Topic 1.6 - Chemical Equilibria, Le Chatelier’s principle and K c
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Define the term dynamic
equilibrium.
The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the
rate of the reverse reaction.
(Hence, the concentrations of reactant and product do not
change)
Give an essential condition
for an equilibrium mixture.
● Equilibrium occurs in a closed system (where
reactants and products cannot escape)
OR
● Macroscopic properties do not change with time
State Le Chatelier’s
principle.
If a system at equilibrium is disturbed,
the equilibrium moves in the direction
that tends to reduce the disturbance.
CH 4(g) + H 2 O (g) ⇌ CO (g) + 3H 2(g)
ΔH°= +210 kJ mol-1
What effect would increasing the temperature
have on the position of equilibrium?
The equilibrium position shifts to
the right.
(This is because the forward reaction is endothermic.
Yield of hydrogen increases.)
In the equation:
CH 4(g) + H 2 O (g) ⇌ CO (g) + 3H 2(g)
ΔH°= +210 kJ mol-1
What effect would increasing the pressure
have on the position of equilibrium?
The equilibrium position shifts to the left.
This is because the forward reaction is produces more moles of gas than the
reverse reaction (4 moles of product, 2 moles of reactant). Yield of hydrogen
decreases.
The reaction:
CH4(g) + H 2 O (g) ⇌ CO (g) + 3H 2(g) ΔH°= +210 kJ
mol-1
Suggest and explain why an industrial chemist
may use a high pressure for this production
of hydrogen from the above reaction?
1. The high pressure increases the collision frequency,
increasing the rate of reaction.
2. This is a compromise pressure between an economically
viable rate of reaction and a slightly lower yield of hydrogen.
What effect does a catalyst
have on the position of
equilibrium?
No effect.
(because catalyst affects rate of forward and reverse reactions equally)
What condition affects the value of K c ?
Temperature
2[A] + 3[B] + [C] ⇌ [D]+ 4[E]
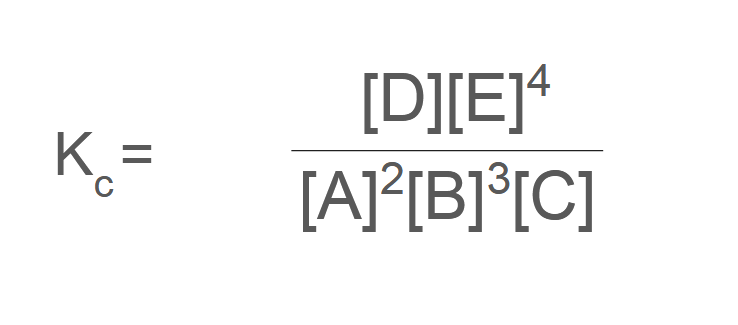
Deduce units for the value of K c
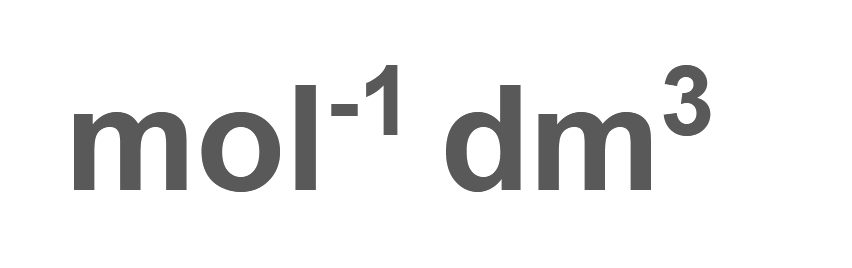
What type of system is K c
relevant for?
Homogeneous systems in
equilibrium
What does K c being greater
of lesser than 1 suggest for
the position of equilibrium?
Greater than 1 = over to the right
Lesser than 1 = over to the left
What effect does decreasing the
temperature in an endothermic
reaction have on K c ?
K c decreases
What effect does increasing the
temperature in an endothermic
reaction have on Kc ?
K c increases
What effect does decreasing the
temperature in an exothermic
reaction have on K c ?
K c increases
What effect does increasing the
temperature in an exothermic
reaction have on K c ?
K c decreases