7 - Mood Disorders & Suicide
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Mood disorders
experiences emotions that are extreme and, therefore, abnormal
Extreme sadness
Mild sadness
Normal emotions
Mild elation
Extreme elation
Range of Emotions:
Unipolar Depressive Disorders
Bipolar Depressive Disorders
What Are Mood Disorders? (2)
Unipolar Depressive Disorders
Only depressive episodes.
Bipolar Depressive Disorders
Manic and possibly depressive episodes (but not necessary).
women
Mood Disorders:
About twice as common in ____
Mild, Brief Non-Depression
Can be normal and adaptive
Sadness, hopelessness, and pessimism are common human experiences.
Mild
Moderate
Severe
Severity of depression:
Single Episode
Recurrent Episode
Course of depression:
Persistent Depressive Disorder (Dysthymic Disorder)
Mild to moderate version of depression
Persistent Depressive Disorder (Dysthymic Disorder)
Lasts a long time
Intermittent normal moods occur briefly
Major depressive episode
Extremely depressed mood lasting at least two weeks
Cognitive symptoms – feelings of worthlessness, indecisiveness
Disturbed physical functioning (sleep and eating)
Anhedonia
Anhedonia
loss of pleasure/interest in usual activities
- Single episode - highly unusual
- Recurrent episodes (2 or more major depressive episodes separated by at least 2 months of no depression) - more common
With Seasonal Pattern
At least two or more episodes in past 2 years that have occurred at the same time (usually fall or winter), and full remission at the same time (usually spring)
No other nonseasonal episodes in the same 2-year period.
Major depressive episode with melancholic features
Severe major depressive episode with psychotic features
Major depressive episode with atypical features
Major depressive episode with catatonic features
Major Depressive Disorder - Specifiers: (4)
(Pointers!!!)
Persistent major depressive disorder
Seasonal affective disorder
Major Depressive Disorders: (2)
Persistent major depressive disorder
Major depression does not remit (disappear) for more than two years.
Seasonal affective disorder
Recurrent depressive episodes with a pattern (change of seasons)
the episodes occur during the fall and winter months and remit during the spring and summer months.
Heredity
Altered neurotransmitter activity
Hormones
Genes
Disruptions
Biological Causes of Unipolar Mood Disorders: (5)
Serotonin-transporter gene
Three combinations
Gene-environment interaction research
Genes:
Sleep
Circadian rhythms
Exposure to sunlight (seasonal)
Disruptions:
Stressful life events
Risk-related vulnerability factors
Neuroticism or negative affectivity
Parental loss
Psychological Causal Factors for Depression:
Freud
Behaviorists
Cognitive model
Theorists in Depression: (3)
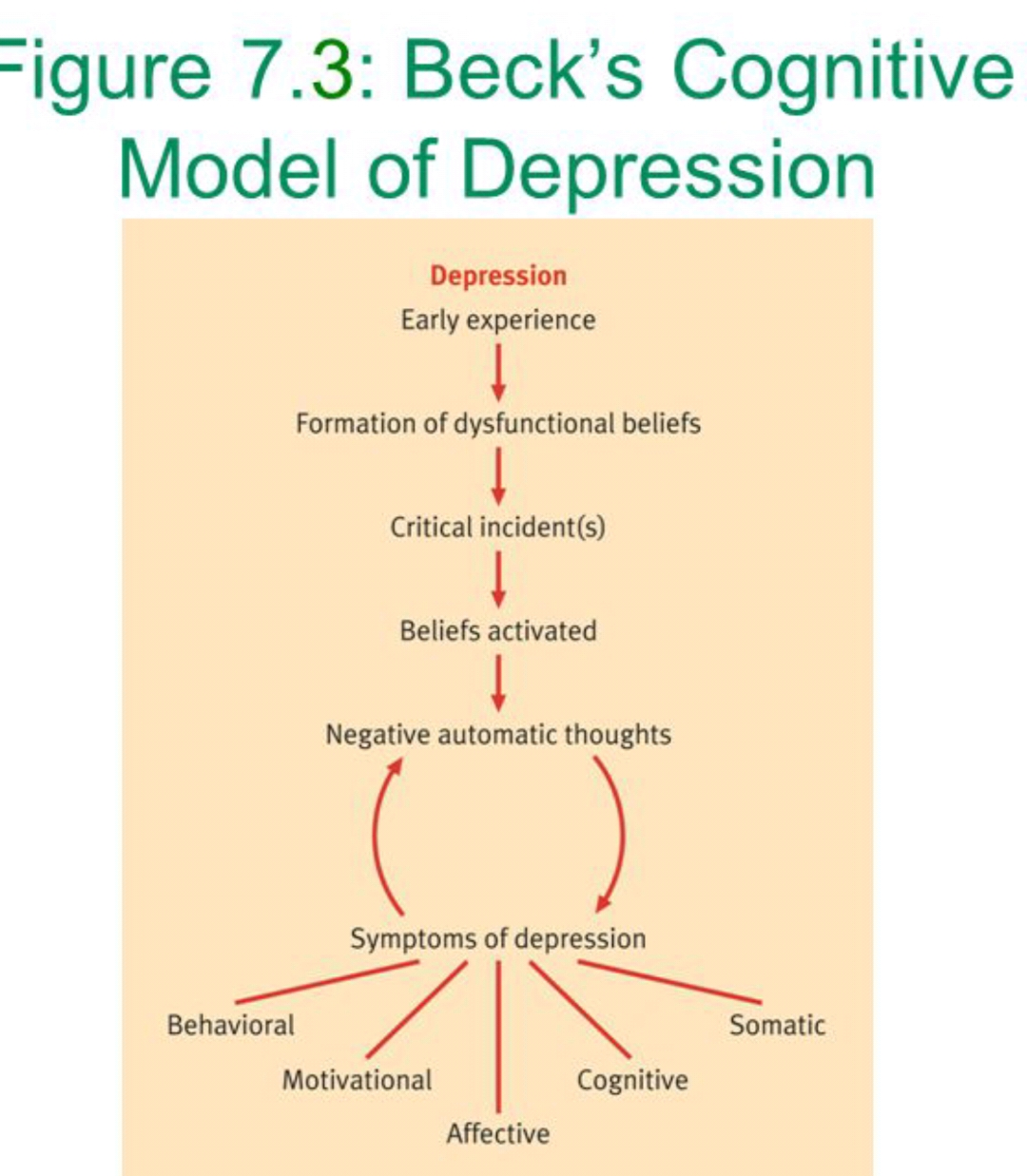
Early experience
Formation of dysfunctional beliefs
Critical incident(s)
Beliefs activated
Negative automatic thoughts
Symptoms of depression:
- Behavioral
- Motivational
- Affective
- Cognitive
- Somatic
Beck's Cognitive Model of Depression:
(Pointers!!!)
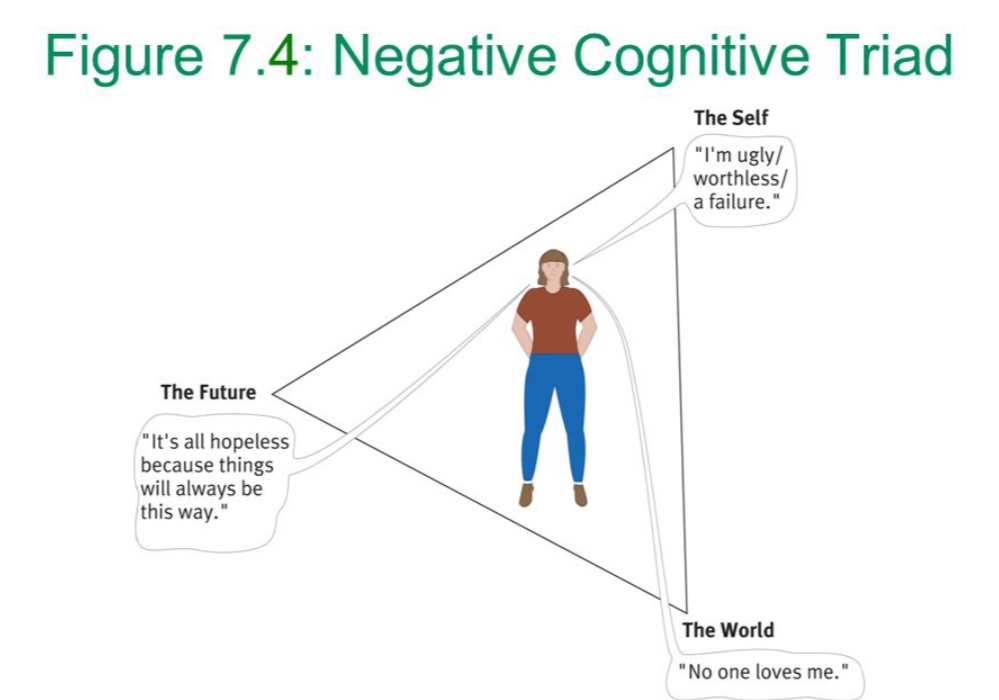
The Self
The Future
The World
Negative Cognitive Triad:
(Pointers!!!)
Reformulated helplessness theory
suggests that depression arises when individuals attribute negative events to internal, stable, and global causes.
Internal: Believing the cause is due to their own personal failings.
Stable: Believing the cause is permanent and unchangeable
Global: Believing the cause will affect all aspects of their life.
Hopelessness theory
This theory proposes that a particular subtype of depression is caused by feelings of hopelessness
Excessive rumination
This refers to a repetitive and passive focus on one's symptoms of distress and possible causes and consequences of these symptoms, rather than on solutions.
Mania / Manic episode
Elevated, expansive mood for at least one week
Inflated self-esteem
Decreased need for sleep
Excessive talkativeness
Flight of ideas or sense that thoughts are racing
Easy distractibility
Increase in goal-directed activity or psychomotor agitation
Excessive involvement in pleasurable but risky behaviors
Impairment in normal functioning
Symptoms for Manic episode:
(At least 3 of the following)
Hypomanic episode
Less severe than a manic episode, lasting at least 4 days
Bipolar I disorder
Includes at least one manic or mixed episode.
Bipolar II disorder
Includes hypomanic episodes but not full-blown manic or mixed episodes.
Cyclothymic Disorder
Less severe than those of bipolar disorder
Symptoms present for at least 2 years
Lacking severe symptoms and psychotic features of bipolar disorder
males and female
adolescence or young adulthood
18 to 22
Bipolar Disorders (I and II) - Characteristics
Occur equally in _____.
Usually start in ________.
Average age of onset is ______ years.
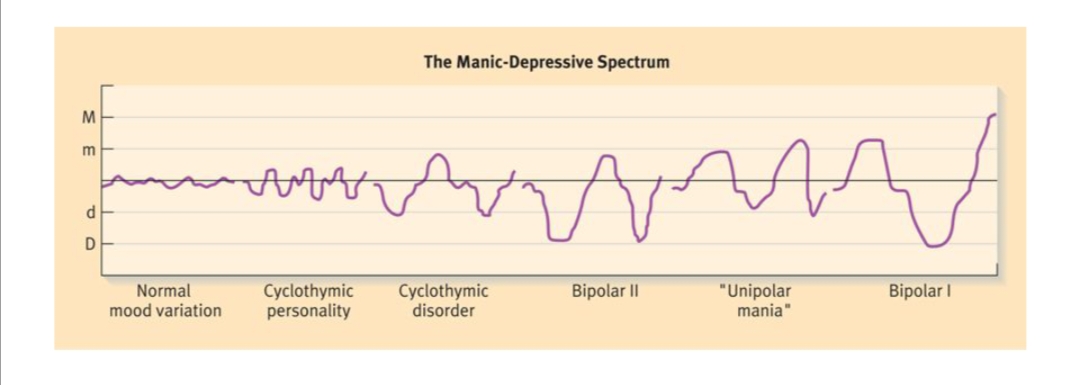
The Manic-Depressive Spectrum:
Heredity
Neurotransmitters like norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine
Abnormalities in ion transportation across the neural membrane
Cortisol levels
Shifting patterns of blood flow to prefrontal cortex
Disturbances in biological rhythms
Biological Causal Factors in Bipolar Disorder:
Stressful life events
Personality variables
Low social support
Pessimistic attributional style
Psychological Causal Factors in Bipolar Disorder
Native Americans
African-Americans
__________ have relatively high rates of depression
__________ have relatively low rates
Pharmacotherapy
Alternative biological treatment
Psychotherapy
SSRI
Treatments for Bipolar Disorder (Mood Disorders): (3)
Pharmacotherapy
involves using antidepressants, mood-stabilizing, and antipsychotic drugs to treat mood disorders
Lithium
common mood stabilizer for bipolar disorder.
Selective Serotonergic Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
Specifically block reuptake of serotonin
Fluoxetine (Prozac)
is the most popular SSRI
Selective Serotonergic Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
pose some risk of suicide particularly in teenagers
Negative side effects
Electroconvulsive therapy
Transcranial magnetic stimulation
Deep brain stimulation
Bright light therapy
Alternative Biological Treatments in Bipolar Disorder:
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
Effective for cases of severe depression.
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
Involves applying a brief electrical current to the brain, resulting in temporary seizures.
Usually requires six to 10 outpatient treatments.
Side effects are few and include short-term memory loss.
It is uncertain why ECT works.
Relapse is common (60%).
Cognitive-behavioral therapy
Behavioral activation treatment
Interpersonal therapy
Family and marital therapy
Forms of Effective Psychotherapy in Mood Disorders:
Helps change negative thought patterns to improve behavior and emotions.
Reintroduces positive activities to uplift mood and break negative behavior patterns.
Focuses on improving current relationships to enhance mental well-being.
Helps families and couples build healthier relationships and improve communication.
Suicide risk
is a significant factor in all types of depression.
Suicide
ranks among the top ten leading causes of death
low but increasing
10-14
Suicide in Children:
- Rates are very ________.
- Suicide in children age ____ has increased by 70% since 1981.
- Multiple risk factors are involved.
tripled
Suicide in Adolescents and Young Adults:
- Rates ____ between the mid-1950s and mid-1980s.
- Multiple risk factors are involved.
Impulsivity
Aggression
Pessimism
Family psychopathology or instability
Genetics
Sociocultural factors
Psychosocial Factors in SUICIDE:
Genetics
Reduced serotonergic activity
Biological Causal Factors in SUICIDE:
Whites
Ethnicity: ____ have higher rates of suicide than African Americans.
communicate
nonlethal
Suicidal Ambivalence:
- Some people do not wish to die but instead want to _______.
- Methods are _____.
- Actions are arranged so that intervention by others is likely.
notes
love and concern
hostile
Suicide Notes:
- Only 15-25% of completed suicides leave ____.
- Some notes include statements of _________
- Others include very ____ content.
Treatment of a person's current mental disorder(s).
Crisis intervention.
Working with high-risk groups.
Suicide Prevention and Intervention:
Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS).
Crisis Intervention utilizes the _____________
Antidepressant medication or lithium.
Benzodiazepines.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy.
Prevention of suicide can take the form of treatment of the underlying mental disorder(s) using: (3)
Hotlines
Hotline Efficacy
Crisis Interventions: