FSF Module III (Biophysics Theory)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms

What is this symbol?
Phase velocity (velocity of osccillations), also look at image
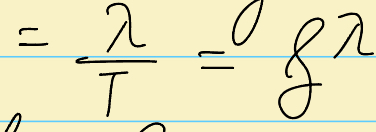
What is P?
Power, how much energy is rpoduced epr second (watts or joules per second)- can be found by doing change in energy over change in time
How can intensity be found using power and amplitude?
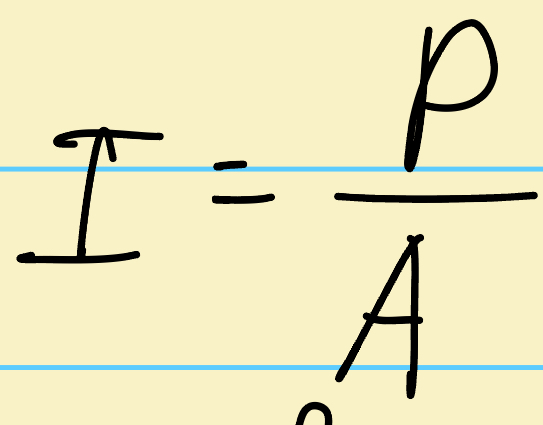

What is this symbol?
The absorption or attenuation coefficient (which is dependant on the type of wave and material-changes), also sometimes seen as image provided and as a combination of of photoelectric, compton and pairing effects.

Give the equation for intensity
Where x is thickness of material passed thru, I(x) is the value absrobed by passing thru thickness…. The quation shows how strong of an interaction it is (high value- absorbs a lot, low value-absorbs little)

What is the equation for kinetic energy produced by a photon in radioactivity?
Where Ec: kinetic energy, E phot: is the energy of a photon, and Eion is the threshold value needed to cause and electronto be ejected ——Here, increasing wave intensity will increase photon numbers but not kinetic energy produced, while increasing wave frequency will increase the energy of the photons, but not the number of photons, hence increasing kinetic energy.

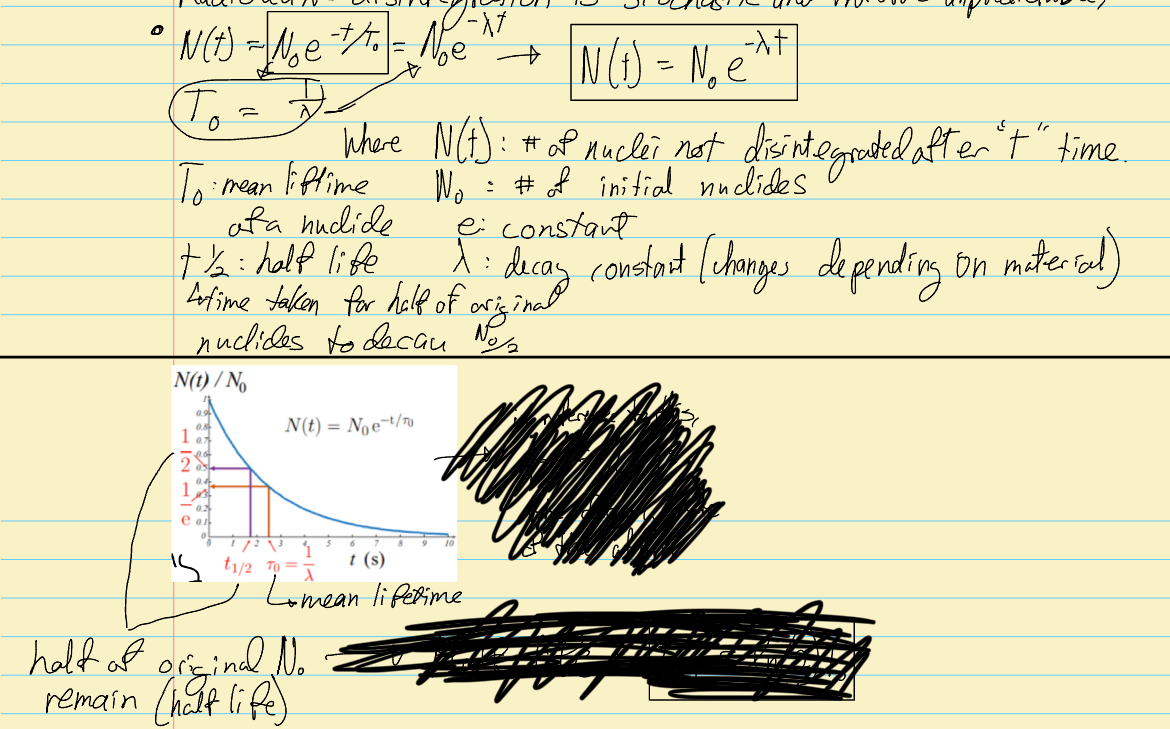
What is the equation for number of nuclei disintegrated after t time? Explain it.
Radioacive disintegration is stochasticc and threfore unpredictable, however there is an equation to estimate the process. It is the equation seen in the image
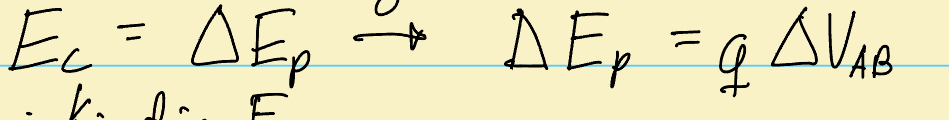
What is teh equation for X-ray tube energy release?
Where Ec is kinetic energy, change in Ep is change in potential energy as particle moves thru x-ray tubes, Q is the charge of the particles (q=electron), and Vab is the difference increasing wave intensity voltage between the two x-ray tubes——— The nergy released can also be seen as “I” (electrical current measures in amps)- which is NOT TO BE CONFUSDE WITH INTENSITY which is also seen as “I”
What is specular reflection
Direction of reflected waves are parallel to one another

What is diffuse relfection?
Directions of reflected waves follow different trajectories (unequal surface)
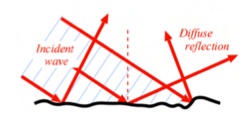
What is dispersion?
The change in direction of a wave after passing thru a non-homogenous material
What is normal and back scattering?
Normal: degree of dispersion is very small
Back scattering: high dispersion degree, the beam rebounds backwards (NOT REFLECTION)

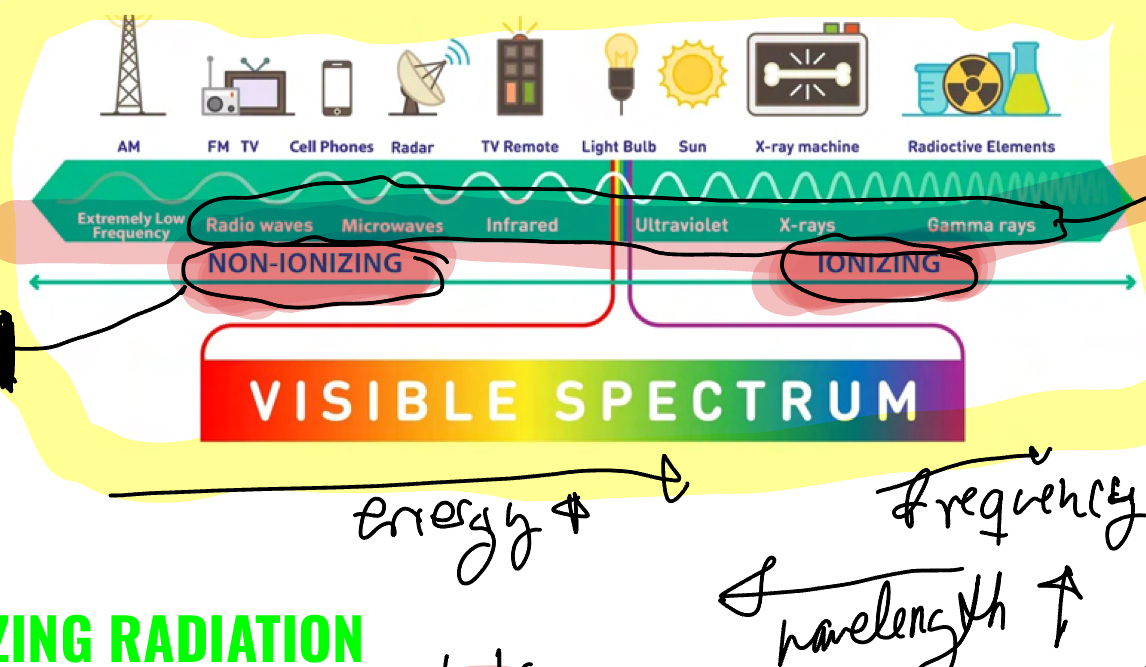
Describe ionizing In comprasion to non-ionizing EM waves.
Ionizing break chemical bonds, non doesnt but produces heat, both may burn skin
Ionizing ( over 10eV), non (under 10eV)
Ionizing is charcterized by photon interactions, while in non, the chrged particles begin to vibrate and oscillate the same frequency as teh field instead of being displaced like with ionizing radiation.
What is radioactivity
Emission of some nuclei of energy as EM waves or as subatomc particles in order to obtain a more stable state- can be natural or artificial.
Explain natural/artificial radioactivity
Natural is form isotopes present in nature with unstable nuclei, seeking to become more stable by decaying into other elements or isotopes, while artificial is created mainly using electricity, by exerting force on an electron, it becomes accelerated which can then interact with matter.
What is the photoelectric effect?
When the frequency of the incisdent wave is higher than the threshold value (Eion), the photons emmited in the wave causes the electrons to be ejected while th ephoton is destroyed, the greater the intensity the more electrons dislodged, however the more frequency the greater the kinetic energy of the electrons disloged.

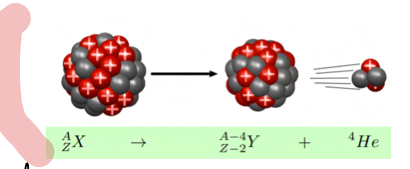
Explain alpha radiation
Unstable nucleus releases alpha prticle (helium nucleus)(monoenergetic nucleus)
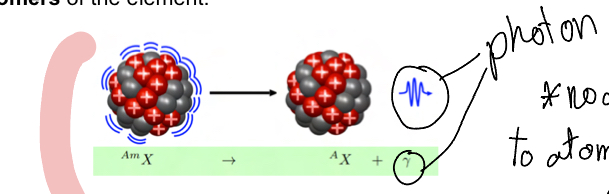
Explain gamma radiation
Unstable isotope release phton (monoenergetic) (no change to atomic structure unlike in alpha)
Explain beta radiation
Beta (-) radiation (known as usual beta radiation) Disintegration of a neutron into a proton, which releases an electron and an antineutrino)
Beta (+) radiationproton turning into a neutron, and so a positron (positive charge) and a neutrino are ejected — used for PET scanes (positron emission tomography)

What is the compton effect/compton scattering?
Interaction between photon which transfers part of its energy to the electron, which will be used to surpass ionization energy and teh remainign energy will create another photon from the electron(carrying less than original photon)
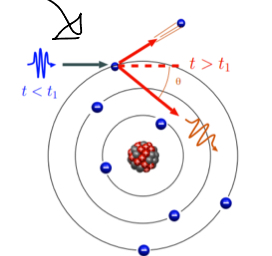
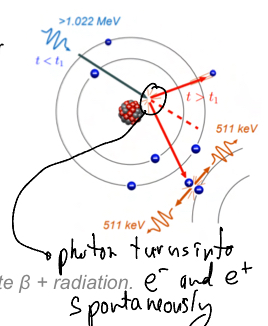
Explain pair production.
Used only in radiotherapy not radiology, High energy photon spontaneously splits into an electron and a positron making some energy be transferred to matter— since positron is not natural, it will move away and collaide with another electron making both of them turn into photons which will propagate in opposite directions.
How is does determined- equation?
Measured in joule/Kg which is also called Gray (Gy)

WHat are stochastic effect of doses
Purely probabilistic effects without thresholds- cannot be well predicted.
What are deterministic effects?
Seriousness increases with number of incident particles so it can be predicted
What is equivalent dose?
Known as (H), and untis of Sv (sievert) it Takes into account the damage that the radiation may cause Wr is a weighing factor dependant on the radiation type
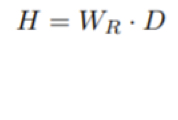
What is effective dose?
Known as E and units of Sv (Sievert), it takes into account that tissues react to radiation and Wt is different for each tissue.
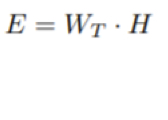
What emissions are ionizing? DO QUESTION
What emissions are nonionizing
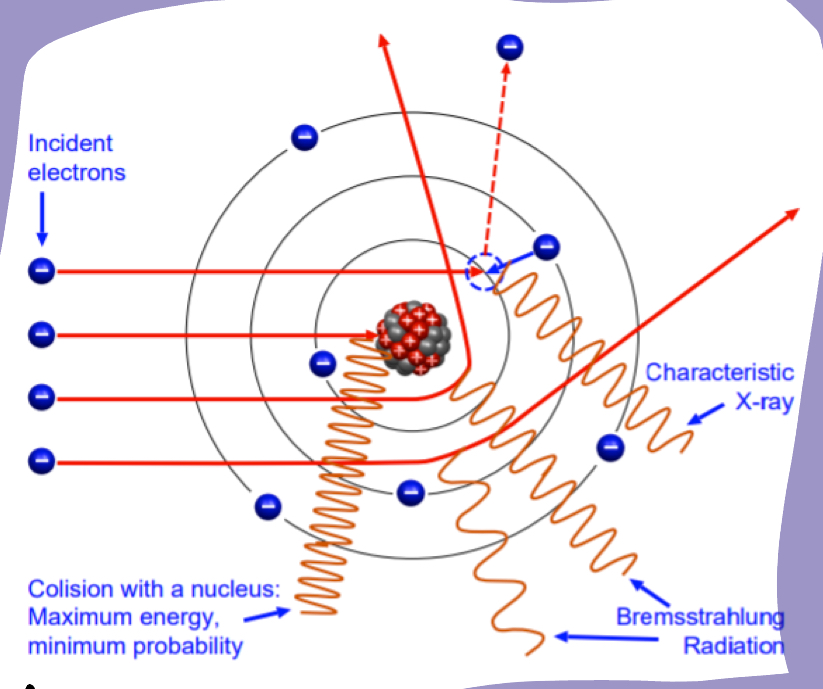
Bremsstrahlung effect explain
The incident electrons interacts with other particles inside the atom which make it deviate from its path and conseqently release Bremsstrahlung radiation.
Penetration length in waves?
It represents teh distacne that th charged particles can tarvel (also known as range)