7: Ch 7--Mucogingival Deformities and Conditions
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
absence of disease states
Mucogingival Deformities and Conditions
• normal mucogingival condition there is an a_____ of d____ s_____
thin scalloped
thick flat
thick scalloped
Mucogingival Deformities and Conditions
• periodontal biotypes:
• t_____ s______: thin tissue and bone, slender triangular teeth, subtle scalloped tissue
• t_____ f_____: prominent tissue and bone thickness, square-shaped teeth, broad zone of keratinized tissue
• t______ s______: thick fibrotic tissue, triangular teeth, slender shaped, pronounced gingival scalloping, lack of keratinized tissue
aberrant frenum
a_____ f______: unusual or strong frenum attachment/ frenum attachment is in the wrong place or is pulling too hard
normal (with recession)
what mucogingival condition is this?
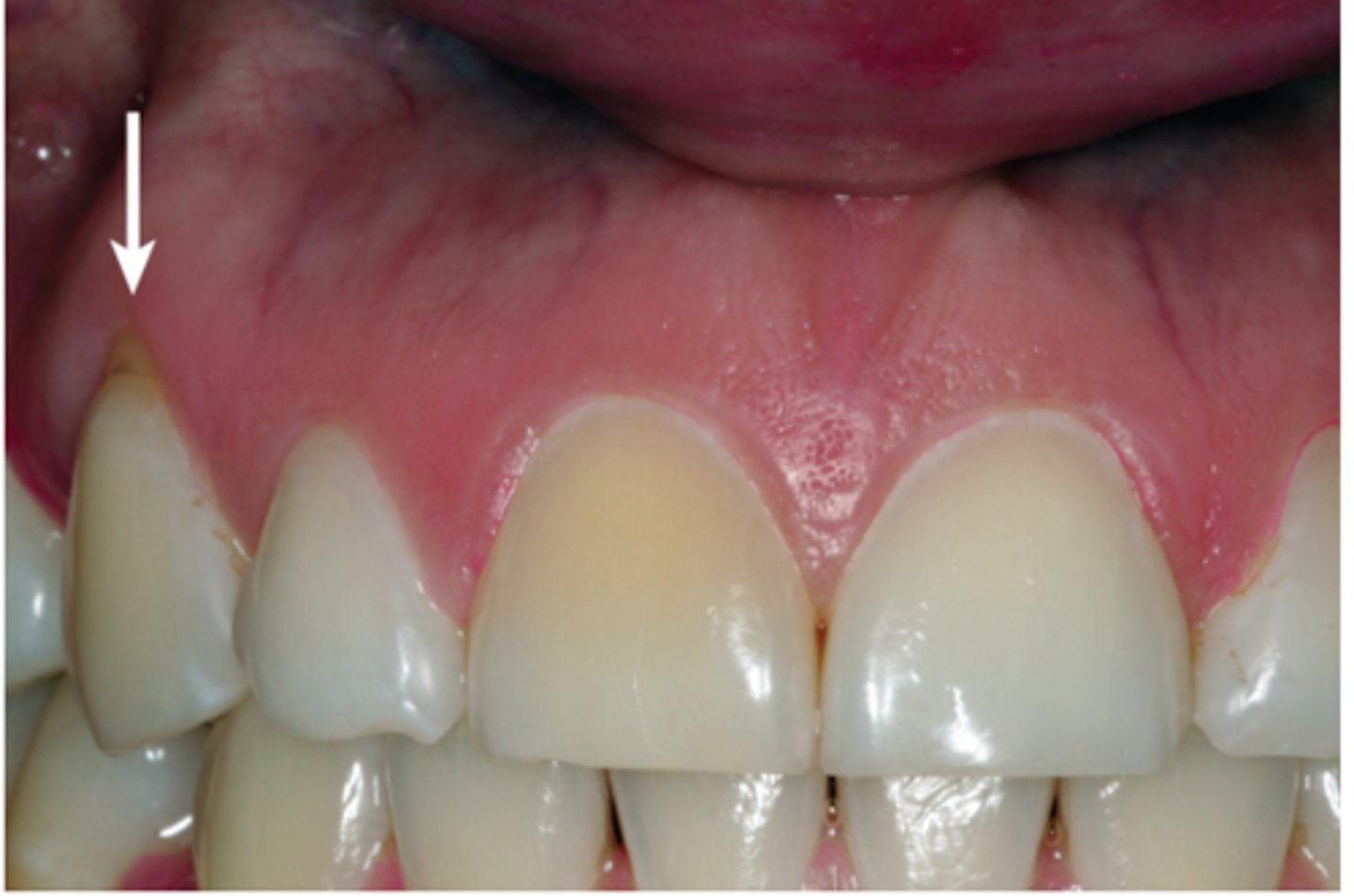
keratinized tissue
very thin keratinization
thick scalloped
(not wide zone of attachment)
Describe this tissue type
• there is lack of k____ t_____
• v___ t_____ k_______
• biotype: t____ s______
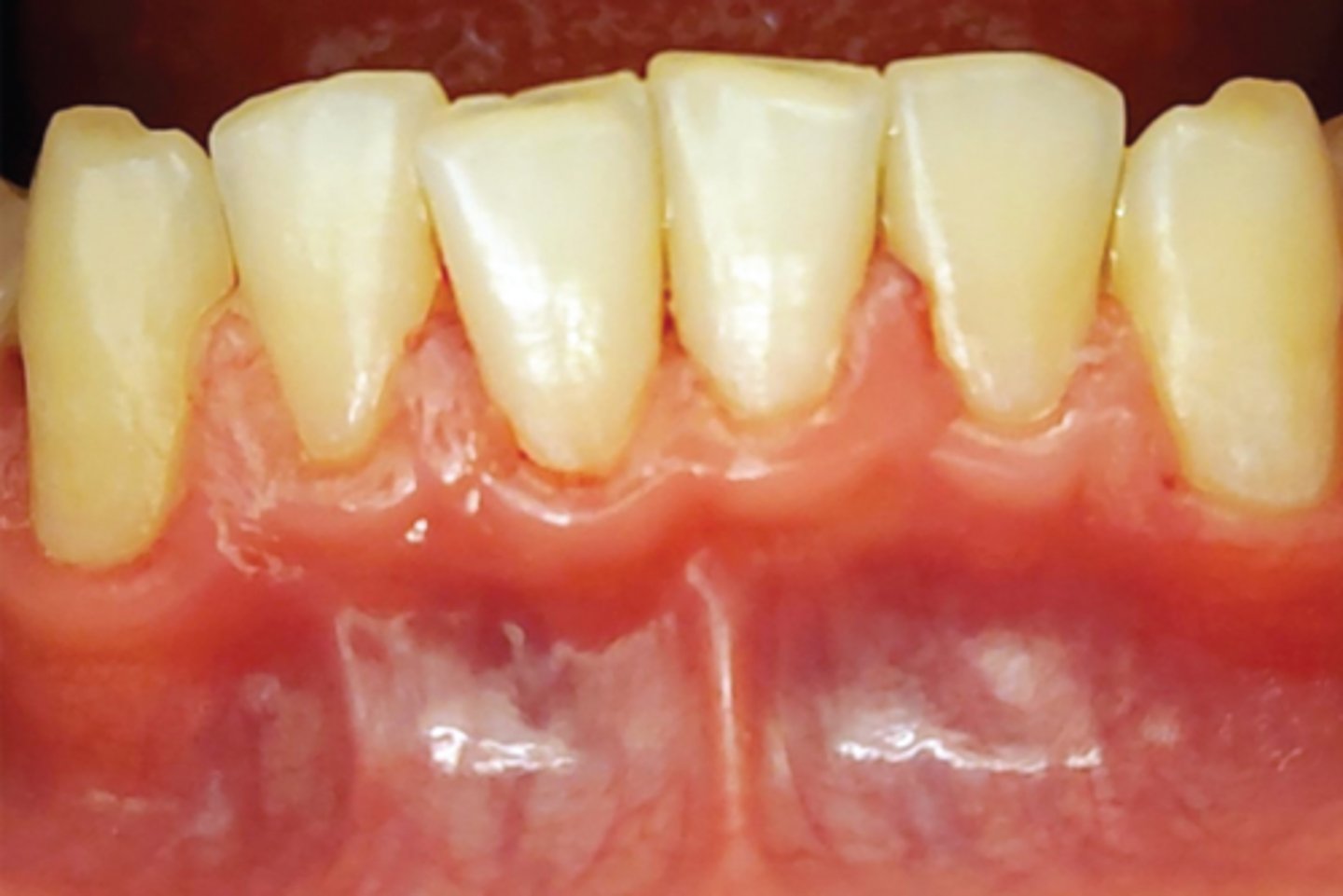
aberrant frenum
decreased vestibular depth
narrow zone of keratinized tissue
scalloped
Describe the tissue type:
• a_______ f______
• d______ v______ d_____
• n_____ z_____ o_ k______ t_____
• likely s____ biotype: more likely disease with frenum because of thin attachment
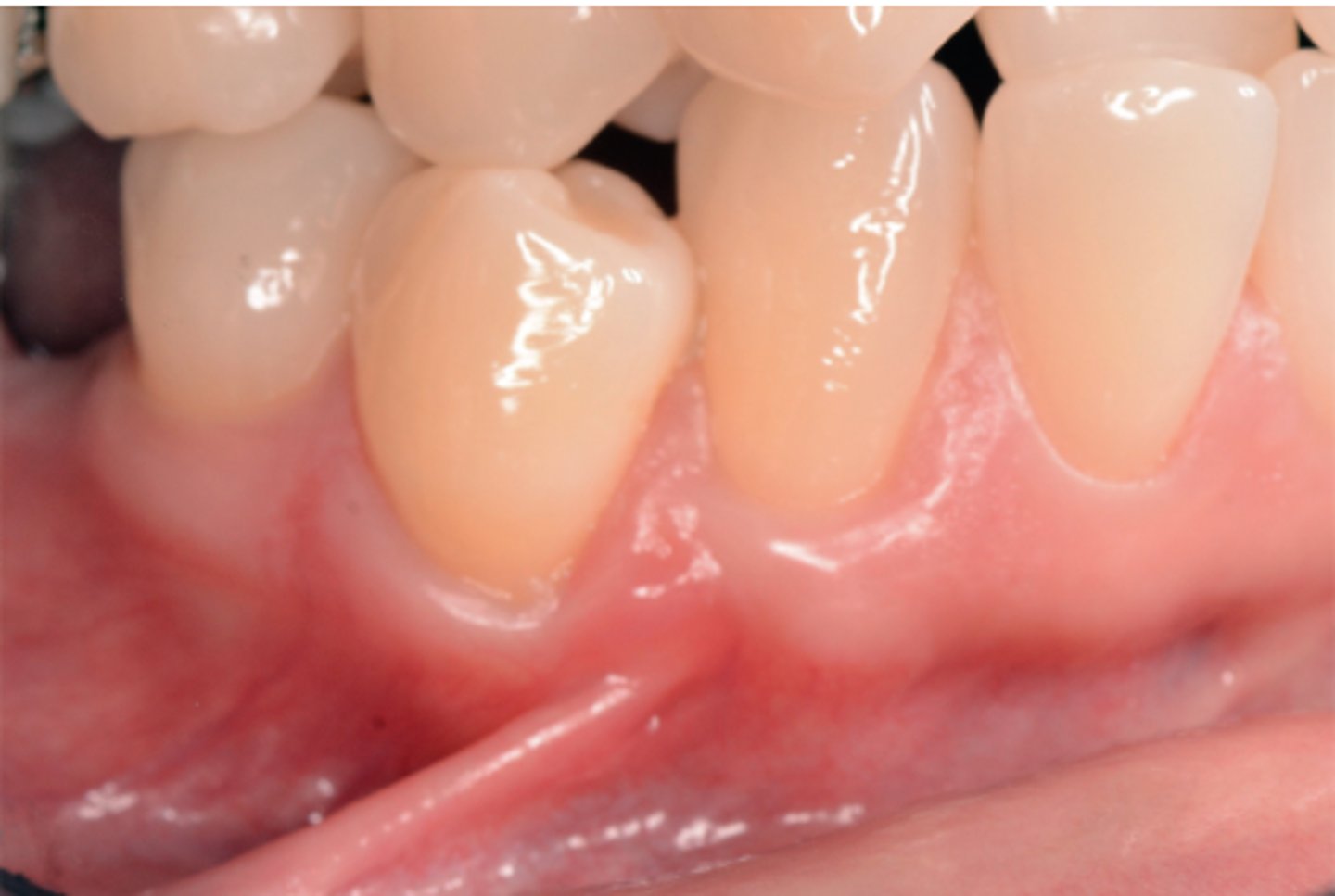
square
thick
Describe the teeth shape and gum type:
• ______ shaped teeth
• ____ gums
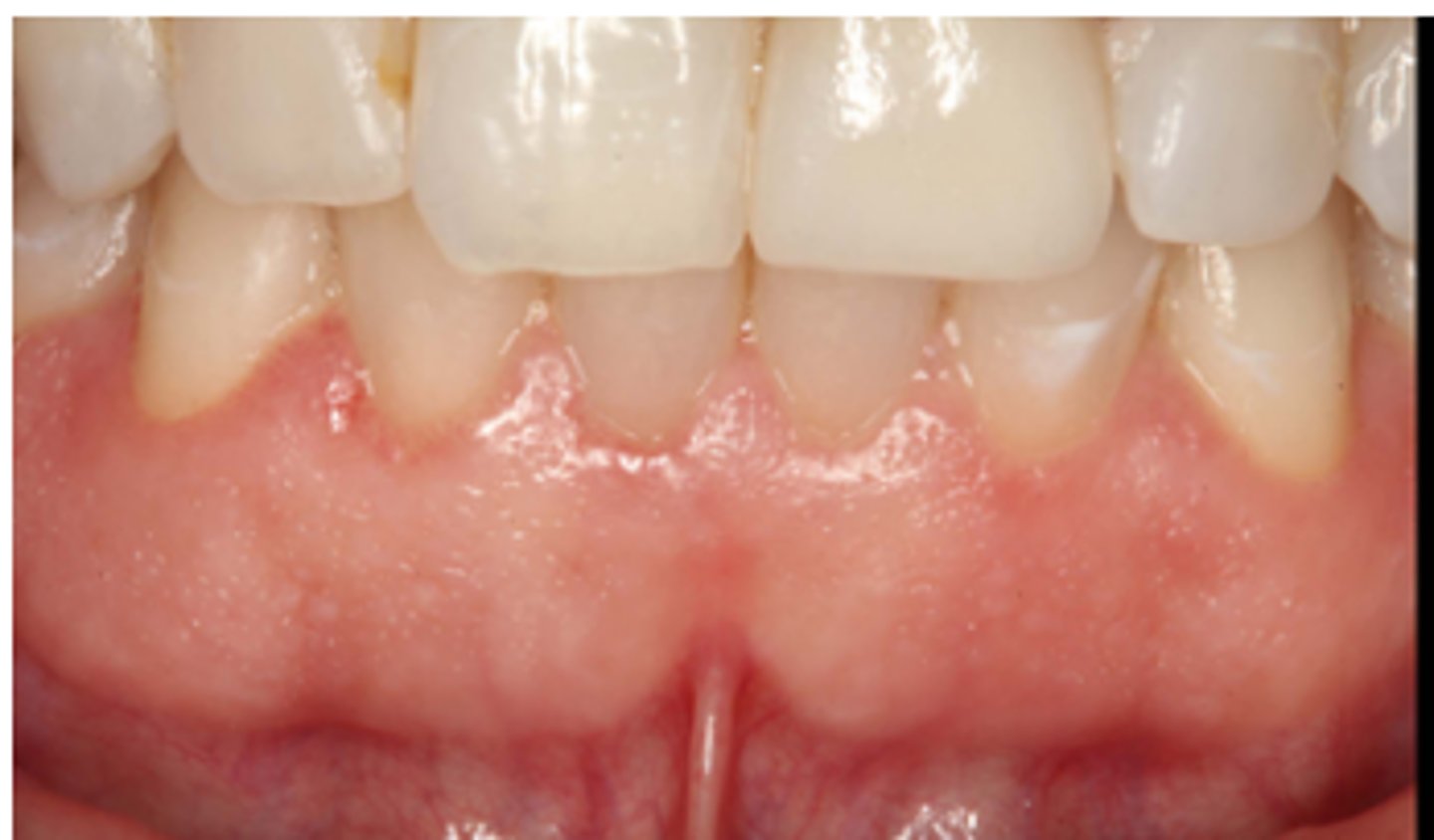
triangle
thin
Describe the teeth shape and gum type:
• ______ shaped teeth
• ____ gums
• significant because bacteria can go through this tissue easily
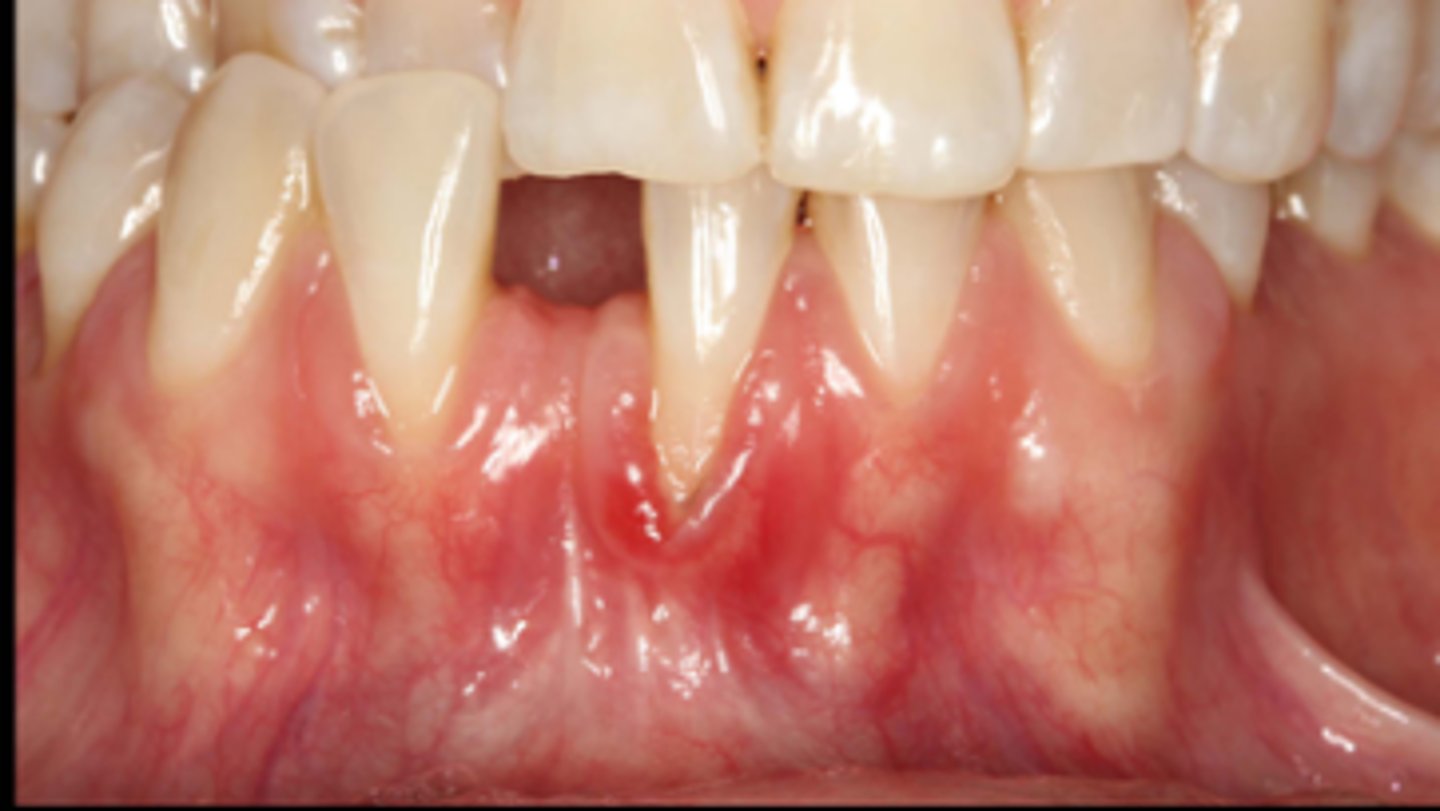
thin
____ biotype:
• thin scalloped biotype (15% prevalent less common than other biotypes)
• distinct disparity between location of gingival margin facially and interproximally (thick point between teeth gives it a triangular shape)
• delicate and friable soft tissue
• small amount of attached gingiva
thick
____ biotype:
• thick flat biotype--more prevalent (85%)
• adequate amount of attached gingiva
• dense fibrotic soft tissue
• ideal for placing implants
thin
thin scalloped
triangular
delicate, friable
small, attached
____ biotype:
• t____ s_____ biotype (15% prevalent less common than other biotypes)
• distinct disparity between location of gingival margin facially and interproximally (thick point between teeth gives it a _______shape)
• d_____ and f_____ soft tissue
• s____ amount of a_____ gingiva
thick
thick flat
adequate, attached
dense fibrotic
square
implants
____ biotype:
• t_____ f____ biotype--more prevalent (85%)
• a______ amount of a_____ gingiva
• d_____ f_____ soft tissue
• _____ shaped teeth
• ideal for placing i______
thick, flat periodontal biotype because there are square teeth, large zone of attached gingiva, smaller embrasures, dense fibrotic gingiva
what biotype is this and why?
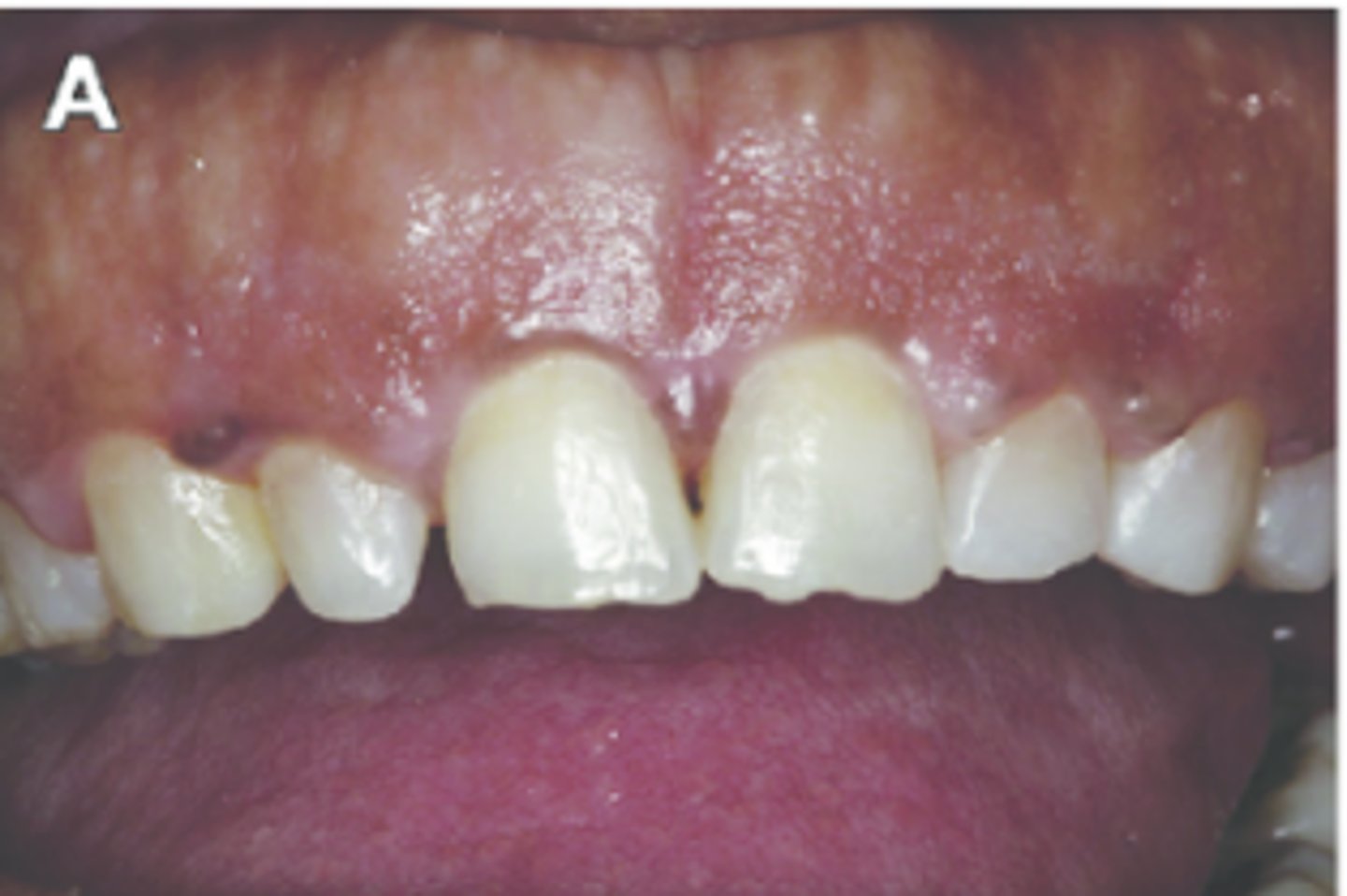
thin periodontal biotype due to scalloped gingiva with a narrow zone of attachment, triangular teeth, thin periodontium reveals undulating contours of the prominent roots of the teeth and bone
what biotype is this and why?
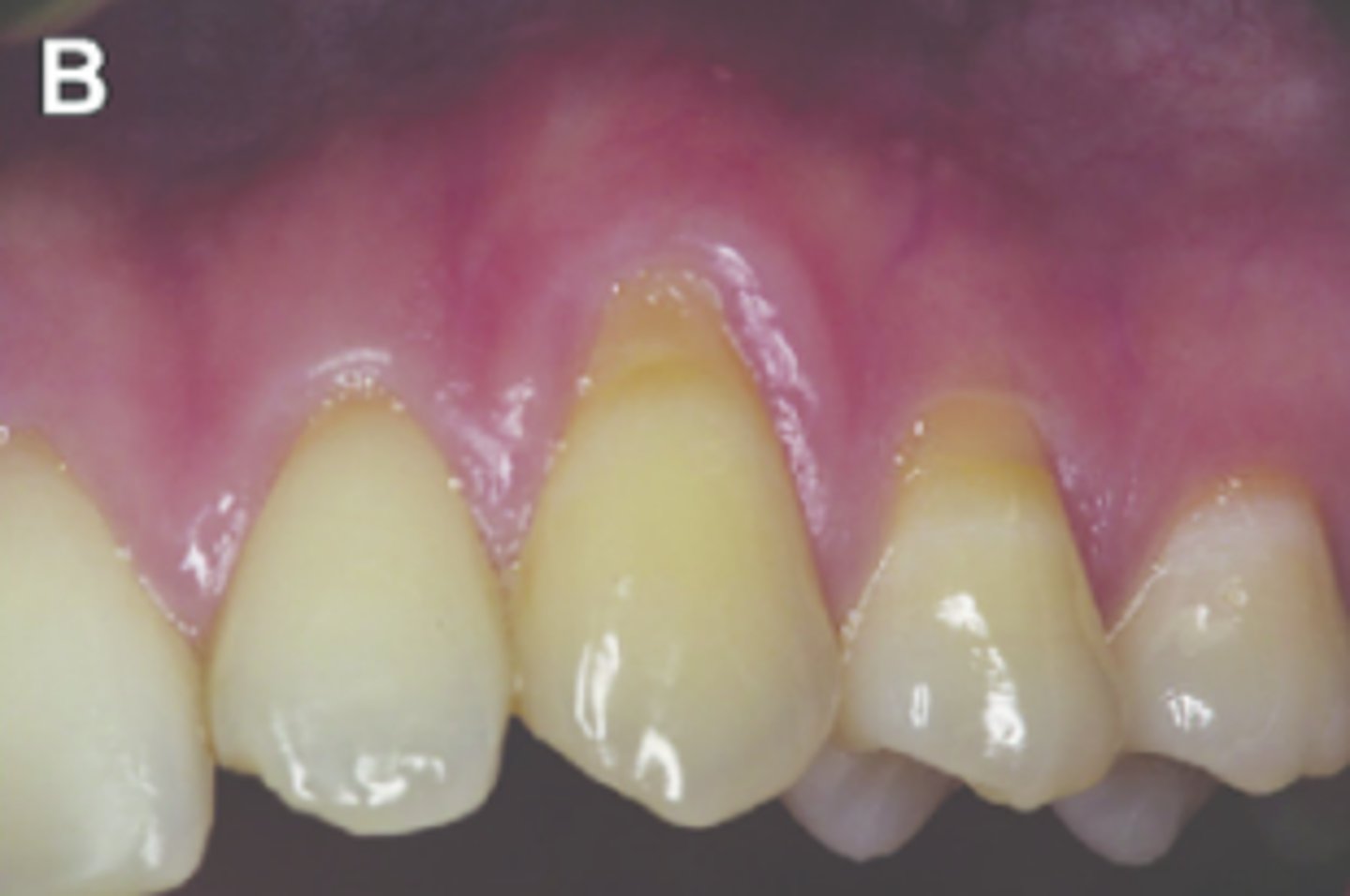
false
KNOW
• t/f: thin biotype is more prevalent/common
true
KNOW
• t/f: thick biotype is more prevalent/common
thick
Gingival Deformities
• most common is t____
thin
attached gingiva
alveolar bone
traumatic toothbrushing
recession, slowly
Gingival Deformities
• risk factors for development
• t___ biotype
• absence of a____ g____
• thickness of the a_____ b____
• trauma associated with recession most commonly from t_____ t______
• ortho can cause r____, need to move teeth s_____
frenum
frenectomy
tissue graft
pt ed
extra soft, Stillmans
What is this recession caused by and what are some treatment methods for this pt?
• caused by: ________
• treatment:
• f______
• t_____ g_____
• p__ e___
• product recommendations: e____ s____ TB, s______ TB technique
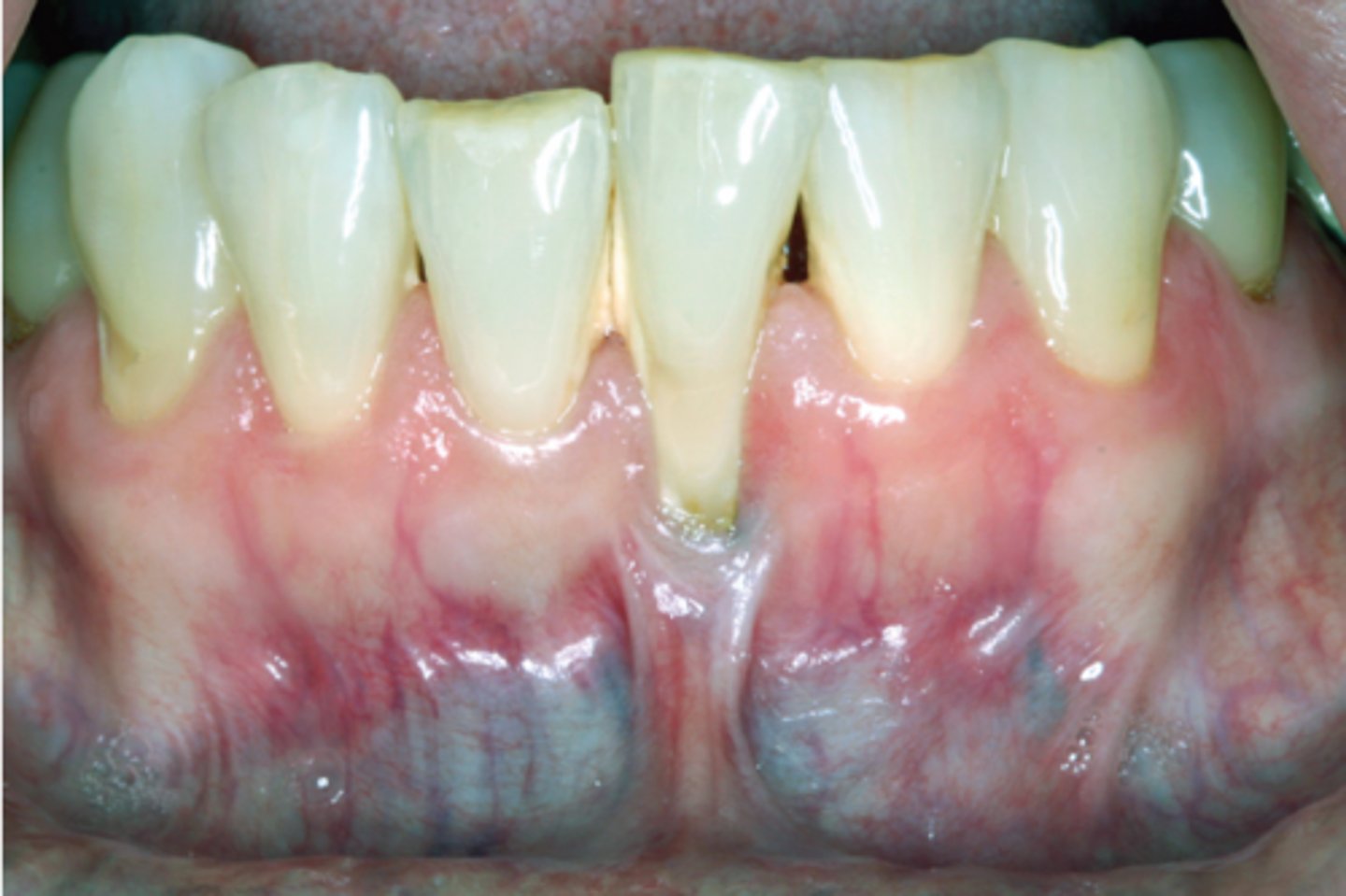
frenum
What is this recession caused by?
• hint: look at neighboring teeth for recession
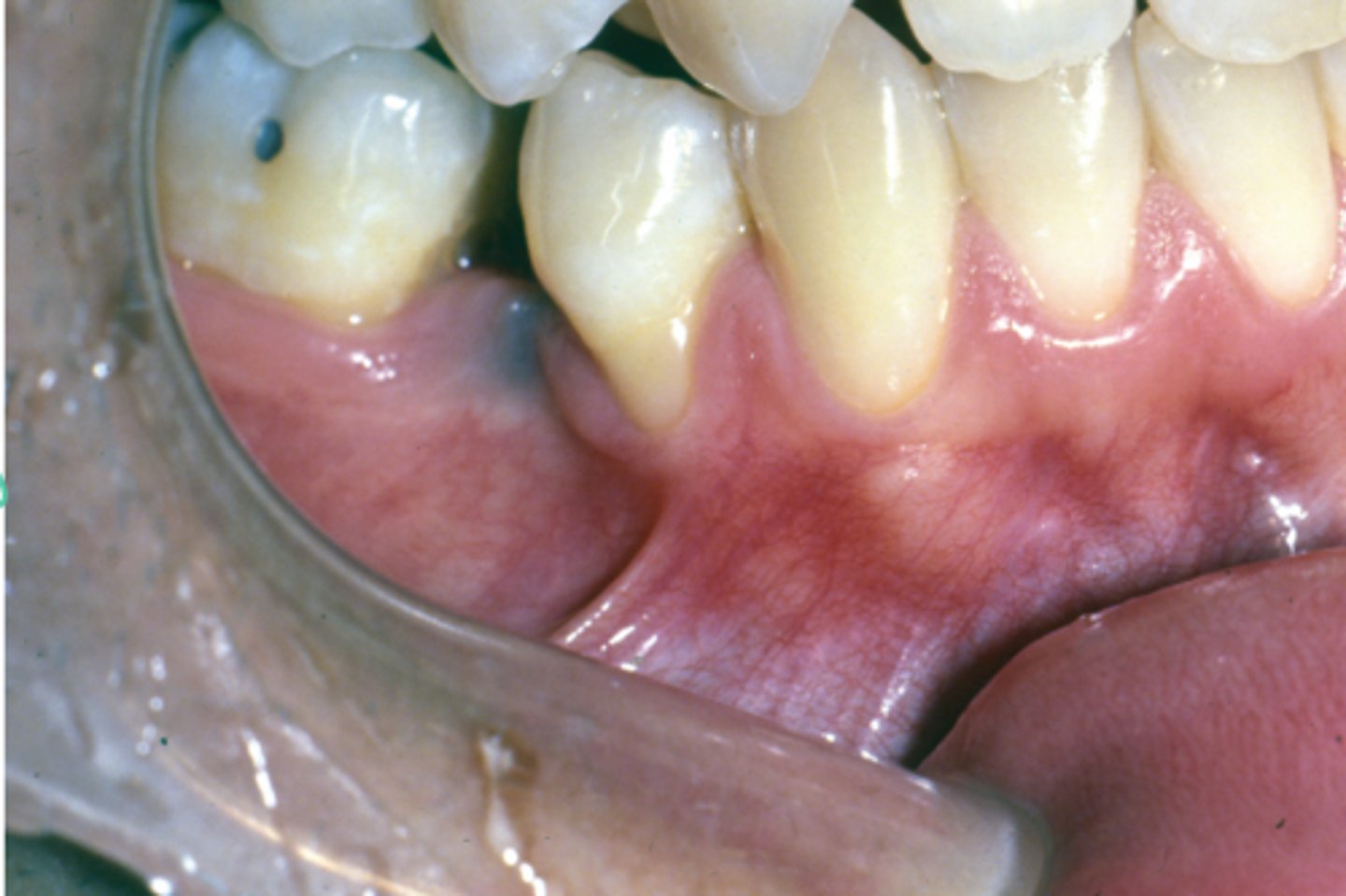
MGJ
not
tissue loss
KNOW
Miller Classifications
• reasons we DON'T use this anymore
• hard to find ___
• reliability has n___ been tested
• doesn't define t____ l____ compared to Cario
1, RT1
KNOW
Cairo Classification System
• Type __ (___)
• no loss of interproximal attachment
• attachment loss only on facial or lingual--can't see CEJ on mesial or distal
• most likely from traumatic TB
2, RT2
KNOW
Cairo Classification System
• Type __ (___)
• interproximal attachment loss is LESS than or equal to the buccal/facial attachment loss
• associated with horizontal bone loss
3, RT3
KNOW
Cairo Classification System
• Type __ (___)
• recession with loss of interdental attachment
• the proximal attachment loss is greater than the buccal attachment loss
• seen with infrabony defect
• associated with vertical bone loss
Cairo recession type 1, RT1
KNOW
• what recession type is associated with traumatic toothbrushing?
Cairo recession type 2, RT2
KNOW
• what recession type is associated with horizontal bone loss?
Cairo recession type 3, RT3
KNOW
• what recession type is associated with vertical bone loss?
Cairo recession type 2 (because there is interproximal attachment loss and it is less than the facial attachment loss)
KNOW (possible question)
• facial attachment loss of 4mm and there is 3mm of interproximal attachment loss. What Cairo classification system is this?
Cairo recession type 3 (because proximal attachment loss is greater than the facial attachment loss)
KNOW (possible question)
• facial attachment loss of 6mm and there is 8mm of interproximal attachment loss. What Cairo classification system is this?
caries, enamel
Product recommendations for recession
• need to recommend something for c___ control because it is NOT protected by e_____
sensitivity
Product recommendations for recession
• need to recommend something for s_______
proxy brush
Product recommendations for recession
• need to recommend something for embrasure spaces for example a _____ _____ would be a good recommendation
finger, thumb
Product recommendations for recession
• pt education: have patient hold TB with their _____ and ____ in a pinch grasp
MGJ
Product recommendations for recession
• see ____ deformities with recession
frenum, attachment, 2
Product recommendations for recession
• always check f_____ and carefully measure a______ (__mm is concerning)
bone loss
Product recommendations for recession
• need to educate pt that with recession comes ____ _____