Statistics Exam 3
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PSYC 211
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
What is descriptive research?
summarizes and describes behavior
describes the prevalence of a behavior
cannot determine causality
only one variable is being measured
What is correlational research?
discovers the relationship between two variables
cannot determine causality
no manipulation of an independent variable
cannot rule out confounding variables
What is experimental research?
how one variable affects another variable
manipulation of an independent variable
random assignments to group
attempt to control confounding variables
What is quasi-experimental research?
how one variable affects another when random assignment is not possible
can provide low-moderate support for a causal relationship among variables
passive manipulation of an independent variable, no random assignment
Correlation does not mean causation.
true
When should you use the independent samples t-test?
one dichotomous independent variable
one continuous dependent variable
between-subjects design
What is the purpose of independent samples t-test?
to determine whether the means of two groups are different than one another (i.e., are the means of two groups significantly different)
What is a null hypothesis?
when two groups are not different from one another
What is an alternative hypothesis (non-directional)?
when two groups are different from one another
What results in a higher t-score?
a larger difference between groups
What results in a lower t-score?
a greater deal of variability between groups (i.e., less likely to find significant difference)
What does degrees of freedom tell us?
how many values are free to vary
What is the critical t-value?
the cutoff t-value
What do you use to find the critical value of t?
alpha (.05) and degrees of freedom
When do you reject the null hypothesis?
when there is less than a 5% chance that the null hypothesis is true (i.e., difference is not due to chance)
When do you fail to reject the null hypothesis?
when there is a greater than 5% chance that the null hypothesis is true (i.e., difference is due to chance)
What is Cohen’s d?
standardized difference between two means
How do you calculate Cohen’s d?
by dividing the differences between the means by the pooled standard deviation
What does correlation test?
covariance between variables
What is required to establish causality?
a true independent variable
What is an independent variable?
a variable that the experimenter manipulates (i.e., a variable that is changed, manipulated, or controlled in a study to see how it influences other variables)
What does a study need to be considered experimental?
at least one independent variable
What is a potential problem when evaluating the independent variable?
faulty manipulation may result in failed experiment (i.e., did we actually manipulate what we thought we were manipulating?)
What is a dependent variable (or measured variable)?
an outcome variable
You may observe different values on a dependent variable depending on levels of an independent variable.
true
How many dependent variables must an experiment have?
at least one
What is a confounding variable?
a variable other than the iv that differs systematically between conditions
How does a confounding variable invalidate an experiment?
it is unclear whether differences are due to iv or confound
Should confounding variables be eliminated or restricted as much as possible?
yes
What are some common confounding variables?
demographic variables, individual differences, individual habits, and external factors
What are subject variables (or individual differences)?
characteristics of the participant (e.g., age, race, hobbies, income, sex)
Are subject variables true independent variables?
no, but they can be treated the same during an analysis
What does correlation do?
measures and describes the relationship between two variables
When conducting a correlation, what are we interested in?
the covariance of two variables
What is covariance?
how do variables change (vary) in relation to one another
Direction of positive correlation
two variables tend to change in the same direction (i.e., as variable X increases, variable Y also increases & vice versa)
Direction of negative correlation
two variables tend to change in the opposite direction (i.e., as variable X increases, variable Y decreases & vice versa)
What does a sign represent in correlation coefficient?
direction of relationships (e.g., -1 to 1)
What is the magnitude (strength) of a relationship determined by?
the absolute value of the correlation coefficient (e.g., value of 0 is no relationship, value of -1 or 1 is perfect correlation)
How do lines impact the strength of the relationship?
the closer (or straighter) the line the stronger the correlation
What does statistical significance tell us?
if there is no correlation between x and y in the population, what is the probability of getting a correlation as large or larger than what we found in our sample
chance of finding the correlation when the null hypothesis is true
rejecting the null hypothesis when it’s true (aka type 1 error)
the probability of finding correlation
What can you use to determine statistical significance?
a critical value table of r
Aspects of restricted range
interpret with caution
may differ from full-range correlation
don’t generalize beyond sample range
What are outliers?
extreme x and/or y values
What can outliers do to correlation?
may inflate or deflate correlation
Correlation is necessary for causation, but not sufficient
true
What is causation determined by?
experimental methodology, not the analysis used
What is the criteria for inferring causation?
correlation (two variables must vary together)
temporal precedence (iv before dv)
no plausible alternative explanations (manipulation of a iv, random assignment to groups)
What can correlations be used to measure?
validity
reliability
prediction
What is pearson’s correlation coefficient?
the most commonly used correlation coefficient (r)
Aspects of Pearson’s correlation coefficient
both variables must be continuous
at least interval scale of measurement
data must be linear
pearson’s r is strongly impacted by outliers
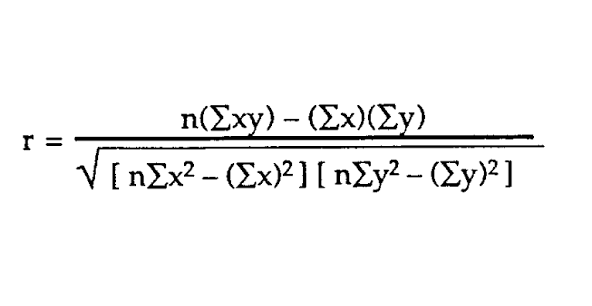
Aspects of Spearman’s correlation coefficient
uses pearson’s formula
scores are converted to ranks
measures relationship consistency independent of form
ordinal, interval, and ratio scales
nonlinear relationships
Aspects of Point-Biserial correlation coefficient
uses pearson's formula
one continuous variable
one dichotomous variable
What is the formula for degrees of freedom?
df = n1 + n2 - 2
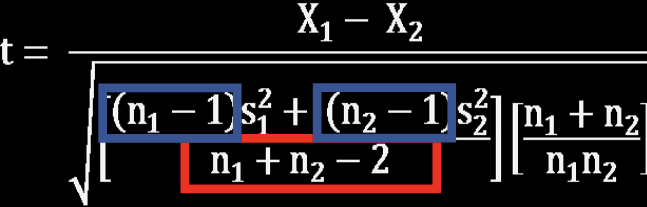
What is the p-value?
the probability of something occurring due to chance
Aspects of an experimental group
exposed to iv manipulation
can have multiple experimental groups for different iv levels
Aspects of a control group
not exposed to the iv manipulation
a “baseline”
When may there be no “groups”?
if the iv is continuous
We want groups to be equal on all variables except?
the iv
What is simple random assignment?
equal chance of being assigned to any group/condition
Aspects of matched/stratified random assignment
participants are matched into subcategories
participants within a subcategory are randomly assigned to conditions
deliberate effort to make sample groups representative of target population
Each participant experiences only ___ level of the independent variable in a between-subject design
one
What is necessary for a between-subject design to be effective?
random assignment
All participants experience ___ levels of the independent variable in within-subject design
all
What are the advantages of within-subject design?
requires fewer participants
more statistical power
ability to detect the effect of an iv if there is one
reduces effects of subject variables
What are the disadvantages of within-subject design?
order effects
carryover
practice
sensitization
fatigue
What is carryover?
effect of one iv level is still present when the next level is tested
What are practice effects?
performance improves with repeated testing (e.g., sat)
What are fatigue effects?
latter-session performance is worse because the participant gets tired or bored
What is sensitization?
participant realizes what your hypothesis is
Aspects of internal validity
determines degree to which we can draw accurate conclusions about effects of iv
highest when all confounds are eliminated
achieved through experimental control and sound research design
What is differential attrition?
different numbers or types of people drop out from each group
What is demand characteristics?
participants may perform in the way they believe the experimenter wants them to
What is placebo effect
change as a result of the mere suggestion of change
Aspects of external validity
degree to which a study’s results would hold true in other situations
the more internally valid a study is (greater experimental control), the less likely it will be externally valid (generalizable to the real world)