Antibiotics: Other types
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Describe cephalosporins
- More bactericidal on G+ve than G-ve
- Resistant to β-lactamase.
- Has a six membered ring so has less ring strain so is more stable to acid hydrolysis than penicillins.
- Work by preventing transpeptidase enzyme to prevent cell wall synthesis.
Compare the activity of cephalosporins to penicillins.
Have a lower activity but have a broader spectrum of activity.
How does cephalosporin interact with the transpeptidase enzyme?
- Beta lactam is essential to activity.
- Free carbonyl is essential to activity
- Bicyclic system (two rings next to eachother) is essential
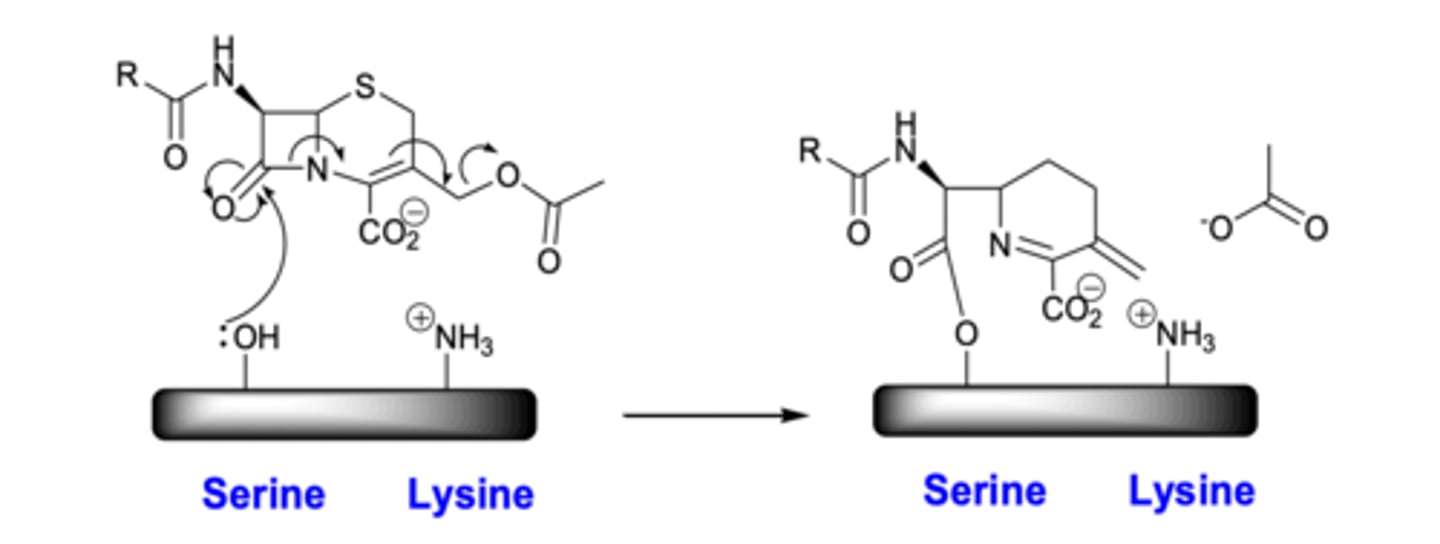
What can effect activity of cephalosporins?
Hydrolysis of acetate reduces compound activity therefore blocking metabolic hydrolysis prolongs activity.
Why are people with penicillin allergies allergic to cephalosporins?
Penicillin and cephalosporins have very similar chemical structures so there may be cross-sensitivity.
Describe cycloserine.
- An anti-mycobacterial agent
- Inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis
-Used as an anti-tuberculosis drug.
What type of antibiotic target bacterial cell metabolism?
- Sulfonamide
What are issues with sulfonamides?
Have limited applications due to toxicity.
What is a prodrug?
A compound that becomes an active drug upon administration.
What is the prodrug of sulfonamide?
Protonsil

How do sulfonamides work?
- Prevent folic acid synthesis by competing with PABA for the active site of dihydropteroate synthase.
- Folic acid is essential in nucleic acid synthesis in bacteria.

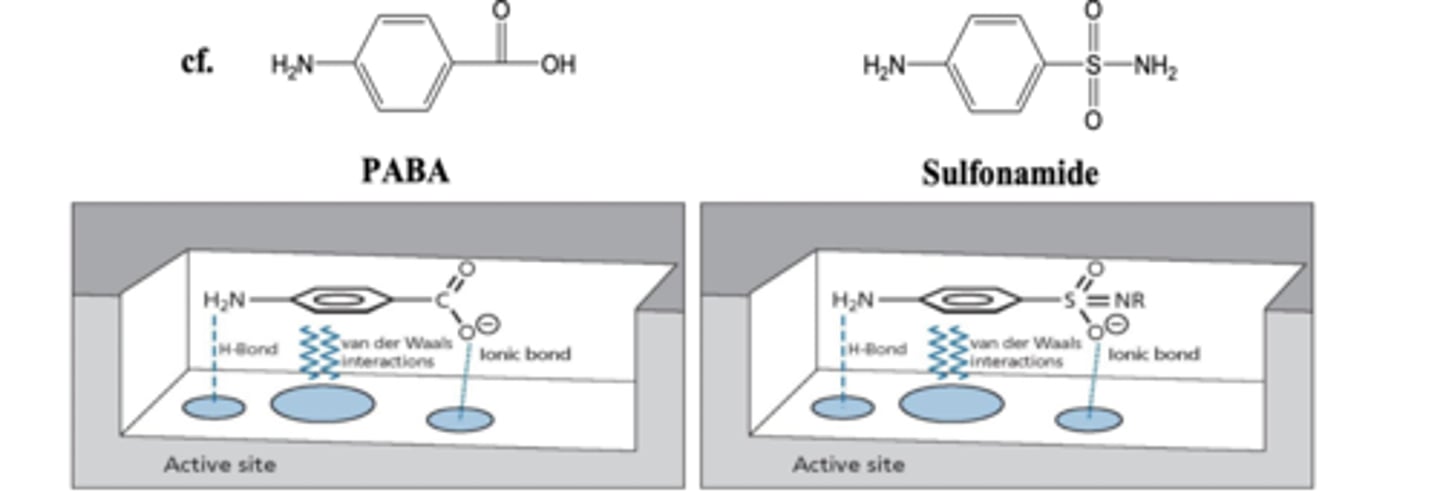
What interactions must sulfanomides have in order to compete with PABA?
To bind to the active site of dihydropteroate synthase it must have:
- H bond donor
- Van der Waal (aromatic)
- Ionic bond.
Also cannot be too big as it wont fit in the active site.
What does bacteriostatic mean?
Inhibits growth of bacteria. They don't kill bacteria however gives the body the chance to amount an immune response.
What does bacteriocidal mean?
Kills bacteria
Are sulfonamides bacteriostatic or bactericidal?
Bacteriostatic as they block nucleic acid synthesis which stops cell growth and division.
What groups are essential for activity in sulfonamides?

How can sulfonamides be resisted by bacteria?
- Increased concentrations of PABA in bacteria.
- Enzyme mutations.
How can increased concentration of PABA cause resistance to sulfonamides?
Sulfonamides are reversible competitive inhibitors of dihydropteroate synthase and therefore high concentrations of PABA can prevent sulfonamides working.
How does enzyme mutations cause resistance to sulfonamides?
Mutations in dihydropteroate synthase in bacteria prevents sulfonamides binding to it so it cannot work.
What is Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole used for?
- Both used simultaneously as antibiotics.
- Used together as they inhibit two steps in the same biosynthetic pathway (sequential blocking).
- This allows lower doses of each drug which reduce side effects.
Describe aminoglycosides
- Broad spectrum antibiotics.
- Bacteriocidal
- Examples include streptomycin and gentamicin.
Describe chroamphenicol.
- Broad spectrum bacteriostatic antibiotic.
- Can be toxic especially in newborns.
- Binds to the large ribosomal subunit and blocks peptide bond formation.
Describe macrolides.
- Bind to the large ribosomal subunit and blocks peptide bond formation.
- Examples include Clarithromycin and Erythromycin.
Describe tetracyclines.
- Most widely prescribed broad spectrum antibiotic after penicillin.
- They bind to the small ribosome unit preventing tRNA binding.
- They are transported into cells by active transport and diffusion.
Describe the structure activity relationship of tetracyclines.
- Can change Rs to increase activity.
- Cannot change anything else as will decrease antibiotic activity.

How are tetrocyclines made:
- Semi synthetically.
- Natural tetracyclines are made via bacterial fermentation.
- Natural tetracyclines are then altered synthetically.