evr- concepts of population dynamics
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Population Dynamics
A general study of population changes
Population
Group of individuals of the same species living in the same area
Species
All individuals that are capable of interbreeding; made up of population
Demography (Demographics)
The statistics of human populations
1. Abundance
2. Birth Rates
3. Death Rates
4. Growth Rates
5. Age Structure
5 Key Properties of Population
As people increase in age, increase in the inability to reproduce/repopulate
Why is Age Structure (in Population) even more important than the other properties?
crude
Human population is often reported as ____ rates
Crude Rates
per 1,000 people (ex. 2 births per 1000 people per year)
Exponential growth
A population increasing by a constant percentage per unit time
Human Population growth peaked at 2.1% from 1965-1970, and has since slowed down to 0.9% in the present, despite predictions of it continuing to climb through the years
How has human growth grown/decayed exponentially from the 20th century? What was predicted?
4
How many stages of Human Population Growth are there?
Early period of hunter and gatherers; total population, a few million
Stage 1 of Human Population Growth
Stage 2 of Human Population Growth
Rise of agriculture, production of food without having to be hunter-gatherers; Increase in population density and human population bc people focused on other things besides next food source
Stage 3 of Human Population Growth
Industrial Revolution; Improvement in health and food security by transportation of goods lowered death rates and led to double in population
Stage 4 of Human Population Growth
Current stage; allowed for increase in population density and human population to be over 8B
Saltaire (UK); The owner, Sir Titus Salt, removed his workers from slums and poor living conditions and provided better resources for workers bc he realized it improved worker productivity, which made him more money; this idea spread and lead to growth of life expectancy and worker value
What was the largest industrial building in the world? How is it relevant to human population growth?
Industrial Revolution
An era of vast improvements in medicine, technology, and sanitation; reduced diseased and extended life expectancy
Green Revolution
An era of advances in plant breeding techniques, fertilizer use, and irrigation and agricultural mechanization that helped avoid the huge population crisis coming out of WW2 by helping prevent mass starvation
The Bubonic Plague (Black Death) in Europe
What event in history was the only time global death rates exceeded growth rates?
Doubling Time
Time required for a population to double in size; calculated by Rule of 70
Rule of 70
used to calculate doubling time for exponential growth; found by dividing annual growth rate (%) into 70
Doubling Time (Years) = 70 / Annual Growth Rate (%)
Calculations for Rule of 70
Logistic Growth
S-shaped curve that TEMPORARILY increases exponentially to the inflection point; reaches upper population limit at the logistic carrying capacity where growth rate=0
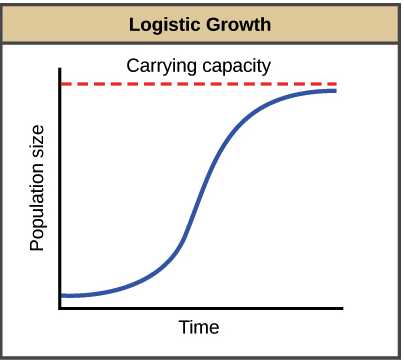
Exponential growth shows unrestrained, rapid population increase (J-curve) with unlimited resources, while logistic growth models realistic growth, starting exponentially but slowing as it nears the environment's carrying capacity (K), resulting in an S-shaped curve as resources become limited.
Logistic Growth vs Exponential Growth
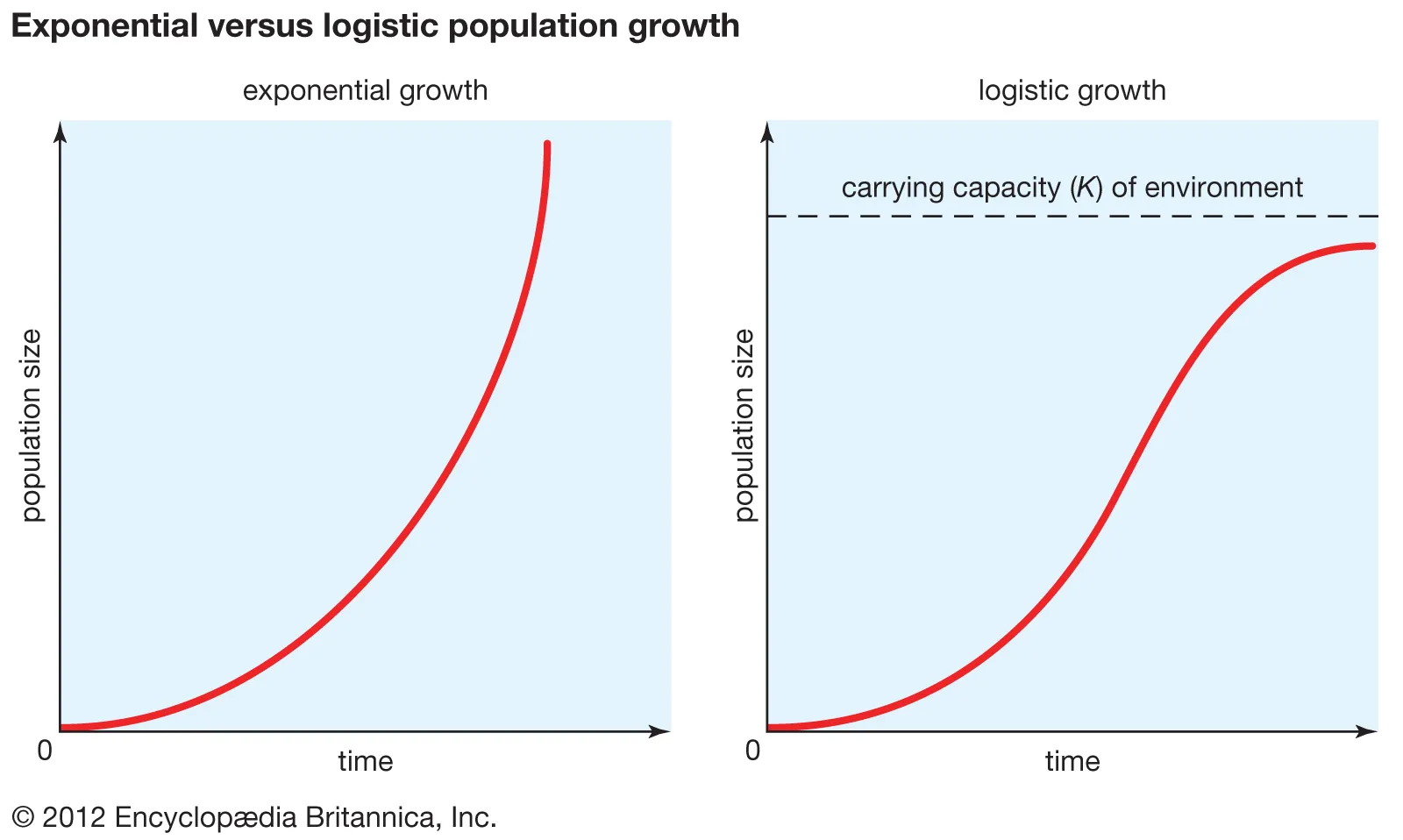
No, they do not have a constant environment, constant carrying capacity, or a homogenous population; the death rate also wouldn’t be as low if such
Do animal populations actually follow the Logistic Growth Curve?
Total Fertility Rate
Number of children born to an average woman over her lifetime; strongly influenced by the opportunities women have in society
Total Fertility Rate; repopulation is necessary for population growth
What statistic is most important in population growth? Why?
Social Factors: Cultural expectations, Economic issues
Technical Factors: Access to birth control, economic
resources
First Child Decisions- Lengthen time between generations; slow growth
What 3 factors control Total Fertility Rate?
These curves ignore characteristics of the environment that affect different age groups (food, water, shelter, disease); Age structure is used to rectify this
Why are exponential and logistic growth curves not always reliable to measure data? What is used to rectify this?
Age Structure
Express how population is divided among age groups; displays implication of current and future social, economic, and environmental conditions
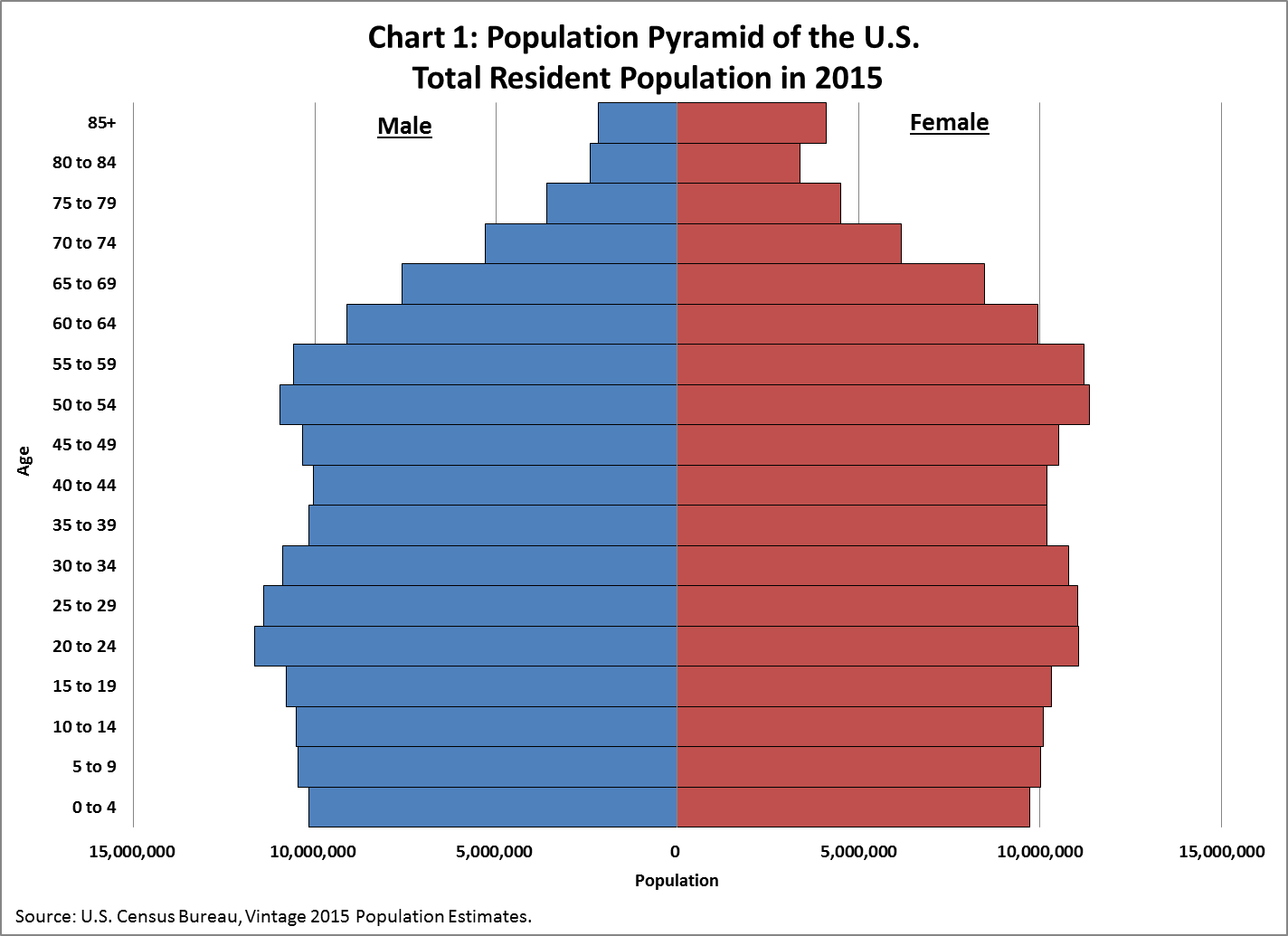
Pyramid
Inverted Pyramid
Column
Column with buldge
4 Types of Age Structure
Pyramid Age Structure
shows a population with many young and high death rate (short average lifetime)
Inverted Pyramid Age Structure
Population with large elderly population and small youth (declining growth)
Column Age Structure
birth rate AND death rate are low, little change in pop
Column with bulge
Event in the past caused a high birth or death rate for some age group
Demographic Transition
A 3-stage pattern of change in birth rates and death rates
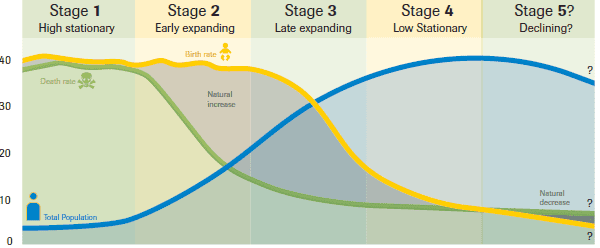
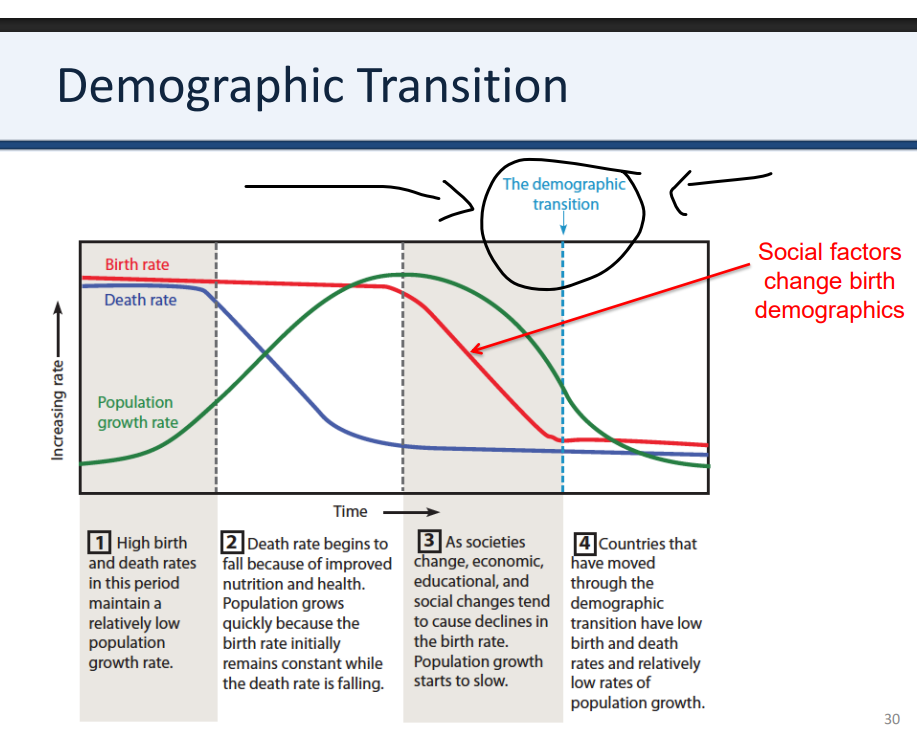
High Birth & Death Rates (Pre-Industrial)
Stage 2: Death Rate Falls, Birth Rate Stays High (Early Expanding)
Birth Rate Falls (Late Expanding)
What are the 3 stages of Demographic Transition?
Population growth rate
Birth Rate + Death rate= ___________
True
T/F: The demographic transition is not always the same for all countries (diff economies, diff cultures/religion, etc.)
Maximum Lifetime
Max possible age to which an individual in a species can live
Life expectancy
Average number of years an individual in a species can expect to live
Acute and Chronic diseases
What is a common aspect of life that heavily impacts life expectancy rates?
Number of People
Impact of each person on the environment
How does human population affect the environment? (2 factors)
T= P (population size) x I (environmental impact per person)
Formula for the total impact of human population on the environment
Modern tech
_____ increases the use of resources and enables us to impact the environment in new ways
Human Carrying Capacity
The maximum population the planet can sustain indefinitely; depends on quality of life people desire, willing to accept
Extrapolation from past growth (problem-solving)
Packing problem approach (only allow certain amount in certain places)
Deep ecology (sustain the biosphere)
Estimation Methods for Human Carrying Capacity
Short-term
Intermediate Term
Long Term
Limiting Factors of Human Carrying Capacity
Short Term Limiting Factors of Human Carrying Capacity
Affect population immediately (e.g.food shortages)
Intermediate-term Limiting Factors of Human Carrying Capacity
Affect population for 1-10 years (e.g. desertification, dispersal of pollutants)
effects not apparent until after 10 years (e.g. soil erosion, decline in groundwater supply, climate change)
Long-term Limiting Factors of Human Carrying Capacity
Delay age of first child bearing
Birth control
National programs to reduce birth rates
What are some approaches for achieving Zero Population Growth?