IB Chem Unit 7 (Heat)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Heat and Temperature
Heat is the energy transferred from one body to another due to a temperature difference.
The total kinetic energy of random motion of particles in a substance
What is temperature?
Measure of particles’ average kinetic energy
Energy of random motion of particles in a substance
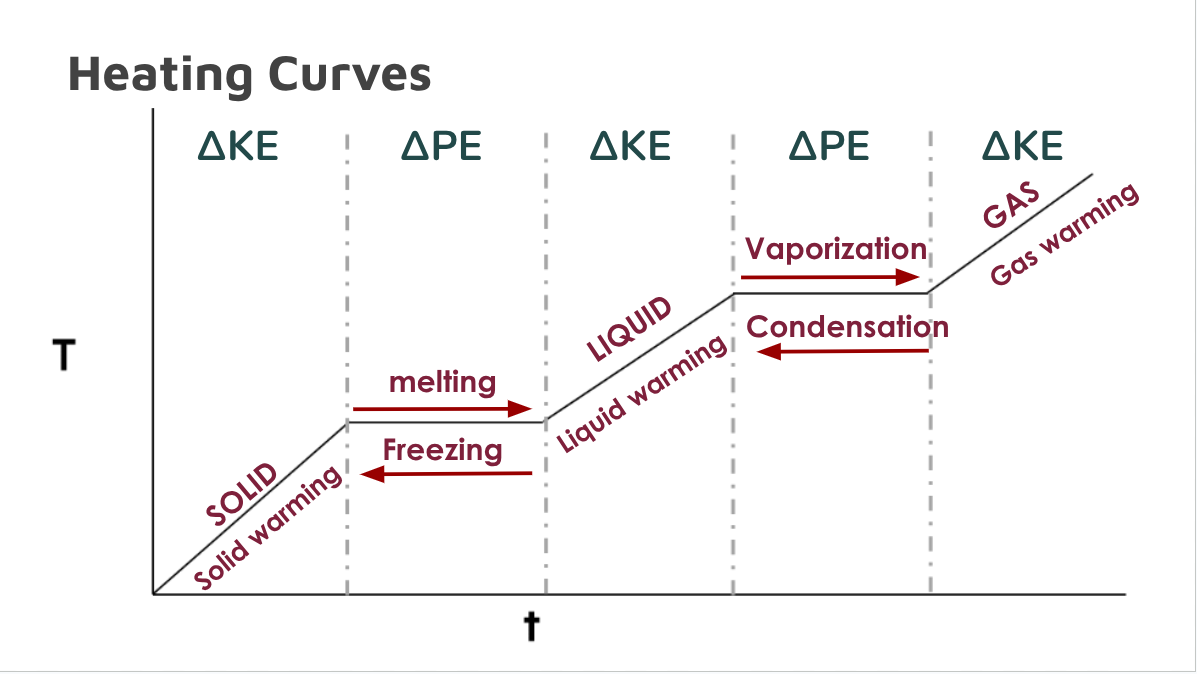
Heating Curves
Heating curves show the energy (heat) needed to overcome intermolecular forces and change the state of matter
Shows how much energy is needed to melt ice (s → l) or boil water (l → g).
Why does temperature remain constant during a phase change?
Because energy is being used to overcome intermolecular forces of attraction
Forces of vibration > forces of attraction
Energy is used to break out of crystal lattice
After particles are free to move, motion and temperature increase
Change in kinetic energy (∆KE)
Happens when there are changes in temperature.
Slopes
Changes in potential energy (∆PE)
Happens when there are changes of state of matter
Plateau or flat lines
Heating Curve Diagram (not a Flashcard)
Heat Equation
q = heat absorbed or released (J)
m = mass of sample (g)
c = specific heat capacity (J/g °C)
ΔT = change in temperature (Tf – Ti)

Specific Heat Capacity, c
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius (1°C)
This is different for every substance.
Measuring Energy During a Phase Change
During a phase change, temperature stays constant!
We need a NEW equation since we cannot use ΔT
q = m·ΔH
q = heat absorbed or released (J)
m = mass (g) or mole
ΔHfusion or ΔHvaporization = enthalpy (J/g)
Heat of Fusion
ΔHfusion is the heat for a phase change from solid to liquid
Heat of fusion is energy added to 1 gram or 1 mole of a solid at its melting point
All of the added energy is used to increase the kinetic energy of the molecules to cause the change from solid to liquid
Temperature remains constant
Heat of Vaporization
ΔHvaporization is the heat for a phase change from liquid to gas
Heat of vaporization is energy added to 1 gram or 1 mole of a liquid at its boiling point
All of the added energy is used to increase the kinetic energy of the molecules to cause the change from liquid to gas
Temperature remains constant
Two and Three Steps Heat Equation
Deals mostly with water (H2O)
KEY points:
Water freezes at 0°C
Water boils at 100 °C
Measuring Changes in Heat Energy
Calorimeter or Bomb Calorimeter
Used to measure heat energy as it is transferred to water
Q = mcΔt
Δt of water
m = mass of water
Cp of water
Assumptions in Calorimeter and Bomb Calorimeter
assumed that their is no heat loss and that all heat is absorbed by water.