From slides - Marketing 2024 Final
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
marketing concept
= the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering and exchanging offerings that have value of customers, clients, partners, and society
goals of marketing
attract new customers by promising superior value
keep + grow current customers by delivering value + satisfaction
marketing management orientations/philosophies
product orientation, sales orientation, marketing orientation, value based orientation
sales orientation
focus on sales force and promos to encourage buying
sell as much as possible
market / marketing orientation
focus on understanding consumer needs and wants (of target market)
deliver better satisfaction
marketing mix
4 ps
product
price
promotion
place
importance of customers
products are solutions to needs and wants
want ppl to buy products
how to build customer relationships
offer products that perform
exceed expectations
realistic pricing
give buyer facts
offer commitment to the product and after sale support
solve problems
cultivate relationships
customer equity
refers to the amt of value the customer base generates
better to build relationships w customers
less costly
strong competition
customer loyalty
effective marketing strategy
survive Econ downturn
how to build the relationship
identify customers
understand customer values
understand how the customer wants to interact
importance of customer satisfaction
needs/wants are met
positive feelings created
product / interaction has exceeded / met expectations
org:
org objectives met
building relationship w customer
s/h are happy
strategic marketing process
org allocates its market mix resources to reach its target market + objectives
maintain a fit between the org’s objectives and resources and evolving market opportunities
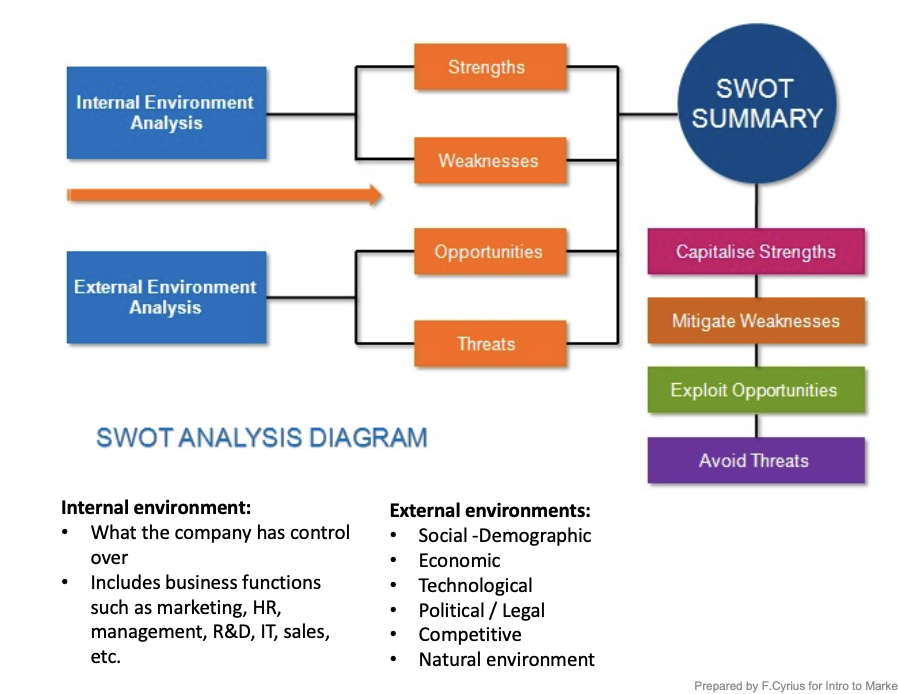
swot analysis
INTERNAL
strength: the things that the company does well
weakness: things the company does poorly
EXTERNAL
opportunities: conditions in the external env that favour strengths (not strategies)
threats: trends that don’t relate to existing strengths / favour areas of weakness
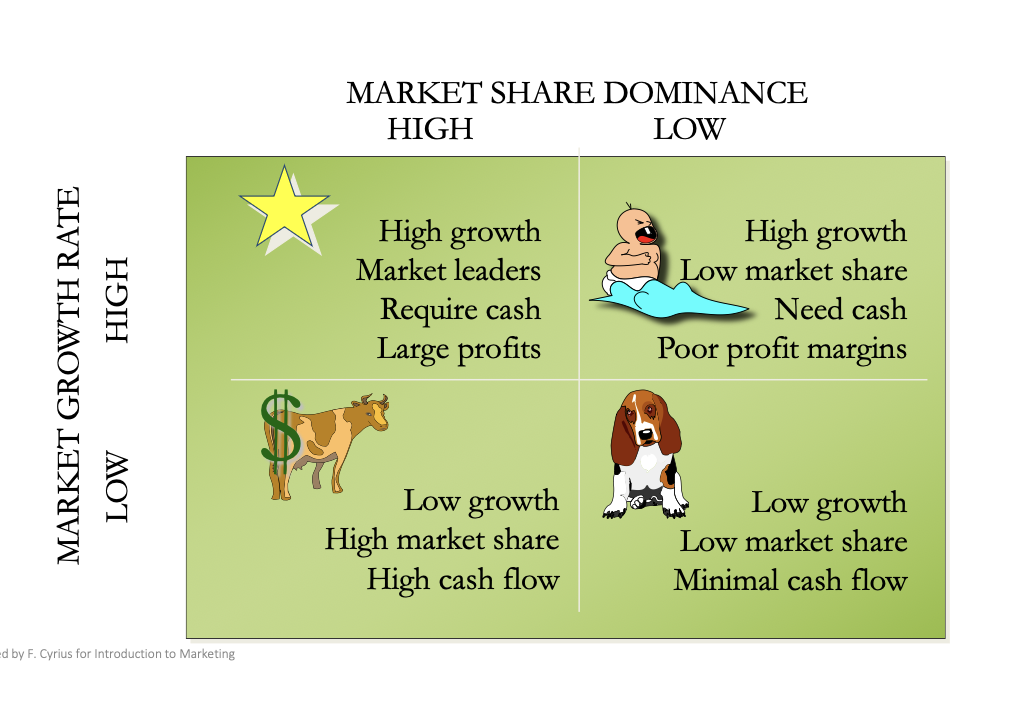
bcg matrix
market share dominance x market growth rate
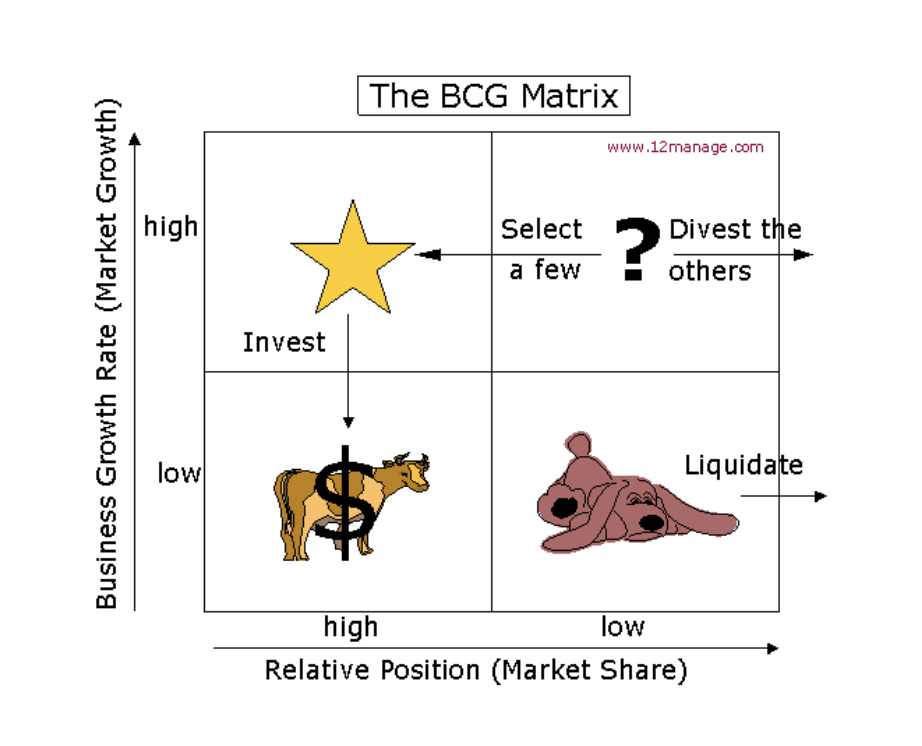
stars | problem Childs
cash cows | dogs
market product growth strategies
Market penetration
Increase market share by selling more of the same products or services in the current market.
Product development
Create new products or modify existing ones to attract new customers and increase market share.
Diversification
Expand into new markets or introduce new products to reduce dependency on a single market or product line.
Market development
Sell existing products or services in new markets to broaden market share. For example, a bakery could start selling to businesses.
Strategic partnerships
Partner with other brands to access their audience.
various external environments
economic: median income, interest rate, debt, unemployment, etc
natural: climate, crime, shortage of natural resources, inc migration, etc
tech: obsolescence, computers, wireless tech, inc in private funding, ai, etc
sociodemographic: minority, foreign, origin
cultural: courtships, dance, music, gift giving, tool making, etc
understand how to ID the trends in the external environments that support/hinder your marketing strategy
generations: traditionalists (value authority, hard workers), boomers (expect deference to opinions), gen x (work as hard as needed), millenials (respect must be earned), gen z (still emerging)
political / legal environment
protection of industries
native land claims
deregulation
Labour laws
political stability
inc in local taxation
foreign trade regulations
canadian competitive act
social welfare policies
predatory pricing
price cutting that lessens competition
price discrimination
charging different prices to competitors buying like quantities of products
misleading price advertising
misrepresenting the usual selling price
resale price maintenance
suppliers requiring subsequent resellers to offer products at a stipulated price
federal legislation affecting marketing
section 34- pricing - forbids suppliers from charging diff prices to competitors purchasing like quantities of goods - forbids price cutting that lessens competition
section 36 - pricing and advertising - forbids ads that misrepresented the usual selling price
s. 38 - pricing - forbids suppliers from req subsequent resellers to offer products at a stipulated price
s. 33- mergers - forbids mergers by which competition is or likely to be lessened to the detriment of the interests of the public
national trademark & true labelling act - CS as a national trademark. req commodities to be properly labelled / described in ads for the purpose of indicating material content / quality
consumer packaging and labeling act - provides a set of rules to make sure that full info is disclosed by the manufacturer, packer,/distributor
req all products to be in French and English
traditional Canadian std units of weight, volume, measure
motor vehicle safety act - mandatory safety standards for motor vehicles
food and drug act - prohibits the ad and sale of adulterated or misbranded foods, drugs, cosmetics
personal info protection & electronic documents act - establishes rules to govern the collection, use, and disclosure of personal info the recognizes right of individual privacy
law recognizes the needs of an org to collect, use, / disclose personal info for appropriate purposes
market share calculation ($)
your brand sales $ / total segment sales $
market share calculation (units)
your brand sales units / total segment sales units
market share
= the % of the total market (in units or $) that ur brand/ product controls
step down approach to estimating market size
size of overall mkt in comparison to all of Canada
size of mtl market compared to all of QC
size of price sensitive (or other adjective) segment of mtl consumers
size of (specific product) sales in mtl

fixed costs (FC)
do not fluctuate with changing volumes of production (eg advertising, overhead)
Variable costs (VC)
directly associated with volume of production (eg labour, materials)
Contribution margin
how much is left over after accounting for the variable costs to cover fixed expenses
the % tells you the % of each $ that goes towards FC
Contribution margin formula
in units: CM (unit) = SP (unit) - VC (unit)
as a %: CM (units as a %) = (SP (unit) - VC (unit))/SP (unit)
Profit contribution
represents how much is left after accounting for all costs (both FC and VC
100% = (for profit contribution)
VC (% of sales or price) + CM (% of sales or price)
per unit contribution (CM)
unit SP - unit VC
per unit profit margin
per unit contribution - per unit fixed costs
Breakeven analysis
BE (units) = total FC / (SP (unit) - VC (unit) or CM
BE ($):
= total FC /((SP(unit) - VC (unit))/SP(unit))
= total fc/(1-(VC(unit)/SP(unit))
price elasticity
measures how responsive demand would be to change to a change in price
price elasticity: %∆ in demand
= new - old / old
% ∆ in selling price
beginning - new / new
PE
= % change in demand / % change in selling price
interpreting price elasticity
PE < 1 - price inelastic
decrease in price = dec in demand
lower price usually = dec profits, raising price = inc profits
PE > 1 - price elastic
dec in price yields a greater inc in demand
higher price = less demand (vice versa)
lowering price = inc profit
raising price = dec profit
PE = 1
unit elastic
an inc or dec in price yields the same change in demand
cross price elasticity
examines the relationship of changing the price of one product and measuring the effect on the demand on a second product
complementary products
raising the price of one will decrease demand in the other (burgers and fries)
substitute products
raising the price in one will lead to a demand for the other (eg butter and margarine)
find cross price elasticity
find ∆ in P1 (N - O / O)
find ∆ in D2
CPE = ∆P1/∆D2
price chains, CM % on SP
= (SP(unit) - VC(unit))/SP (unit)
price chains, % markup on cost
= (SP(unit) - VC(unit))/VC(unit)
price chains, formula when CM on SP is known but not SP or VC
SP = (VC (unit))/(100%-CM % on SP)
price chains, formula when you know markup % on cost but not SP or VC
SP = VC (Unit) + markup % on cost x VC (unit)
market
individuals / orgs w needs and wants and the ability to buy (and who will buy)
segmentation
dividing a mkt into smaller homogenous segments
do this bc too many buyers have diff needs and preferences
better allocation of limited resources
target
selecting segments to focus the company’s resources
value proposition, positioning, differentiation
placing the product int he consumer’s head relative to competition
segmentation bases
demographic
geographic
behavioural
psychographic
targeting strategies
evaluating the attractiveness of each segment & selecting 1+ to serve
mass/undiff marketing
differentiated/segmented markering
concentrated (niche) mkting
micromarketing - local or individual marketing
deciding factors for targeting strategy
size of segment
attractiveness
potential growth & sustainability
accessibility of markets
objectives & resources
differentiability and comp
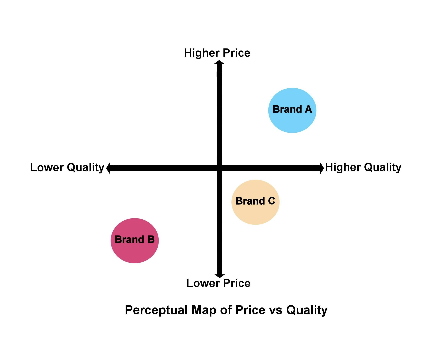
perceptual maps/positioning maps
refers to place the offering occupies in consumer’s minds on important attributes relative to competitive products
design cost effective marketing strategies
brand leadership
head on, challenger
innovation
lifestyle
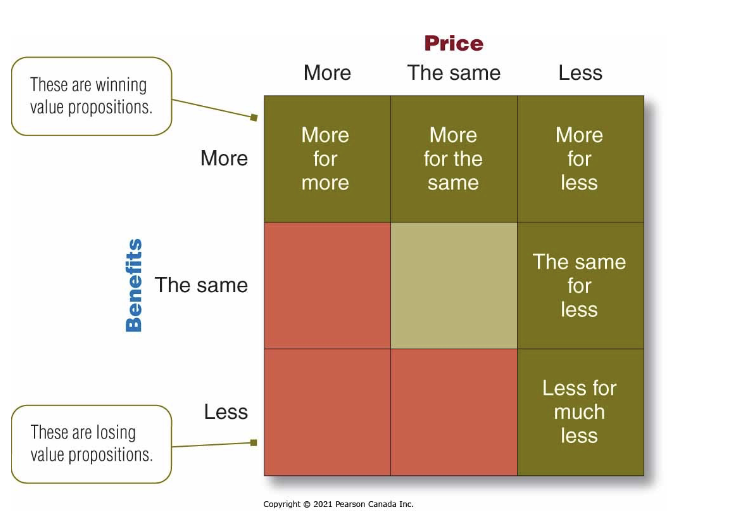
value propositions - examples
more for more - most upsecale
more for the same - high quality, lower price
more for less - best winning prop
the same for less - good deal
less for much less - lower performance at a lower price
consumer purchase decision process
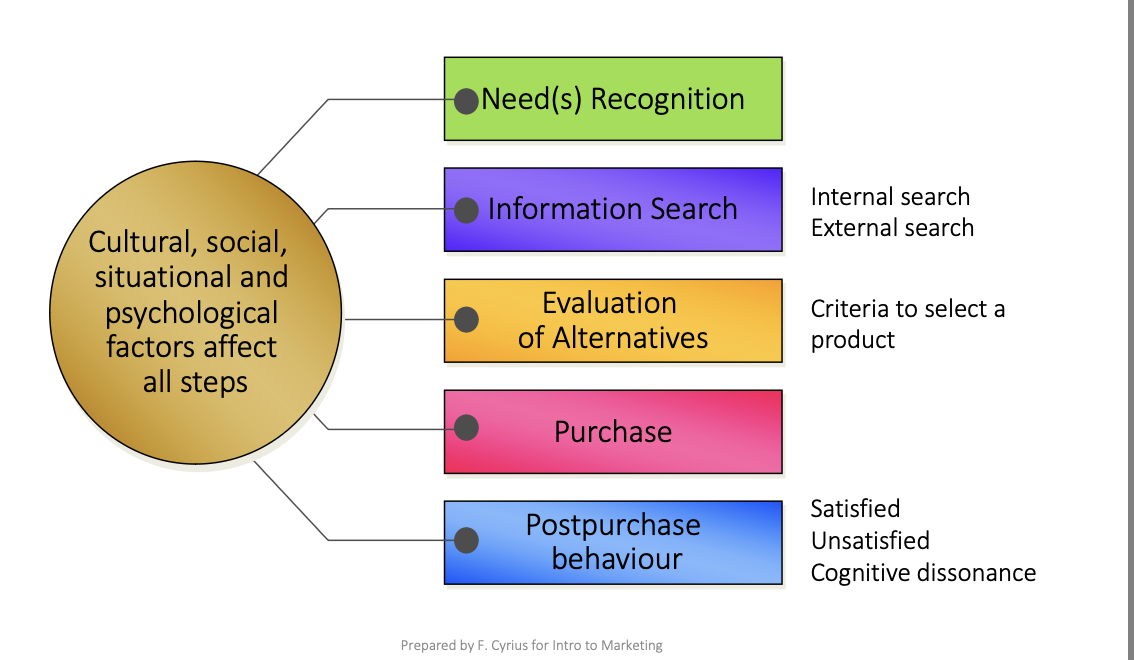
influences on consumer purchase decision process
previous experience
time
interest level
perceived risks - social, financial, performance, etc
info available
types of buying decisions
extensive problem solving
limited problem solving
routine response behaviour
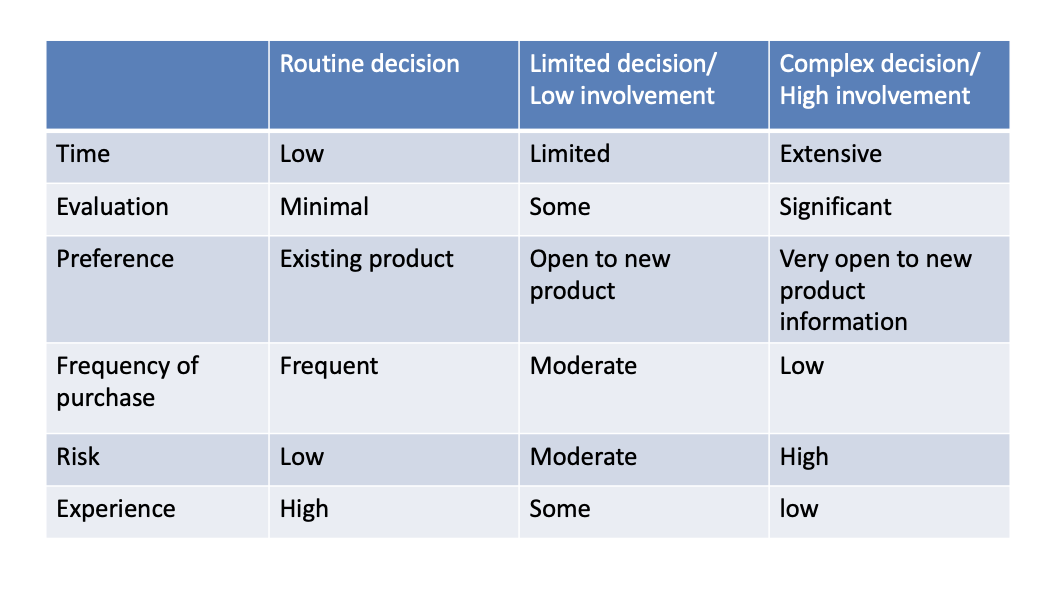
situational factors
specific to the situation that influence / override psych and social issues
related to the purchase and shopping situation & temporal state
involves the 4 P’s —> within marketing’s control
psychological influences
perception - one’s view of reality - type of risks (financial, social, psych, physiological, performance)
motivation - drive behind actions (Maslow)
learning - consumers learn from other consumers
attitudes - positive or negative feelings associated
age and family life cycle - stage in family dev
personality, gender, self concept lifestyle
types of consumer products
convince product
shopping product
specialty product
unsought product
product
soln to consumer needs and wants
bundle of tangible and intangible benefits that a buyer receives in exchange for money / other considerations
when developing new p/s
recog the various terms that pertain to p/s
id the ways that consumer goods can be classified
explain the various components of product strategy
product line
grouping of product items that have major attributes in common
product portfolio
the # of product lines offered by company
packaging
contains the product and informs and persuades - legal standards
simplify label (eg rx bar)
types of consumer products - convenience product
a relatively inexpensive item that merits little shopping effort (eg milk)
types of consumer products - shopping product
requires comparison shopping bc it is more expensive & found in fewer stores (car, appliances)
types of consumer products -specialty product
particular item that consumers search for extensively & are reluctant to accept substitutions (eg custom furniture)
types of consumer products - unsought products
product unknown the potential buyer or a known product that the buyer doesn’t actively seek (eg funeral products)
product life cycle
theory that describes the stages that a new product goes through in marketplace
steps of NPD process
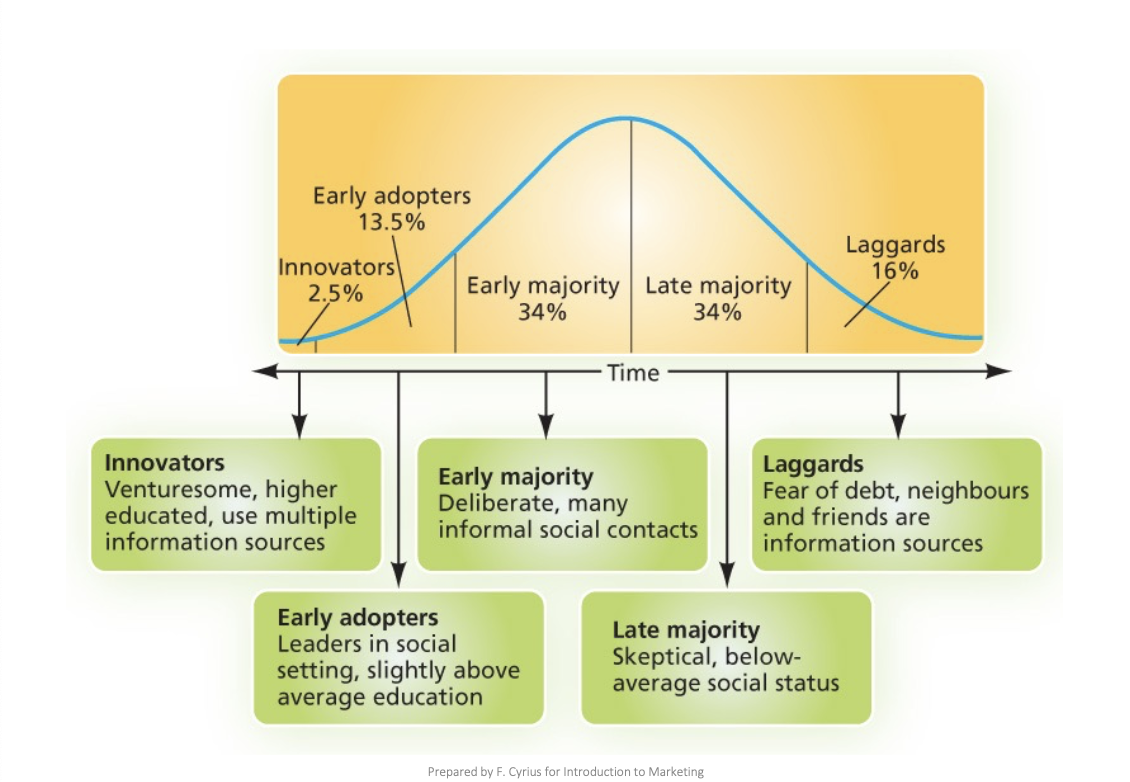
innovator
early adopter
early majority
late majority
laggards
lower prices
major ads
comp enters mkt
strong comp
high prices
recover r and d costs
basic version of product
avail in stores
cupons, sample
BCG dog
influencer
product avail everywhere
negative profit
high profit
BCG cash cow
BCG stars
new features to product
new mkt
reduce promo
peak sales
BCG question marks
max market share
trial phase - important
changing product image / positioning
new segments adopt product
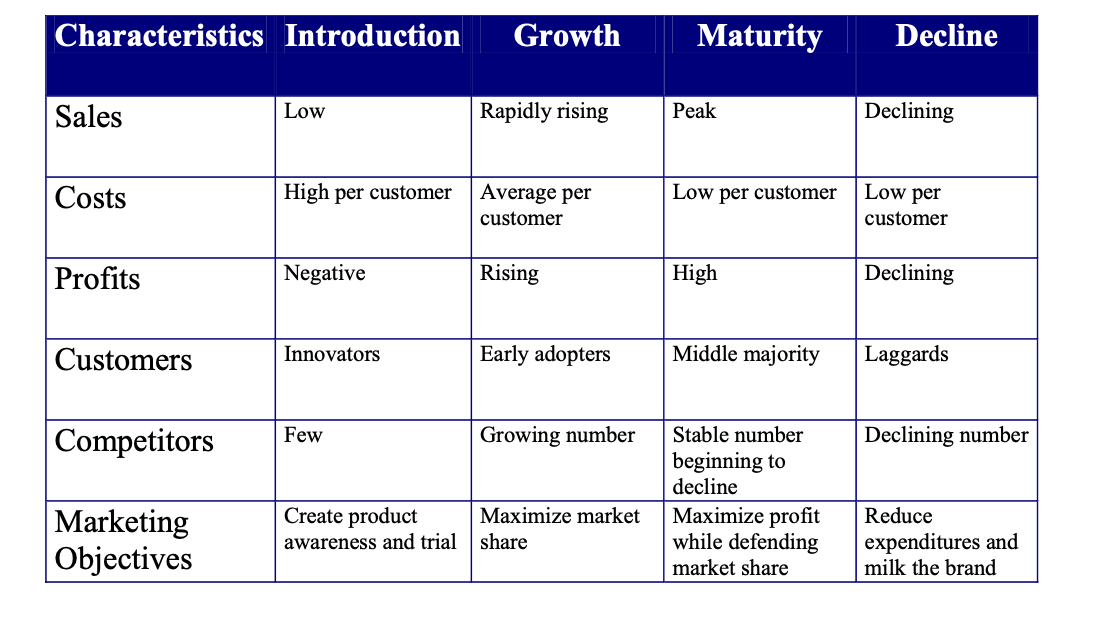
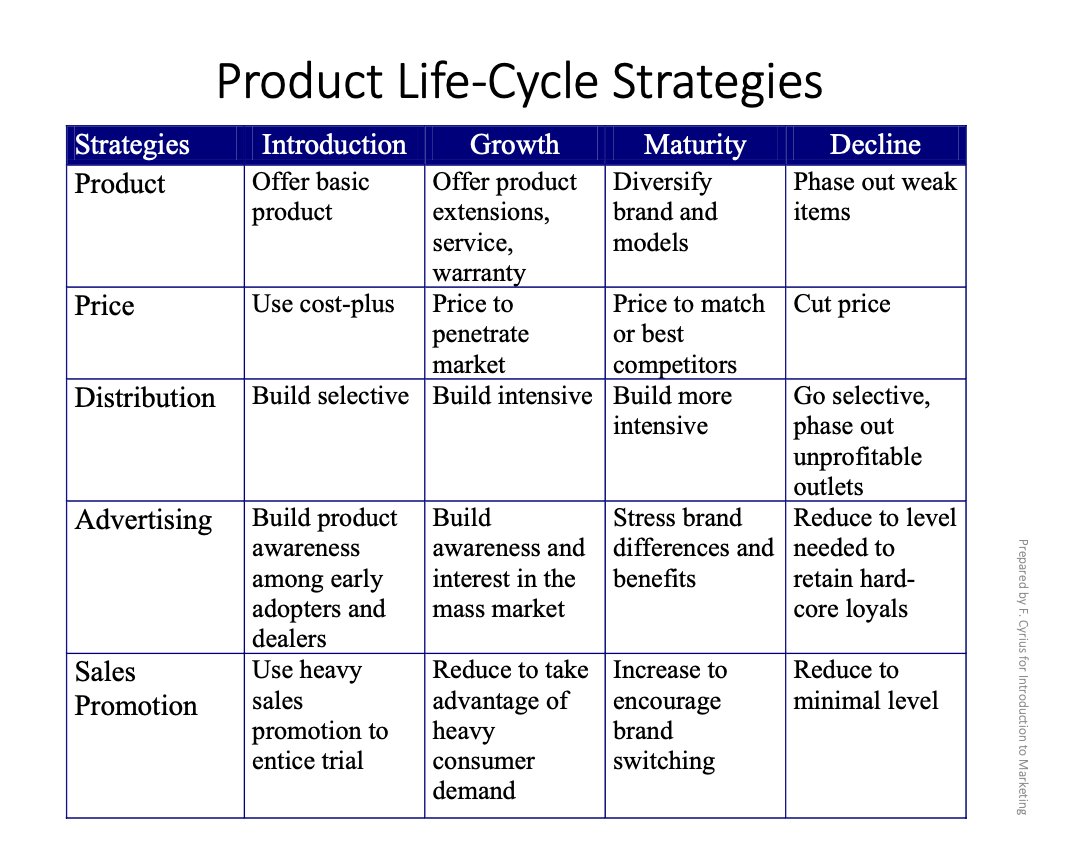
NPD - new product development - why?
1) innovation
2) market sat and competition
3) changes in external env - political, natural, economic
adopting the product curve
BCG matrix
price
what the consumer pays in exchange for p/s (tuition, interest, rent, fare, fee, retainer, toll, tips, dues)
5 c’s of pricing
comp
costs and constraints
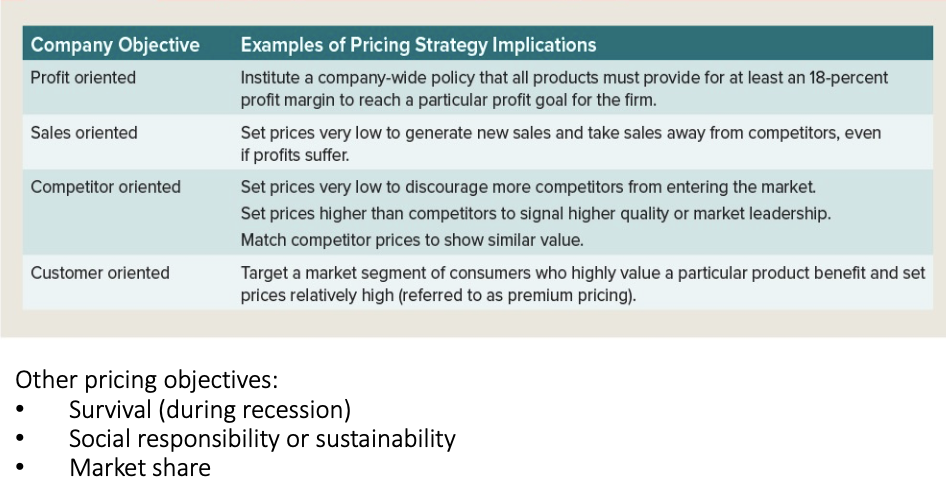
company objectives
customers
channel members
company objectives and pricing strategy implications
examples of pricing constraints
demand
newness/PLC
single vs product line
cost of prod
price elasticity, cross elasticity, cannibalization
external env trends - comp, economy, socio-demographic, regulatory, tech, environment
various pricing strategies and objectives: competition based pricing
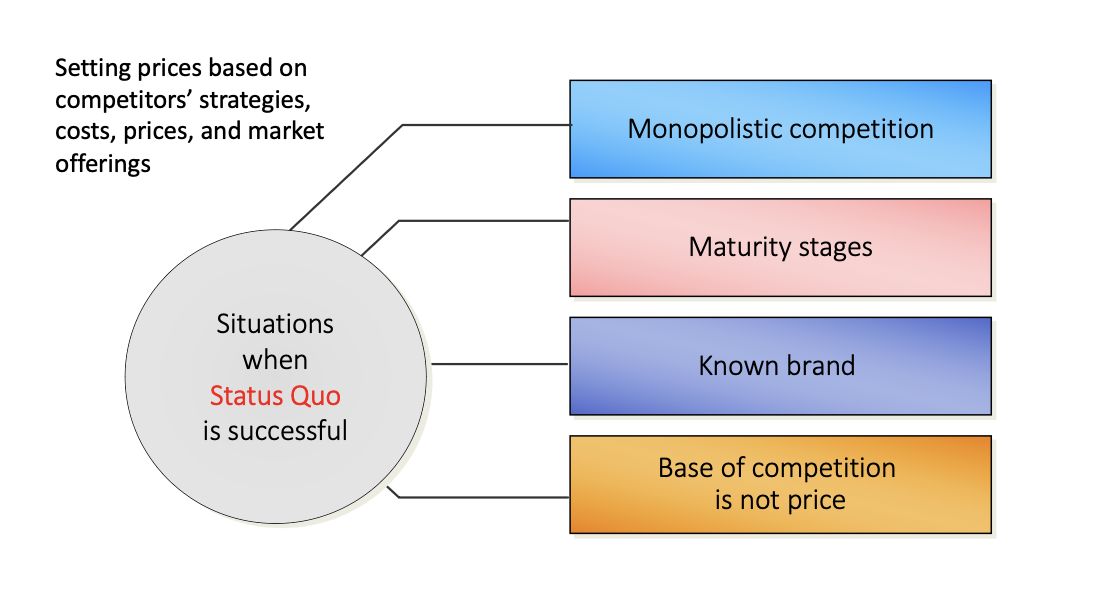
various pricing strategies and objectives: price skimming
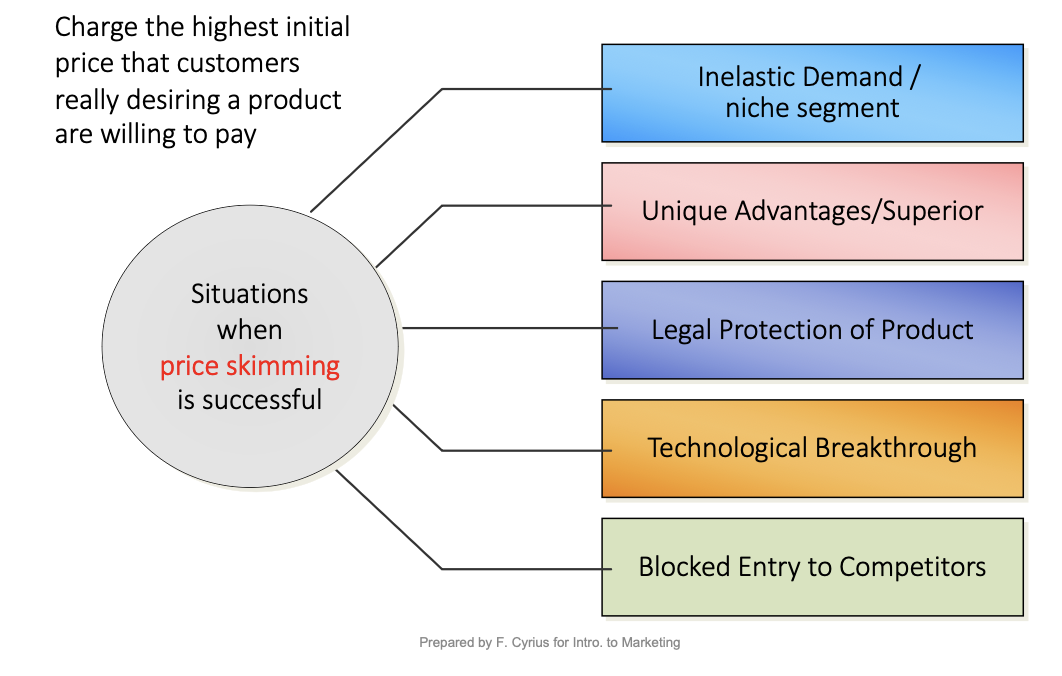
various pricing strategies and objectives: prestige pricing
pricing a good higher than comp to make it seem of higher quality (eg Hermes)
various pricing strategies and objectives: price penetration
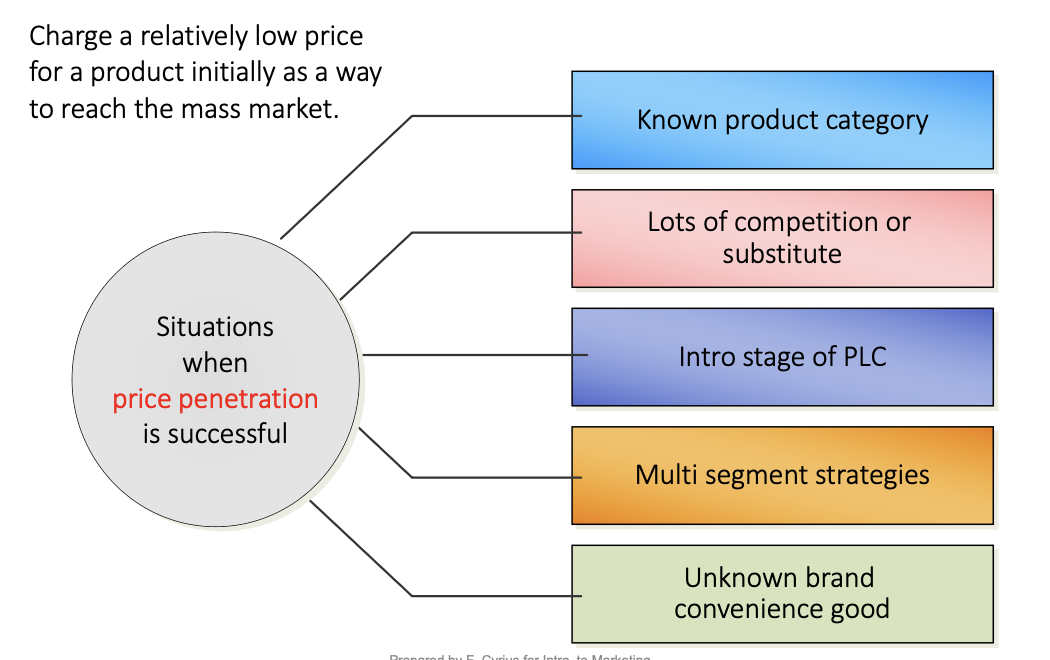
pricing lining
establishing a price floor & ceiling for an entire line of similar prods and setting price pts in between to rep diffs in quality
value based pricing
price based on how much consumer believes product is worth
std markup pricing
adding a fixed % to the total cost of all items in a specific product class
cost plus pricing
summing total unit cost of providing p/s & adding a specific amt to the cost to arrive at the price
distribution components
inbound partners supply raw materials, components, info, finances, expertise to create p/s
outbound partners serve as distr channels that link firm and customers
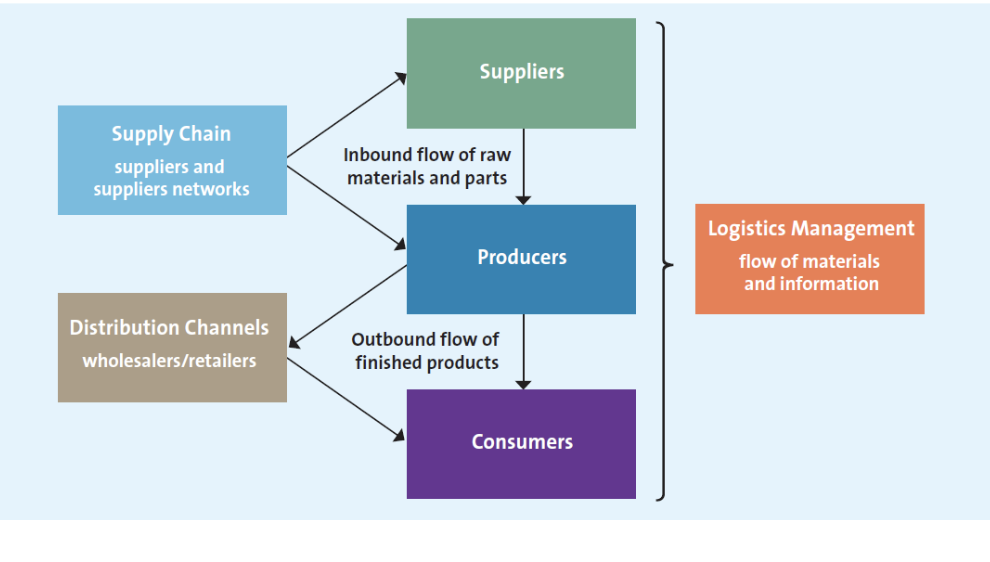
manufacturer
make product in large quantities, can sell directly to consumer, mostly from secondary sector
wholesaler & distributor
middle player in supply chain
buying / handling of merch and reselling to orgs, retailers, wholesalers
retailers, e-tailer, m-tailer
business activities involved in selling p/s to end consumers for personal use
last step in supply chain
SKU - stock keeping unit

designing distribution channels
direct
indirect
multichannel
consists of entities involved in the process of making a p/s available for use or consumption by consumers or industrial users
vertical marketing
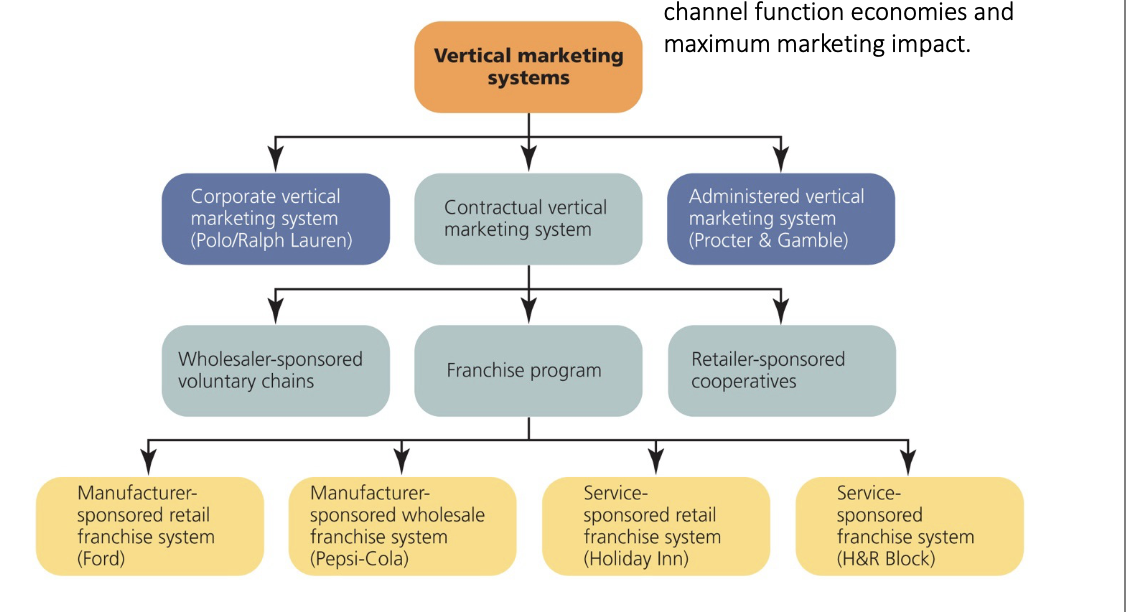
vertical marketing system: corporate systems
involve combining successive stages of production and distribution under a single ownership
forward integration would occur when a producer owns an intermediary at the next level down in the Channel
backwards integration might occur when a retailer owns a manufacturing operation
VMS: wholesaler sponsored voluntary chains
involve a wholesaler that develops a contractual relationship with small independent retailers to standardize and coordinate buying practices, merchandising programs, and inventory management efforts
VMS: contractual systems
consists of independent production and distribution firms integrating their efforts on a contractual basis
they obtain greater functional economies and marketing impact than they could achieve above
VMS: franchising
is a contractual arrangement between a parent company and an individual or firm that allows the franchisee to operate a certain type of business under an established name and according to specific rules