Reproductive system
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Functions of the male reproductive system
formation of sperm
produce hormones: aid in production of gametes, regulate sexual maturation and development of secondary sex characteristics
transmission of sperm into female
Components of male reproductive system
organs: testes
ductal system
glands
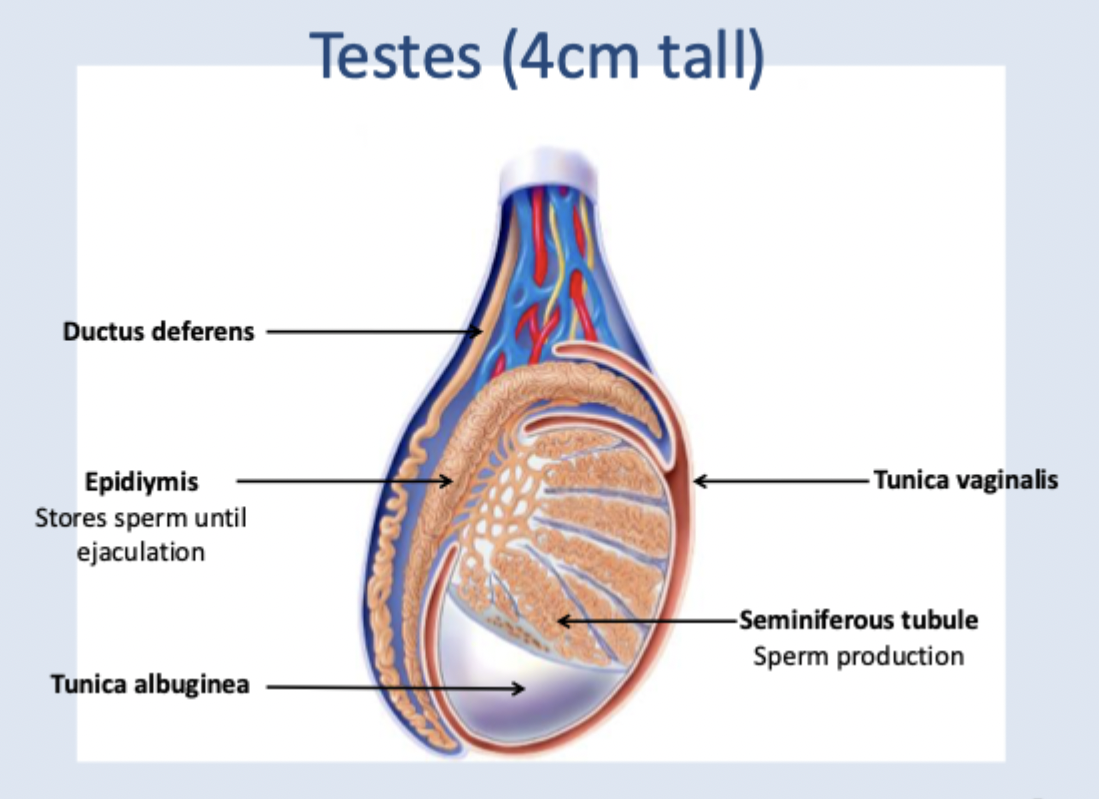
Components of the testes
Ductus deferens
epidiymis (stores sperm until ejaculation)
tunica albuginea
seminiferous tubule (sperm production): sertoli cells (support sperm development, Leydig cells (secrete testosterone), Smooth muscles (produces peristalsis which propels sperm into epidiymis
tunica vaginalis
has its own blood supply
components of seminiferous tubule
sertoli cells: support sperm development
Leydig cells: secrete testosterone
smooth muscle: produces peristalsis which propels sperm into epidiymis
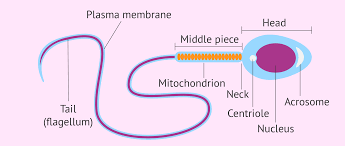
Components of sperm cell
acrosome (enzymes to break down outer layer of ovum)
Head: contains 23 chrosmosomes in nucleus
midpiece: contains mitochondria = energy
tail: propels sperm
organs of male reprodutive system
testes
scrotum
penis
Components of penis
root
shaft
glans (tip)
prepuce/ foreskin
urethra runs down center
Epididymis
stores sperm
where sperm matures/ learns how to swim
Vas Deferens
at its end, forms ampulla - leads into ejaculatory duct
propels sperms using strong peristaltic waves from epididymis during ejaculation
Accessory organs producing semen
seminal vesicles
prostate
Cowper’s gland
Passage of sperm assisted by
ejaculation
accessory gland secretions (semen: nurtients, protection, activates sperm, transport medium)
chemical signals towards oocyte
Describe the process of fertilisation and implantation
Describe the function of the female reproductive system
formation of eggs
reception of sperm
provision of suitable environment for fertilisation and fetal development
Childbirth (parturition)
lactation
Describe the structure of the female reproductive system
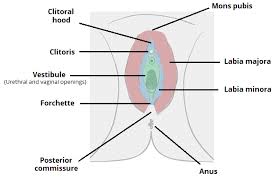
External genitalia: clitoris, labia minora + majora, urethra, vestibule, hymen
reproductive organs (ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus)
(note: all held in place in the pelvis by ligaments)
Label the female external genitalia
Vagina
rooched/ layered when female is within reproductive age, then smoothens out again
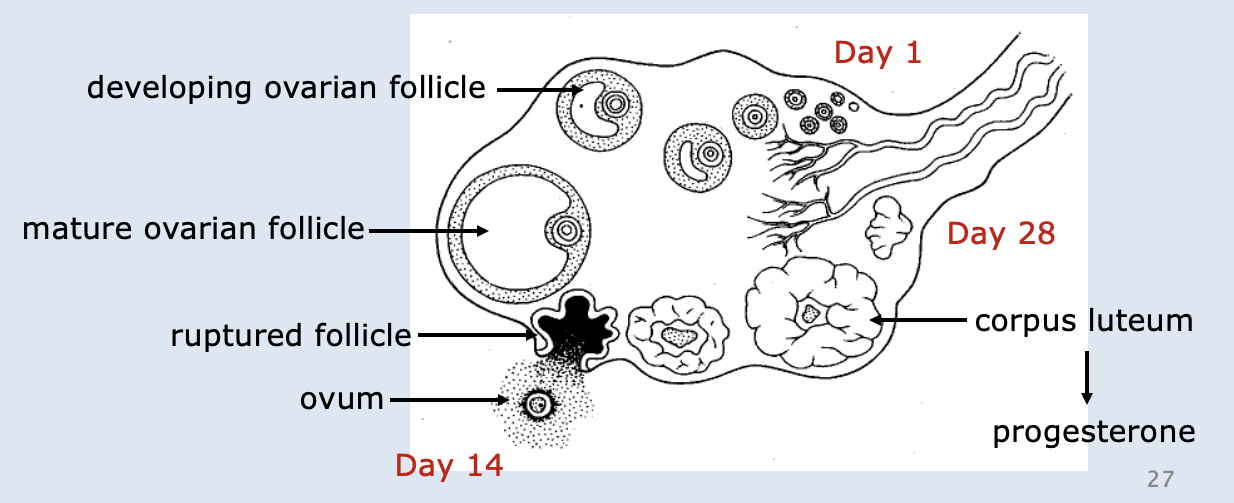
Ovaries
•Produces female sex hormones & ova (eggs).
•Contains ovarian follicles in various stages of maturity.
•Follicle maturation stimulated by FSH and oestrogen.
•Ovulation triggered by LH: ovum released every 28 days.
Process of releasing an ovum
Day 14: ruptures out of ovary - pain
Corpus Luteum left after ovum released = produces progesterone and then degenerates (if prego, continues to produce progesterone until placenta takes over production of progesterone)
Fallopian tube
•Fallopian tubes/uterine tubes/oviducts are the first of 3 organs that form the female duct system.
•Each fallopian tube is about 10 cm long.
•After ovulation, the ovum is moved towards the fimbriae.
•Fimbriae have ciliated finger-like projections at the ovarian end but do not touch the ovary.
•Cilia on the fimbriae and lining the oviducts beat gently to guide the egg towards the uterus.
•Fertilization takes place in the ampulla.
•Takes 5 days to reach the uterus (by peristalsis and ciliary movement)
Uterus
In pelvic cavity.
Uterine walls have 3 layers:
–Perimetrium - outermost layer
–Myometrium - middle smooth muscle layer; contracts during birth & menstruation
–Endometrium - innermost layer made of simple columnar epithelium and connective tissue. Contains glands, arteries & veins which help to nourish the implanted embryo. Varies in thickness during the uterine cycle and breaks down / excreted during menstruation.
Menstrual cycle prepares uterus to receive, nourish and protect a zygote.
Menstrual Cycle
Collective cyclical changes that occur within the ovaries and uterus over approx. 28 day period.
•Common for women to have cycles longer or shorter.
•Day 1 is the first day of menstrual flow.
•Changes in maturation of follicles = ovarian cycle.
•Changes in uterus = uterine cycle.
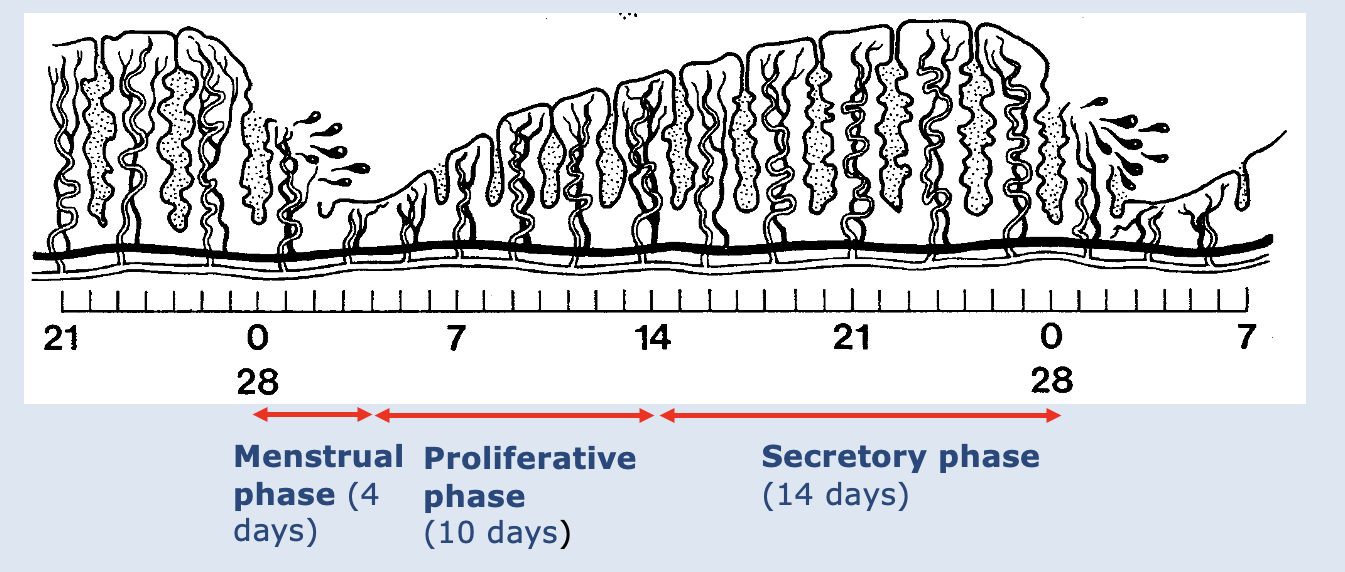
Events of the menstrual cycle
Menstrual – Days 1-5
–50-150mls
–Endometrium lost to basal layer.
Proliferation - Days 4-13
–Growth of endometrium
–Spiral arteries
–Tubular glands
–Vascular mucosa
–Receptor cells primed.
Ovulation – Day 14
Secretory phase – Days 15-28
–Spiral arteries tortuous
–Receptor cells secrete glycogen etc.
Degeneration –no progesterone
–Blood supply cut
–Lysosomes released
–Autodigestive.
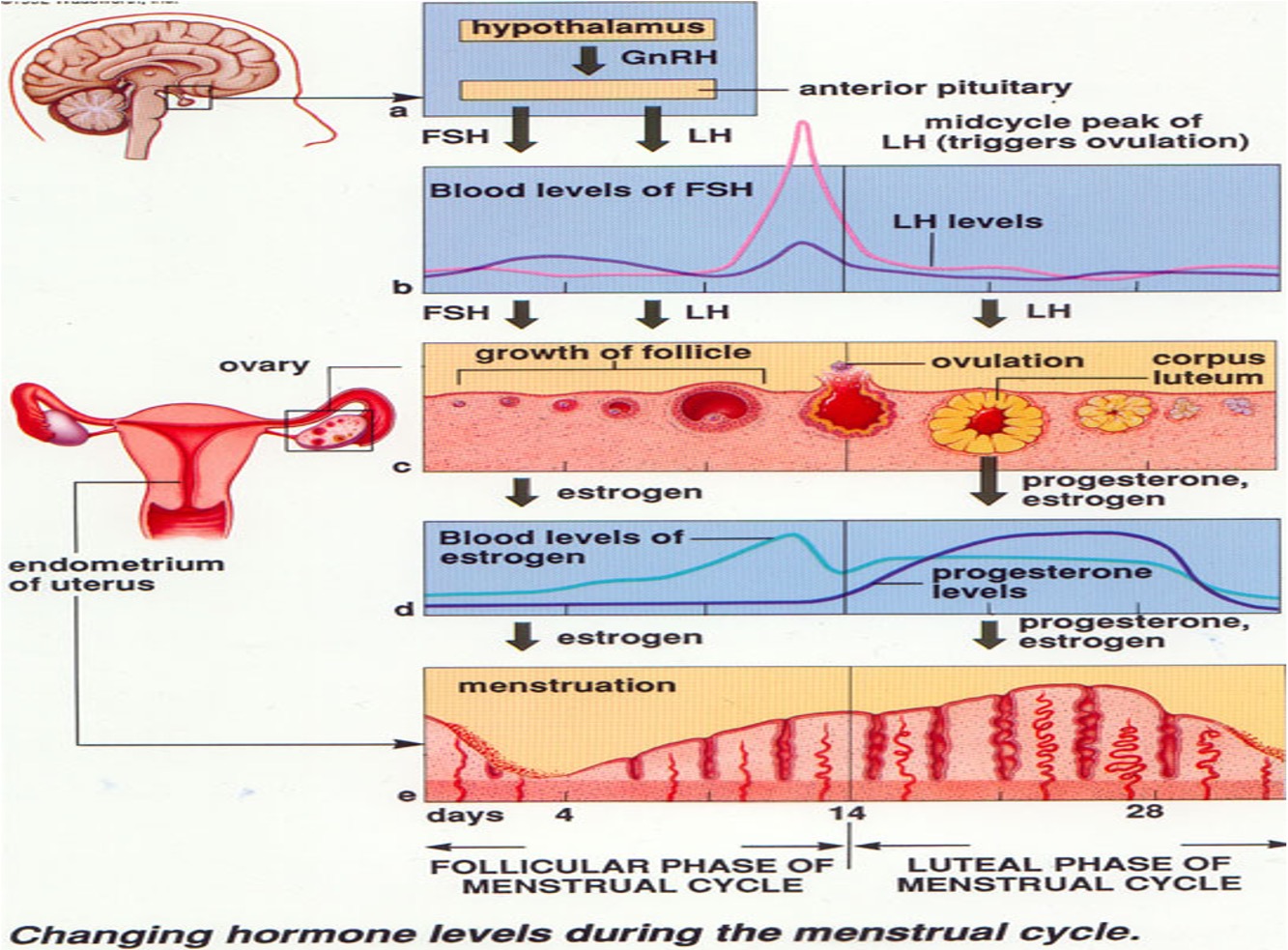
Ovarian Cycle
2 phases:
Follicular phase:
Luteal phase
Follicular phase
–day 1 until ovulation (day 14 in the 28 day cycle)
–ovarian follicles develop from primordial cells to Graafian follicles due to influence of FSH
–developing follicles à release increasing amounts of oestrogen
–increased oestrogen causes sudden increase in LH (LH surge) which stimulates ovulation.
Luteal Phase
–day of ovulation (rupture of the follicle to release egg) until day before the menstrual flow begins (day 28)
–LH surge causes development of the corpus luteum & corpus luteum secretes progesterone (corpus luteum means yellow body)
–corpus luteum will degenerate 10 days after ovulation if no pregnancy event.
Uterine Cycle
•Describes the changes that occur in the endometrium during the menstrual cycle (Menstruation is the shedding of the endometrium)
•Cycle starts and ends with menstruation
•There are three phases of the uterine cycle:
1.Menstrual phase
2.Proliferative phase
3.Secretory phase
Menstrual phase
•Lasts from approx. days 1-5
•Ovarian hormones are at their lowest levels in the cycle
•Functional part of the endometrium breaks down and is sloughed
•Passes out of the body through the cervix & vagina as menstrual flow
Proliferative phase
•Days 6 (menstrual flow stops) to 14
•Blood vessels & glands that form the endometrium regenerate due to increasing amounts of oestrogen from the developing follicle
Secretory Phase
•Lasts from days 15-28
•Endometrial glands secrete glycogen and vascularisation of the endometrium continues
•Changes are caused by increased progesterone levels by the corpus luteum
•If there is no fertilization, the corpus luteum degenerates towards the end of this phase and progesterone decreases
•Decreasing progesterone thus decreases blood supply to endometrial cells, cells die, the endometrium breaks down and menstrual flow starts again
FSH
FSH | LH | Oestrogen | Progesterone | |
Source | Anterior pituitary | Anterior pituitary | Developing follicles & corpus luteum After 6 wks of pregnancy: placenta | Corpus luteum After 6 wks of pregnancy: placenta |
Stimulus | GnRH | GnRH | FSH (and LH) | LH |
Primary Effects | Stimulate maturation of ovarian follicle | Stimulate maturation of ovarian follicles; ovulation | Growth & maturation of reproductive organs & breasts; promote proliferative phase of the uterine cycle; facilitate oogenesis; stimulate capacitation of sperm; stimulate growth of uterus and mammary glands in pregnancy | Facilitates growth of breasts; promotes secretory phase; during pregnancy quiets the myometrium and enhances the ability of mammary glands to produce milk; increases body temperature |
2ndary Effects | Stimulates production of oestrogen | Stimulates production of oestrogen & progesterone | Promote long bone growth & feminisation of the skeleton; inhibit bone resorption; promote female pattern of fat deposit; female libido, etc. |
LH
FSH | LH | Oestrogen | Progesterone | |
Source | Anterior pituitary | Anterior pituitary | Developing follicles & corpus luteum After 6 wks of pregnancy: placenta | Corpus luteum After 6 wks of pregnancy: placenta |
Stimulus | GnRH | GnRH | FSH (and LH) | LH |
Primary Effects | Stimulate maturation of ovarian follicle | Stimulate maturation of ovarian follicles; ovulation | Growth & maturation of reproductive organs & breasts; promote proliferative phase of the uterine cycle; facilitate oogenesis; stimulate capacitation of sperm; stimulate growth of uterus and mammary glands in pregnancy | Facilitates growth of breasts; promotes secretory phase; during pregnancy quiets the myometrium and enhances the ability of mammary glands to produce milk; increases body temperature |
2ndary Effects | Stimulates production of oestrogen | Stimulates production of oestrogen & progesterone | Promote long bone growth & feminisation of the skeleton; inhibit bone resorption; promote female pattern of fat deposit; female libido, etc. |
Oestrogen
FSH | LH | Oestrogen | Progesterone | |
Source | Anterior pituitary | Anterior pituitary | Developing follicles & corpus luteum After 6 wks of pregnancy: placenta | Corpus luteum After 6 wks of pregnancy: placenta |
Stimulus | GnRH | GnRH | FSH (and LH) | LH |
Primary Effects | Stimulate maturation of ovarian follicle | Stimulate maturation of ovarian follicles; ovulation | Growth & maturation of reproductive organs & breasts; promote proliferative phase of the uterine cycle; facilitate oogenesis; stimulate capacitation of sperm; stimulate growth of uterus and mammary glands in pregnancy | Facilitates growth of breasts; promotes secretory phase; during pregnancy quiets the myometrium and enhances the ability of mammary glands to produce milk; increases body temperature |
2ndary Effects | Stimulates production of oestrogen | Stimulates production of oestrogen & progesterone | Promote long bone growth & feminisation of the skeleton; inhibit bone resorption; promote female pattern of fat deposit; female libido, etc. |
Progesterone
FSH | LH | Oestrogen | Progesterone | |
Source | Anterior pituitary | Anterior pituitary | Developing follicles & corpus luteum After 6 wks of pregnancy: placenta | Corpus luteum After 6 wks of pregnancy: placenta |
Stimulus | GnRH | GnRH | FSH (and LH) | LH |
Primary Effects | Stimulate maturation of ovarian follicle | Stimulate maturation of ovarian follicles; ovulation | Growth & maturation of reproductive organs & breasts; promote proliferative phase of the uterine cycle; facilitate oogenesis; stimulate capacitation of sperm; stimulate growth of uterus and mammary glands in pregnancy | Facilitates growth of breasts; promotes secretory phase; during pregnancy quiets the myometrium and enhances the ability of mammary glands to produce milk; increases body temperature |
2ndary Effects | Stimulates production of oestrogen | Stimulates production of oestrogen & progesterone | Promote long bone growth & feminisation of the skeleton; inhibit bone resorption; promote female pattern of fat deposit; female libido, etc. |
Function of Human chorionic gonadotrophin (HCG) during pregnancy
Acts like luteinising hormone (LH) to maintain corpus luteum (and preventing menstuation), normally corpus luteum atrophies.
Function of Oestrogen during pregnancy
Myometrial hypertrophy, external genitalia enlargement softening of pelvic ligaments.
Function of Progesterone during pregnancy
Proliferation of endometrium, inhibition of uterine contractions, development of alveoli in mammary glands.
Function of Prolactin during pregnancy
Milk production when oestrogen falls after parturition. Inhibits FSH release and ovulation after parturition.
Function of Relaxin during pregnancy
Produced for the flexibility of tissues.
Function of Oxytocin during pregnancy
For uterine contractions during labour.
Scrotum
sac of skin and superficial fascia that hangs outside of the abdominopelvic cavity at the root of the penis; contains the testes
temperature regulation of the scrotum
changes occur to maintain constant temperature
when warm = scotal skin is flaccid = lowers testes (hanging outside the body is 3 degrees cooler)
when cold = testes draw closer to warmth of body
Muscles used in this process: Dartos and Cremaster
Penis function
deliver sperm into female
penis structure
consists of a root (inside body) which runs into the shaft (external)
skin covering the penis = loose and forms a cuff over the glans (the tip) = prepuce or foreskin
urethra runs through center
erectile tissue: 3 cylinders running lengthways across penis made of sponge-like connective tissue and smooth muscle separated by vascular spaces
corpus spongiosum: Surrounds urethra, located in middle along the ventral side.
corpora cavernosa: Paired structure that run side by side along the dorsal surface.
Components of the male ductile system (transport system)
Epididymis
Ductus (or Vas) Deferens
Ejaculatory Duct
Urethra
Epididymis
•4 cm long.
•Lies on the lateral side of each testis.
•Long coiled tube where sperm matures (learn to swim) – can take up to 20 days.
•Sperm can be stored for months in the epididymis and eventually phagocytized by its epithelial cells - this ensures only good sperm is used
•Sperm are stored near the tail portion and in the Vas Deferens until they are ejaculated.
•During ejaculation (expulsion of sperm) smooth muscle walls of the epididymis contract strongly and move sperm to the Vas Deferens.
Ductus (Vas) Deferens
•About 45 cm long.
•Runs up through the spermatic cord into the pelvic cavity, loops medially and descends along the posterior bladder wall.
•At its terminus, forms the ampulla to lead to the ejaculatory duct.
•Function = propel sperm using strong peristaltic waves from the epididymis during ejaculation.
Ejaculatory Duct
•The ampulla of the Vas Deferens joins with the duct of the seminal vesicle. (a gland) to form a short ejaculatory duct.
Urethra
•Carries both urine and semen (sperm + accessory gland secretions)
–Prostatic urethra – surrounded by prostate gland
–Membranous urethra – in the urogenital diaphragm
–Spongy (penile) urethra – runs through the penis to the external urethral orifice.
•Mucosa lining contains scattered urethral glands which secrete mucous into the lumen just before ejaculation.
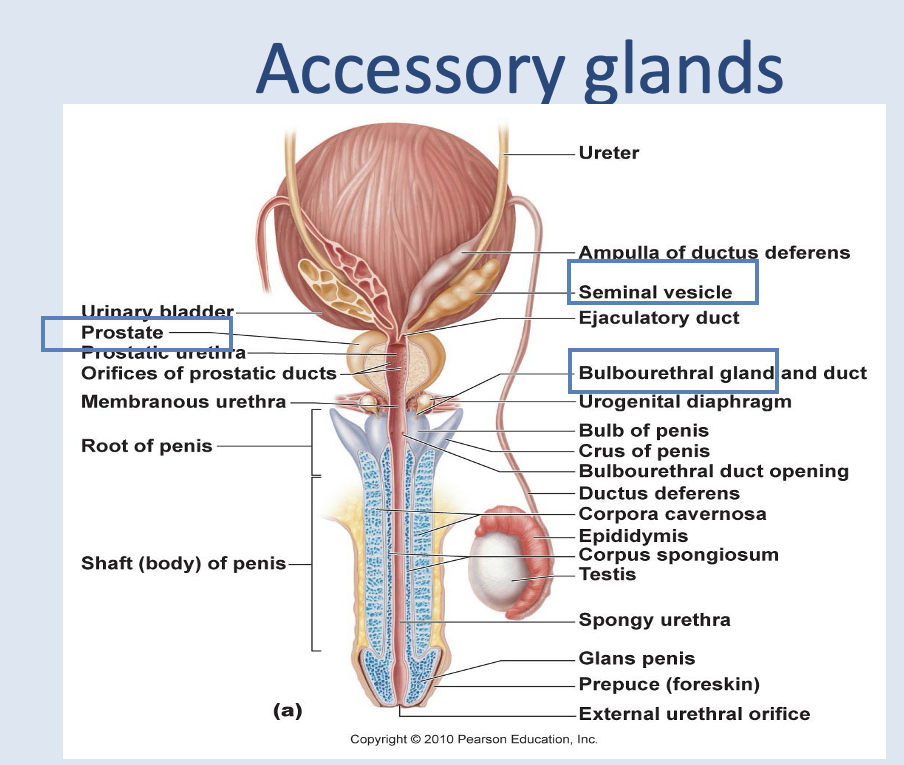
Accessory glands of male reproductive system
seminal vessicle (around 70% semen produced here) - Duct of each vesicle joins the ductus deferens on that side to form the ejaculatory duct.
prostate
bulbourethral gland
They produce most of the volume of the semen: sperm and accessory gland secretions
Seminal fluid
a yellowish, viscous fluid.
Provides a transport medium for sperm.
Provides nutrition for sperm (fructose).
Enhances motility (relaxin hormone & enzymes).
Causes semen to coagulate so it will stick to walls of vagina (coagulating enzymes).
Decreases the viscosity of cervical mucus (prostaglandins).
Neutralises the acidic conditions of the vagina (alkaline).\
Induces contractions in the fallopian tubes to move sperm towards the ova - reverse peristalsis (prostaglandins).
Prostate structure
A single doughnut shaped gland about the size of a chestnut.
Located below the base of the bladder.
Surrounds the proximal segment of the urethra.
Prostrate gland secretions enter the prostatic urethra via several ducts when prostatic smooth muscle contracts during ejaculation.
Prostate secretions
Milky, slightly acidic – makes up 30% semen volume.
Contains: citrate (nutrition), enzymes such as fibrinolysin (liquefies sticky semen after deposited in vagina to allow sperm to swim), and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) (activates sperm).
Cowper’s Gland (aka Bulbouerethral gland)
•Located below the prostate.
•Paired, pea-sized.
•Produce a thick clear mucus that runs into the urethra.
•Secretions of this fluid prior to ejaculation. neutralises acidic urine remaining in urethra.
Semen
•Amount of semen propelled out of the male duct system during ejaculation is relatively small (2-5 ml), but consists of 50 and 130 million sperm per ml.
•Sperm must reach fallopian tubes and are viable for 48 hours before the majority degenerate (only about 200 reach oocyte!)
How is the passage of semen into vagina assisted?
•Ejaculation propels sperm at a speed up to 500 cm/s (~11 miles/hour)
•Accessory gland secretions – transport medium which provides nutrients, protects sperm, activates sperm and facilitates their movement
•Female orgasm
Chemical signals directing sperm toward oocyte.
Fertilisation (aka conception) definition
•The joining or fusion of sperm and ova
Process of fertilisation
•Sperm penetrate the corona radiata and the zona pellucida.
•Takes many sperm to release enough enzyme from the acrosome to penetrate the egg.
•Depolarisation of the cell membrane of the fertilised egg and release of calcium ions to prevent polyspermy (fertilisation by more than one sperm).
-the acrosome of a sperm secretes enzymes that digest the zona pellucida of the egg.
-the sperm then binds to the plasma membrane of the egg and enters the cell.
-the genetic information of the sperm fuses with the egg nucleus to complete fertilization.
•Fertilisation of an egg by sperm forms a zygote.
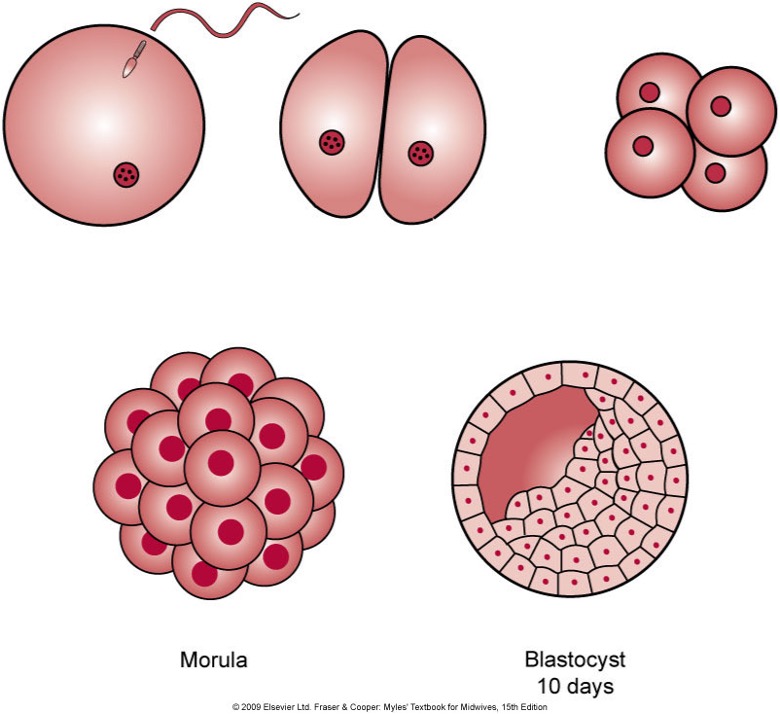
Stages of early development
•Zygote - fusion of gametes to 8 cells.
•Morula - clump of cells undergoing mitosis. Morula: means mulberry because looks like blackberry
•Blastocyst - day 4-20 inner cell mass to bilaminar disc. inner layer develops into fetus and outer layer develops into placenta
•Embryo – day 21 to 56 (8 weeks) from somites through organogenesis.
•Fetus - week 9 to birth.
Role of uterus in pregnancy
•Zygote embedded in endometrium.
•Nourished by uterine secretions until placenta established.
•Placenta secretes progesterone: prevents uterine contractions.
•After 40 weeks oestrogen & oxytocin promote uterine contractions.
Role of placenta in pregnancy
provides nutrients (oxygen and nutrients) and removes waste to fetus
provides immunity/ protection
secretes progesterone which prevents uterine contractions
amniotic fluid
cushions/ protects fetus
nourishes fetus