KAAP309 - Unit 2: Nervous System EXAM
1/270
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
271 Terms
Define mastication
chewing

What are the 5 tastes?
sweet, sour, salty, bitter, umami
What is the pathway through the ear (auditory)?
Auricle/pinna -> auditory canal -> tympanic membrane -> malleus -> incus -> stapes -> oval window -> scala vestibuli -> cochlear duct -> scala tympani -> secondary tympanic membrane->vestibulocochlear nerve->temporal lobe
What would happen to a sound if its cycles/second increased?
We would perceive it as getting higher
What would happen to a sound if its amplitude increased?
We would perceive it as getting louder
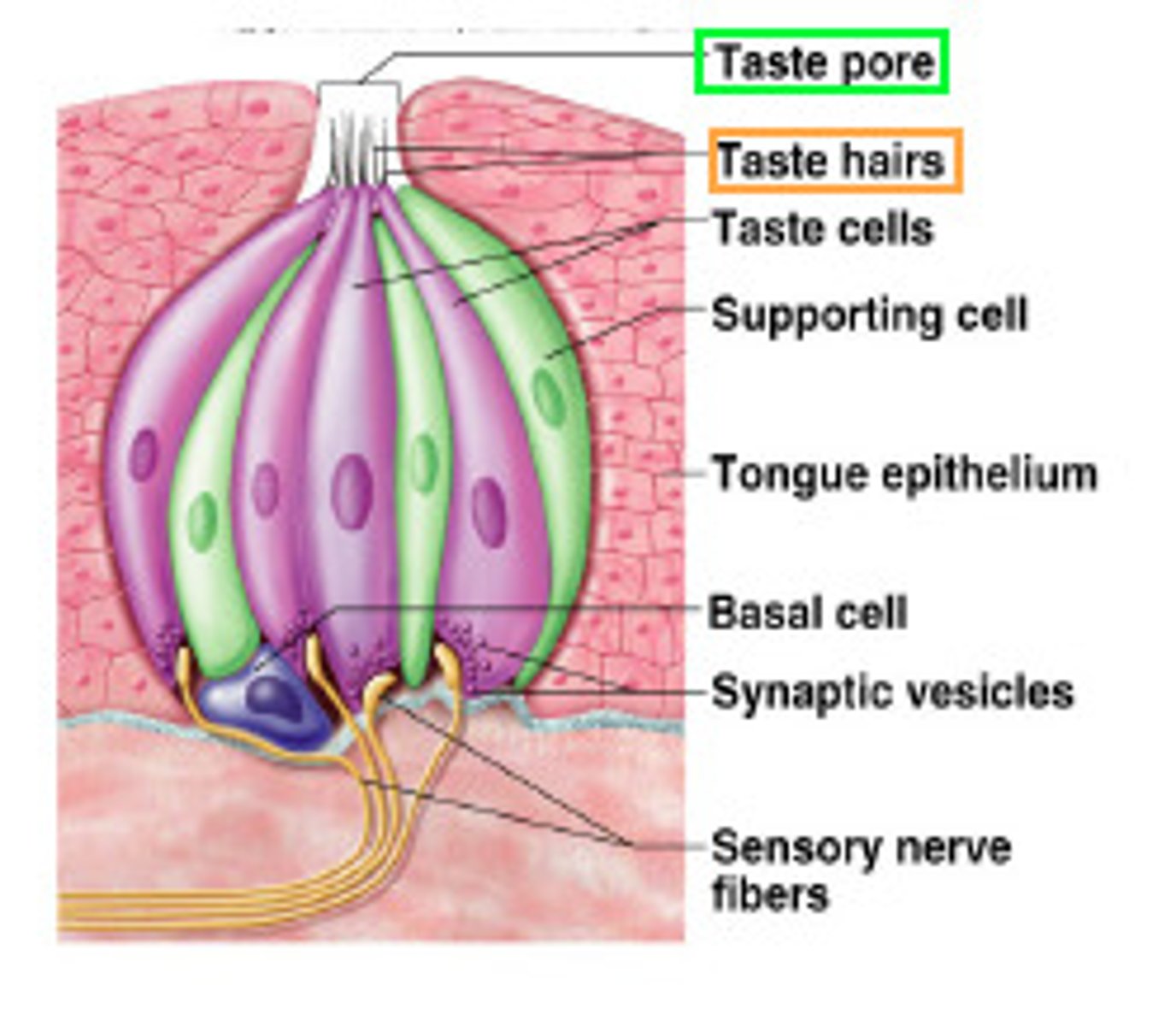
Explain the process by which tastants activate gustatory receptors
Ions come into contact with the taste pores and their gustatory hairs. The ion then binds to the taste receptor in the taste bud
What are the components of the outer ear?
auricle (pinna), external auditory canal, tympanic membrane
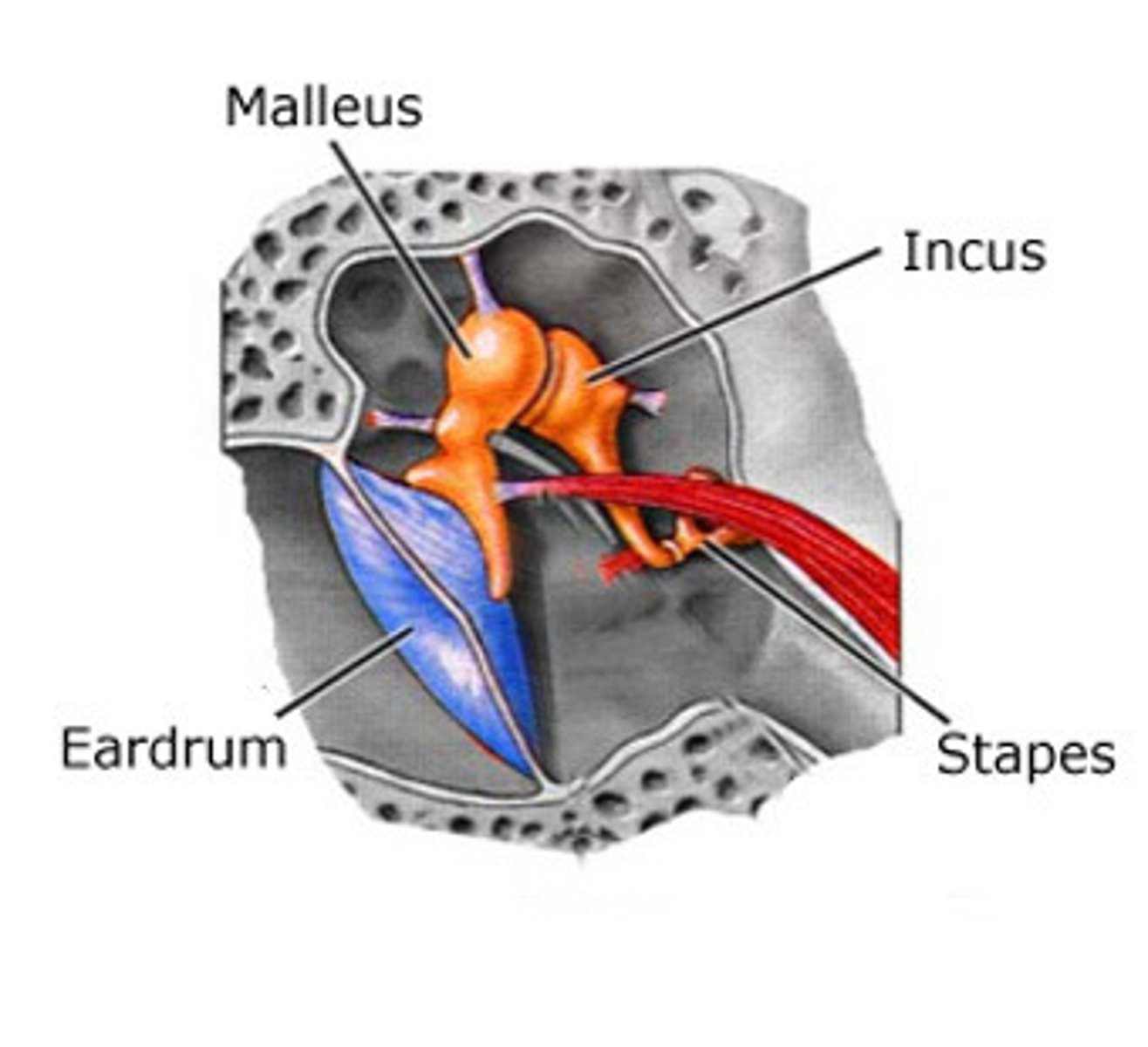
What are the components of the middle ear?
tensor tympani muscle, tympanic membrane malleus, incus, stapes, auditory tube
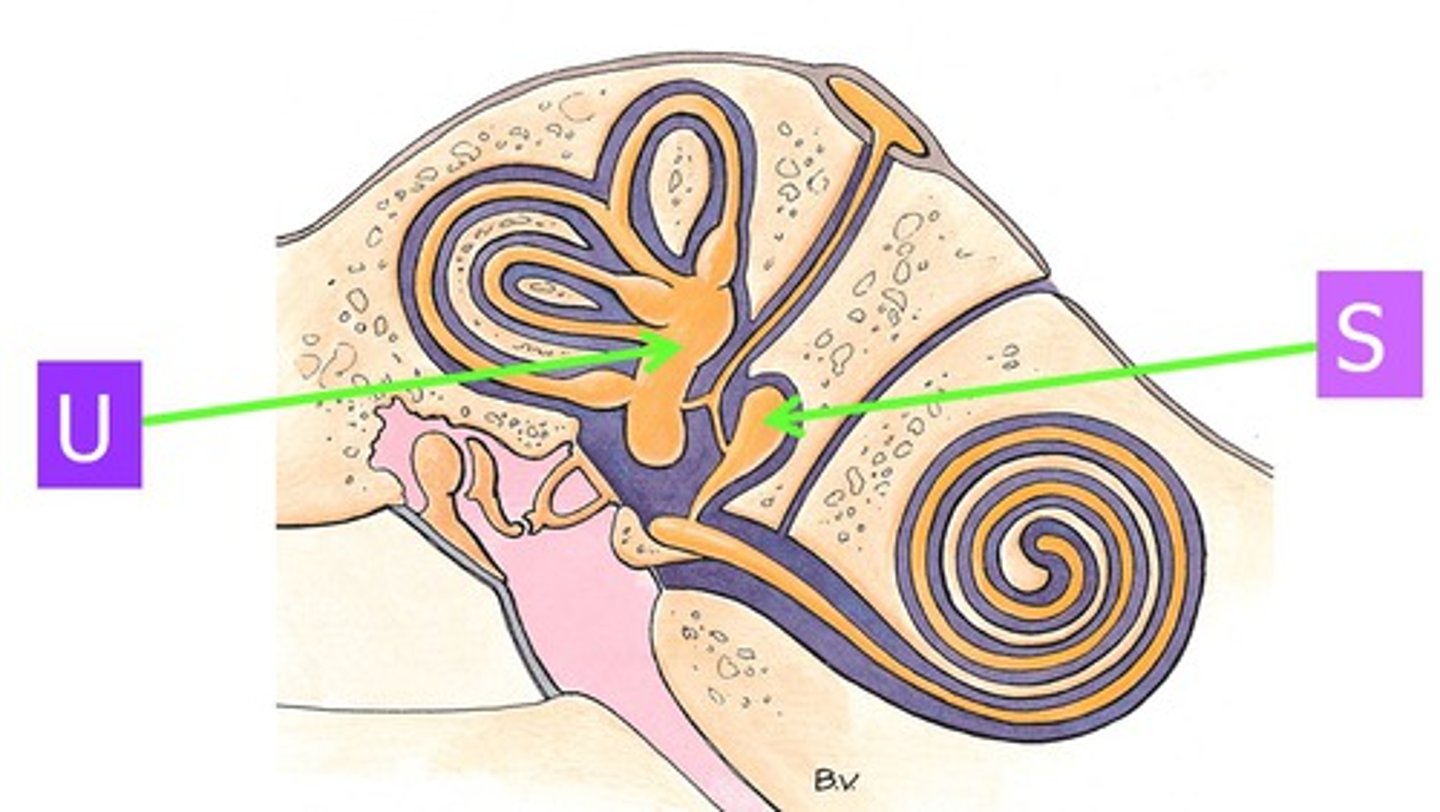
What are the components of the inner ear?
cochlea, macula, otolithic membrane, crista ampullaris, vestibule, semicircular canals
What is the structure and function of teeth?
-Structure: 4 layers (enamel, dentin, cementum, tooth pulp)
-Function: grinding, cutting, and crushing up food
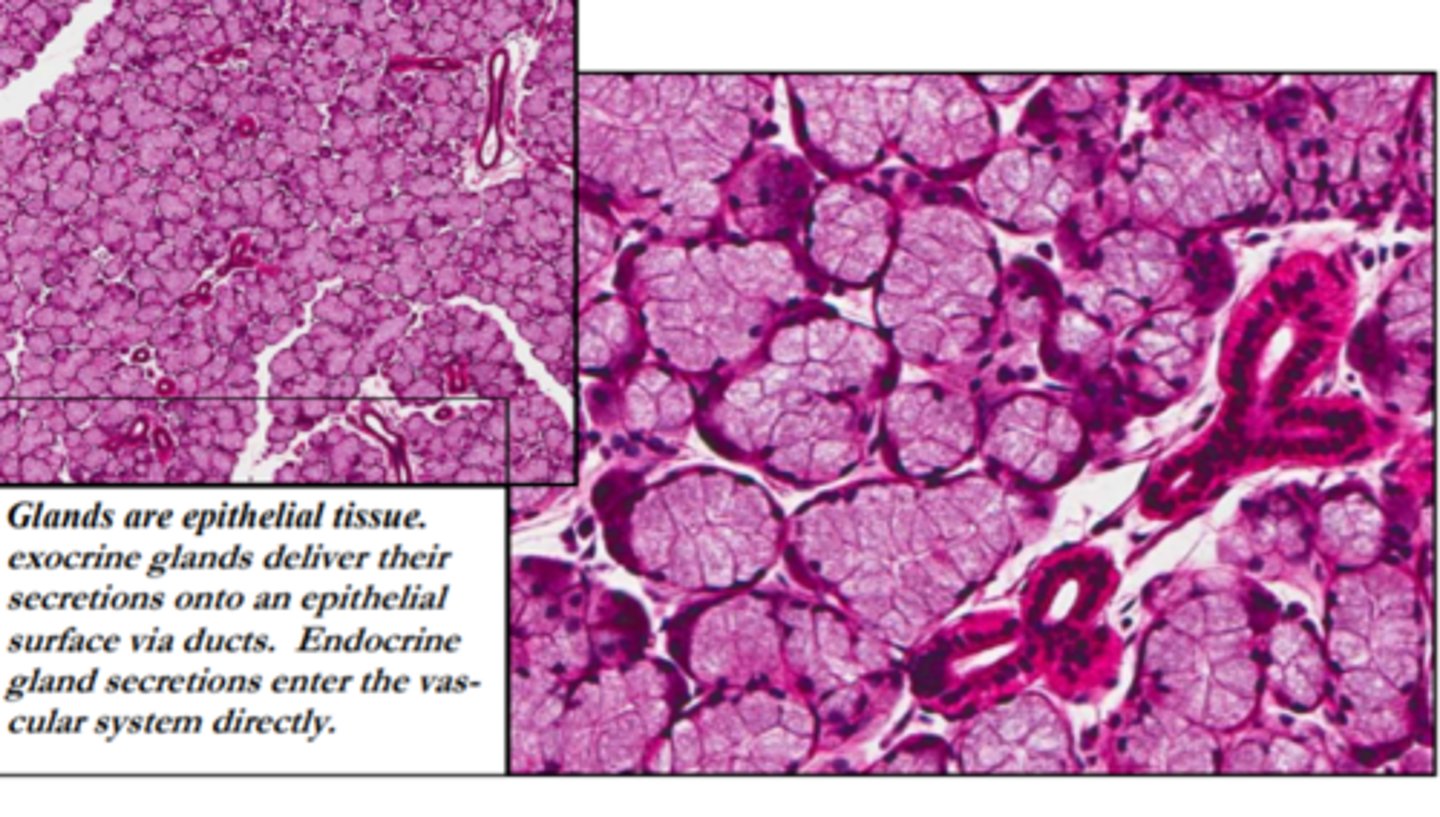
What is the structure and function of salivary glands?
-Structure: exocrine glands
-Function: help moisten food, as food needs to be dissolved in water to be tasted, protecting teeth, protect digestive tract, produce saliva
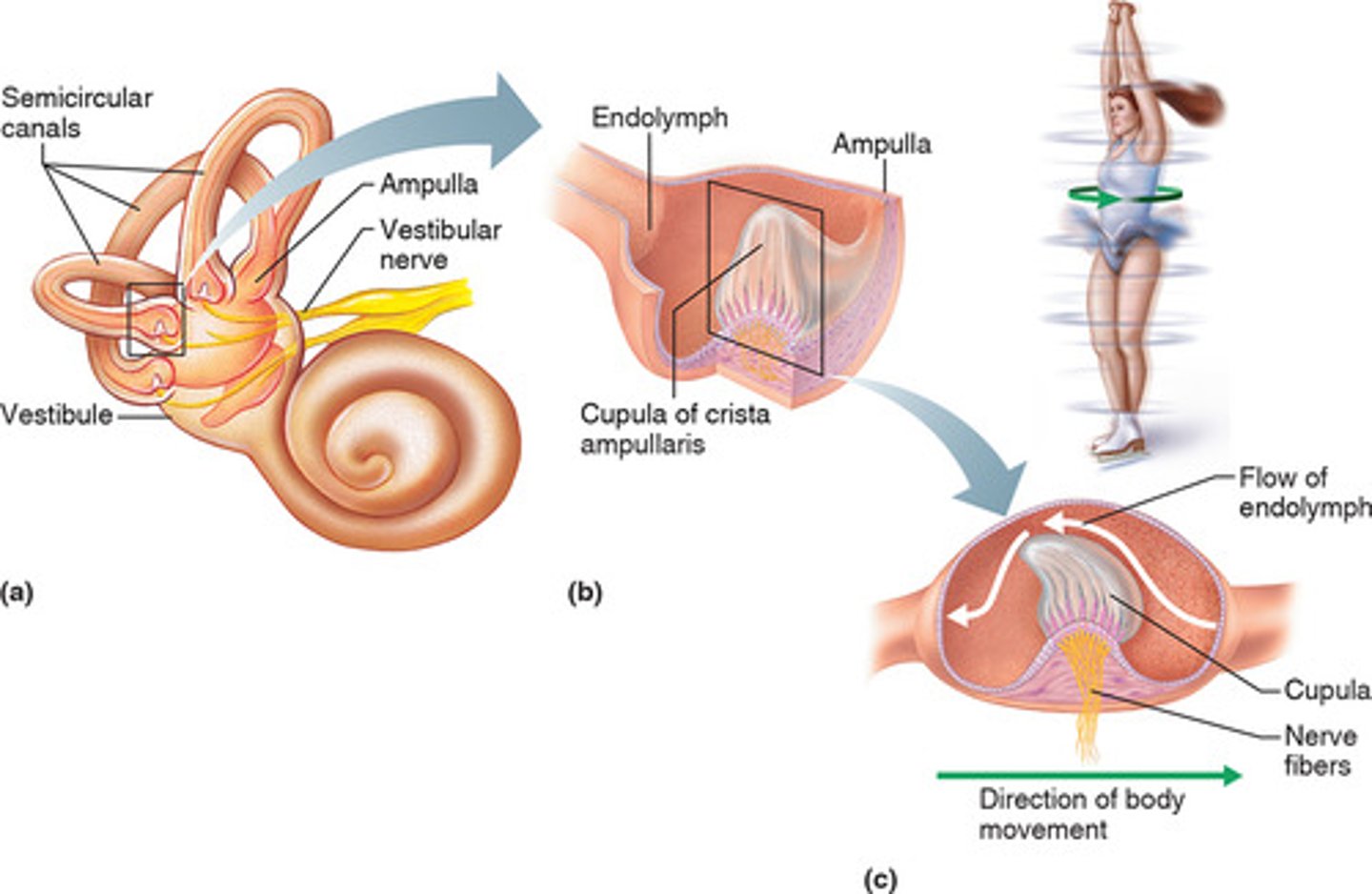
What is the function of macula in equilibrium?
-Function: monitors position of head relative to its vertical position
What is the function of crista ampullaris in equilibrium?
-Function: sense acceleration and deceleration of the head
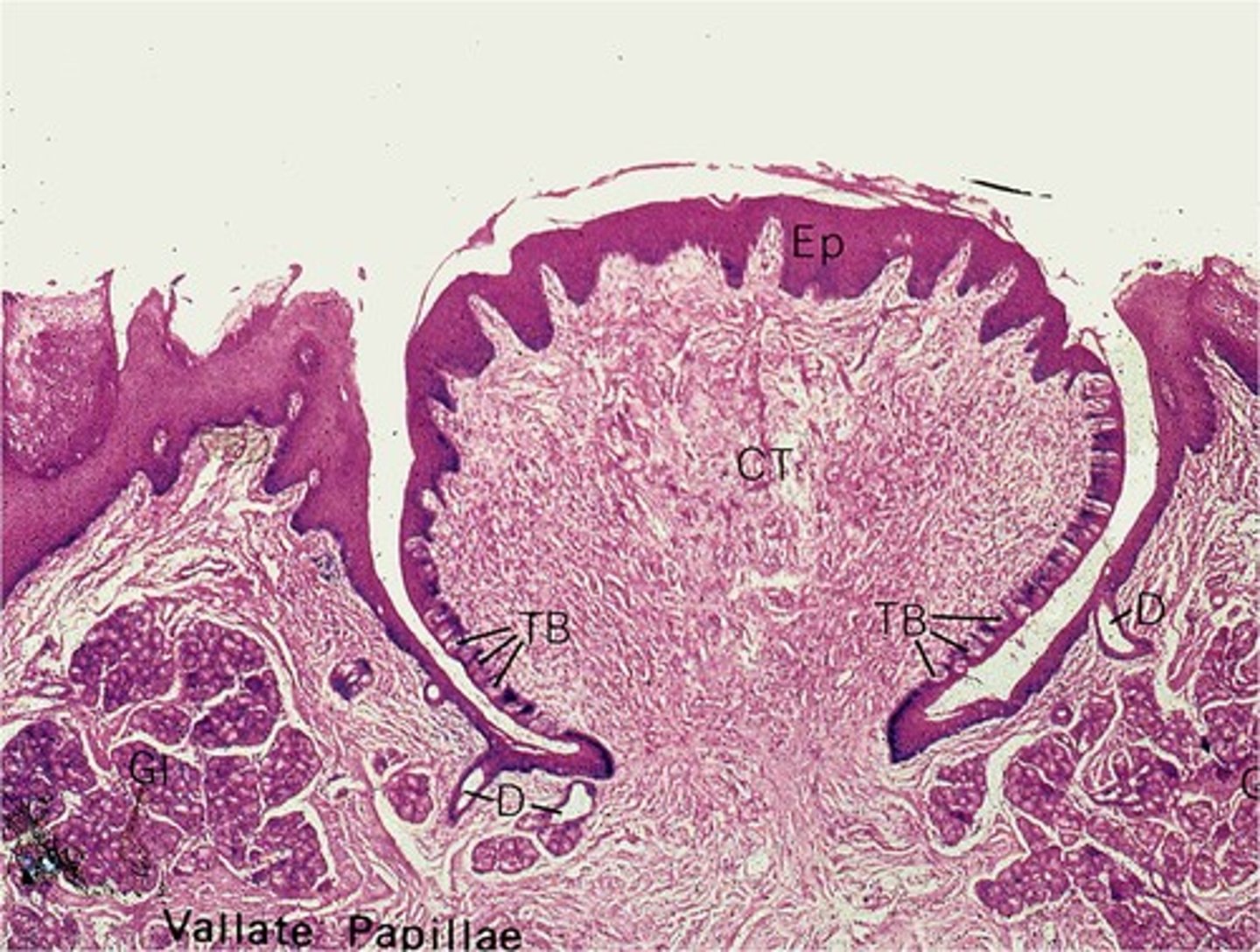
What are the four types of lingual papillae?
filiform, fungiform, vallate, foliate
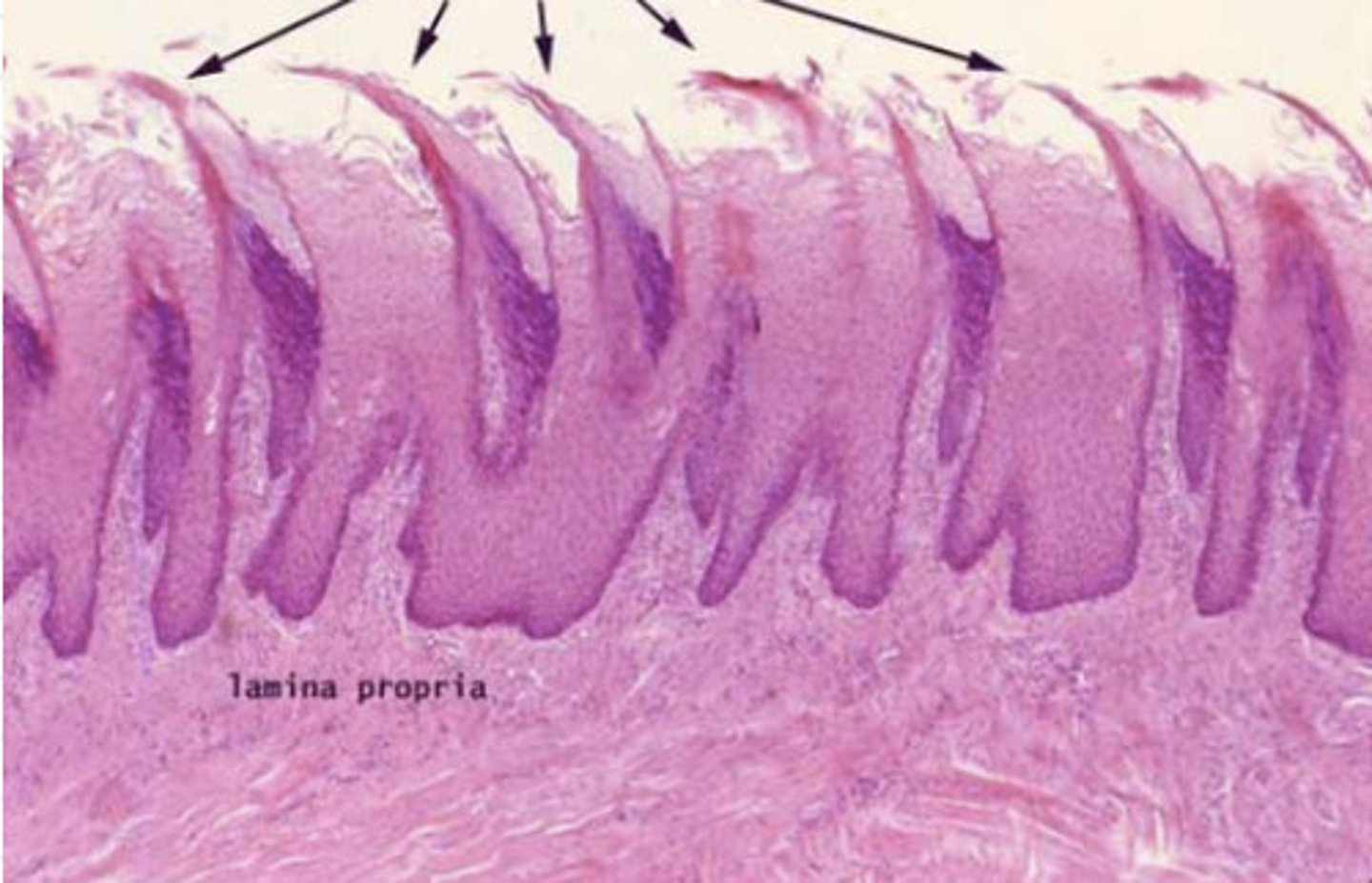
What is the structure of filiform papillae?
Tiny spikes found mostly on the middle of the tongue, does not contain any taste buds
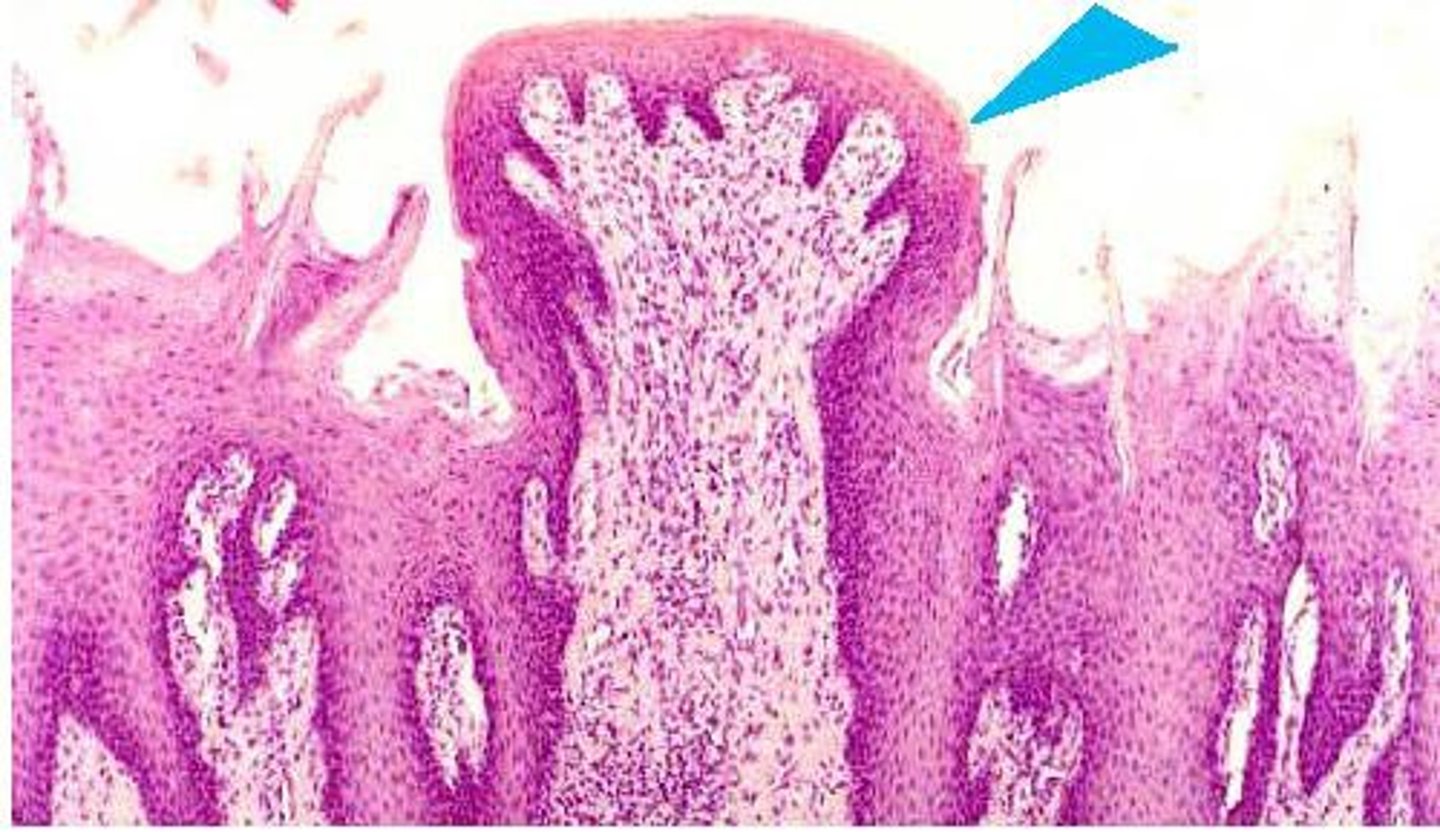
What is the structure of fungiform papillae?
Mushroom-shaped bumps concentrated at the tip and sides of tongue
What is the structure of vallate papillae?
Large circular bumps that form a V towards the back of the tongue
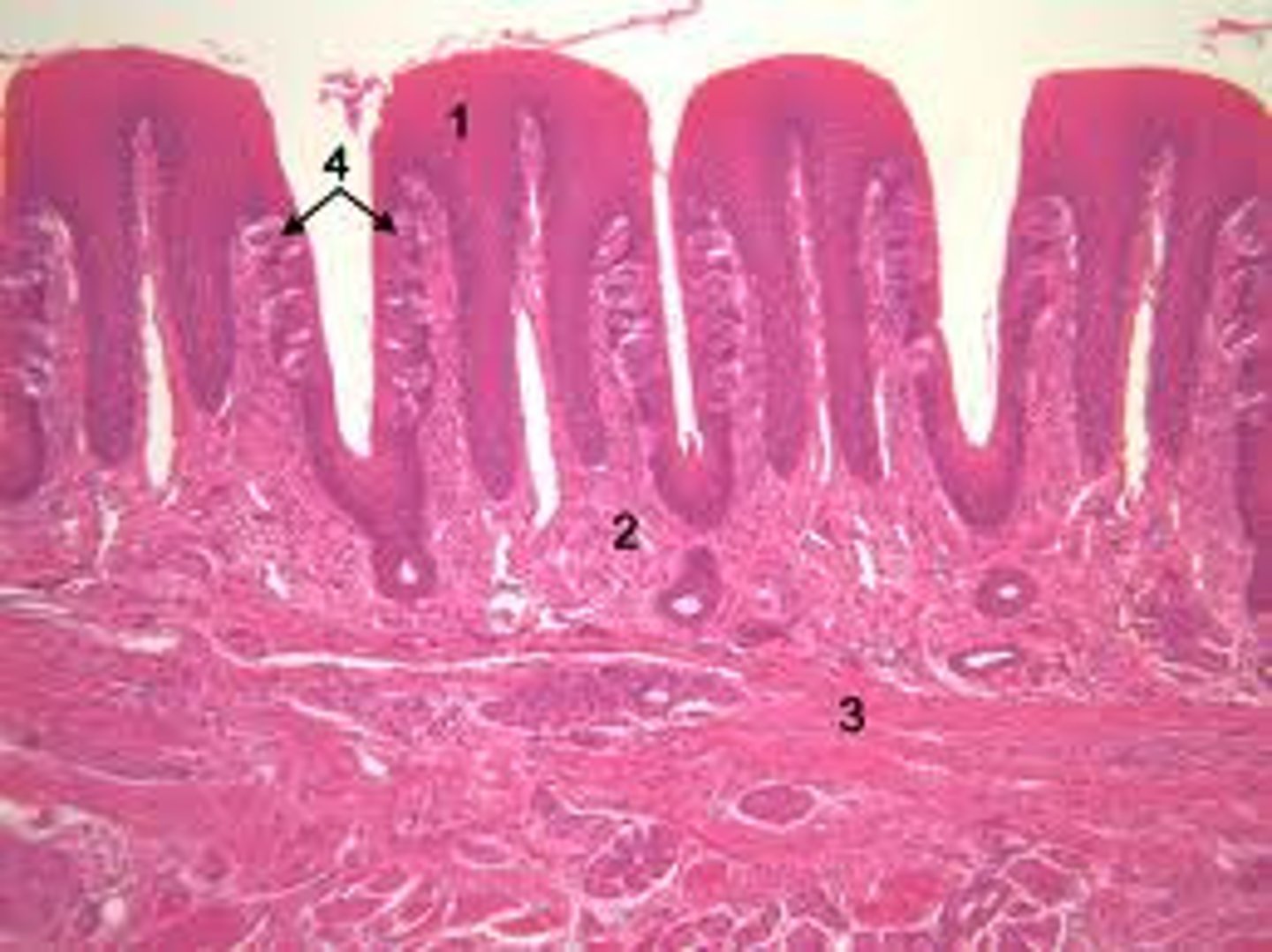
What is the structure of foliate papillae?
Two parallel ridges on the sides of the tongue
What is the structure and function of the organ of Corti/spiral organ?
-Structure: fluid-filled structure with hair cells and a basilar membrane
-Function: convert sounds into electrical impulses
What do lamellar corpuscles sense?
deep pressure, stretch, tickle, vibration
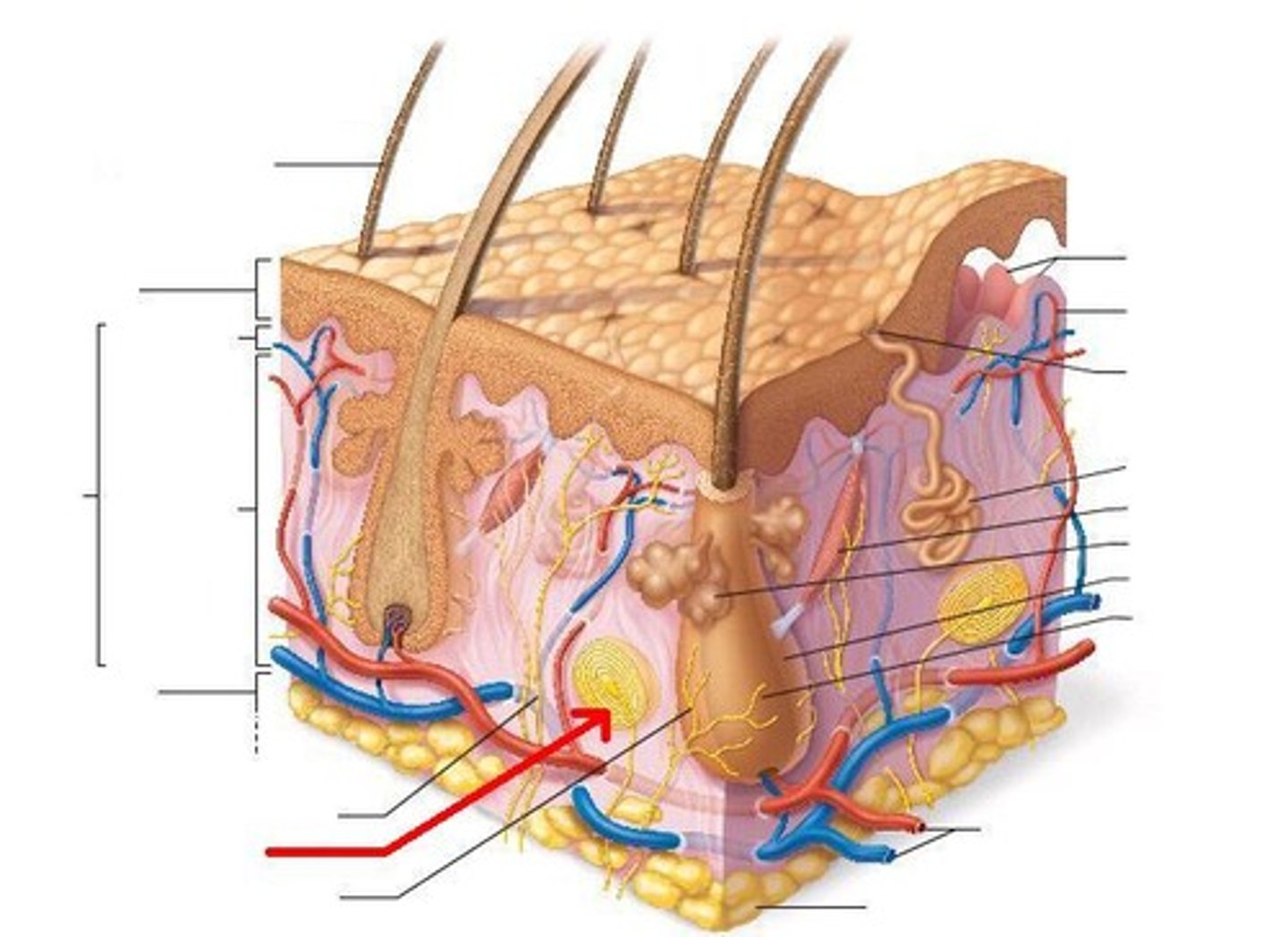
What do hair receptors sense?
light touch, movement of hairs
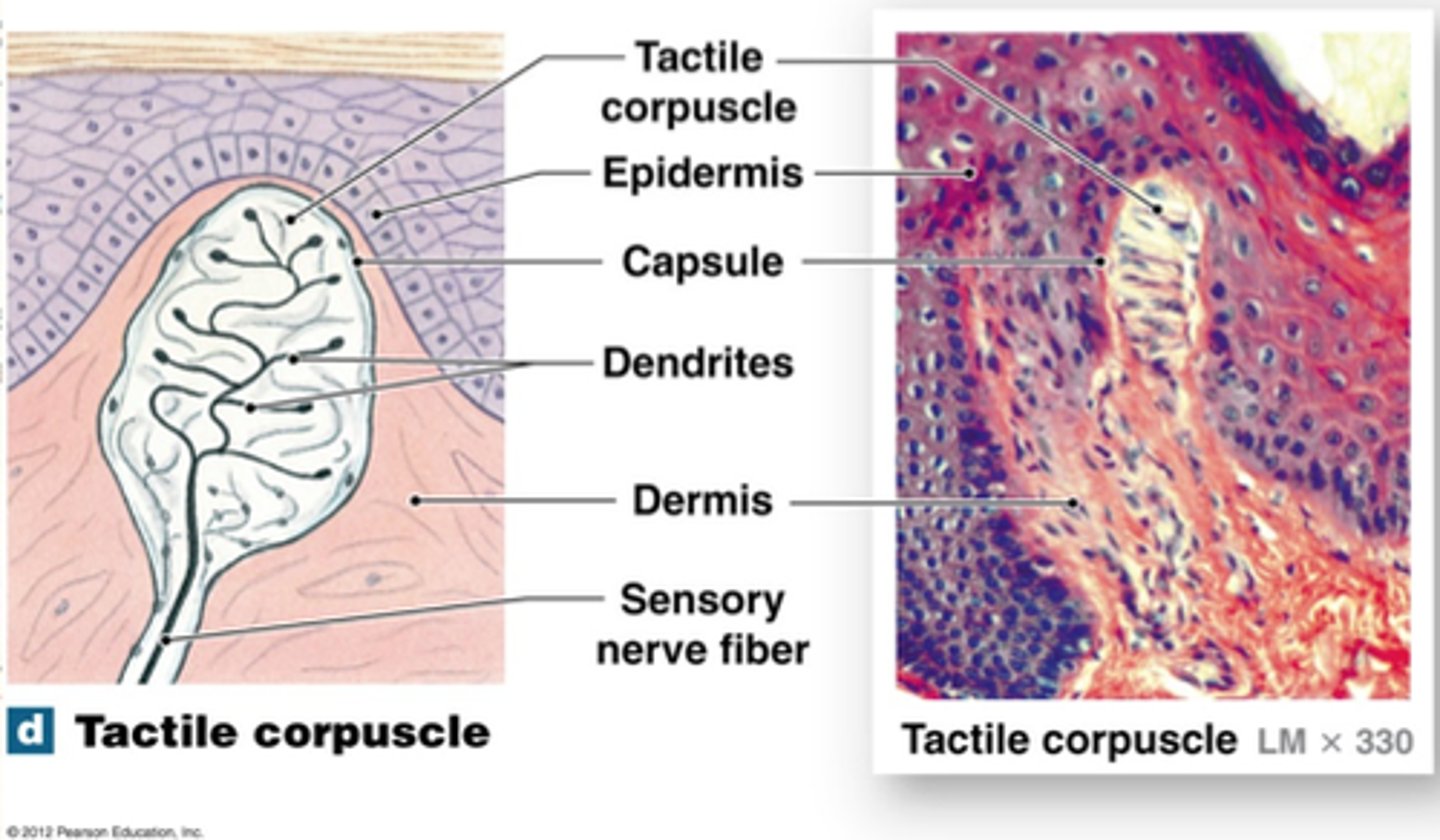
What do tactile corpuscles sense?
light touch, texture
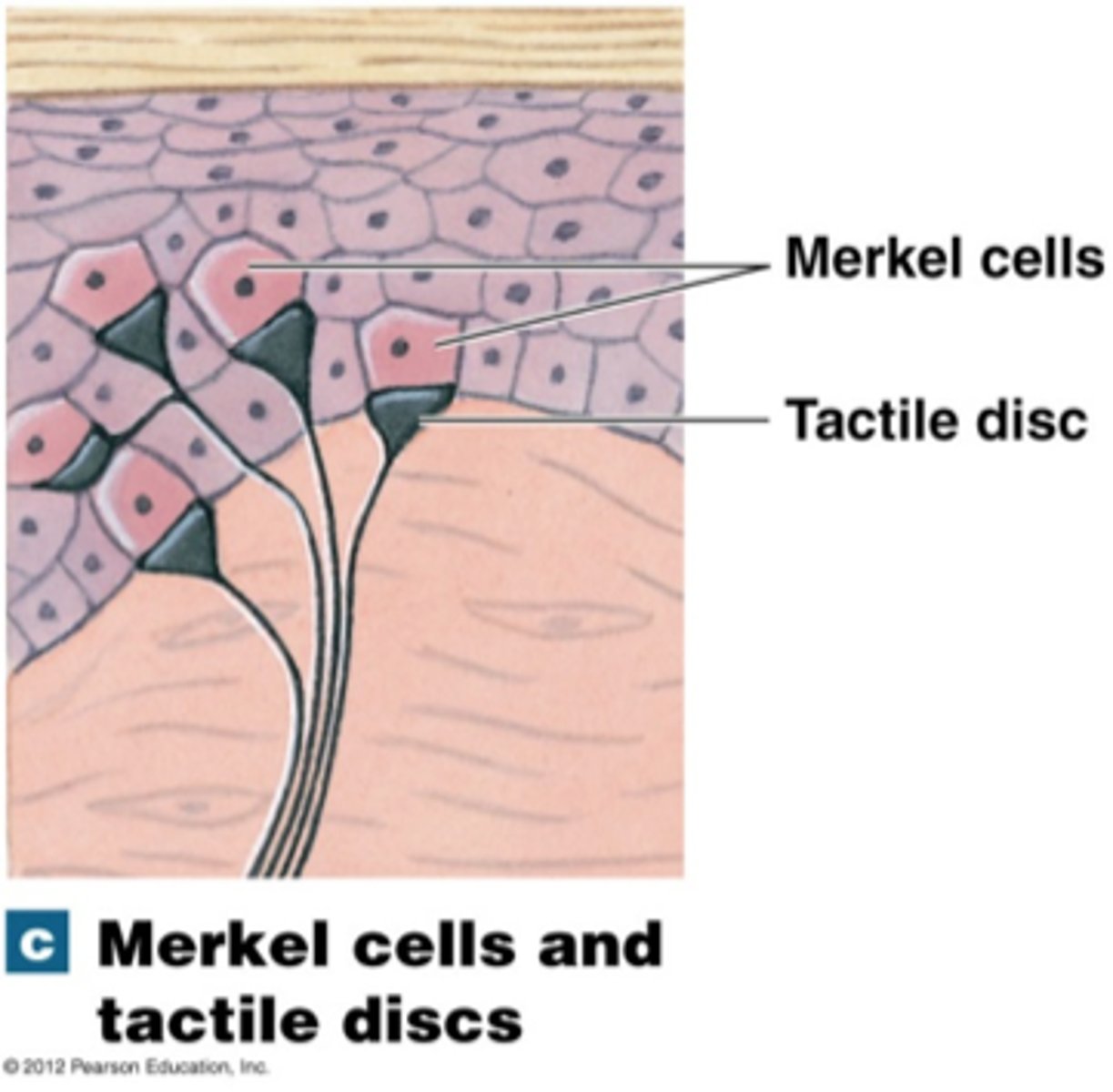
What do tactile discs sense?
Light touch, pressure
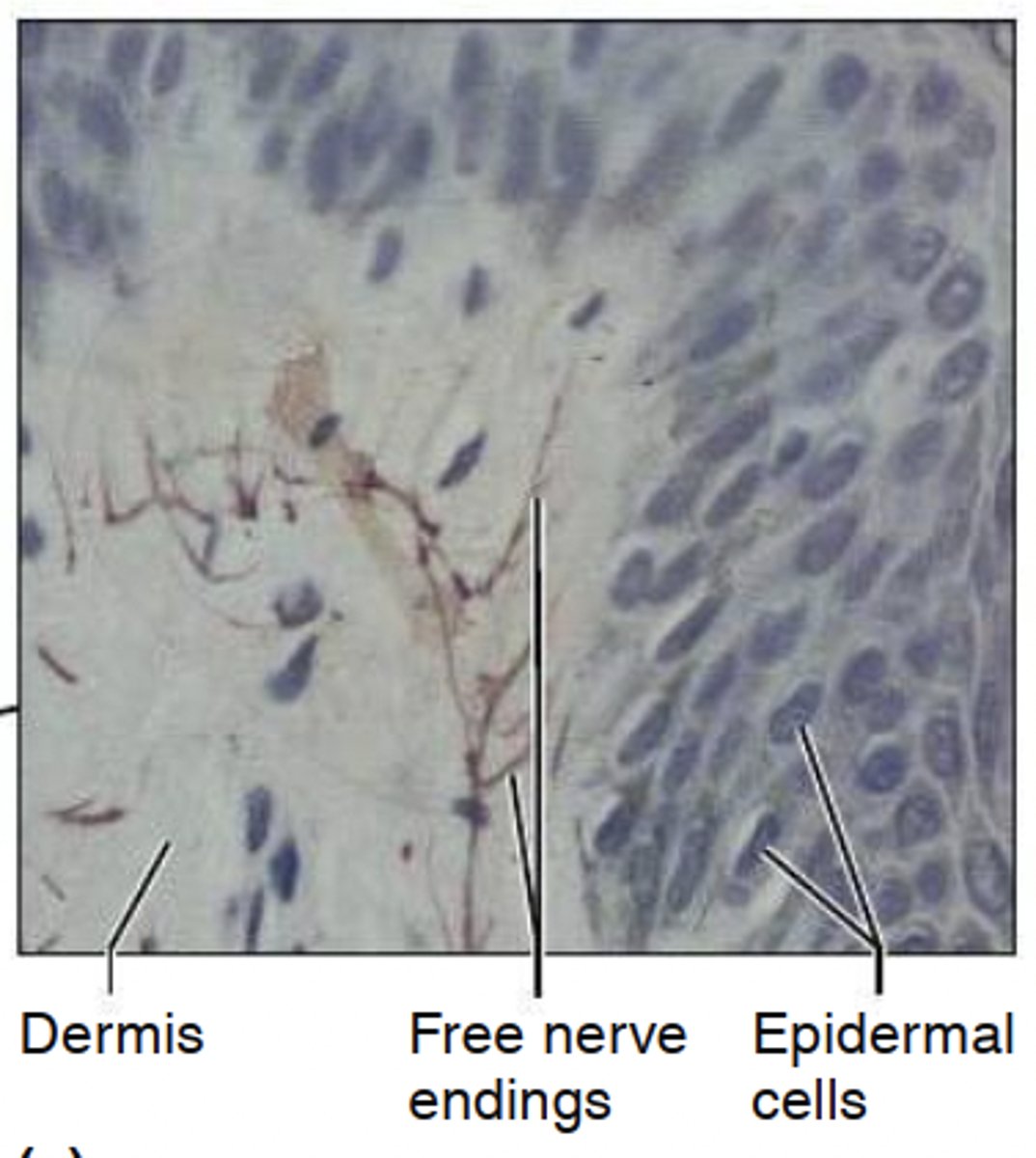
What do free nerve endings sense?
temperature, pain
Most encapsulated nerve endings are what kind of receptor?
Mechanoreceptors
What is the taste pathway?
Taste buds -> CN 8, 9, 10 -> foramina -> solitary nucleus (medulla) -> thalamus (some go to hypothalamus and amygdala) -> gustatory cortex (insula)
What is the auditory pathway? (start from the inner ear)
organ of corti -> CN 8 -> medulla (both sides) -> cochlear nucleus and superior olivary nucleus (pons) -> inferior colliculus (midbrain) -> thalamus (binaural) -> bilateral auditory cortex (temporal lobe)
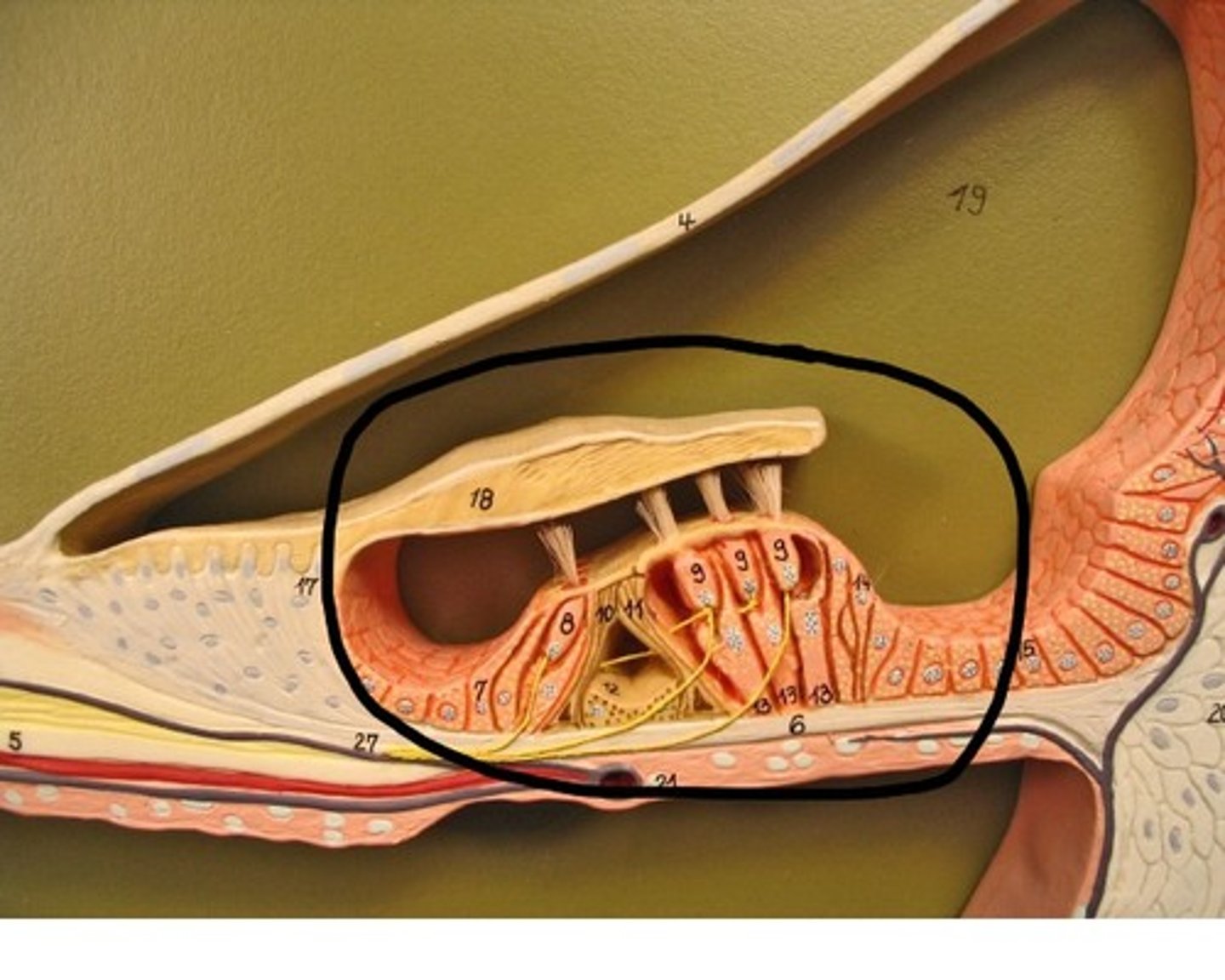
How are action potentials generated in the organ of Corti?
Hair cells bend to movements in the perilymph and stimulate the dendrites of the spiral organ, which transduces the sound into neural impulses
How is vibration amplified in the ear?
The ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) amplify it
True or false: loudness is related to frequency
False
True or false: pitch is related to basilar membrane location
True
# of neurons in ascending tracts?
3 (1st, 2nd & 3rd order )
What kind of information do ascending tracts carry ?
general sensory information
where do ascending tracts start?
in a dorsal root ganglion
Where do ascending tracts finish ?
in the somesthetic cortex (postcentral gyrus)
What are the 2 kinds of ascending tracts?
Dorsal White Column (DCML) & Spinothalamic "anterolateral system"
What is the order of the Dorsal White Column Tract?
Dorsal Root Ganglion -> (1st order) → medulla (synapse) -> (2nd order & decussation ) → thalamus (synapse) -> (3rd order) → Somesthetic Cortex
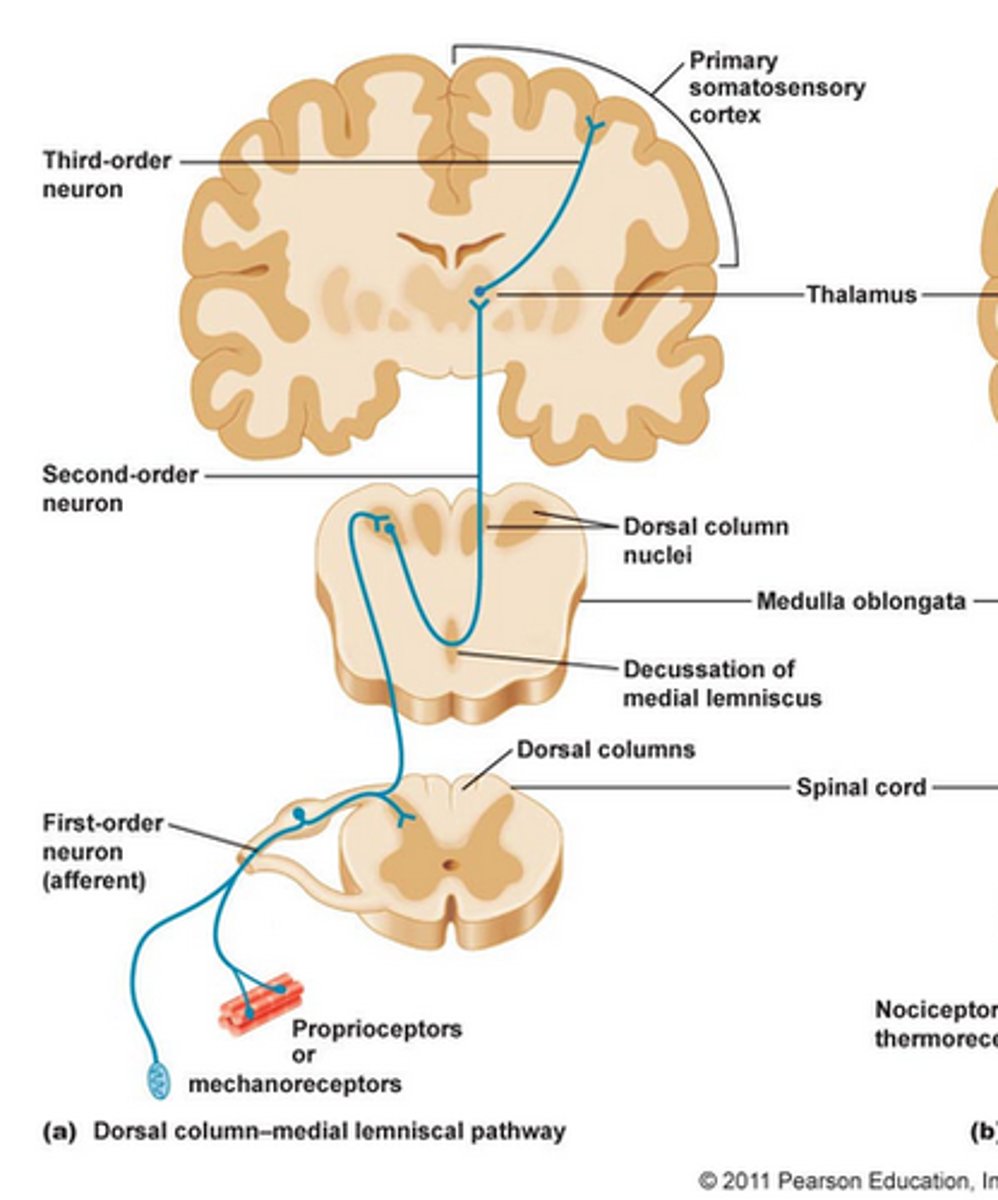
What is the order of the Spinothalamic Tract?
Dorsal Root Ganglion (1st order) -> Dorsal Horn of the Spinal Cord (synapse) → (2nd order & decussation ) -> Thalamus (synapse) -> (3rd order) -> Somesthetic Cortex
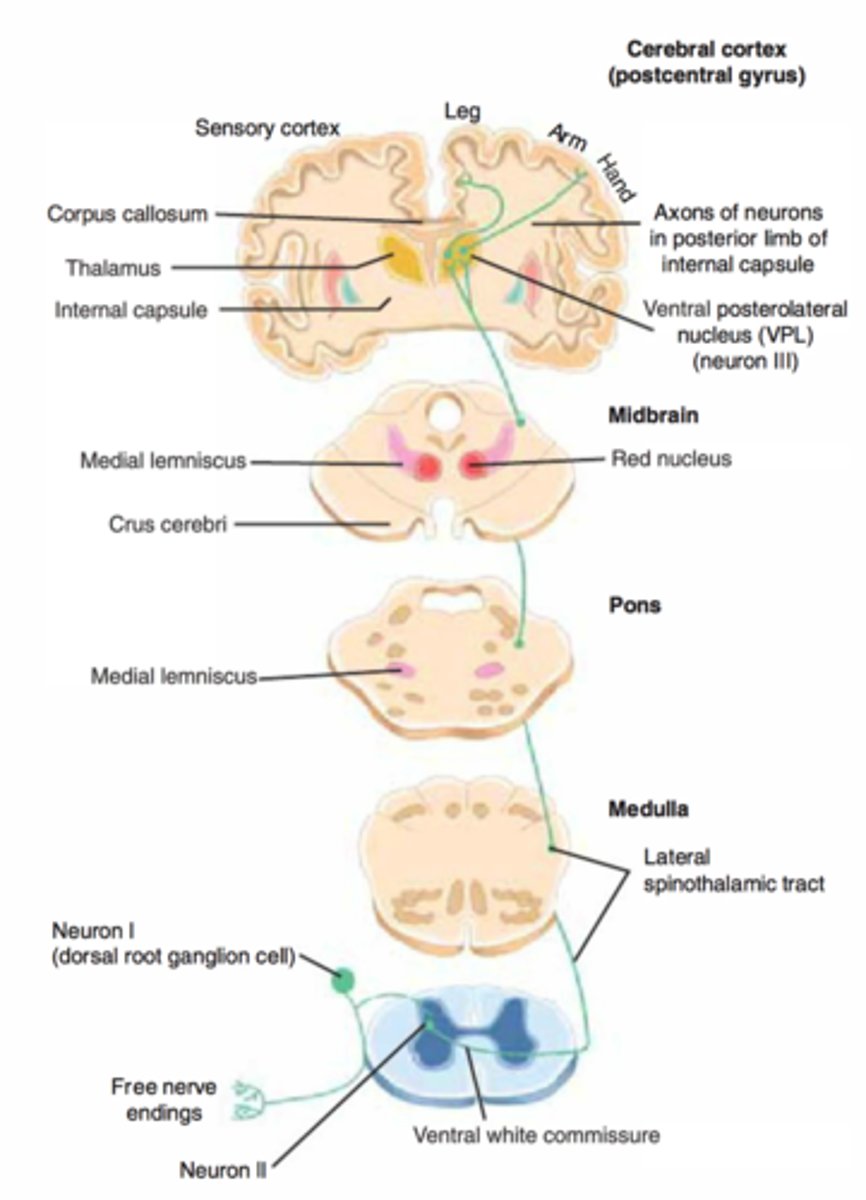
where do descending tracts start?
Primary motor cortex (precentral gyrus )
# of neurons in descending tracts?
2 (upper motor neuron & lower motor neuron)
What kind of information do descending tracts carry ?
general motor information
where do descending tracts end?
skeletal muscle
what are the kinds of descending tracts?
Lateral corticospinal tract & Anterior corticospinal tract
What is the order of the Lateral corticospinal tract?
(upper motor neuron) precentral gyrus → medulla (decussates at pyramids) → lateral funiculi → ventral horn (lower motor neuron, also in ventral horn, place of synapse)- > skeletal muscle
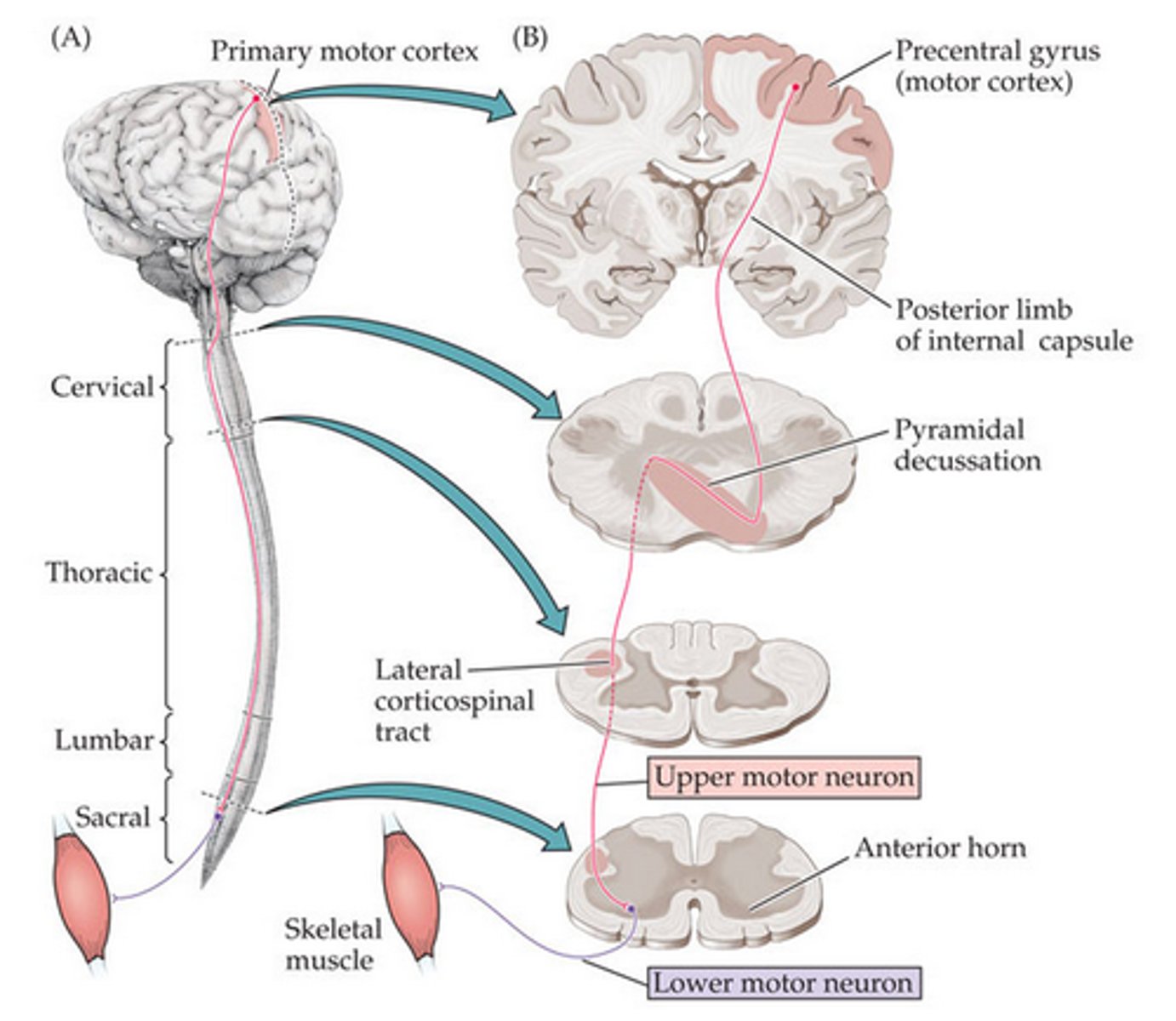
What is the order of the Anterior corticospinal tract?
(upper motor neuron) precentral gyrus → medulla → lateral funiculi → ventral horn, decussates (lower motor neuron, also in ventral horn, place of synapse) → skeletal muscle
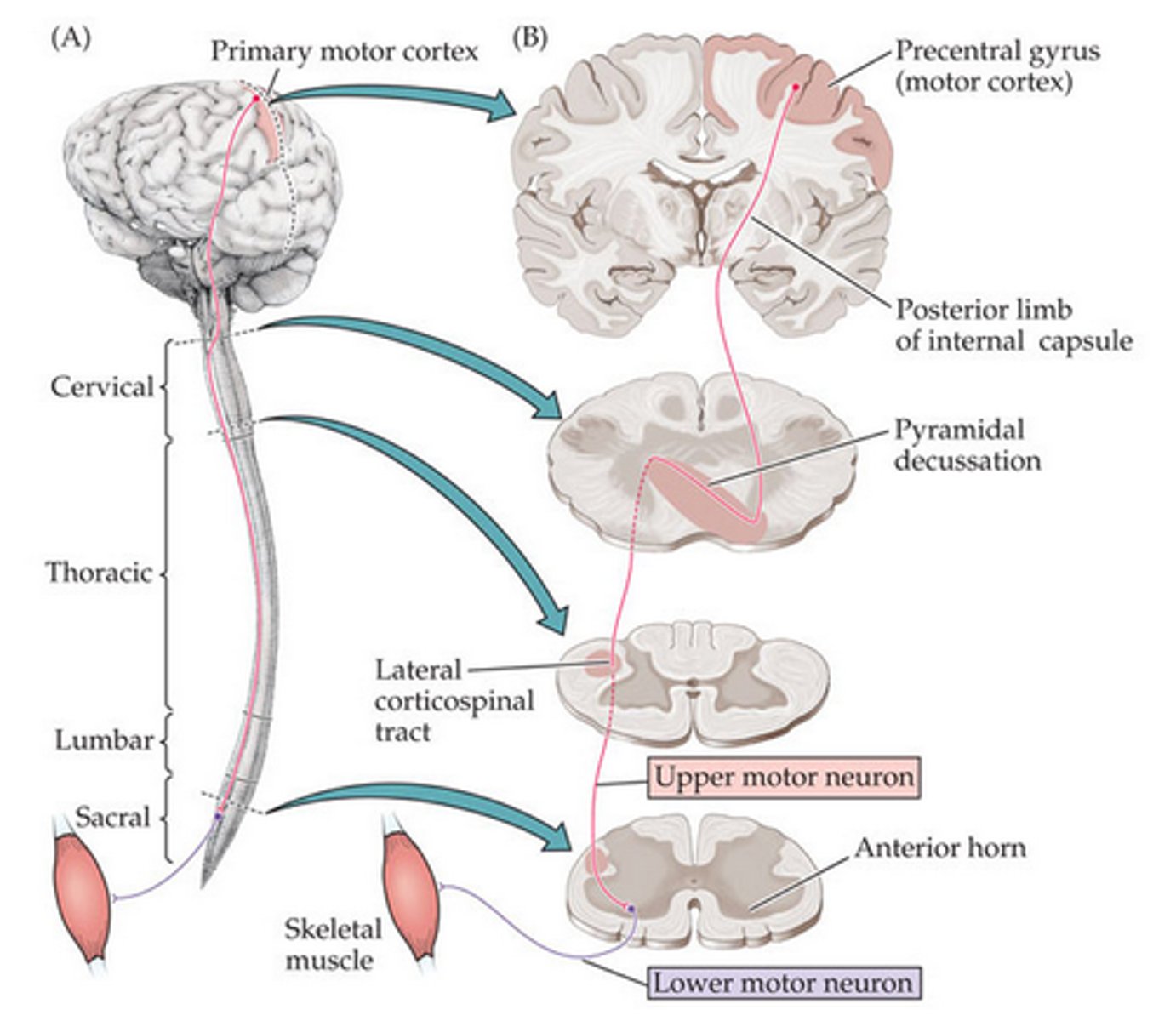
What does decussation?
decussation is the crossing over of neurons, it usually occurs in or right after the medulla in the spinal cord * pyramids of decussation in the medulla
What section of the spinal cord does the DCML enter?
gracile fasciculus & cuneate fasciculus
where does the DCML decussate?
medulla (medial lemniscus )
Where does the lateral corticospinal tract decussate?
in the medulla
Where does the anterior corticospinal tract decussate?
in the spinal cord
what does the autonomic NS control?
Visceral reactions of the body
what does the somatic NS control?
the voluntary motions of the body
what are the 2 divisions of the autonomic nervous system?
sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
What does the sympathetic nervous system do?
arouse the body and prepare for fight, flight, or freeze
what do does the parasympathetic nervous system do?
relax the body and prepare for rest and digestion
What neurotransmitters does the sympathetic nervous system utilize?
the adrenergic system utilizes norepinephrine and epinephrine
what neurotransmitters does the parasympathetic nervous system utilize?
the cholinergic system utilizes acetylcholine
Are preganglionic neurons myelinated or unmyelinated?
myelinated
Are postganglionic neurons myelinated or unmyelinated?
unmyelinated
Where the origin of sympathetic NS?
the lateral horns of T1 & L2 (thoracolumbar)
Fiber lengths of Sympathetic Division
short preganglionic and long postganglionic
Neural divergence of the sympathetic division?
extensive
Effects on system in sympathetic division?
often widespread and general
location of ganglia in sympathetic
paravertebral ganglia adjacent to the spinal column and prevertebral ganglia anterior to it
Where is the origin of the parasympathetic NS?
craniosacral (travels through cranial nerves 3, 7, 9, 10) or the splanchnic nerves
where is the location of ganglia in the parasympathetic division?
terminal ganglia near or within the target organs
fiber lengths of the parasympathetic division?
long preganglionic and short postganglionic
neural divergence in the parasympathetic division?
Minimal
effects on the parasympathetic division?
more specific and local
What are the routes of the Sympathetic NS?
Spinal nerve route & sympathetic nerve route
preganglionic neurons travel through which ramus?
pre - white ramus
postganglionic neurons travel through which ramus?
post - gray ramus
Features of the sympathetic nerve route?
travels through the spinal cord (sympathetic trunk) and synapses in the same ganglion level, does a loop through the ramus and then travels to the ganglion
Features of the splanchnic nerve route?
travels through the splanchnic nerve and becomes apart of the splanchnic nerve after the ganglion
What are the routes of the Parasympathetic NS?
Cranial synapse and sacral synapse
Where does the Cranial synapse interact?
Cranial synapse that travels through the cranial nerves (III, VII, IX, X)
Where does the Sacral synapse interact
travels the anterior rami from the pelvic splanchnic nerves
Chromaffin cells?
cells of the adrenal medulla, they sit on the kidneys and are apart of the sympathetic ns. and are attached to the splanchnic nerve
How many connections do somatic reflexes have?
direct connection to the target cells
How many connections do autonomic reflexes have?
2 step pathway consisting of a preganglionic and post ganglionic neurons
Describe sympathetic autonomic reflexes.
anterior root nerve between T1 and L3
Describe the parasympathetic nervous system.
anterior root nerve in the craniosacral region
Describe adrenergic receptors and neurons (neurotransmitters)
sympathetic ns, alpha is excitatory, beta is inhibitory, primarily uses norepinephrine, and epinephrine
Describe cholinergic receptors and neurons (neurotransmitters )
parasympathetic ns and sympathetic ns, muscarinic receptors, uses acetylcholine
muscarinic receptors are on:
muscles and glands
nicotinic receptors are on:
cells of the autonomic ganglia, adrenal medulla and skeletal muscle
what type of neuron/receptor belongs to both the parasympathetic and sympathetic
nicotinic
how do muscarinic receptors impact different types of muscle?
excitatory towards smooth muscle, inhibitory towards cardiac muscle
is cholinergic receptors and neurons exclusively for the parasympathetic nervous system?
no! they are found in both but mostly sympathetic
How do the cranial bones and the vertebral column protect the CNS?
The cranial bones serve as protection for the brain, while the vertebral column serves as protection for the spinal cord.
List the 3 meninges from superficial to deep
1. dura mater
2. arachnoid mater
3. pia mater
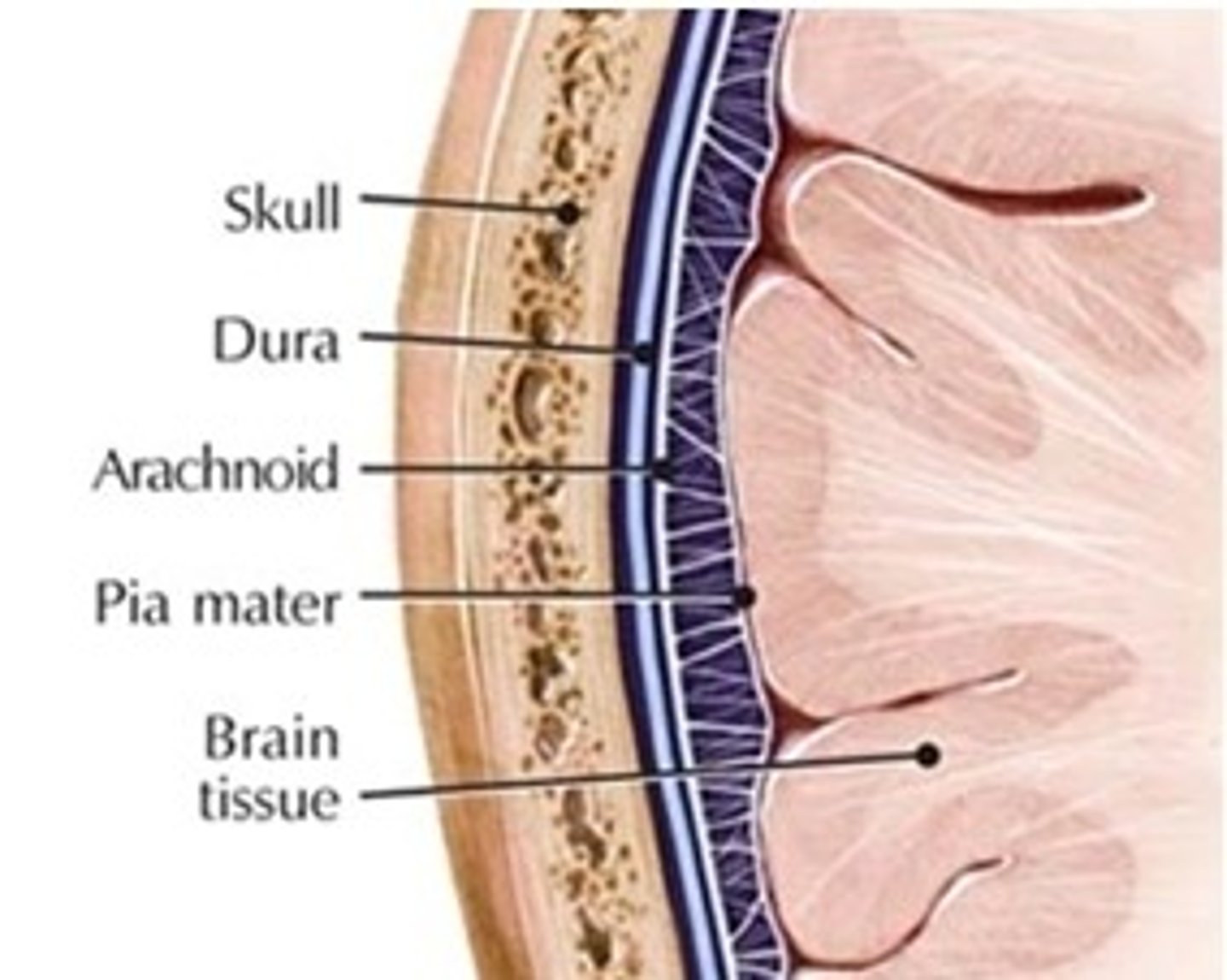
Dura Mater - location and structure (layers, sinuses, folds) in CNS
Location: most superficial meningeal layer located between bone of skull/vertebrae and arachnoid mater
Structure: 2 layers (periosteal and meningeal), dural venous sinuses (space between layers containing blood vessels), 3 dural folds (falx cerebri, falx cerebelli, tentorium cerebelli)
Arachnioid Mater - location and structure in CNS
Location: middle meningeal layer located between dura mater and pia mater
Structure: transparent + contains largest blood vessels of the cerebral surface
Pia Mater - location and structure in CNS
Location: deepest meningeal layer located between the cerebral cortex and arachnoid mater
Structure: thin layer completely adhered to the brain; follows gyri and sulci and has blood arteries penetrating the cerebrum (also: filum terminale is an extension of the pia mater)
dura mater - brain vs spinal cord + reason for difference
brain: meningeal layer + periosteal layer
spinal cord: ONLY meningeal layer
reason: function of the periosteal layer is to provide a tubular sheath-like covering for the cranial nerves as they pass through the different foramina of the skull; as soon as the cranial nerves exit the foramen, the periosteal layer fuses with the epineurium of nerves
dural venous sinuses - location, structure, function
Location: in between the periosteal and meningeal layer of the dura mater
Structure: large space containing veins within the dural sheath; space within dural sheath is created by the collective effort of the dural folds (falx cerebri, falx cerebelli, tentorium cerebelli)
Function: manages blood return from the brain to the normal circulatory system
cranial dural septa (folds) - structure and function
falx cerebri: tough-crescent shaped wall; separates 2 cerebral hemispheres
falx cerebelli: smaller fold; separates 2 cerebral hemispheres through the cerebellum
tentorium cerebelli: crescent shaped fold that stretches like a roof over the posterior cranial fossa; separates cerebrum from the cerebellum
epidural space - location and potentiality
Location: above the dura and below the cranium
Potentiality: potential space in the brain (would become real only in instances of bleeding) but a real space in the spinal cord
*sidenote: site of injection for birth and surgeries
subdural space - location and potentiality
Location: below dura mater and above arachnoid mater
Potentiality: potential space
subarachnoid space - location and potentiality
Location: below arachnoid mater and above pia mater
Potentiality: real space