Exam 1 Bio 228 Lab
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
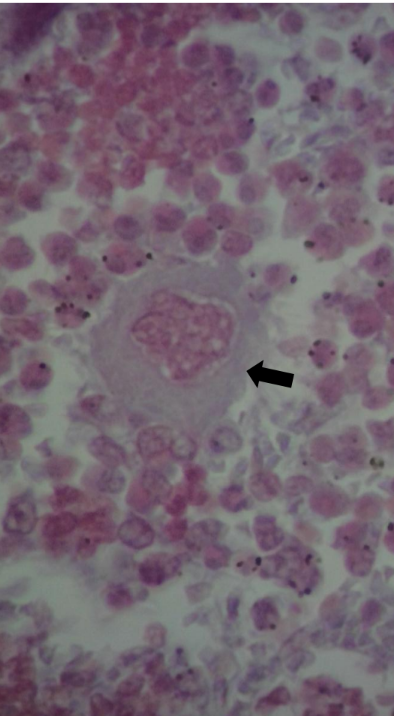
what is this?
megakaryocyte
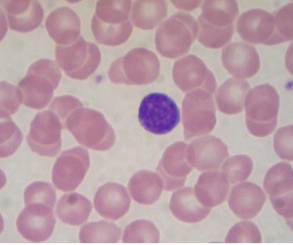
what is this?
lymphocyte
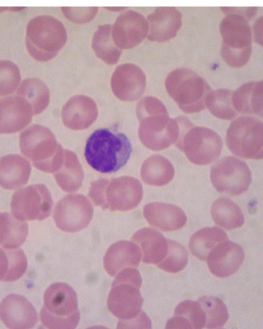
what is this?
monocyte
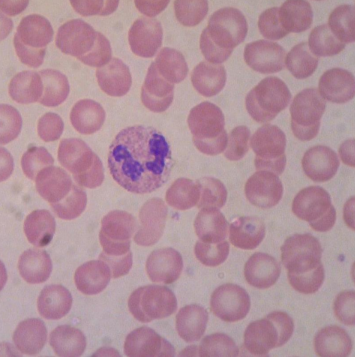
what is this?
neutrophil
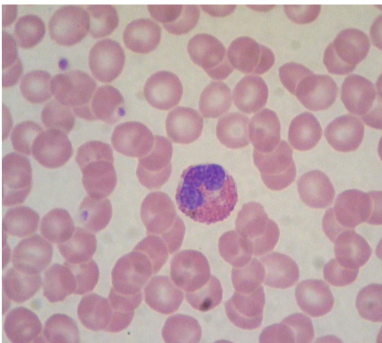
what is this?
eosinophil
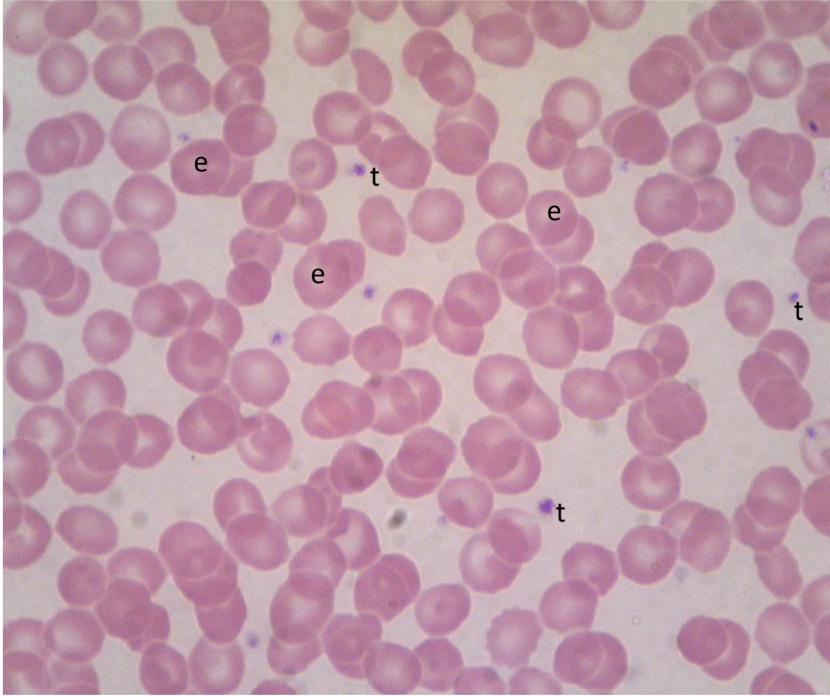
what is t
thrombocyte

what is this?
basophil
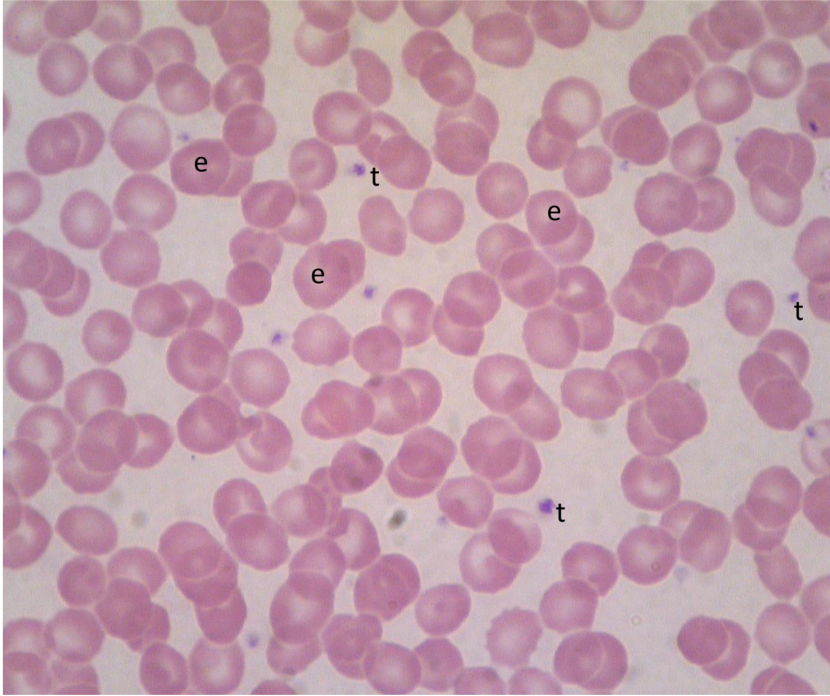
what is e
erythrocyte
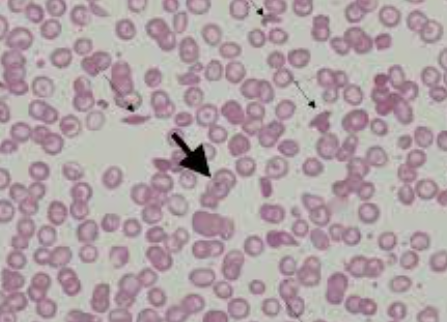
what is this
sickle cell erythrocyte
55% of whole blood
plasma
what is plasma
liquid portion of blood, transports, maintains blood volume and pressure, immunity, pH and electrolyte balance
45% of whole blood
formed elements
what do formed elements do
rbc (transport o2 and co2), wbc( immunicty), platletes (clotting)
what does buffy layer do
used to isolate wbc or platelets
what are the 3 types of granular leukocytes
neurophil, eosinophil, basophil
population of wbc
50-70%
population of eosinophils
1-4%
population of basophil
0.5-1%
what do neutrophils do
fight bacterial infections
what do eosinophils do
fight parasitic infections and neutrolize effects of histamines
what do basophils do
release histamine and heparin involved in inflammatory response
what are the agranular leukocytes
lymphocte and monocyte
populalation of lymphocyte
20-40% wbc
population for monocytes
2-8% wbc
what do lymphocytes do
repsonsible for adaptive immune response to infection
what do monocytes do
phagocytic to disease, increase in chronic infection
what is total rbc count
how many rbc are in your blood
anemia
decrease rbc
polycythemia
increase rbc
what is hematocrit hct
percentage of rbc in whole blood
what is hemoglobin Hb
protein carries o2 in rbc
low hct and low hb indicates
anemia
high hct and high hb indicates
dehydration
low hct normal hb
overhydration
normal hct low hb
iron deficiency
total wbc count test
how much leukocytes per unit volume
leukocytosis
high wbc count
leukopenia
low wbc count
what is differential wbc count
shows percentage of each type of wbc
what does coagulation time test do
used to determine the time required for blood to clot
hemostasis
process that stops blood flow from a damaged blood vessel
what are antigens (agglutinogens)
glycoproteins on rbc surface
what are antiboides
plasma portein associated with antigens
andigens + antibodies is what
agglutiniation (clumping)
what are Rh antigens
Rh+
no Rh antigens is what
Rh-
Rh neg person does not carry anti-Rh except when
they are exposed to Rh + blood
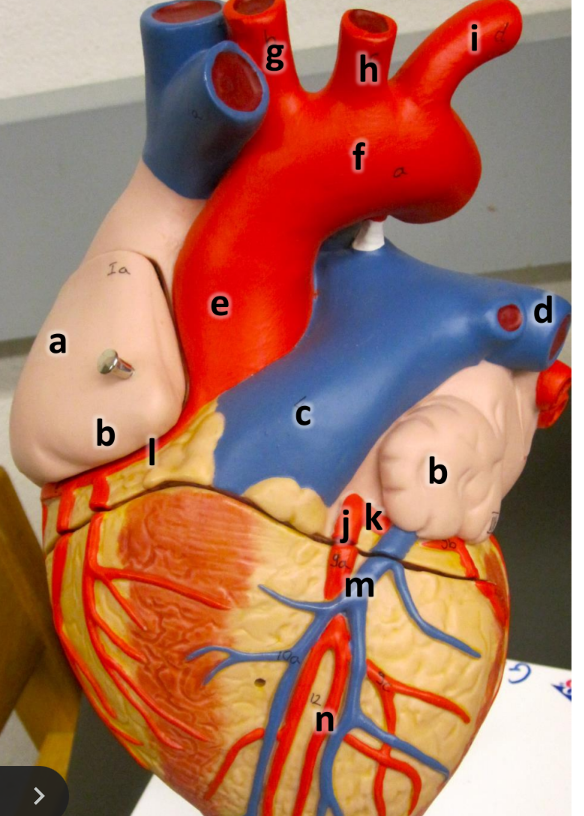
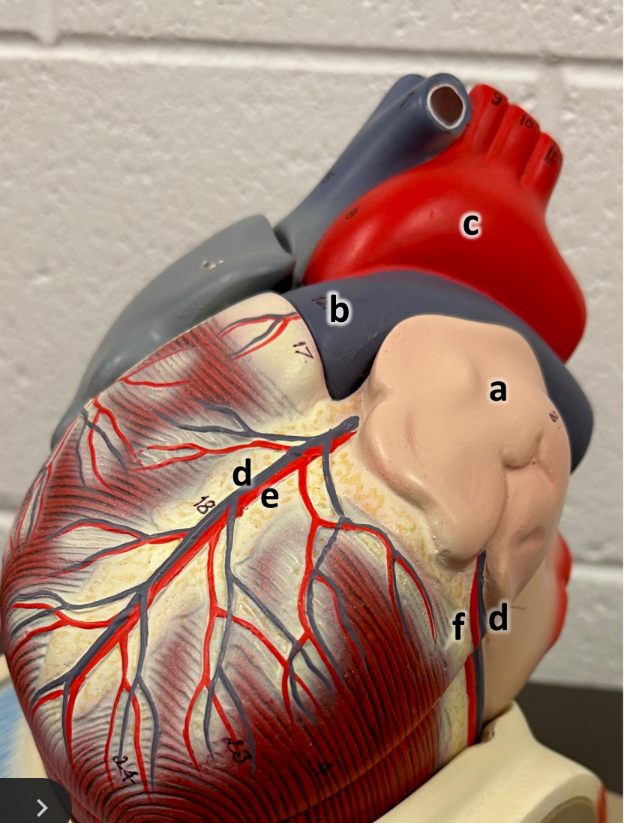
what is a
right atrium
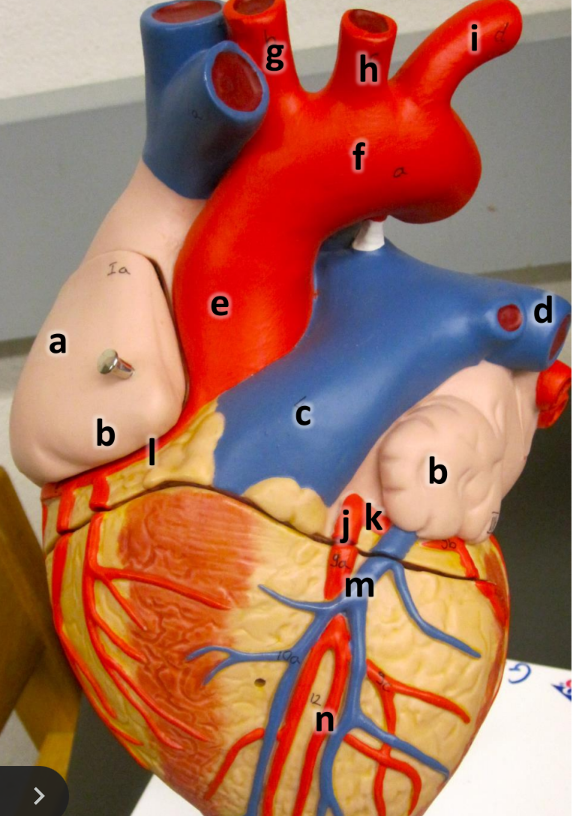
what is b
auricle (L/R)
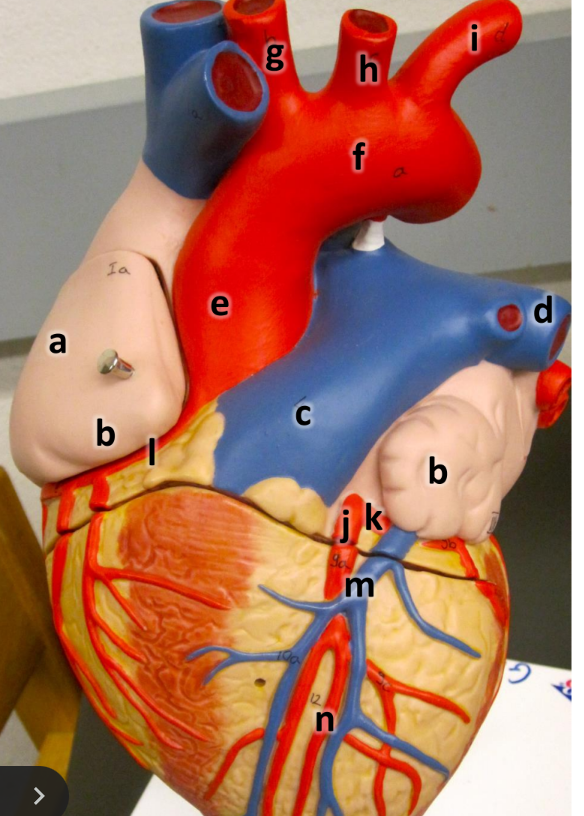
what is c
pulmonary trunk
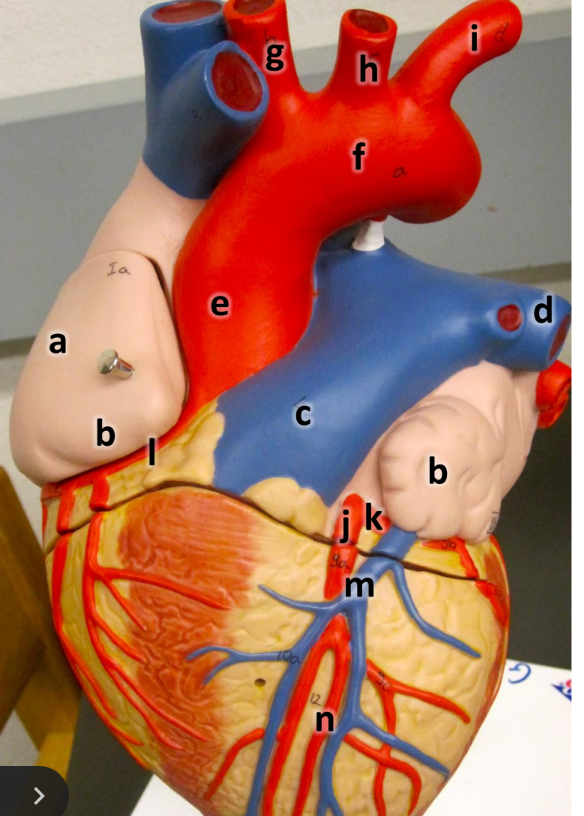
what is d
left pulmonary artery
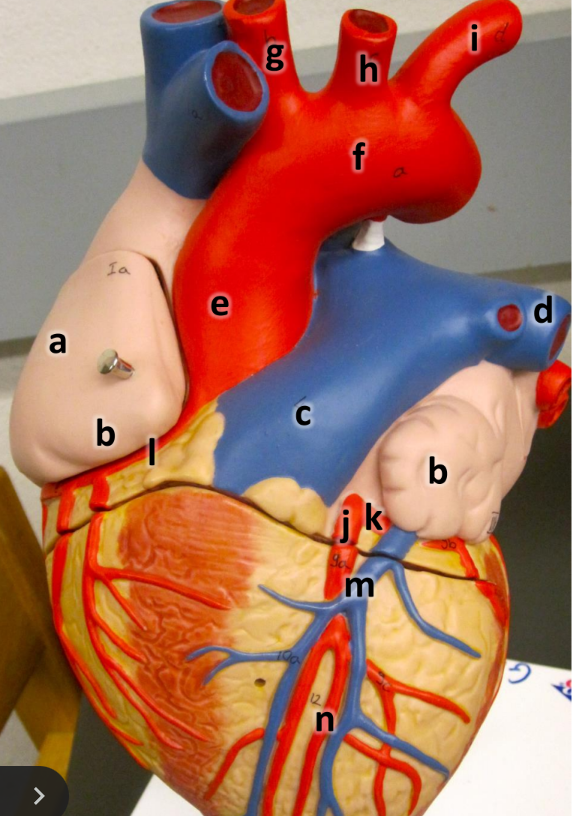
what is e
ascending aorta
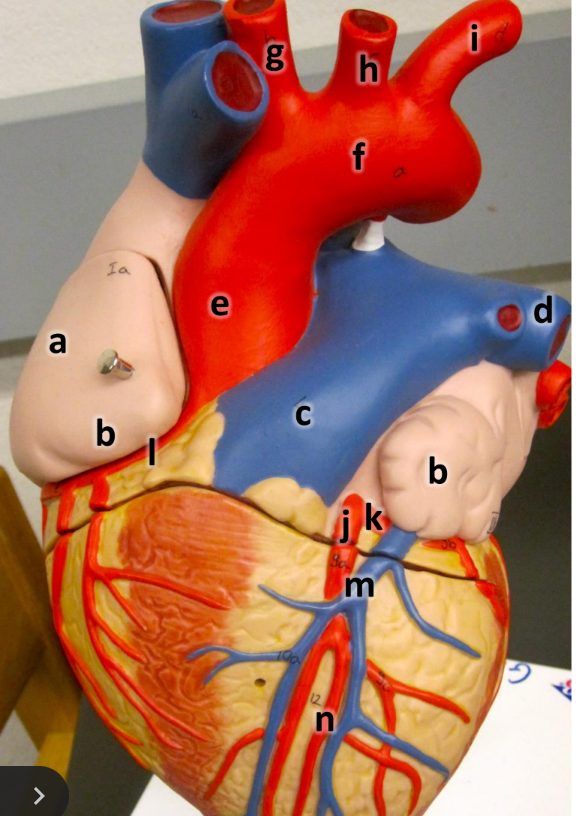
what is f
aortic arch
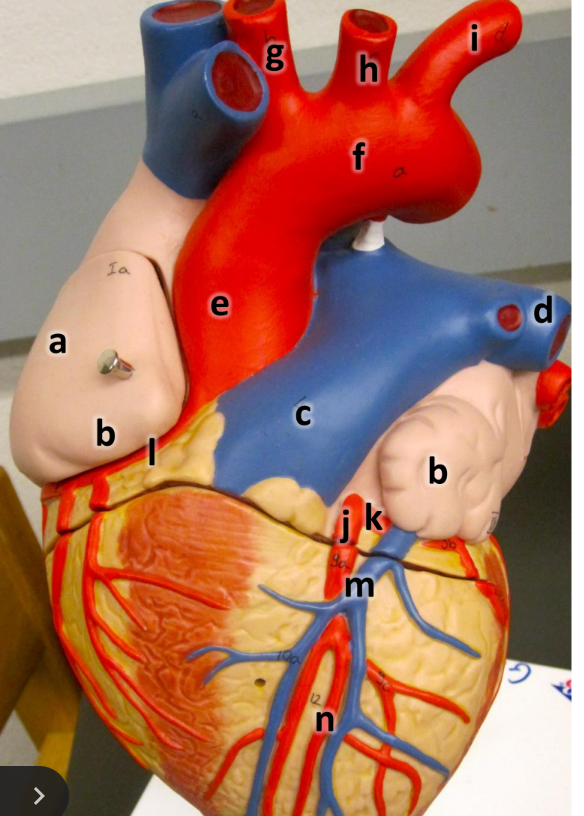
what is g
brachiocephalic trunk
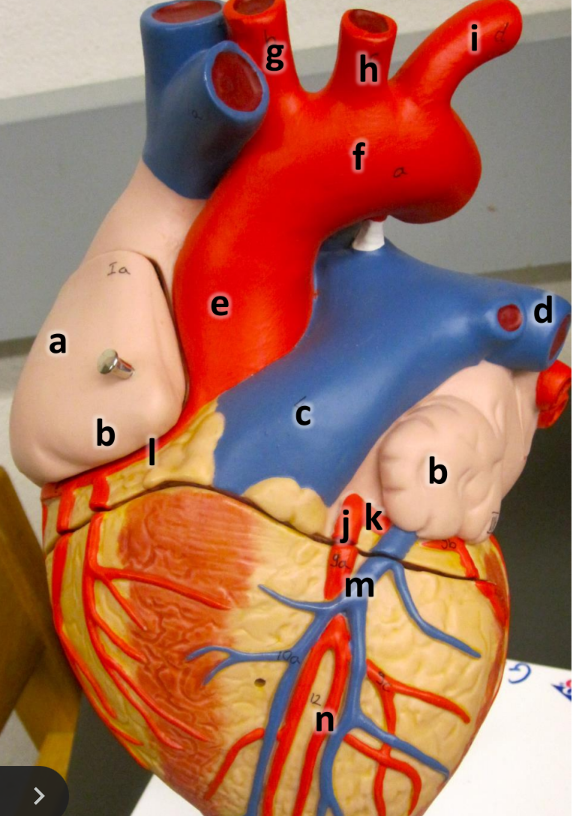
what is h
left common carotid artery
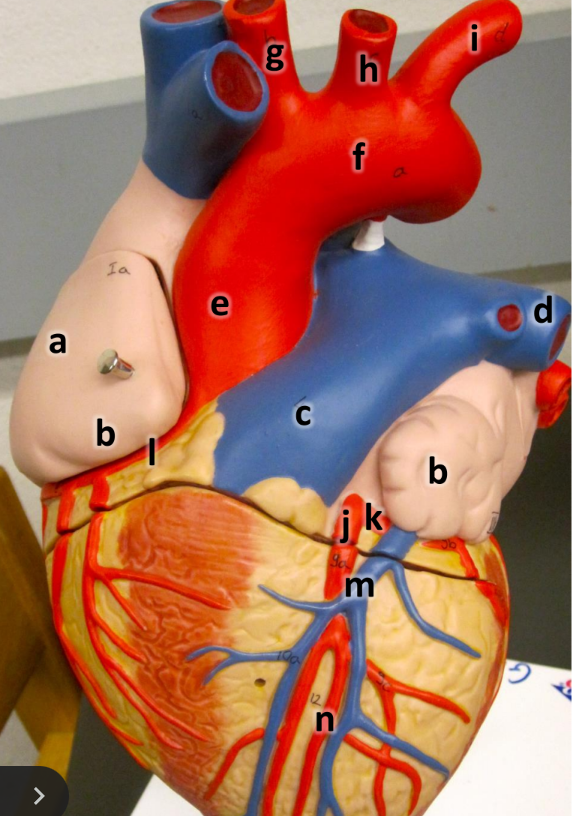
what is i
left subclavian artery
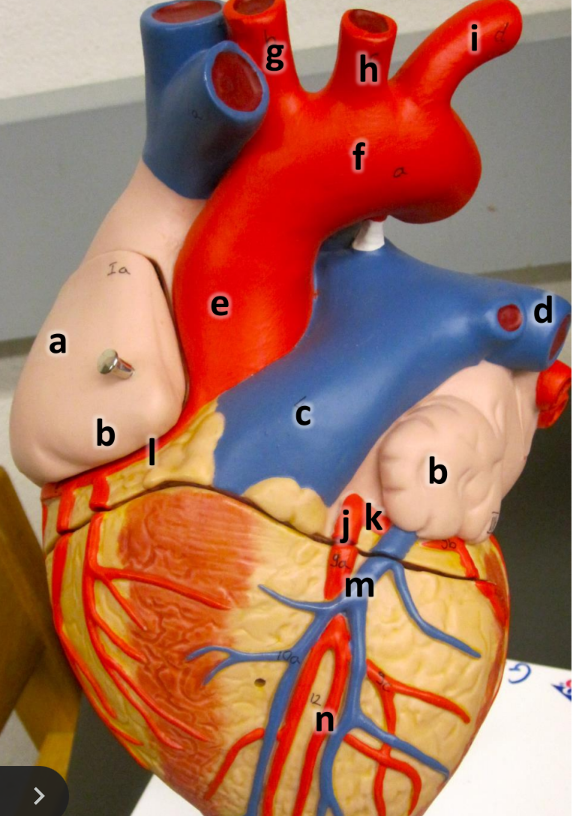
what is j
left coronary artery
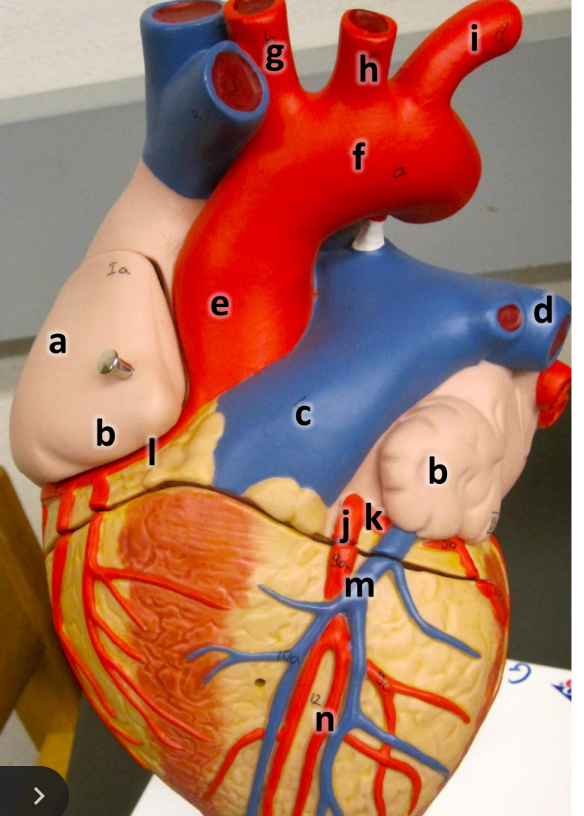
what is k
circumflex artery
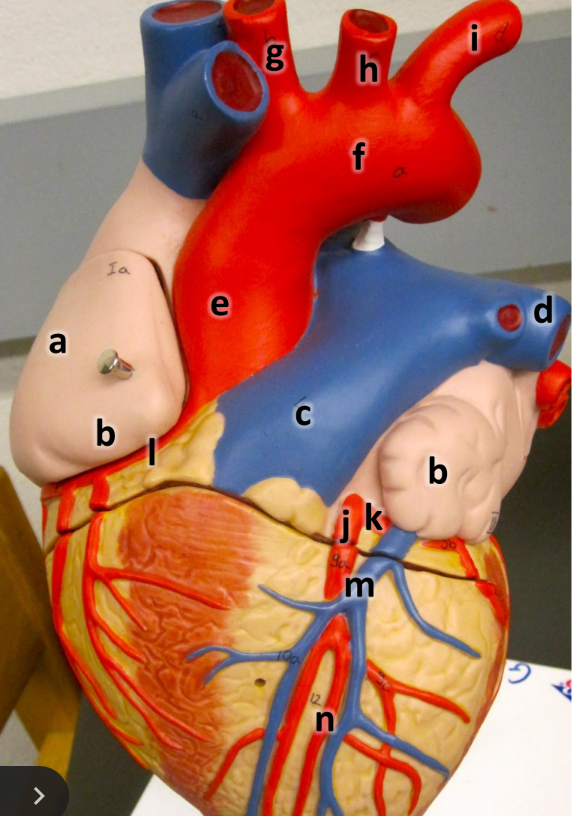
what is l
right coronary artery
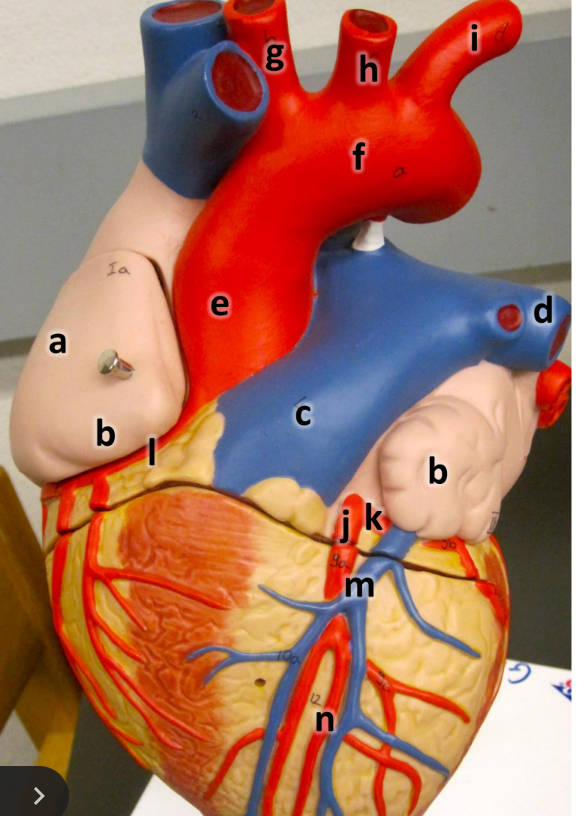
what is m
great cardiac vein
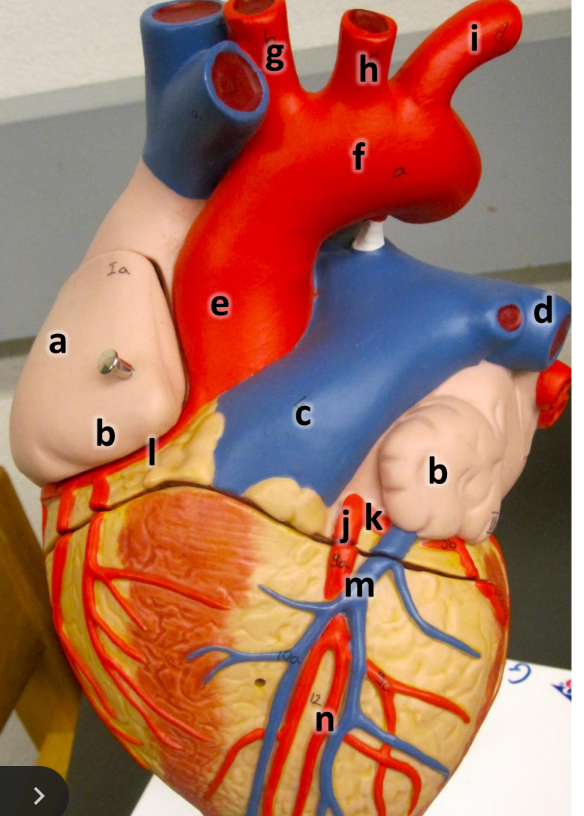
what is n
anterior interventricular artery
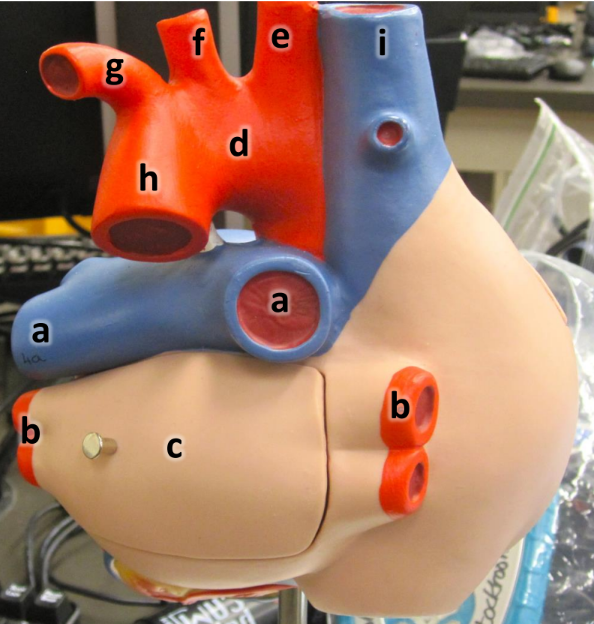
what is a
pulmonary arteries (L/R)
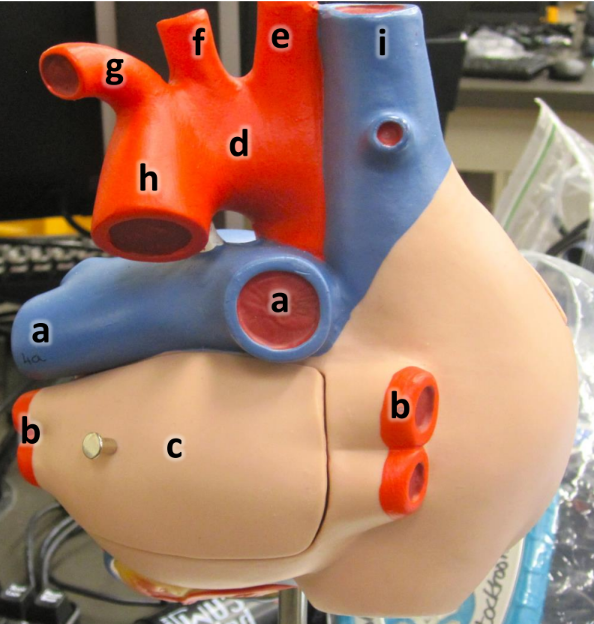
what is b
pulmonary veins (L/R)
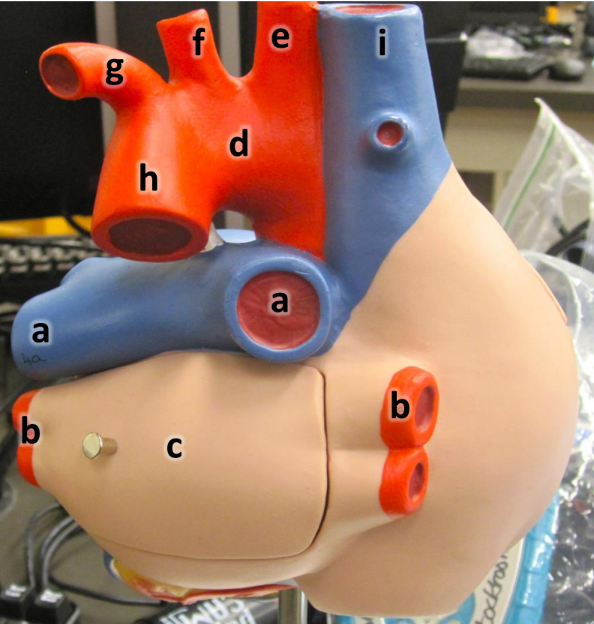
what is c
left atrium
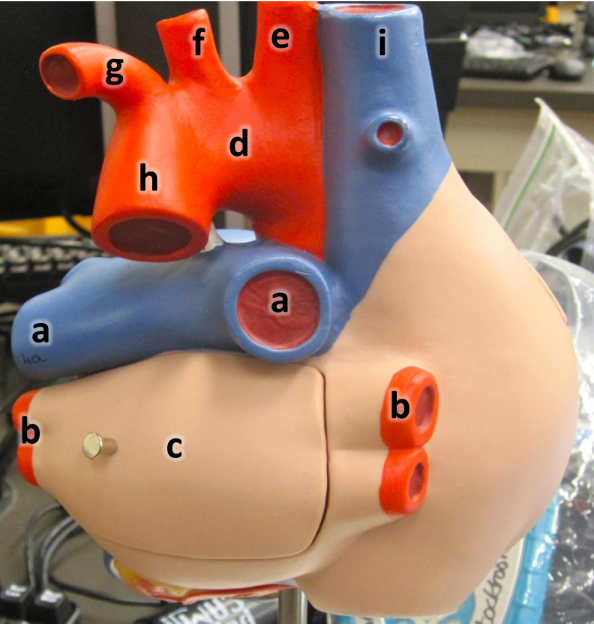
what is d
aortic arch
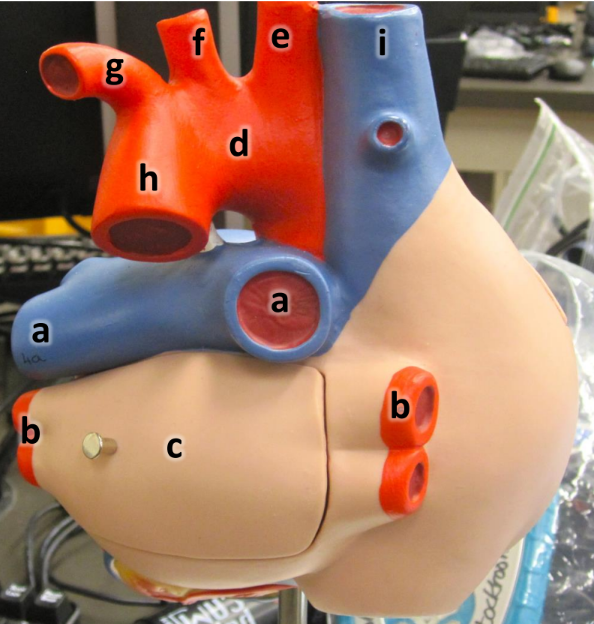
what is e
brachiocephalic artery
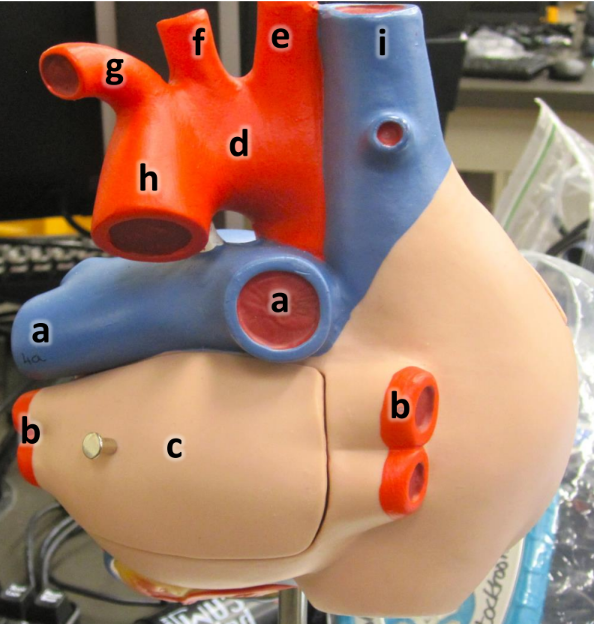
what is f
left common carotid artery
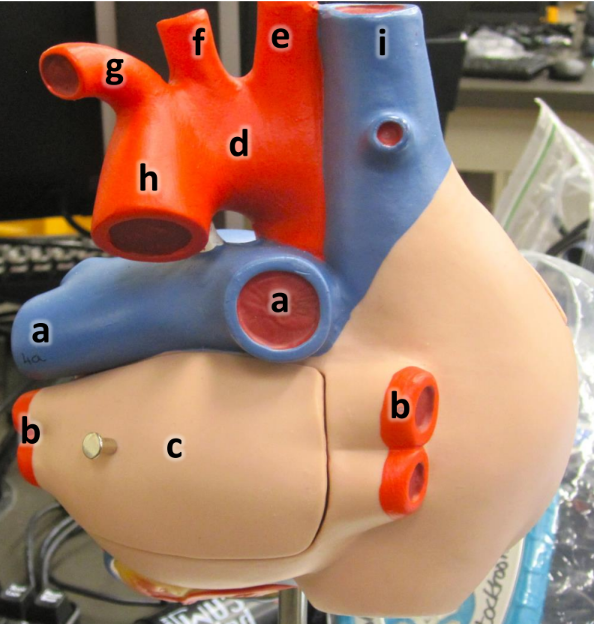
what is g
left subclavian artery
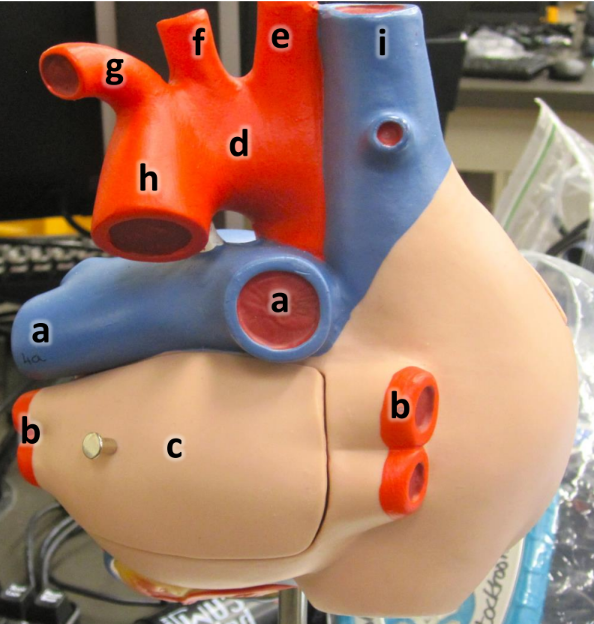
what is h
descending aorta
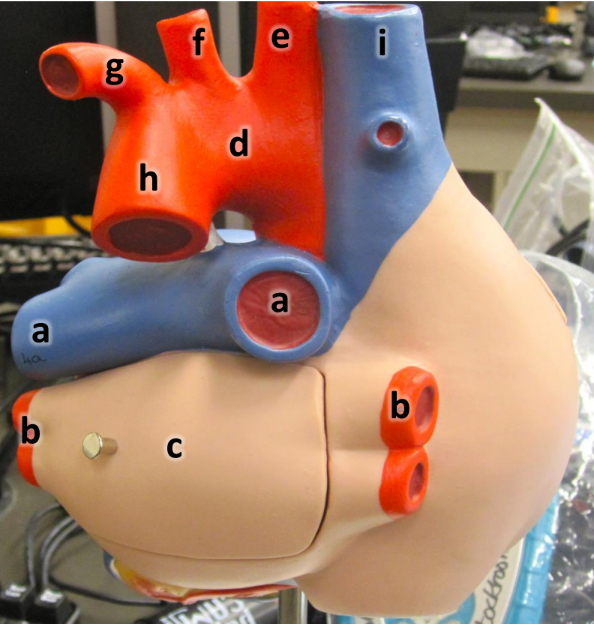
what is i
superioir vena cava
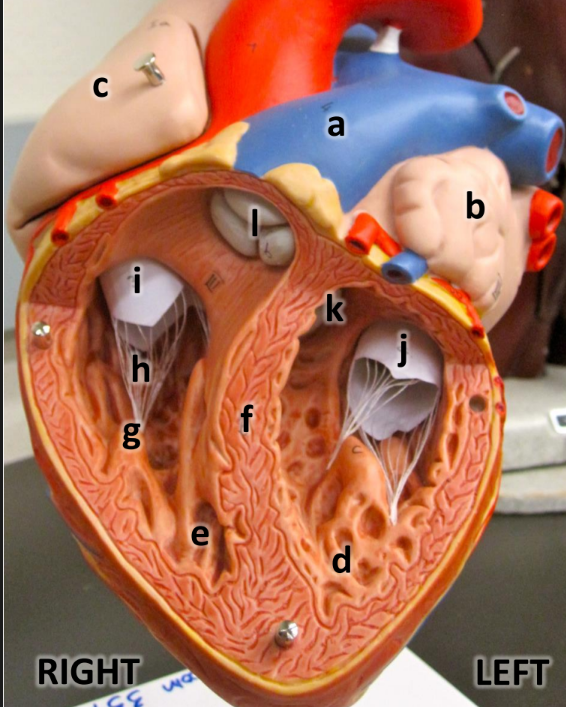
what is a
pulmonary trunk
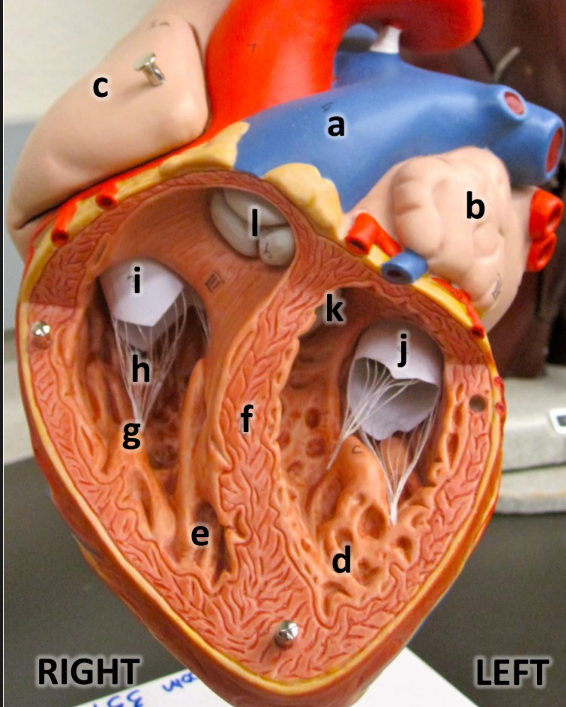
what is b
left atrium with auricle
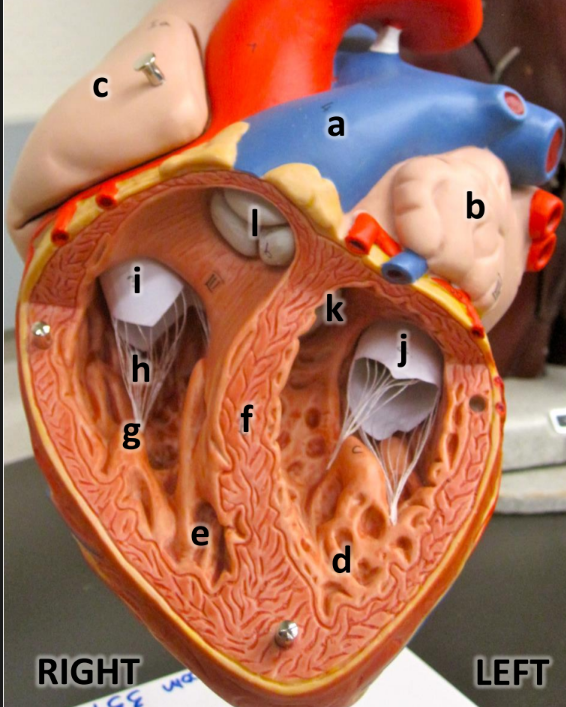
what is c
right atrium with auricle
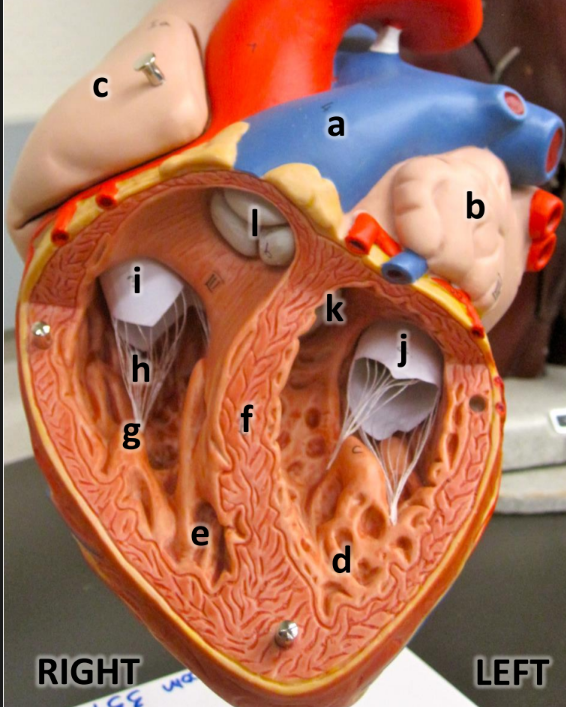
what is d
left ventricle
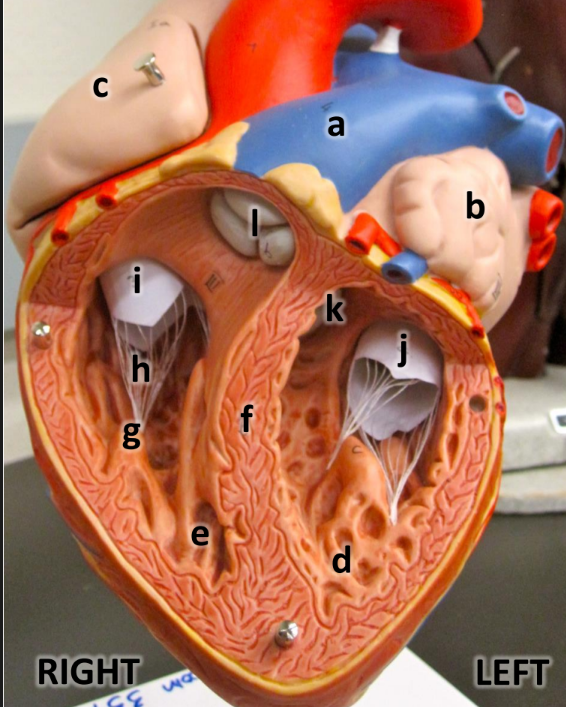
what is e
right ventricle
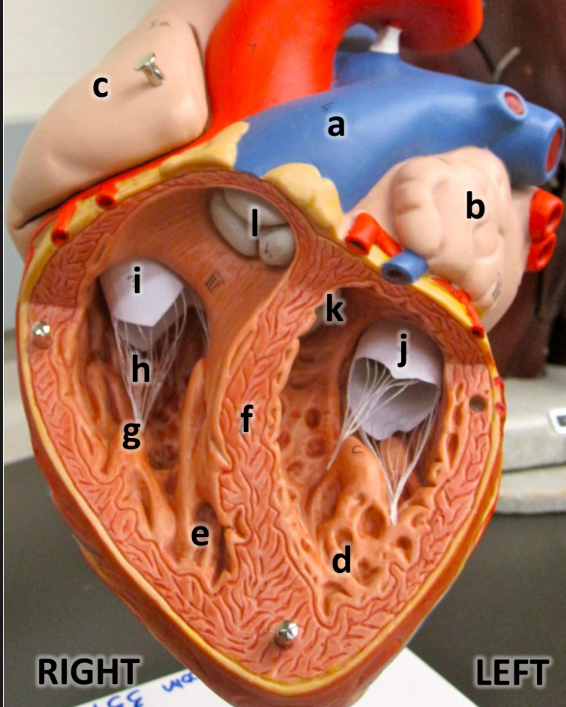
what is f
interventricular septum
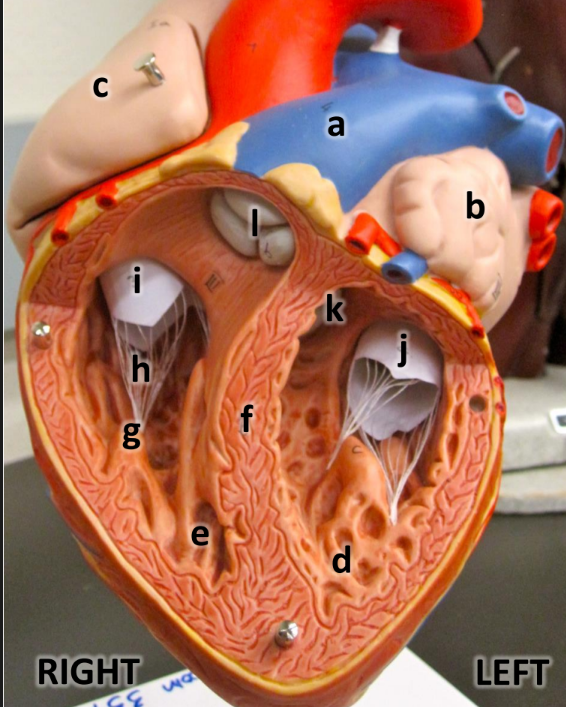
what is g
papillary muscles
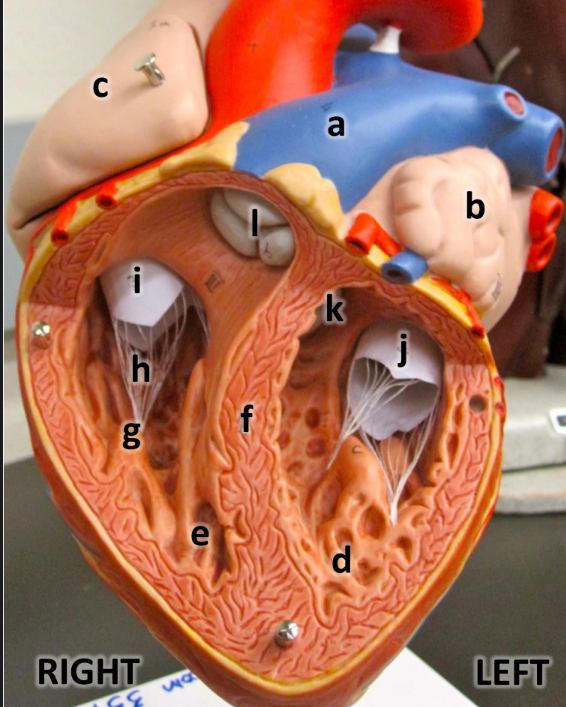
what is h
chordae tendineae
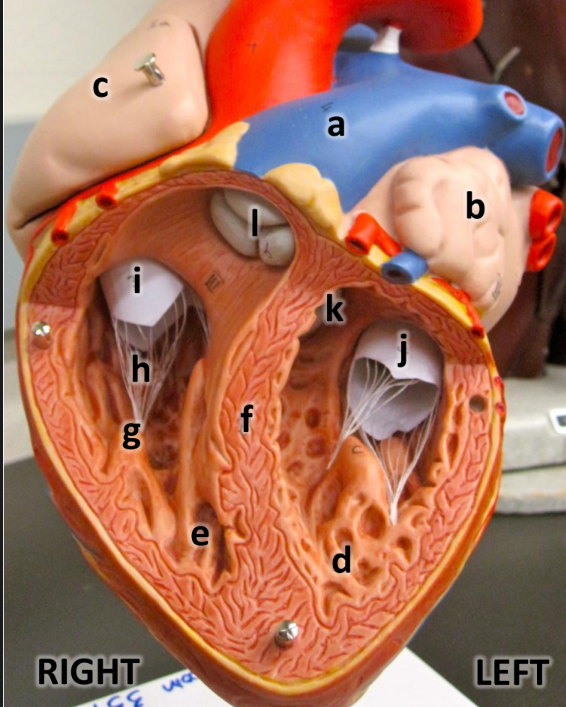
what is i
tricuspid valve
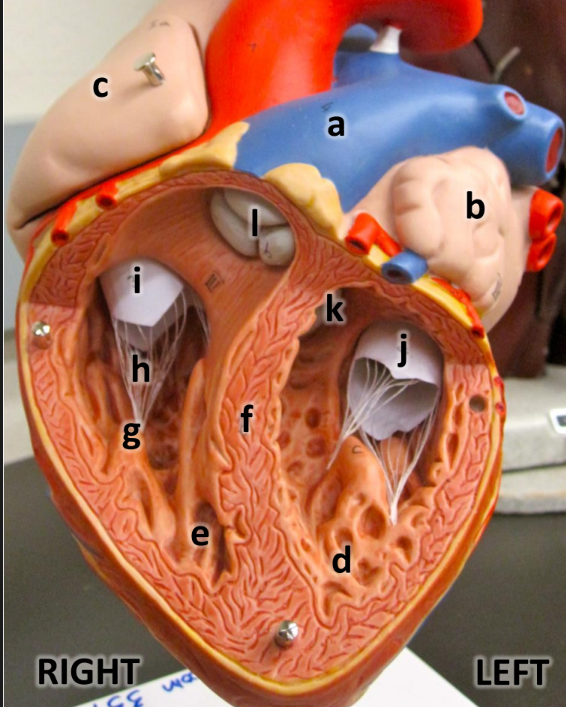
what is j
bicuspid valve
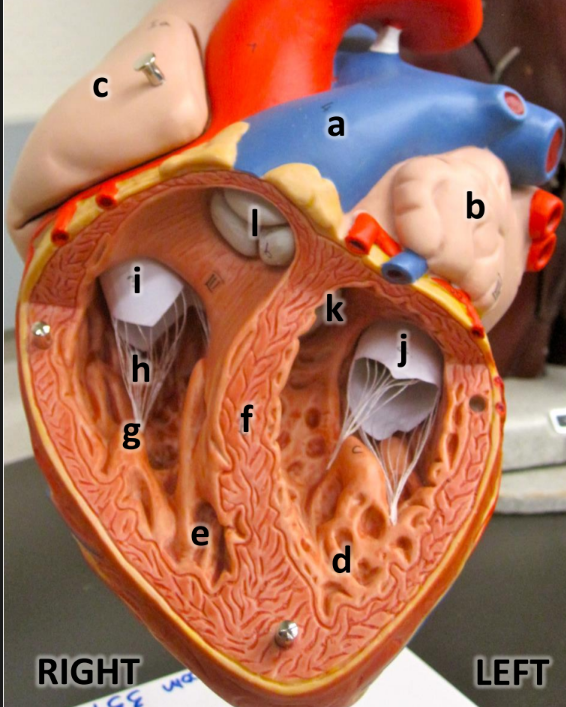
what is k
aortic semilunar valve
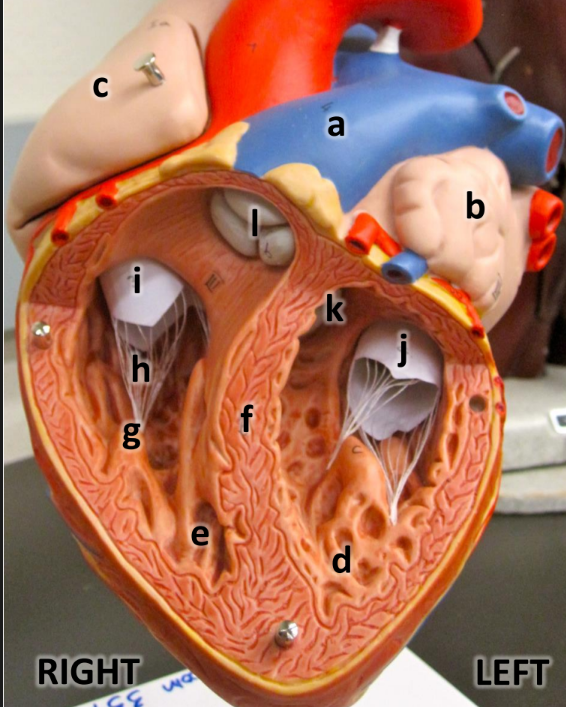
what is l
pulmonary semilunar valve
what is a
right atrium
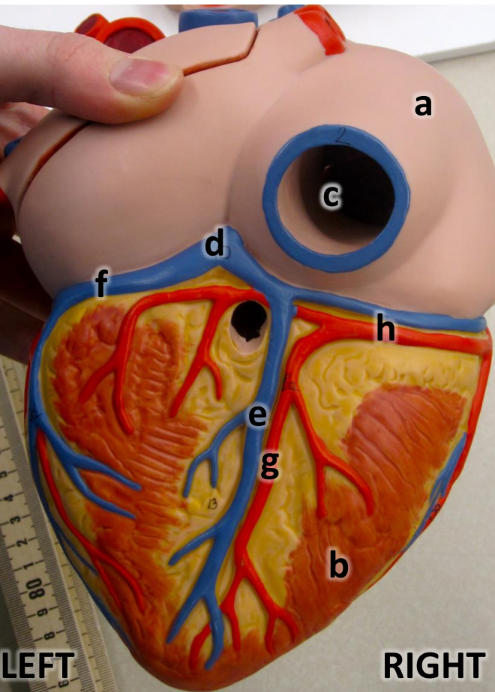
what is b
right ventricle
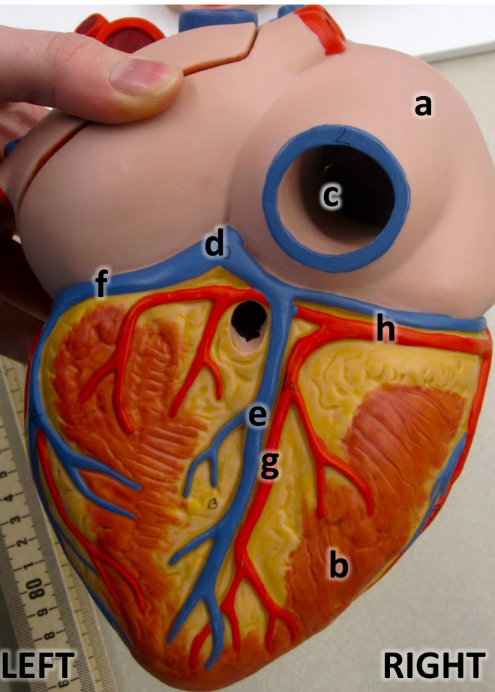
what is c
inferioir vena cava
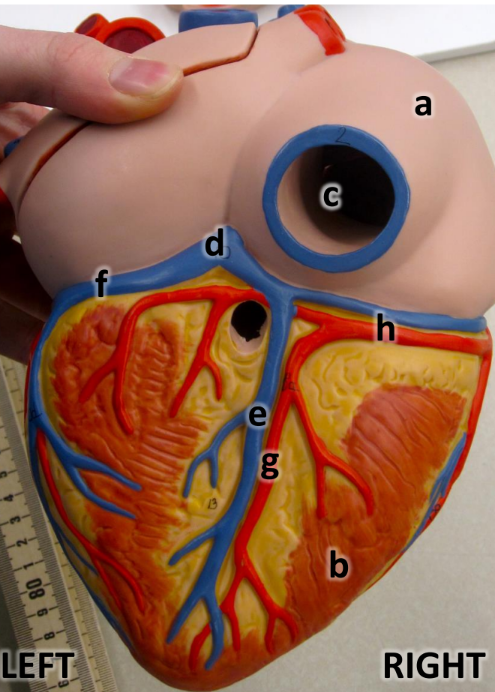
what is d
coronary sinus
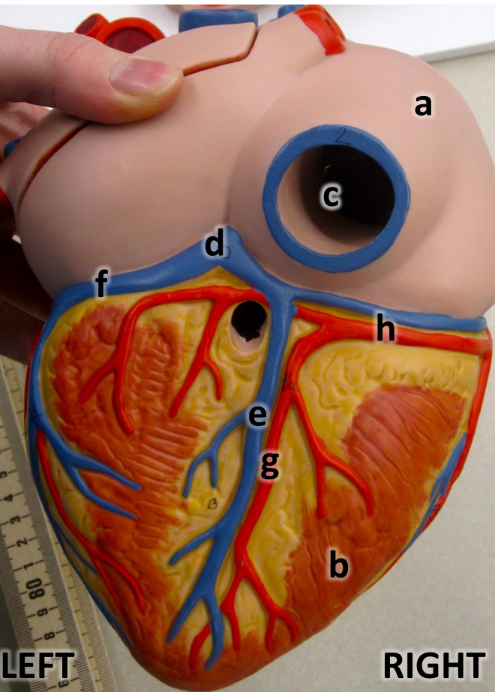
what is e
middle cardiac vein
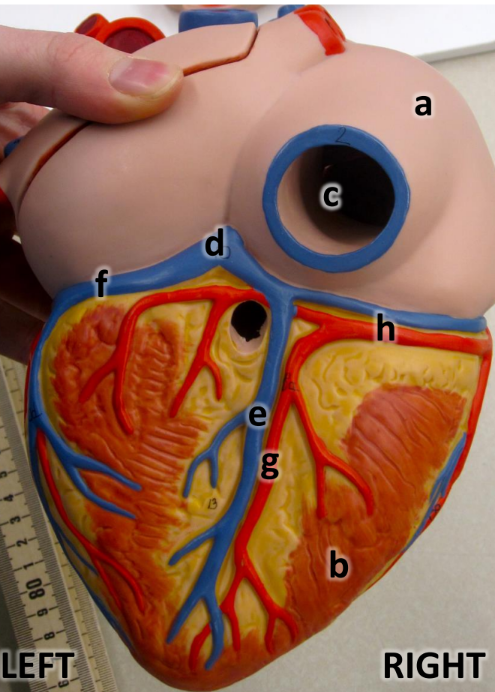
what is f
great cardiac vein
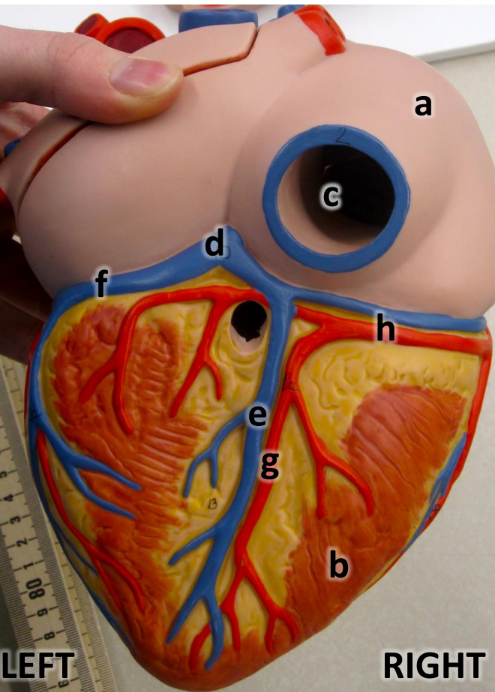
what is g
posterioir interventricular artery
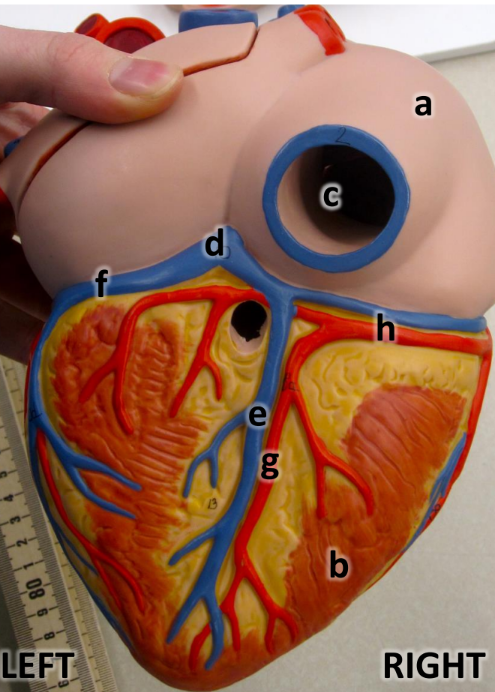
what is h
right coronary artery
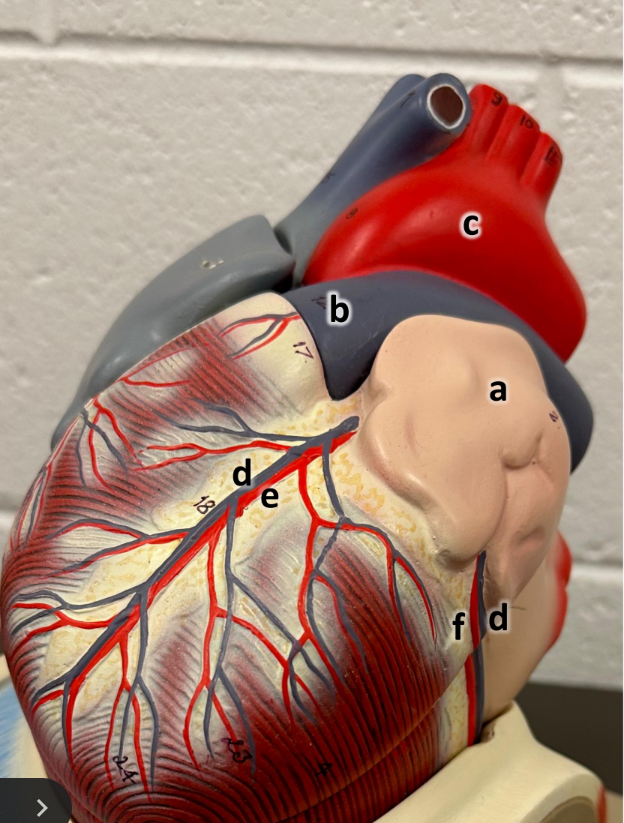
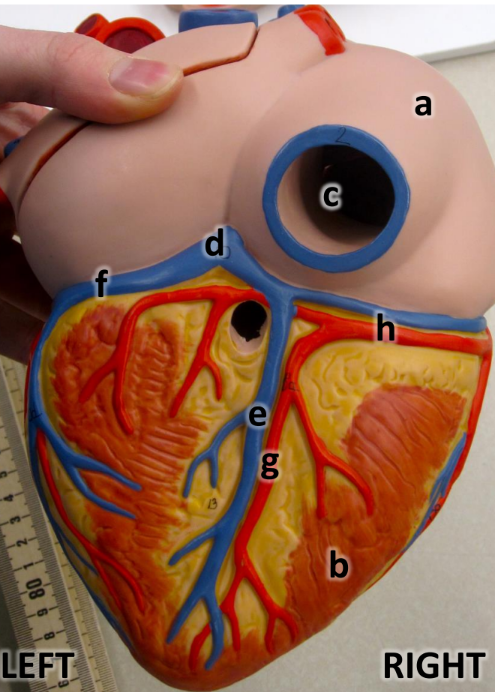
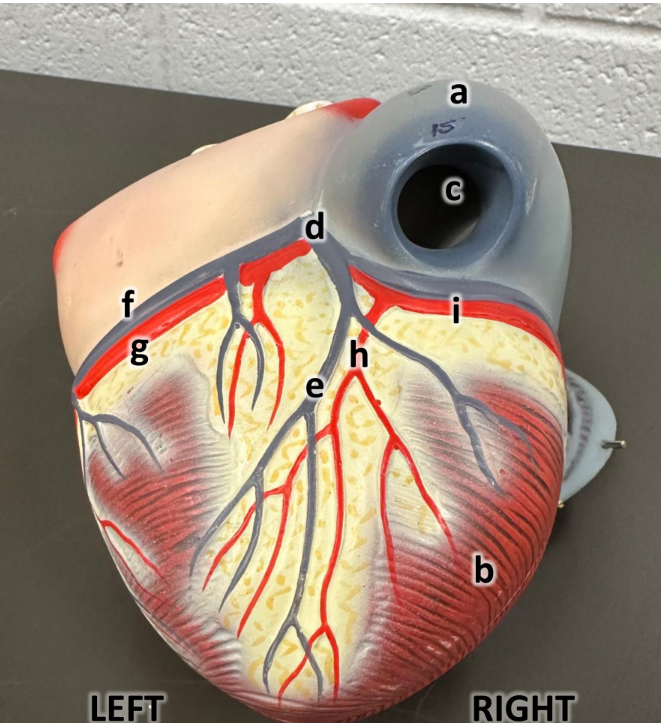
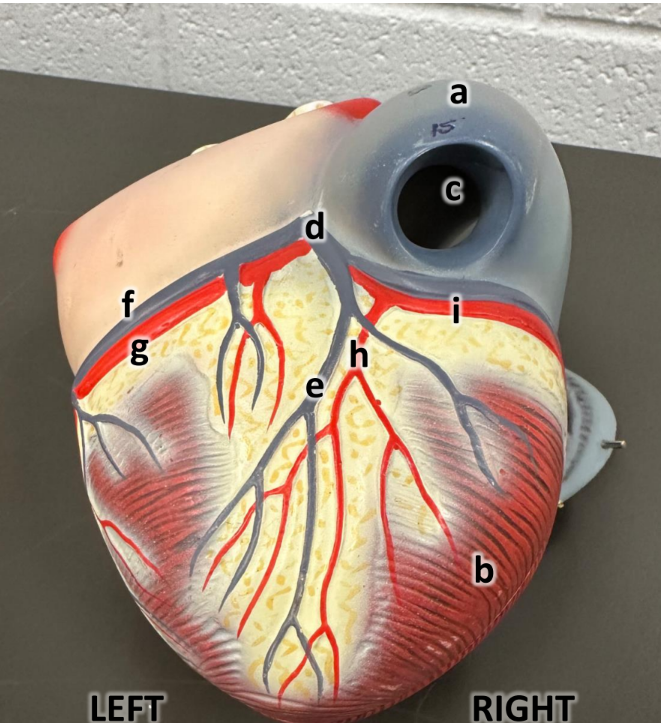
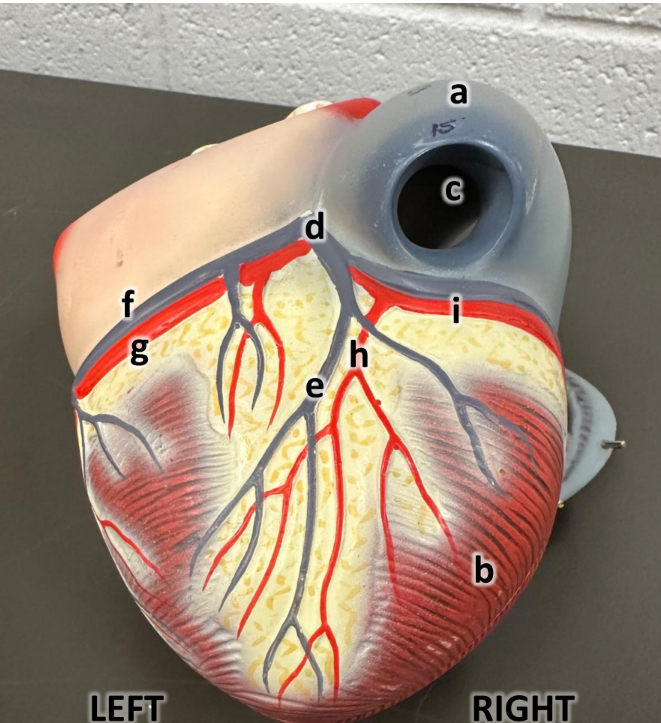
what is a
left atrium with auricle
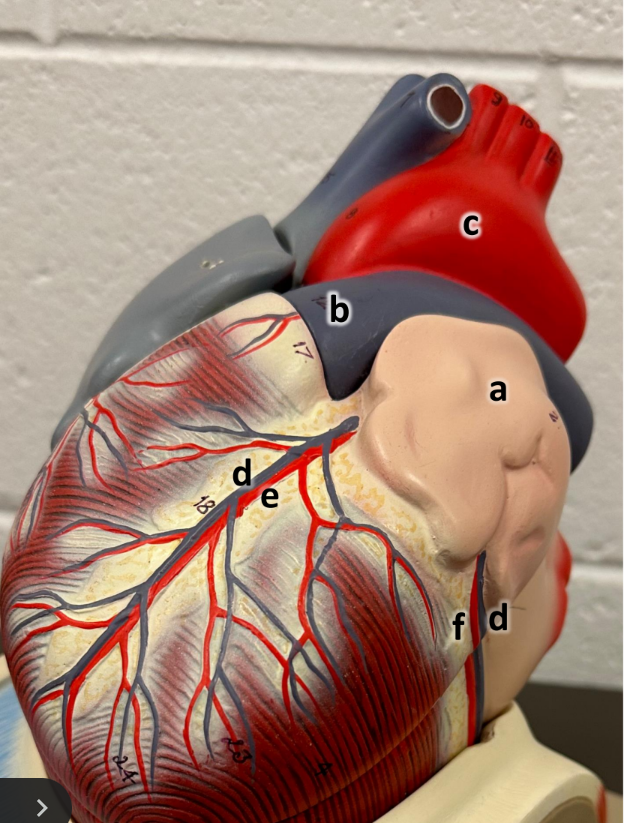
what is b
pulmonary trunk
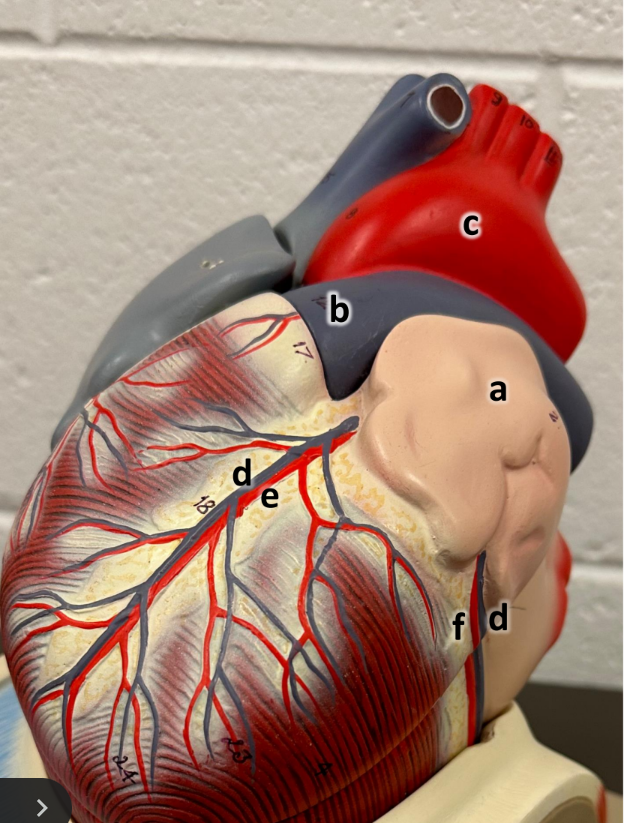
what is c
aortic arch
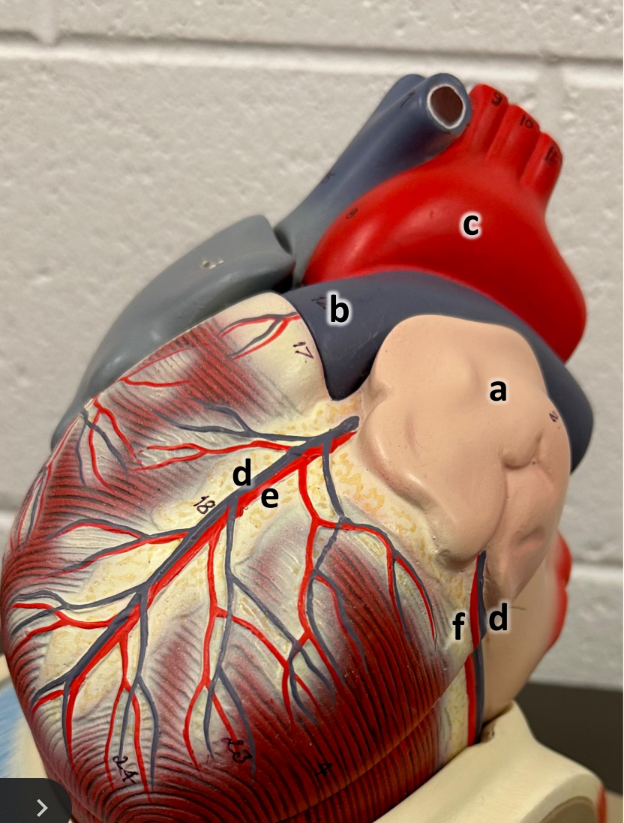
what is d
great cardiac vein
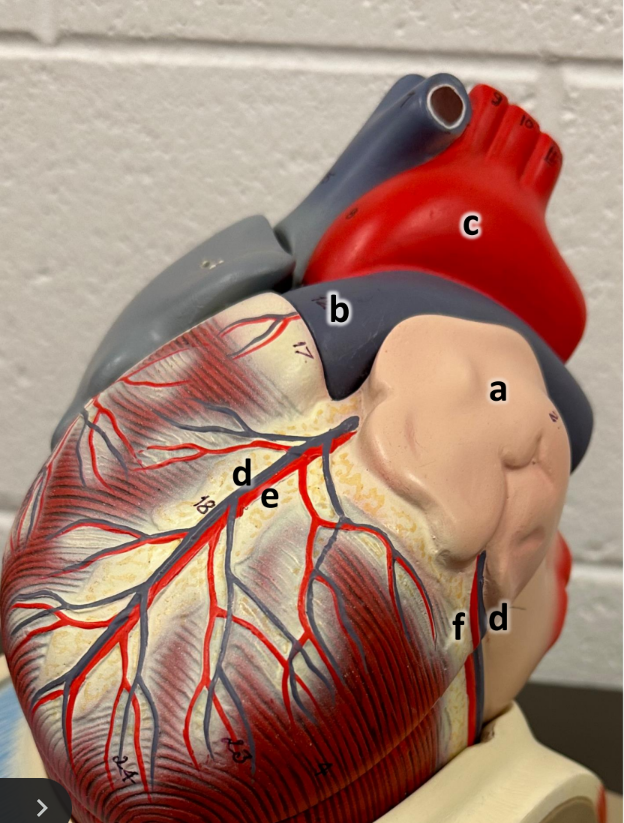
what is e
anterior interventricular
what is f
circumflex artery
what is a
right atrium
what is b
right ventricle
what is c
inferioir vena cava
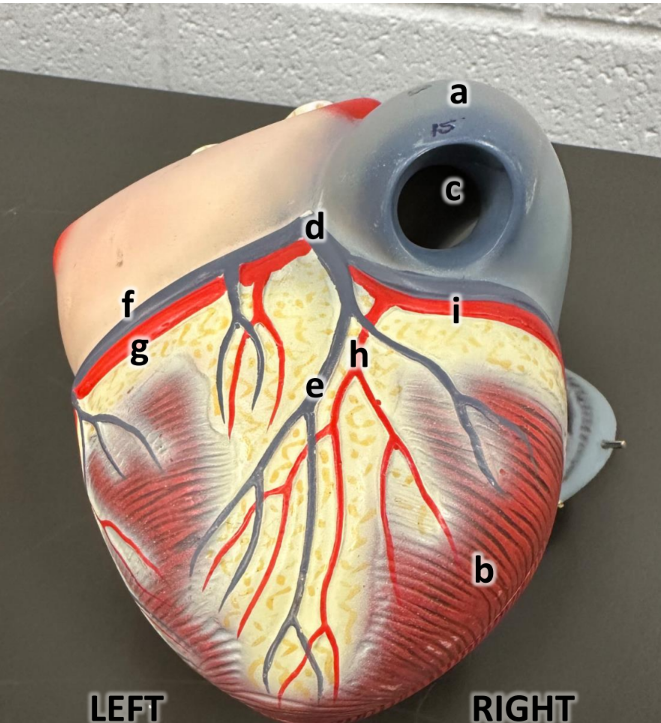
what is d
coronary sinus