New cards
Two trade marks of a sugar
a number of hydroxyl groups (-OH)
carbonyl group C = O
carbonyl group C = O
95
New cards
What makes fructose sweeter than glucose?
they have the same formula C6H12O6
the arrangement of their atoms make them isomers
the shape of molecules are very important because minor differences give isomers vastly different properties
the arrangement of their atoms make them isomers
the shape of molecules are very important because minor differences give isomers vastly different properties
96
New cards
Shape of molecules
the shape of molecules are very important because minor differences give isomers vastly different properties
97
New cards
Carbon Skeletons
The chain of carbon atoms in an organic molecule, forms the backbone of any molecule.
98
New cards
carbon skeletons of glucose and fructose
6 carbons long
other monosaccharides may have 3-7 carbons
other monosaccharides may have 3-7 carbons
99
New cards
most common sugars are
pentose (5 carbon sugar) and hexose (6 carbon sugar)
100
New cards
-ose
sugars