funds 31 promoting bowel elimination
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
structures involved in waste elimination

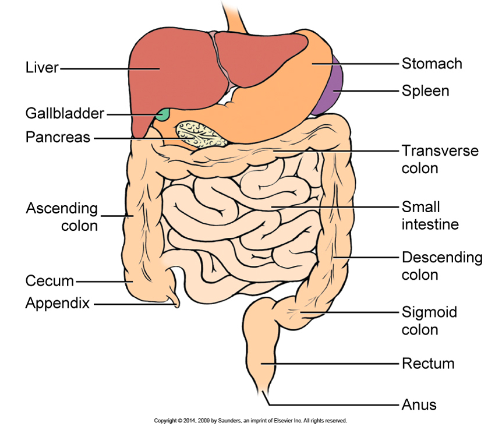
overview of intestinal system
normal transit time in intestine
18h - 72h
aging of intestinal tract
atrophy of villi
decreased absorption of fats, b12
decrease in motility
bowel habits should not change in normal healthy individual
normal stool
color: light - dark brown
consistency: soft in children & adults. ¼ solids, ¾ water
appearance: affected by diet, metabolism and meds eg iron
composition: solid materials 70% undigested carbs, fats, protein, inorganic matter. 30% dead bacteria
abnormal stool
most serious: blood
fresh red blood: colon blood. recent
occult (hidden): upper GI bleed. black stool: melena
pale white / light gray: absence of bile in intestines
steatorrhea: stool w abnormally high fat content
frothy, foul smelling, floats
hypoactive bowel sounds → constipation
indicates decrease in peristalsis → flatus (gas) accumulates
causes: bed rest & immobility, injury to bowel, drugs, surgery
drugs that constipate
general anesthetics
narcotics
diuretics
sedatives
anticholinergics (slow down rest & digest, drying effects)
calcium channel blockers (effect smooth muscles)
barium (contrast). drink 3 ½ liters after, maybe lax
drugs used to treat constipation
72h w/o bm before contacting hcp
stool softeners
colace, surfax, dialose
bulk-forming laxatives
fibercon, metamucil, citrucel - increase fluids!
irritant/ stimulant laxatives
dulcolax, neolid, ex-lax, correctol, senokat
saline laxatives
citrate/ milk of magnesia, phosphoosoda
hyperactive bowel sounds → diarrhea
increase in peristalsis
causes: inflammation of GI tract, infectious diseases, meds eg antibiotics
diverticulitis, ulcerative colitis, crohn’s disease
meds used to treat diarrhea
use for 48h before contacting hcp
camphorated tincture of opium (paregoric)
lomotil
motofen
fecal incontinence
causes: illness, cerebrovascular accident, neurogenic dysfunction, traumatic injury
not a normal part of aging, there is a cause
assessment of pt
does pt have bowel problem?
usual bowel pattern , any changes?
anything used to promote defecation?
enemas or laxative?
eating and exercise habits
foods and disorders that promote diarrhea or constipation
when assessing,
pt supine
is abdomen flat or distended? soft or hard?
auscultate in all quads - order: RL, RU, LU, LL
percuss for presence of excess gas, palpate for masses/ tenderness
nursing dx

rectal suppositories
used to promote bowel movements
Glycerin & Bisacodyl (Dulcolax)
left sims. lubricant. must touch mucosa of rectum
forms gas that expands the rectum
enemas
fluid into rectum via tube. enemas until clear (no fecal matter)
stimulate peristalsis / wash out waste products
often before colonoscopy / xray
school age: 300-500mL. adults: 500-1000mL
4in inside, toward umbilicus
no more than 3 large-volume enemas. check w pcp
may result in fluid / electrolyte imbalance
types of enemas
for cleansing enema, do not administer too rapdily (distention of rectum and colon, will stimulate defecation)
should be 12-18 inches above anus.

if pt undergoing edema has discomfort,
clamp. wait until passes then continue until can no longer retain, then reclamp.
bowel training for incontinence
establishing regular elimination: adequate diet, sufficient fluids, adequate exercise, sufficient rest
regular time should be established
may require digital sphincter to relax anal sphincter
may require drug therapy
bowel ostomy
a diversion of intestinal contents from their normal path
result is an external opening: stoma
types of ostomies
ileostomy: small bowel contents to pouch / stoma. effluent (fecal matter) is liquid
colostomy: diversion of colon. effluent may be liquid / solid, depending on site. may require irrigation
kock pouch: internal pouch near ileum
can be from the sigmoid, descending, ascending, transverse aka double - barrel (mucus & stool)
ostomy care
changed q3-5 days
stoma should appear pink-red
liquid is measured
skin care
stoma & skin washed w mild soap and water. patted dry
skin barrier paste is applied
applying an ostomy appliance / wafer
skin prep applied to peristoma before applying faceplate
measured so the opening is appropriate for stoma/ ab ¼ in around stoma
irrigating
solution instillied into colon via stoma
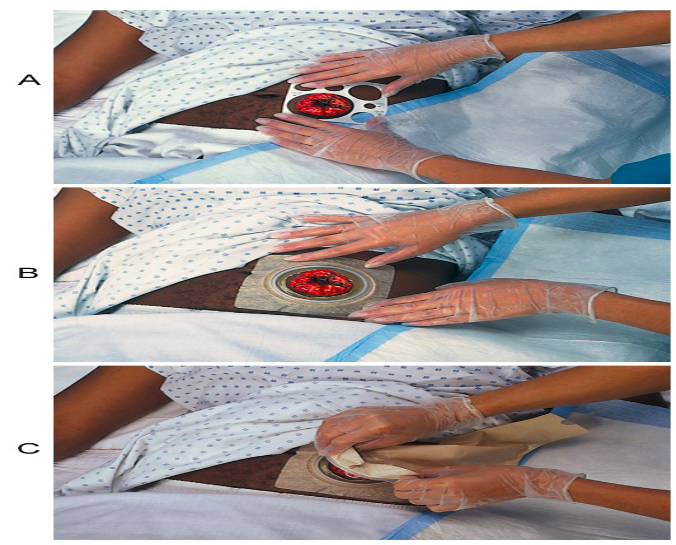
applying ostomy appliance
faceplate / disk: attaches to abdomen. must be measured right size
pouch: collects effluent and gas. empty when 1/3 - ½ full
belt: can support pouch
clamp: at bottom of pouch to secure