ACYMANS5: Standard Costing and Variance Analysis
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
A company controls its production costs by comparing its actual monthly production costs with the expected levels. Any significant deviations from expected levels are investigated and evaluated as a basis for corrective actions. The quantitative technique that is most probably being used is
a. Time-series or trend regression analysis
b. Correlation analysis
c. Differential calculus
d. Standard cost variance analysis
d. Standard cost variance analysis
A primary purpose of using a standard cost system is
a. To make things easier for managers in the production facility
b. To provide a distinct measure of cost control
c. To minimize the cost per unit of production
d. B and c are correct
b. To provide a distinct measure of cost control
The standard cost card contains quantities and costs for
a. Direct material only
b. Direct labor only
c. Direct material and direct labor only
d. Direct material, direct labor, and overhead
d. Direct material, direct labor, and overhead
Of the following variances, the one that is most useful in assessing the performance of the Purchasing Department is the
a. Idle capacity variance
b. Materials purchase price variance
c. Labor rate variance
d. Materials price usage variance
b. Materials purchase price variance
Materials usage variances are normally chargeable to the
a. Production Department
b. Purchasing Department
c. Finished Goods Department
d. Materials Storage Department
a. Production Department
The most probable reason a company would experience a favorable labor rate variance and an unfavorable labor efficiency variance is that
a. The mix of workers assigned to the particular job was heavily weighted toward the use of higher paid, experienced individuals
b. The mix of workers assigned to the particular job was heavily weighted toward the use of new, relatively low-paid, unskilled workers
c. Because of the production schedule, workers from other production areas were assigned to assist in this particular process
d. Defective materials caused more labor to be used in order to produce a standard unit
b. The mix of workers assigned to the particular job was heavily weighted toward the use of new, relatively low-paid, unskilled workers
A favorable fixed overhead volume variance occurs if
a. There is a favorable labor efficiency variance
b. There is a favorable labor rate variance
c. Production is less than planned
d. Production is greater than planned
d. Production is greater than planned
Company X is developing standards for its products. Each unit of output of the product requires 0.92 kilogram of a particular input. The allowance for waste and spoilage is 0.02 kilogram of this input for each unit of output. The allowance for rejects is 0.11 kilogram of this input for each unit of output.
The standard quantity in kilograms of this input per unit of output should be
a. 0.90
b. 0.92
c. 0.79
d. 1.05
d. 1.05
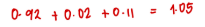
Company X is developing direct labor standards. A particular product requires 0.71 direct labor-hours per unit. The allowance for breaks and personal needs is 0.04 direct labor-hours per unit. The allowance for cleanup, machine downtime, and rejects is 0.12 direct labor-hours per unit. The standard direct labor-hours per unit should be
a. 0.71
b. 0.87
c. 0.67
d. 0.55
b. 0.87


The following July information is for Company X:
Material price variance is
2,610 U
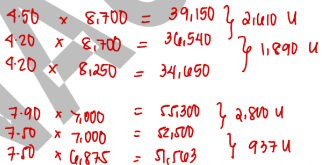

The following July information is for Company X:
Material usage variance is
1,890 U
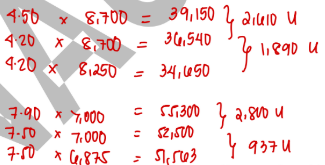

The following July information is for Company X:
Labor rate variance is
2,800 U
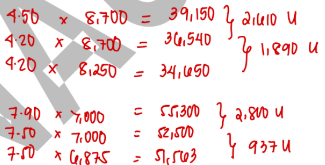

The following July information is for Company X:
Labor efficiency variance
937 U
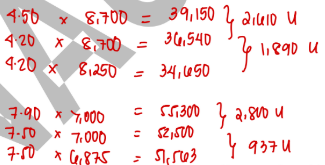
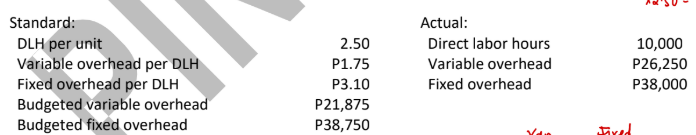
ABC Company uses a standard cost system for its production process and applies overhead based on direct labor hours. The following information is available for the month when ABC made 4,500 units:
Total overhead variance (1-way approach)
9,687 U
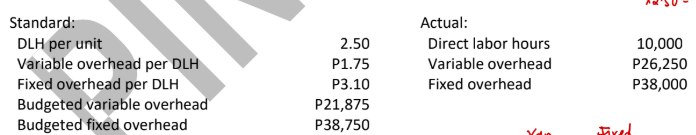
ABC Company uses a standard cost system for its production process and applies overhead based on direct labor hours. The following information is available for the month when ABC made 4,500 units:
Controllable variance (2-way approach)
5,812 U
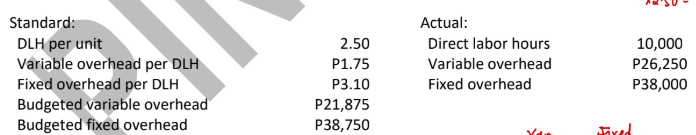
ABC Company uses a standard cost system for its production process and applies overhead based on direct labor hours. The following information is available for the month when ABC made 4,500 units:
Uncontrollable variance (2-way approach)
3,875 U
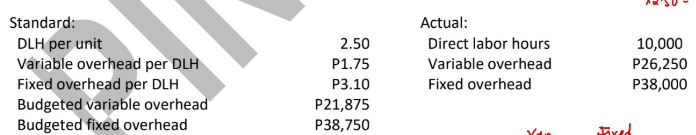
ABC Company uses a standard cost system for its production process and applies overhead based on direct labor hours. The following information is available for the month when ABC made 4,500 units:
Spending variance (3-way approach)
8,000 U
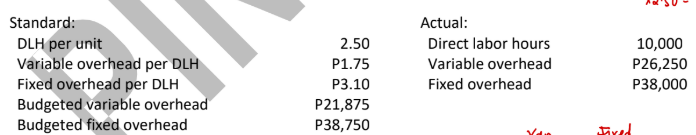
ABC Company uses a standard cost system for its production process and applies overhead based on direct labor hours. The following information is available for the month when ABC made 4,500 units:
Efficiency variance (3-way approach)
2,188 F
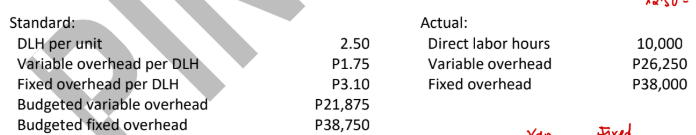
ABC Company uses a standard cost system for its production process and applies overhead based on direct labor hours. The following information is available for the month when ABC made 4,500 units:
Volume variance (3-way approach)
3,875 U
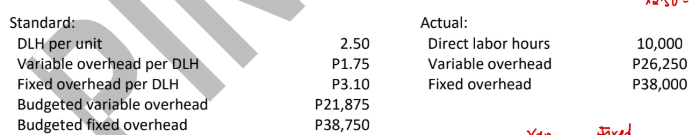
ABC Company uses a standard cost system for its production process and applies overhead based on direct labor hours. The following information is available for the month when ABC made 4,500 units:
Variable overhead spending variance (4-way approach)
8,750 U
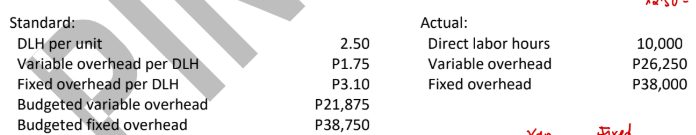
ABC Company uses a standard cost system for its production process and applies overhead based on direct labor hours. The following information is available for the month when ABC made 4,500 units:
Fixed overhead spending variance (4-way approach)
750 F
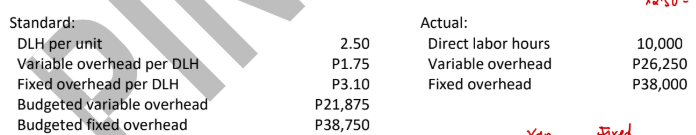
ABC Company uses a standard cost system for its production process and applies overhead based on direct labor hours. The following information is available for the month when ABC made 4,500 units:
Variable overhead efficiency variance (4-way approach)
2,188 F
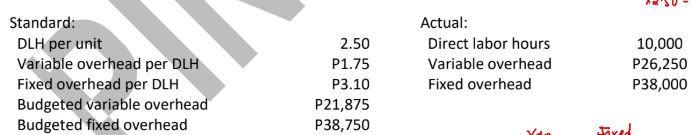
ABC Company uses a standard cost system for its production process and applies overhead based on direct labor hours. The following information is available for the month when ABC made 4,500 units:
Volume variance (4-way approach)
3,875 U
Information on ABC Company’s direct material costs is as follows
Standard unit price P3.60
Actual quantity purchased 1,600
Standard quantity allowed for actual production 1,450
Material purchase price variance – favorable P240
What was the actual purchase price per unit?
a. P3.00
b. P3.11
c. P3.45
d. P3.75
c. P3.45
The information on ABC Company’s direct labor costs for the month of January 2025 is as follows:
Actual direct labor hours 34,500
Standard direct labor hours 35,000
Total direct labor payroll P241,500
Direct labor efficiency variance – favorable P3,200
What is ABC Company’s direct labor rate variance?
a. P17,250 unfavorable
b. P20,700 unfavorable
c. P21,000 unfavorable
d. P21,000 favorable
b. P20,700 unfavorable