Pharmacology Antidepressants / Antipsychotics and epilepsy drugs II
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
How do drugs used to treat schizophrenia differ in action from those used to treat depression?
Antidepressants are thought mainly to increase norepinephrine and/or serotonin levels by blocking reuptake
Antipsychotics are thought to work mainly by decreasing dopamine activity by acting as dopamine receptor antagonists in the dopaminergic tracts in the brain, especially to mesocorticolimbic tract
what are some medical uses of antipsychotic medications?
• Management of Schizophrenia
• Bipolar disorder
• Treatment of Agitated Depression, Acute Mania, and Atypical Psychiatric Disorders (following surgery or MI)
• Tourette’s Syndrome (Haloperidol, Pimozide, Atypicals)
• Prevention of Cancer Chemotherapy-Induced Severe Nausea and Vomiting (Prochlorperazine (Compazine))
• Pre and Postsurgical Prophylaxis Against Aspiration (Metoclopromide, Droperidol)
• Treatment of Intractable Hiccups (Promethazine)
• Motion Sickness (Promethazine)
Worldwide, the prevalence of schizophrenia appears to be %
1%
t/f: Schizophrenia is more prevalent than Alzheimer's disease, diabetes, or multiple sclerosis
true
(prevalence greater among lower SES in urban areas and comparable among men and women_
what is the peak age of onset of schizophrenia?
18-25 years in men
26 to 45 yeara in women
A person with a parent or sibling with schizophrenia has approximately a % risk of developing the disorder compared with a % risk for a person with no family history of schizophrenia.
10%
1%
Research suggests that schizophrenia may be a developmental disorder resulting from…?
impaired migration of neurons in the brain during fetal development (nongenetic factors like environmental stress during fetal development/birth may also contribute)
what are positive symptoms of schizophrenia?
• Delusions
• Disorganized speech
• Hallucinations
• Behavior disturbance
what are negative symptoms of schizophrenia?
• Avolition (lack of goal directed behavior)
• Flattened affect
• Anhedonia
• Social withdrawal
what are 3 typical antipsychotics (D2 antagonists) used to treat schizophrenia?
Phenothiazines: Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)
thioxanthines
Butyrophenones: Haloperidol (Haldol)
1st choice typical
how do typical antipsychotics like Phenothiazines: Chlorpromazine (Thorazine), thioxanthines, and Butyrophenones: Haloperidol (Haldol) work?
block D2 > D1 (dopamine receptors) with varying degrees of selectivity for 3 dopaminergic tracts in the CNS
phenothiazines affect all tracts = lots of side effects
what are the 3 dopaminergic tracts in the CNS that are targets of typical antipsychotics (D2 antagonists)?
nigrostriatial
mesocorticolimbic
tuberinfundibular
antipsychotic agents that act on the nigrostriatal dopaminergic tract helps with…?
extrapyramidal movement disorders (EPS)
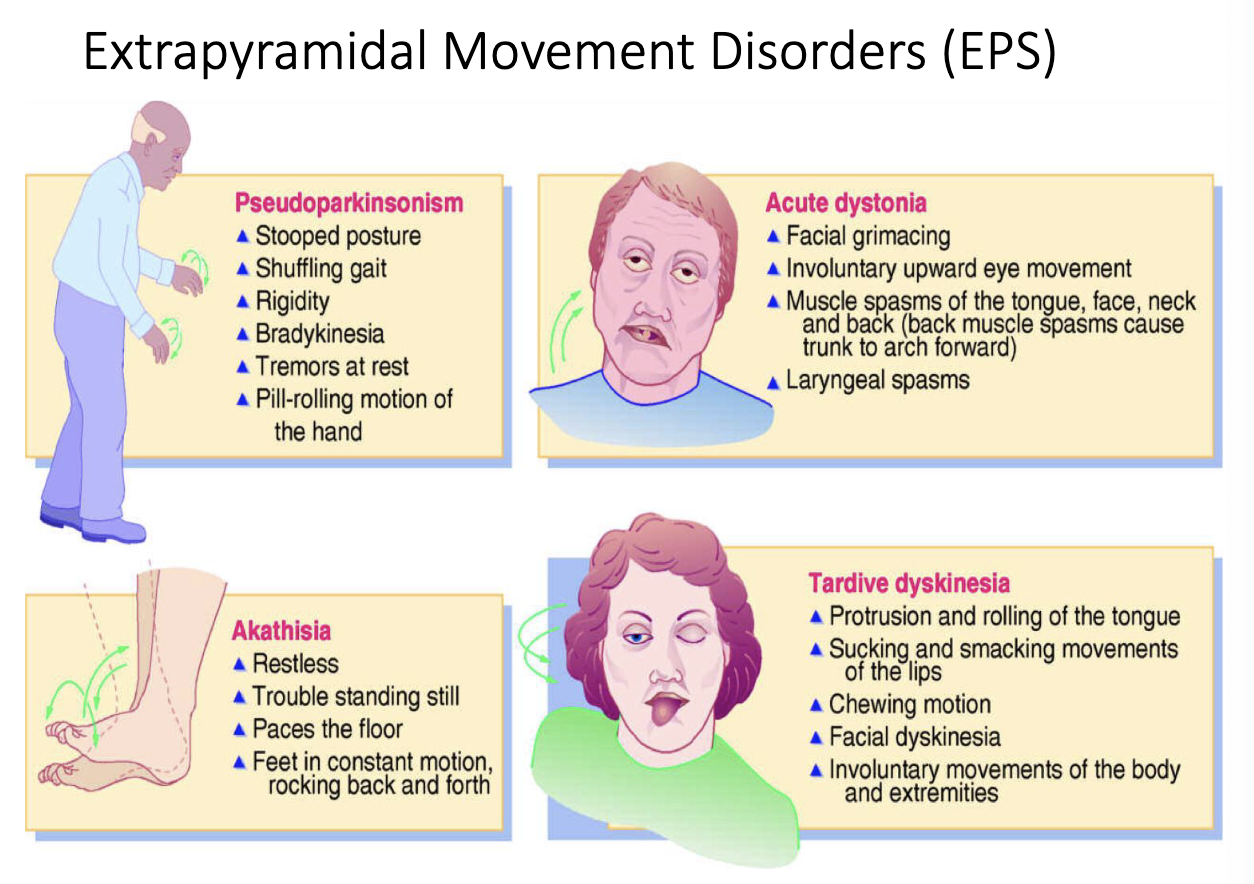
antipsychotic agents that act on the mesocorticolimbic dopaminergic tract helps with…?
relief of hallucinations and delusions
antipsychotic agents that act on the tuberinfundibular dopaminergic tract helps with…?
increased prolactin release
galactorrhea
gynecomastia
sexual dysfunction
menstrual irregularities
early antipsychotic drugs also act on other receptors (non-dopamine) which can explain side effect such as…?
anticholinergic
xerostomia, urinary retention, blurred vision, constipation
antihistamine
sedation
anti-alpha-1 adrenergic
orthostatic hypotension
what are atypical antipsychotics?
block serotonin AND dopamine receptors (decreased side effects like EPS)
dibenzepines
clozapine (Clozaril)
Olanzapine (Zyprexa)
Quetiapine (Seroquel)
benzisoxazoles
Risperidone (Risperidal)
what is one potentially dangerous side effect of Clozapine (atypical antipsychotics)?
agranulocytosis (bleeding disorder)
what are some dental management issues that may arise with patients using antipsychotic drugs?
poor oral hygiene (caries, periodontal disease)
anticholinergic side effects (xerostomia)
EPS and dystonias, postural hypotension
heightened sensitivity to light
informed consent may be issue if pt has trouble understanding oral care instructions
fixed dental appliances preferred to removable appliances
lack of patient compliance
About % of men and % of women suffer from anxiety disorders
6% men
13% women
# Americans have had an anxiety disorder but only % receive treatment
30 million
25%
A typical Dentist will see how many patients per day with some kind of anxiety?
at least one
what is the emotional state in which people feel uneasy, apprehensive, or fearful about events they cannot control or predict, or about events that seem threatening or dangerous?
anxiety (feeling of vulnerability, can persist and become disabling)
what is fear? how is it different from anxiety?
fear: a normal reaction to a known, external source of danger
anxiety: individual is frightened but source of danger not known, recognized, or inadequate to account for symptoms
physiological manifestations are similar
what are phobias?
fear response to a neutral stimulus (unrealistic fears)
what are panic attacks?
A period of intense fear or discomfort that is associated with numerous physical and psychological symptoms such as :
• Palpitations,
• sweating,
• trembling,
• shortness of breath,
• choking,
• chest pain
• nausea
what are anxiolytics used for?
to treat acute anxiety reactions/agitation
adjunctive to other medications to enhance sedation prior to procedures
management of chronic anxiety disorders (generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, PTSD, social phobias)
what are some common antianxiety drug classifications?
benzodiazepines (diazepam, flurazepam, etc.)
what is the benzodiazepine antagonist?
flumazenil (important because you could overdose on benzodiazepine antianxiety drug so it is good that there is a antagonist that can help reverse effects)
Diazepam, Midazolam, Lorazepam, Alprazolam, Triazolam are all examples of …? how do they work?
benzodiazepines
enhance effect of GABA (inhibitory neurotransmitter)
what are the effects of benzodiazepines?
Anxiolytic in low doses, higher doses lead to more general sedation and sleep
acute use well estabilshed
chronic use discouraged (tolerance, withdrawal, addiction)
what is a cautionary warning DDI for benzodiazepines?
Synergistic sedating and respiratory depressant effects with opioids, ETOH and other “CNS depressants”
what are some adverse effects of benzodiazepenes?
Sedation
Tolerance to sedative effects usually in ~2 weeks of daily use, synergistic with opioids
Cognitive impairment
short AND long term use especially in elderly
Ataxia
Increase in falls especially in the elderly and synergistic with opioids
Respiratory depression
In high doses or when combined with other CNS depressants such as EtOH, opioids, barbiturates
Anterograde amnesia
Reduce dose in elderly!
which benzodiazepine drug is often used in pediatric dental procedures?
midazolam (so patients already on long term benzodiazepines may exhibit tolerance and require higher doses (monitor respiration))
what does the FDA black box warning indicate with benzodiazepine use?
FDA black box warning for opioid analgesics, prescription opioid cough products, and benzodiazepine labeling related to serious risks and death from combined use (2016)
There are 3 dopamine tracts in the brain that are acted upon by antipsychotic drugs. Nigrostriatal, mesocorticolimbic, and tuberoinfundibular.
Which tract mediates the relief of the positive symptoms like hallucinations?
Mesocorticolimbic
There are 3 dopamine tracts in the brain that are acted upon by antipsychotic drugs. Nigrostriatal, mesocorticolimbic, and tuberoinfundibular.
Which mediates the extrapyramidal movement disorders caused by antipsychotic drugs?
Nigrostriatal
How do atypical or 2nd generation antipsychotics differ from 1st generation?
They supposedly reduce the negative symptoms in addition to the positive symptoms
They block serotonin 5-HT2 Receptors in addition to dopamine receptors
More selective for DA receptors in mesocorticolimbic system
Reduced EPS side effects
What are some problematic side effects or dental concerns in treating a patient taking antipsychotic drugs?
Patient may have EPS movement disorder like Tardive dyskinesia or akathisia
Drugs cause xerostomia
Patients show poor oral hygiene
May show orthostatic hypotension
Increased sensitivity to light
Benzodiazepines are typically used as anxiolytics. Name 3.
Diazepam
Lorazepam
Midazolam
what is the MOA of benzodiazepines?
they enhance the action of GABA
describe 3 adverse side effects of benzodiazepines?
sedation
cognitive impairment
respiratory depression
anterograde amnesia
what is the FDA warning for benzodiazapenes?
Risk of death when combined with opioids due to severe respiratory depression
Anticonvulsants are typically used to manage the symptoms of _______, which derive from …?
epilepsy
the recurrence of an abnormal discharge of cerebral neurons
what are type 1 anticonvulsants?
sodium channel inactivators
Phenytoin (Dilantin), Carbamazepine (Tegretol)
what are type 2 anticonvulsants?
GABA facilitators
Barbiturates (Phenobarbital), Benzodiazepines: Diazepam (Valium), Lorazepam (Ativan), Clonazepam (Klonopin)
what are type 3 anticonvulsants?
T-calcium current blockers
Ethosuximide (Zarontin)
what are type IV anticonvulsants?
mixed acting (combination of type 1/2/3 with inhibition of EAA activity)
Topiramate (Topamax), Lamotrigine(Lamictal), Valproic Acid (Valproate)
how do type I (sodium channel inactivator) anticonsulsants work? (MOA)
• These agents inhibit synaptic transmission and stabilize hyperexcitable neurons by altering sodium ion influx and efflux
• This dampens only abnormally high neuronal activity, allowing normal conduction of action potentials to occur
Examples: Phenytoin (Dilantin), carbamazepine (Tegretol)
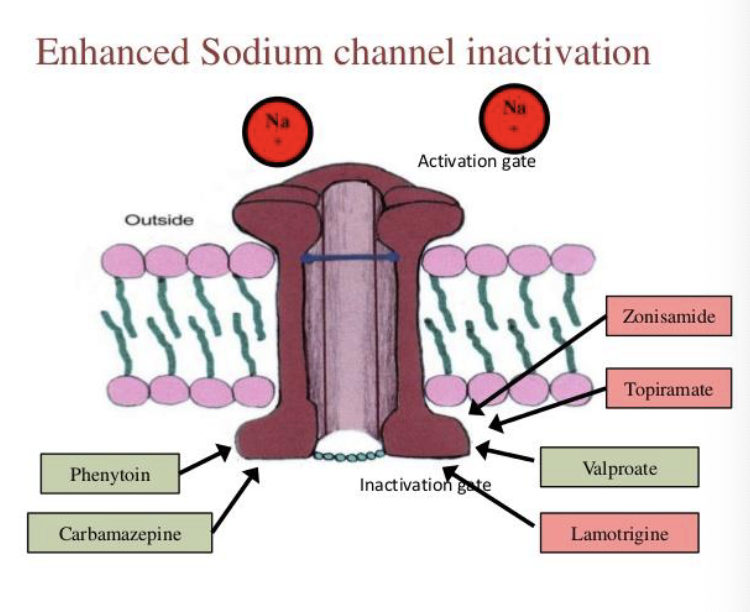
what are some notable side effects of Phenytoin (Dilantin)?
(this is a type I sodium channel inactivator anticonvulsant)
gingival hyperplasia hypertrichosis
teratogenic (cleft palate)
what are some notable side effects of Carbamazepine (Tegretol)?
no dilantin type adverse effects other than 3A4 induction
what are some DDIs of type 1 sodium channel inactivator anticonvulsants?
Induce liver metabolism (3A4) of some drugs
GABA is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS.
Enhancing the activity of GABA has the dual action of …?
preventing the spread of the abnormal neuronal activity from its focus
but also raises the threshold for setting off the focus
which type II anticonvulsants work via faciliation of GABA binding?
Phenobarbital, Benzodiazepines
which type II anticonvulsants work via decreased GABA breakdown and increased GABA synthesis?
valproic acid
what is the MOA of benzodiazapenes?
BDZ receptors are part of a complex containing a CL-channel, GABA-A receptors for the major inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA, and receptors that bind barbiturates.
GABA binds to its receptor, opens the CL-channel, CL- goes into the neuron, hyperpolarizing the cell, decreasing the neuronal firing ability.
BDZs work indirectly via allosteric modification, increasing the affinity of GABA for the GABA receptor and thus enhancing GABA’s inhibitory action.
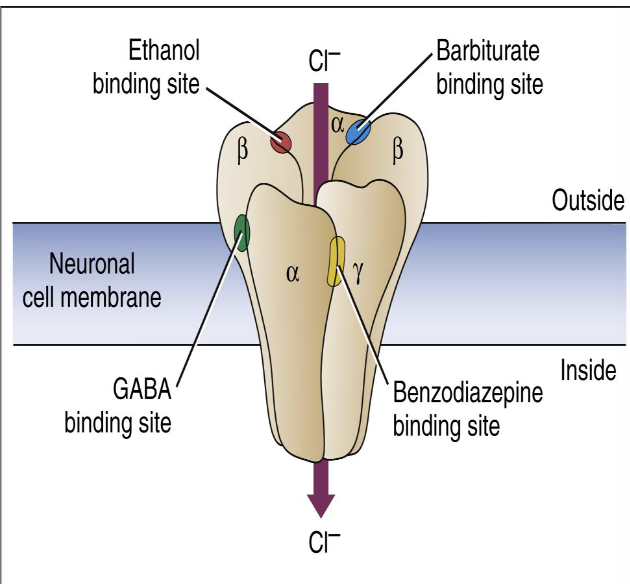
what are side effects of type II anticonvulsant (barbiturates: phenobarbital)?
Sedation and cognitive slowing. Children and elderly patients may show paradoxical excitement
what are potential drug interactions of type II anticonvulsant (barbiturates: phenobarbital)?
additive respiratory depression
generalized inducer of liver enzymes
_______ is the drug of choice (sometimes diazepam due to its wider availability outside the medical setting) for terminating status epilepticus (given IV) and to treat local anesthetic induced seizures
Lorazepam (Ativan)
what is a key DDI with type II gaba enhancing benzodiazepines ?
Opioid abuse combined with BDZs is lethal due to additive respiratory depression
what is the drug of choice for absence seizures?
type III T-calcium current blockers (ethosuximide)
what is the MOA of ethosuximide? (type III T-calcium current blocker)
ethosuximide elevates the firing threshold for seizures and depresses the firing of epileptic foci by blocking low threshold, T calcium channel currents in thalamic relay neurons
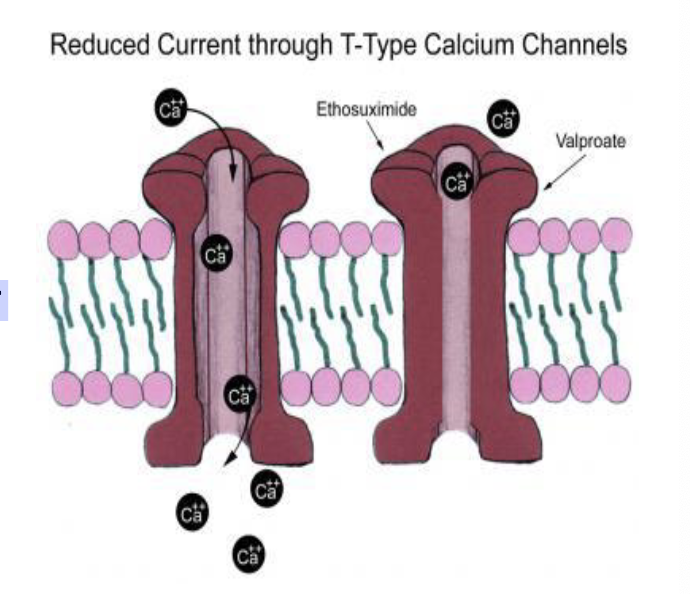
what are some side effects of ethosuximide? (type III T-calcium current blocker)
drowsiness, nausea and vomiting, blood dyscrasia, bone marrow depression, dizziness and skin rashes
MOA of Lamotrigine (Lamictal)? (type IV mixed acting anticonvulsant)
Na+ channel inactivator and decreased EAA (glutamate) activity
MOA of Topiramate (Topamax) (type IV mixed acting anticonvulsant)
Na+ channel inactivator
enhancement of GABA
decreased EAA activity
what are some non-seizure related uses of Topiramate (Topamax) (type IV mixed acting anticonvulsant)?
migraine prophylaxis
bipolar disorder
managing alcohol dependence
obesity
binge eating
smoking cessation
what are some adverse effects of Topiramate (Topamax) (type IV mixed acting anticonvulsant)?
• Can produce speech, language and behavioral problems in children
• Increased incidence of cleft palate
what are some Adverse Side Effects/ DDIs involving anti-seizure drugs?
• Additive CNS depression (most)
• Drug-produced gingival hyperplasia (Dilantin)
• Drug-induced blood dyscrasias may increase susceptibility to infection. (ethosuximide, dilantin, tegretol, valproic acid)
• Induction of drug metabolizing enzymes (Phenobarbital, Dilantin, Tegretol)
• Additive effects on bleeding (Valproic acid)
• Dry mouth resulting in bleeding gums and tooth pain
MOA of Gabapentin and Pregabalin (Lyrica)?
Both bind to the α2δ (alpha2delta) subunit of the voltage dependent calcium channel in the CNS. This reduces calcium influx into the nerve terminals
used for neuropathic pain, depression, bipolar, anxiety
what is a disorder that affects nerve cells in the part of the brain controlling muscle movement and can result in trembling, muscle rigidity, difficulty walking, problems with balance, and slowed movement?
Parkinson’s disease
Many of the signs and symptoms of Parkinson's disease develop when certain nerve cells in an area of the brain called the _______ are damaged or destroyed
substantia nigra
what is the cause of Parkinson’s disease?
Many signs/symptoms develop when half or more of certain nerve cells in the substantia nigra are damaged or destroyed.
Normally, these nerve cells release dopamine — a chemical that transmits signals between the substantia nigra and the corpus striatum.
These signals cause muscles to make smooth, controlled movements.
combination of genetic and environmental factors
Certain drugs, diseases and toxins also may cause similar symptoms
what is the main drug used to treat Parkinson’s disease?
Sinemet (Levodopa + Carbidopa)
how does sinemet work to treat Parkinson’s disease?
Levodopa converts into dopamine by nerve cells in brain (crosses BBB but only small amount actually reach brain)
increase in dopamine may reverse many disabling symptoms
Carbidopa blocks carboxylase that breaks down levodopa in periphery
helps more levodopa reach the brain + prevent breakdown
what are some other, less common drugs used to treat Parkinson’s disease?
dopamine agonists like pramipexole (Mirapex)
causes compuslive gambling behavior
MAO-B inhibitors: elegiline (Eldepryl) and rasagline (Azilect)
Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors. (Entacapone)
what are the implications for dentistry for drugs used to treat Parkinson’s disease?
xerostomia, enamel erosion from frequent nausea and vomiting
Tremoring (difficult for patient to brush teeth)
oral tremors
wjat are problematic DDIs with drugs used to treat Parkinson’s disease?
Levodopa and COMT inhibitors may sensitize heart to epinephrine induced arrhythmias,
avoid use of vasoconstrictor containing local anesthetics
Selegilene is metabolized to amphetamine and metahamphetamine
avoid epi!
Selegilene is an MAOI
avoid meperidine
what are generalized seizures?
both hemispheres of brain involved leading to tonic - clonic symptoms
consciousness and postural control loss
what are absence seizures?
Short loss of consciousness but no loss of postural control (More common in children)
what is status epilepticus?
continuous seizure lasting more than 5 minutes - need to intervene with BDZ (Can be caused by local anesthetic)
how do dopamine agonists (“Miradex”) work to treat Parkinson’s?
gets into CNS and stimulates dopamine receptors
how do MAO-B inhibitors (“selegiline”) work to treat Parkinson’s?
combined with sinemet helps reduce breakdown of DA