GENETICS
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:04 AM on 2/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
1
New cards
**GENETICS**
* the scientific study of how physical, biochemical, and behavioral traits are transmitted from parents to their offspring.
* the science of heredity.
* It explains how genes bring about characteristics in living organisms and how those characteristics are transmitted from parents to offspring.
* It is at the center of all biology because gene activity underlies all biological processes!
* the science of heredity.
* It explains how genes bring about characteristics in living organisms and how those characteristics are transmitted from parents to offspring.
* It is at the center of all biology because gene activity underlies all biological processes!
2
New cards
1. **Molecular/cellular genetics**
2. **Mendelian genetics**
3. **Population genetics**
**THREE LEVELS OF GENETICS**
3
New cards
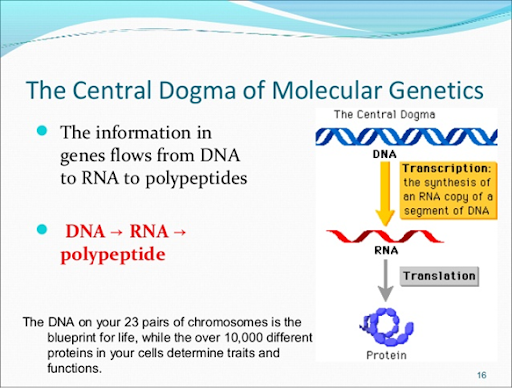
**Molecular/cellular genetics**
* what genes are, what they do
* Studies activities of gene (molecules that carry genetic information from generation to generation).
* Concerned with molecules that compose the genes, molecules that control genes & molecules that are the products of genes.
* Studies activities of gene (molecules that carry genetic information from generation to generation).
* Concerned with molecules that compose the genes, molecules that control genes & molecules that are the products of genes.
4
New cards
**MENDELIAN OR CLASSICAL GENETICS**
* **TRANSMISSION GENETICS**
* inheritance and expression of traits
* Explains patterns of transmission of traits from generation to generation
* Examines phenotypic characteristics & how they are transmitted
* inheritance and expression of traits
* Explains patterns of transmission of traits from generation to generation
* Examines phenotypic characteristics & how they are transmitted
5
New cards
**POPULATION GENETICS**
* Studies variation of genes between & within populations.
* Aims to understand how the observed genetic variation evolved.
* The study of genetics at the population level.
* Aims to understand how the observed genetic variation evolved.
* The study of genetics at the population level.
6
New cards
**MENDELIAN POPULATION**
* a group of sexually reproducing organisms with a close degree of genetic relationship.
7
New cards
**GENE POOL**
* a mixture of the genetic units (Genes or Gametes) produced by a Mendelian population from which the next generation arises. Alleles occur in this pool.
* **EVOLUTION:** Through events such as natural selection, migration, or mutation, the gene pool changes as new alleles enter or existing alleles exit the pool. These changes are the basis for evolution.
* **EVOLUTION:** Through events such as natural selection, migration, or mutation, the gene pool changes as new alleles enter or existing alleles exit the pool. These changes are the basis for evolution.
8
New cards
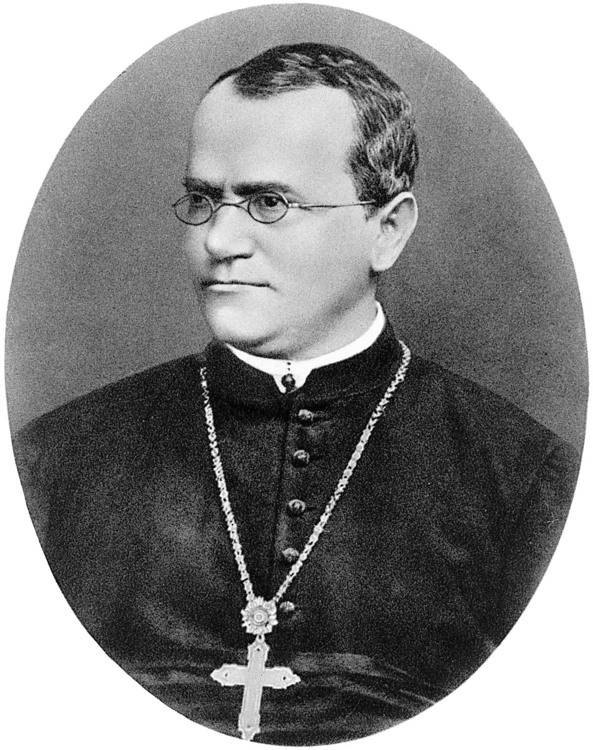

**GREGOR MENDEL**
* an Austrian monk
* He discovered important facts about heredity using garden peas.
* The father of genetics
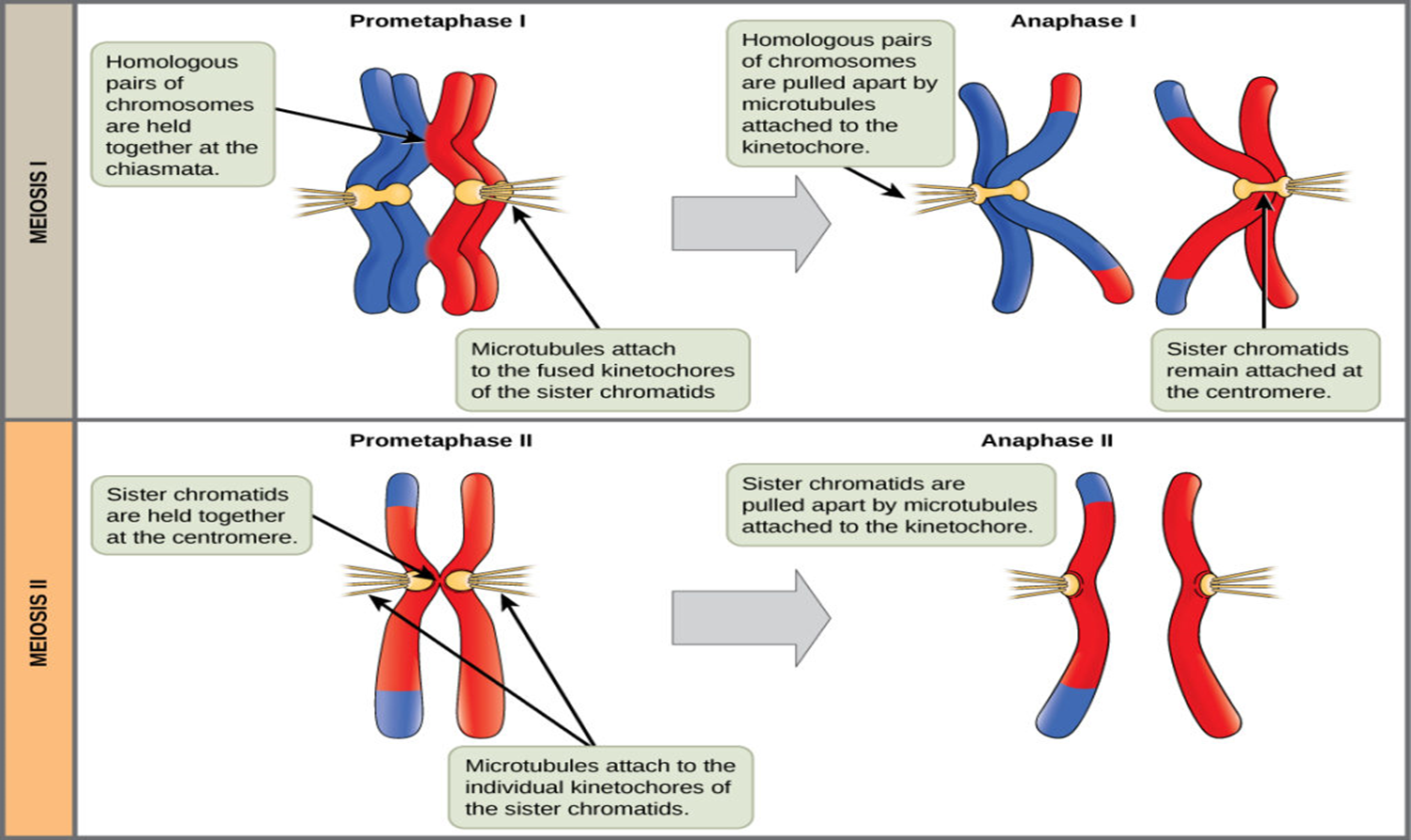
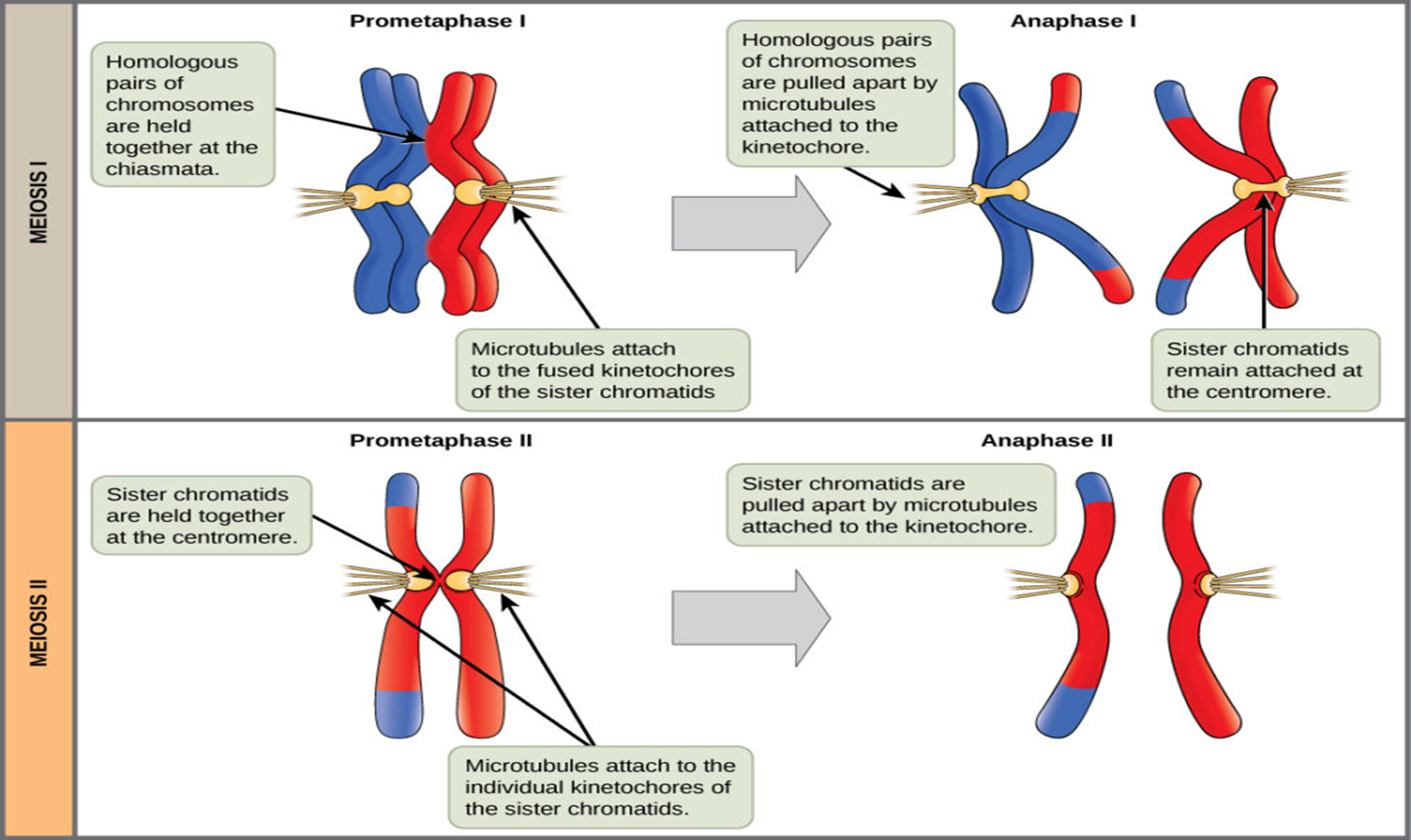
* Grew pea plants, and observed the patterns of the baby pea plants he made and how they differed from their parents - heredity
* He discovered that hereditary characteristics were determined by genes that are transmitted between. generations in uniform predictable manner.
* He discovered important facts about heredity using garden peas.
* The father of genetics
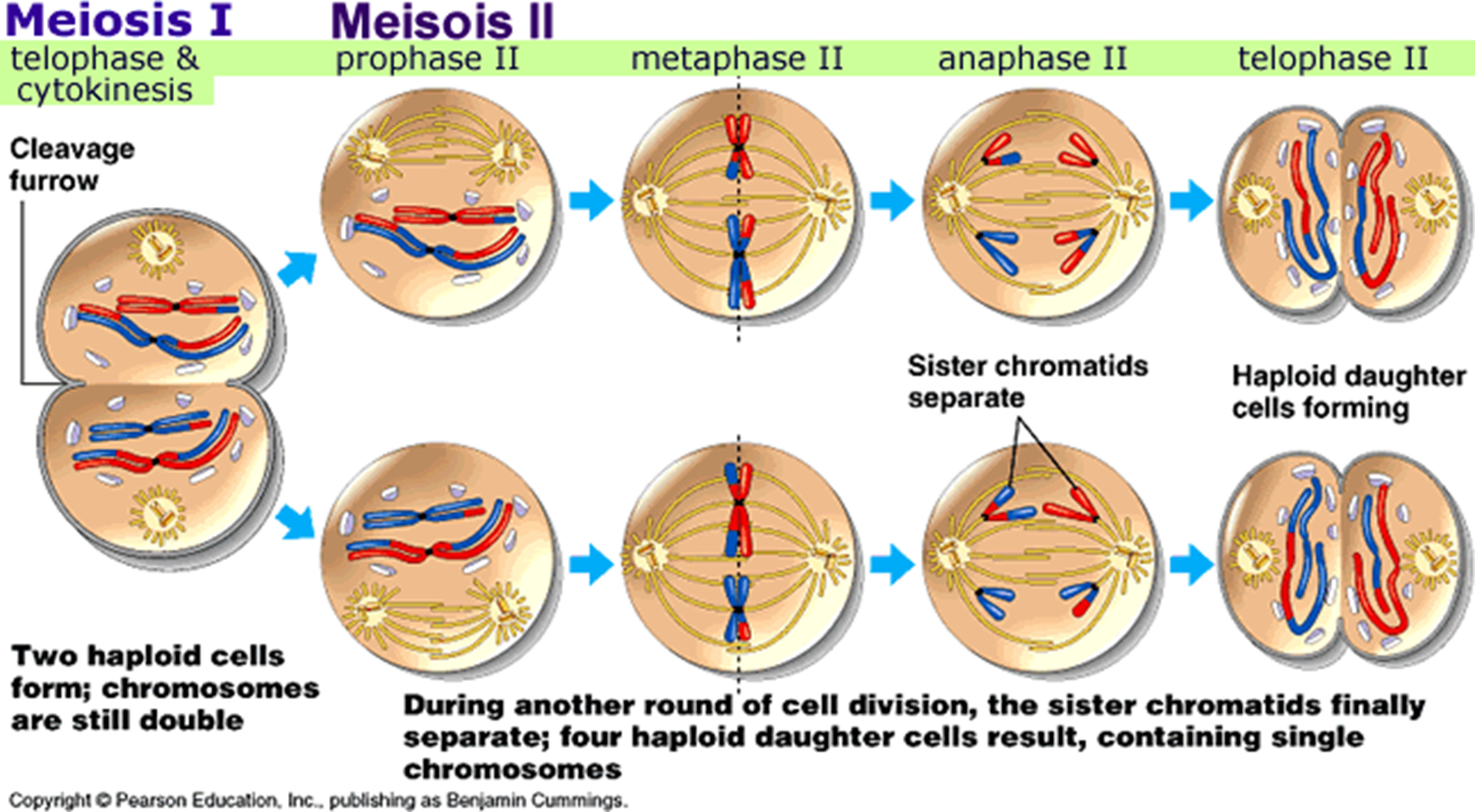
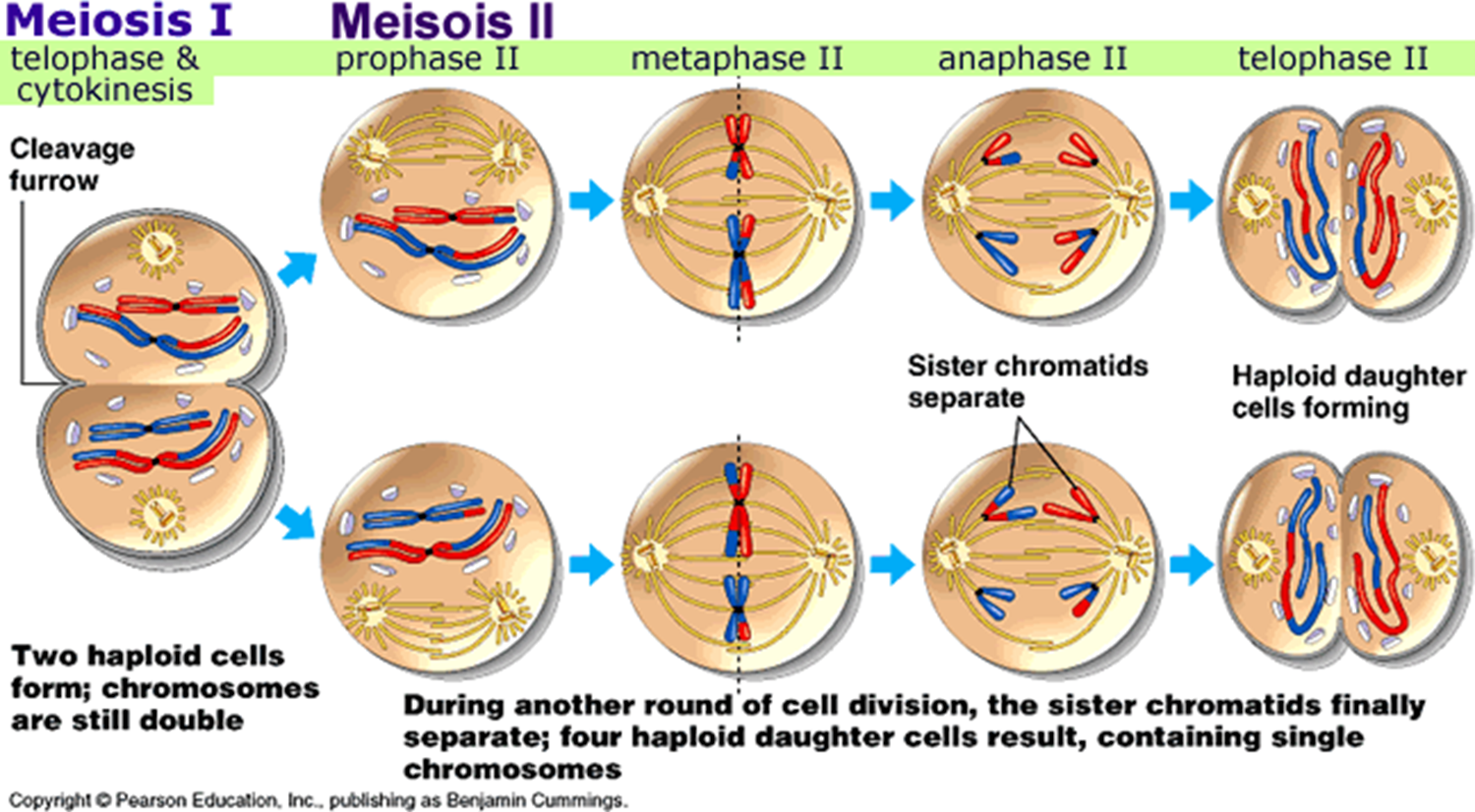
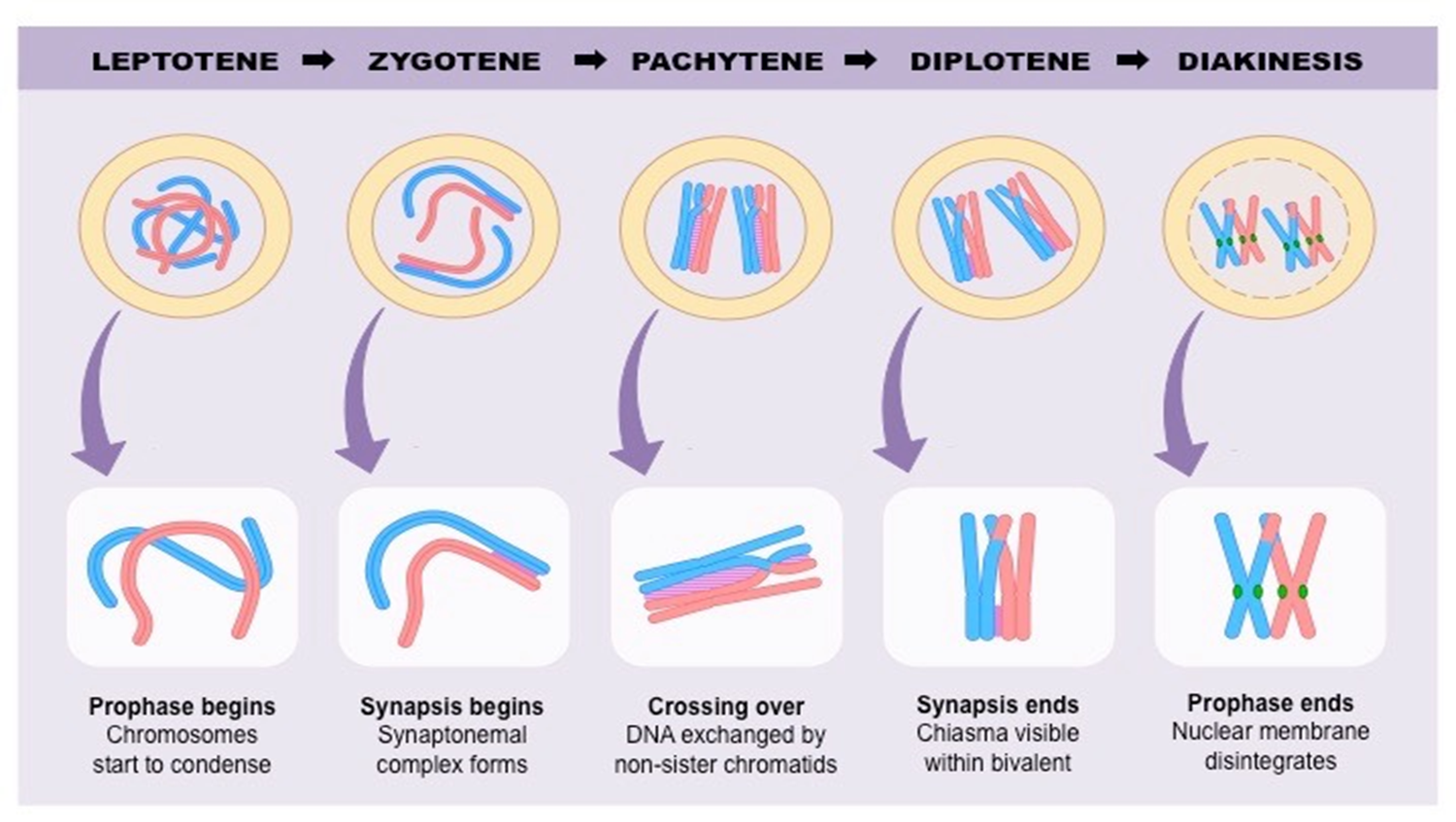
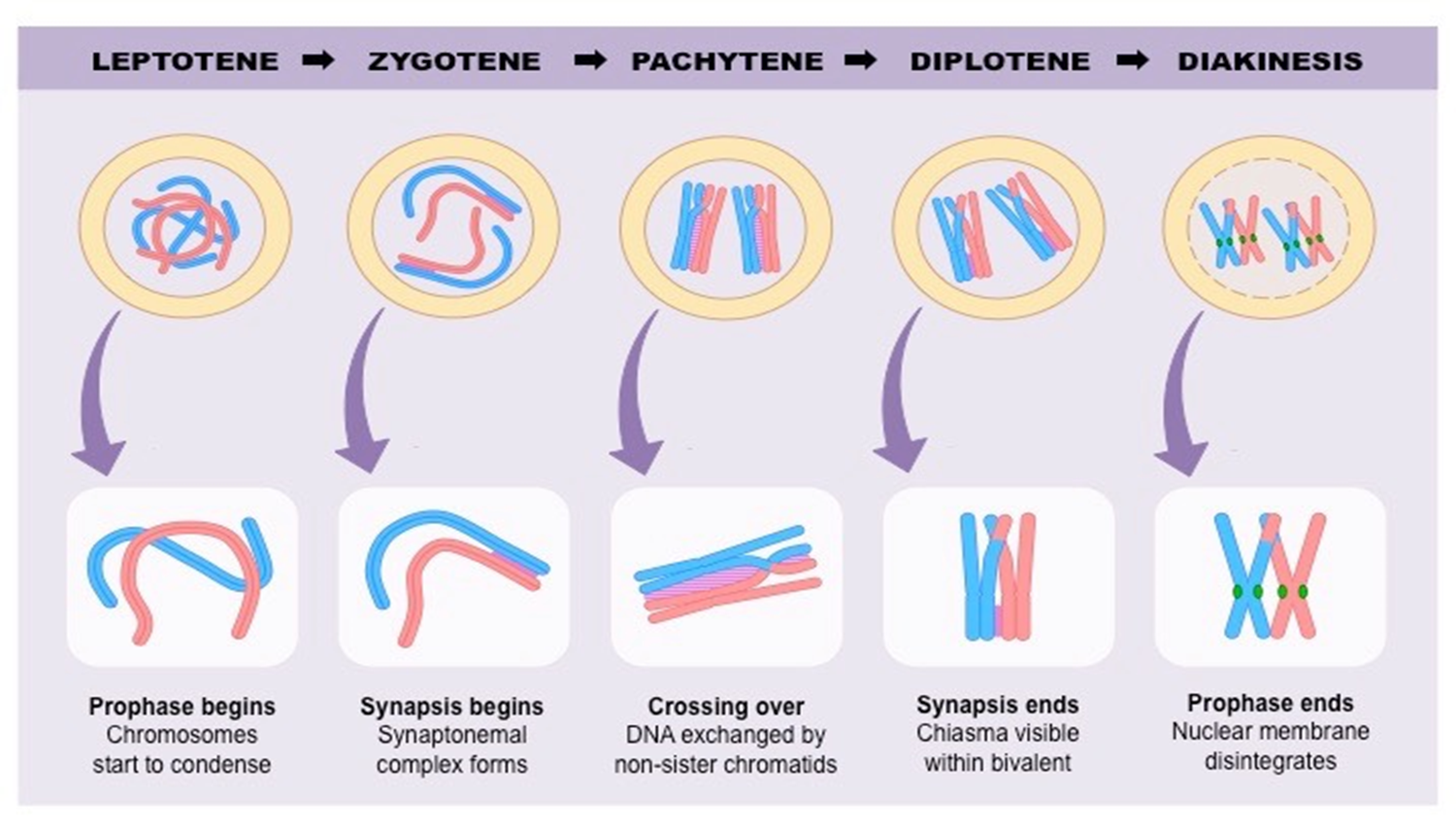
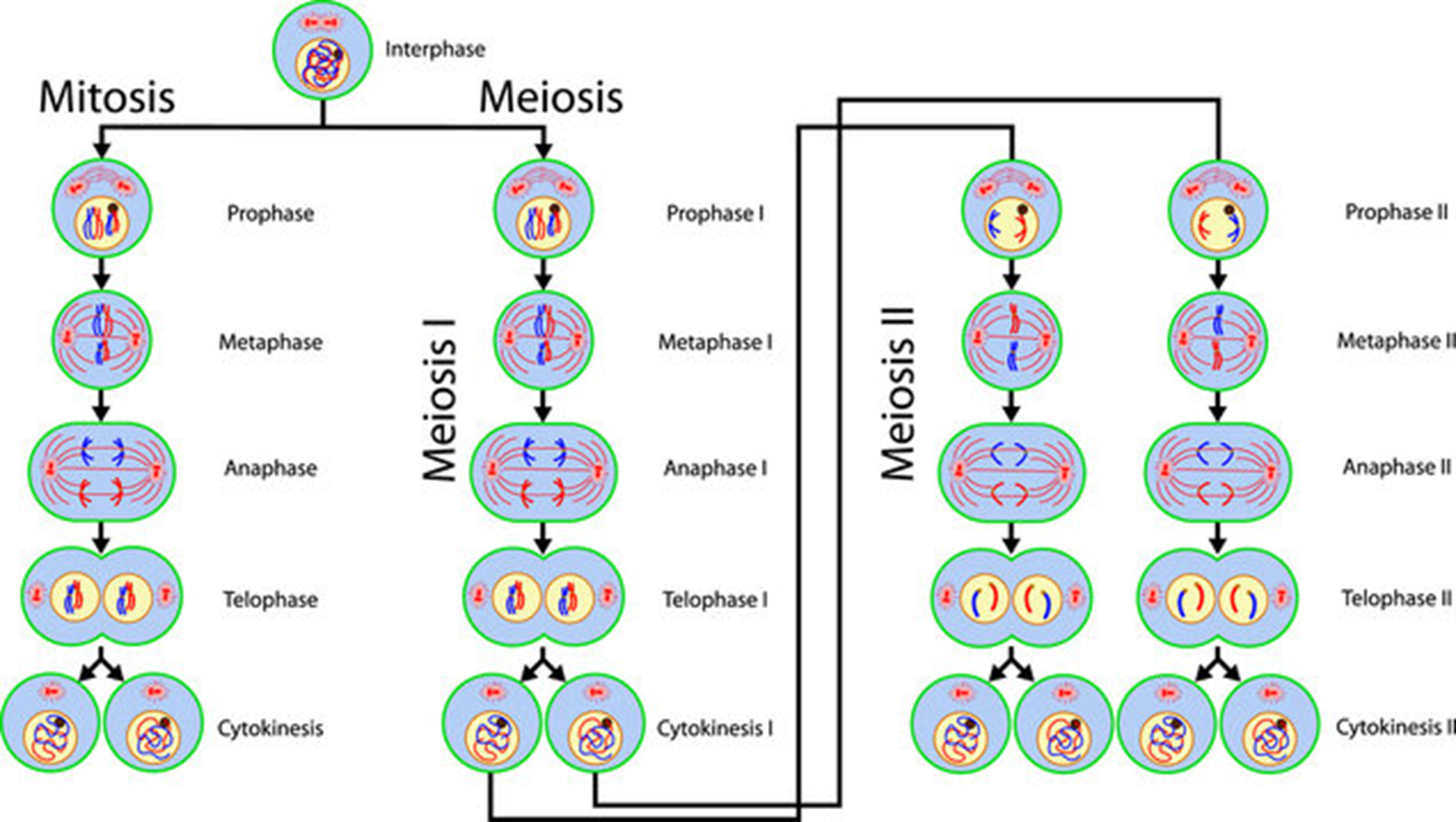
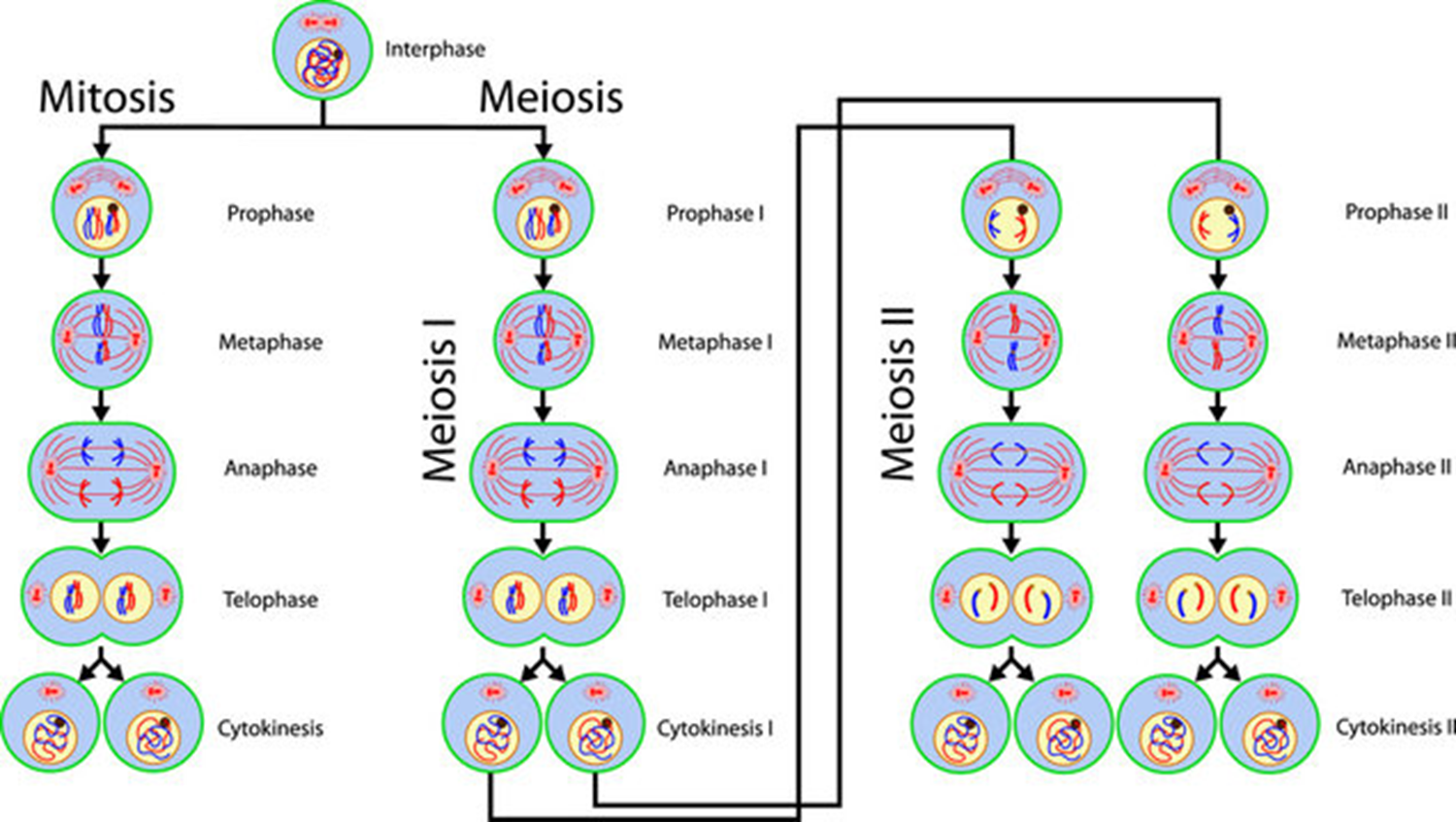
* Grew pea plants, and observed the patterns of the baby pea plants he made and how they differed from their parents - heredity
* He discovered that hereditary characteristics were determined by genes that are transmitted between. generations in uniform predictable manner.
9
New cards
1. The gene is inherited from generation to generation in such a fashion that each progeny has a physical copy of this material.
2. It provides information regarding the structure, function & other biological properties of the characteristic or trait it controls.
**TWO IMPORTANT ATTRIBUTES OF THE GENE**
10
New cards
* Development & maintenance of the individual's unique inherent pattern in dynamic interplay with the environment.
* Deals with the ability of the species to transfer the system to the other generations (primary requirement for continued existence).
* Deals with the orderly variety of patterns among living forms & their changes with time on a geological scale (constitutes accomplishment of evolution).
* Deals with similarities & differences in the patterns encountered within human species.
* Deals with the ability of the species to transfer the system to the other generations (primary requirement for continued existence).
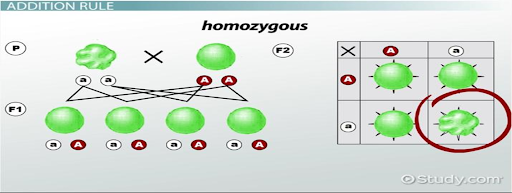
* Deals with the orderly variety of patterns among living forms & their changes with time on a geological scale (constitutes accomplishment of evolution).
* Deals with similarities & differences in the patterns encountered within human species.
**SCOPE OF GENETICS**
11
New cards
1. Field of Medicine
2. Agriculture/Food Production/Industry
3. Legal Application
4. Genetic Counseling
5. Genetic Code
**APPLICATION OF GENETICS**
12
New cards
**MEDICINE**
* Diseases & abnormalities that have genetic bases have been identified & appropriate preventive measures prescribed.
13
New cards
**GENE THERAPY**
Employed to prevent heritable diseases such as hemophilia, diabetes, hemoglobin abnormalities, some forms of mental disorders, blindness & deafness.
14
New cards
**AGRICULTURE**
* Plant, animal & microbial improvement.
* High yielding & pest resistant varieties of rice, corn, wheat.
* Advances in meat production of cattle, swine, poultry.
* Higher efficiency in fermentation that have increased productivity in fermented food & food products.
* High yielding & pest resistant varieties of rice, corn, wheat.
* Advances in meat production of cattle, swine, poultry.
* Higher efficiency in fermentation that have increased productivity in fermented food & food products.
15
New cards
**LEGAL APPLICATION**
* Genetics has helped solve problems of disputed parentage in settling child support, estate claims or even baby mix up in hospitals.
* Traits commonly used are DNA "fingerprints" or profiles, ABO & MN blood types & some enzyme markers.
* DNA profiles of suspects have been found to be an accurate tool in identifying criminals.
* Traits commonly used are DNA "fingerprints" or profiles, ABO & MN blood types & some enzyme markers.
* DNA profiles of suspects have been found to be an accurate tool in identifying criminals.
16
New cards
17
New cards
18
New cards
19
New cards
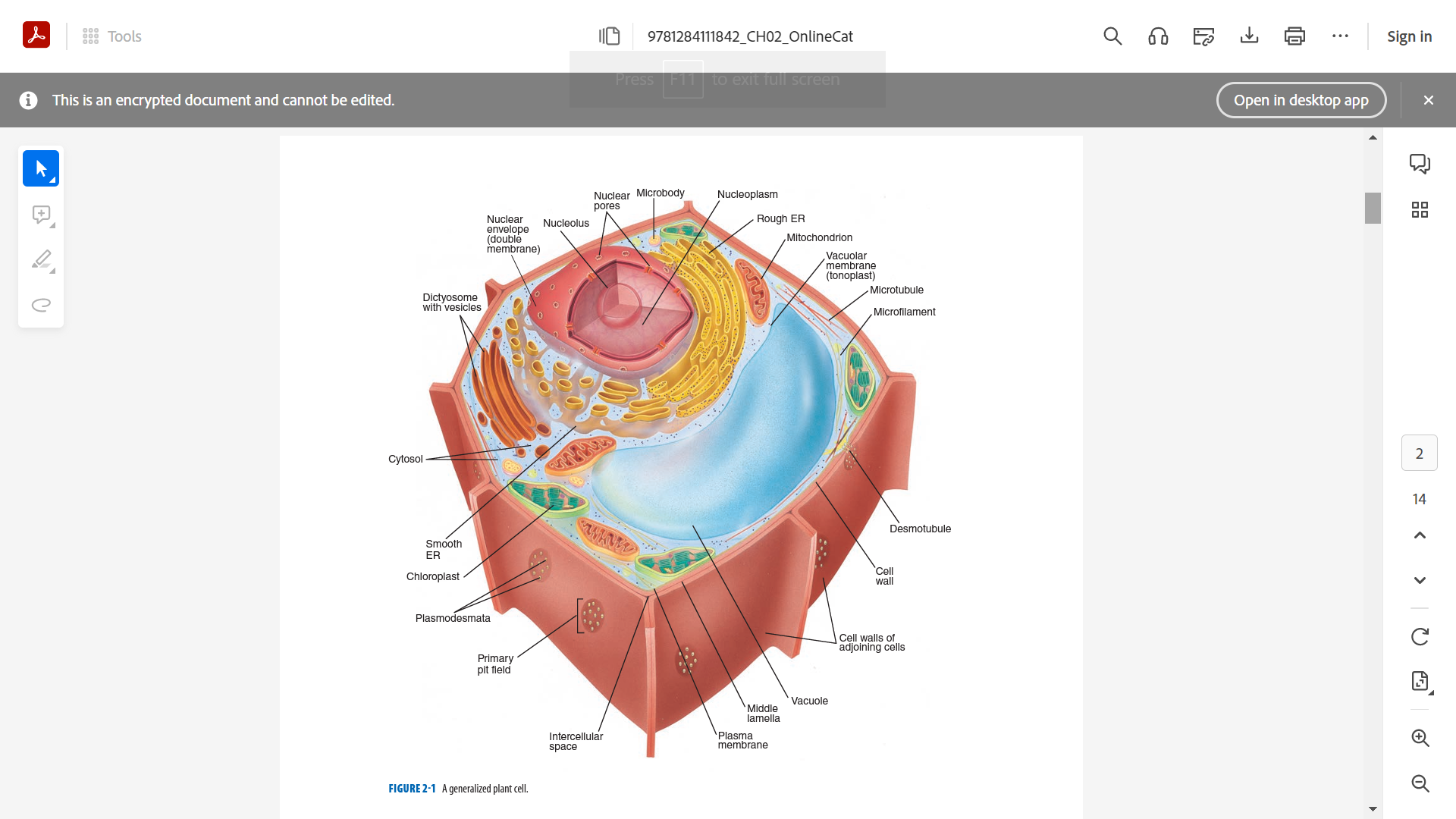
**CELL**
basic unit of life.
20
New cards
330 years ago
When did the study of cells started?
21
New cards
microscope
the cell became visible because of this
22
New cards
* 1665: **Robert Hooke**
* English Scientist and Microscopist.
* Observed sliver of cork.
* Saw a row of empty boxes.
* Discovered and coined the term "cell".
* Observed sliver of cork.
* Saw a row of empty boxes.
* Discovered and coined the term "cell".
23
New cards
1665: **Robert Hooke**
fatherof cytology
24
New cards
1670: **Antoine van Leeuwenhoek**
* Dutch Biologist and Microscopist.
* Described cells (bacteria) in a drop of pond water using a microscope.
* Father of Microbiology.
* Studied the structure of plants.
* Described cells (bacteria) in a drop of pond water using a microscope.
* Father of Microbiology.
* Studied the structure of plants.
25
New cards
1831: **Robert Brown**
* English Botanist
* Discovered the nucleus in plant cells
* Discovered the nucleus in plant cells
26
New cards
1838: **Matthias Jakob Scleiden**
* German Botanist
* Described that the cell is the basic building block of all plants matter
* Described that the cell is the basic building block of all plants matter
27
New cards
1839: **Theodor Schwann**
* German Biologist
* Same idea as Scleiden
* Stated that "cell is the basic unit of life"
* Same idea as Scleiden
* Stated that "cell is the basic unit of life"
28
New cards
1851: **Hugo von Mohl**
* German Botanist
* First person to use the word "protoplasm" (living matter of the cell)
* First person to use the word "protoplasm" (living matter of the cell)
29
New cards
1855: **Rudolf Virchow**
* German Physiologist, physician, pathologist and anthropologist)
* Demonstrated the cell theory
* Demonstrated the cell theory
30
New cards
1855: **Louis Pasteur**
* French Chemist
* Founder of medical microbiology For the causes and prevention of diseases
* Founder of medical microbiology For the causes and prevention of diseases
31
New cards
1855: **Jan Evangelista Purkinje**
* Czech Anatomist and Physiologist
* Named the cell contents as protoplasm
* Named the cell contents as protoplasm
32
New cards
* All living things are made of cells (Theodor Schwann & Matthias Schleiden, 1839).
* Smallest living unit of structure and function of all organisms is the cell.
* All cells arise from pre-existing cells (Rudolf Virchow, 50 years later).
* Smallest living unit of structure and function of all organisms is the cell.
* All cells arise from pre-existing cells (Rudolf Virchow, 50 years later).
**PRINCIPLES OF CELL THEORY**
33
New cards
1. Multicellular
2. Unicellular
**CELL TYPES BASED ON THE NUMBER OF CELLS**
34
New cards
1. Prokaryotic
2. Eukaryotic
**BASIC CELL TYPES**
35
New cards
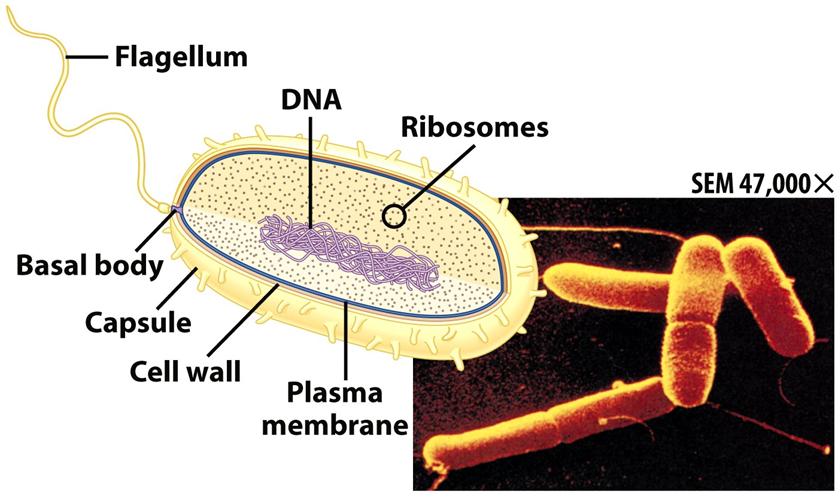
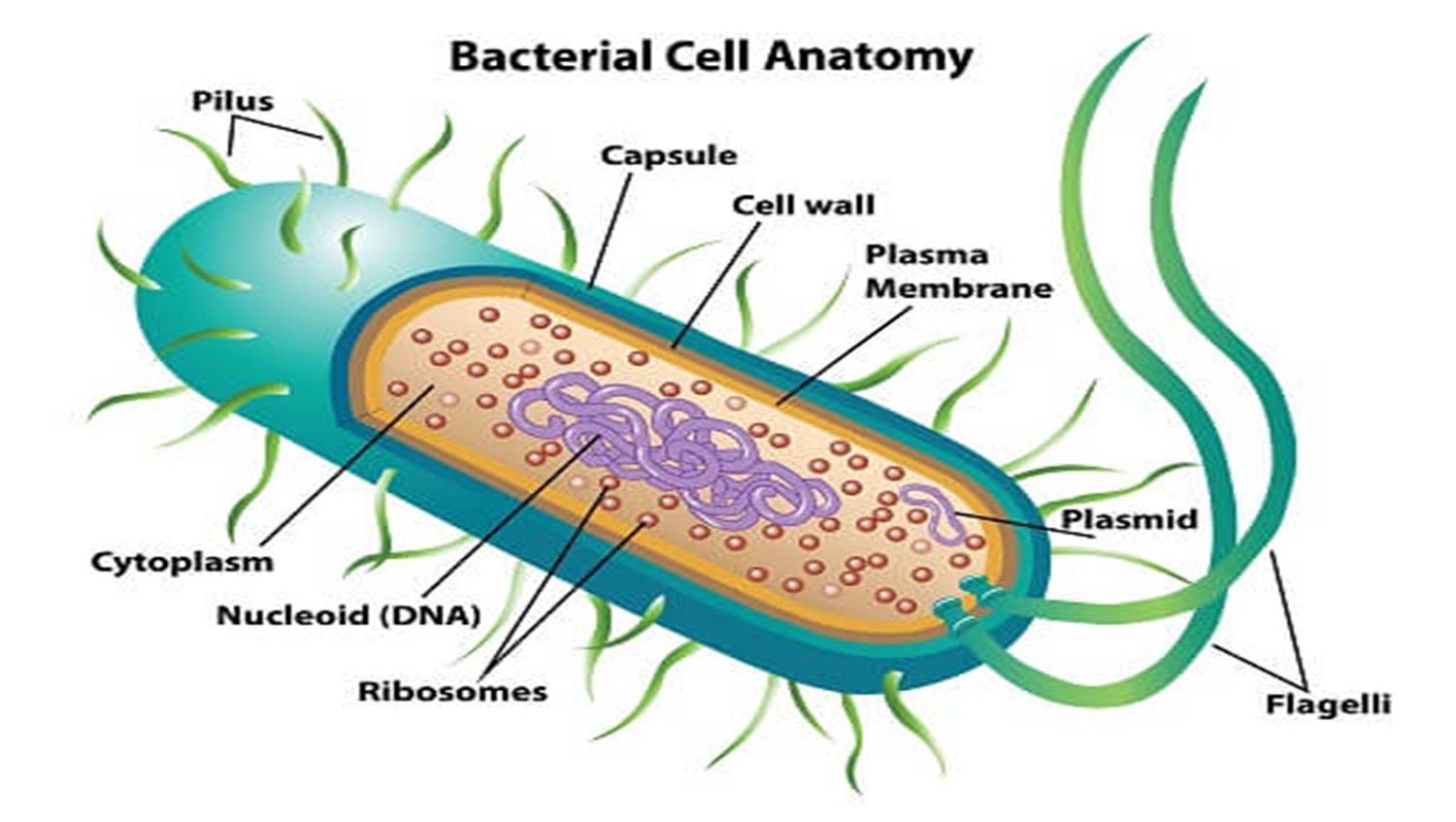
**PROKARYOTES**
* First cell type on earth
* Found only in Domain Bacteria
* bacteria
* Found also in Domain Archaeans
* archaeans
* Represent the most archaic lines of evolution
* with simpler forms
* no membrane bound nucleus
* no membrane Bound organelles
* __nucleoid__ - region of DNA concentration
* Found only in Domain Bacteria
* bacteria
* Found also in Domain Archaeans
* archaeans
* Represent the most archaic lines of evolution
* with simpler forms
* no membrane bound nucleus
* no membrane Bound organelles
* __nucleoid__ - region of DNA concentration
36
New cards
* **BACTERIA**
* serve as decomposers
* agents of fermentation (wine and beer)
* play a role in our digestive system
* involve in many nutrient cycles
* agents of fermentation (wine and beer)
* play a role in our digestive system
* involve in many nutrient cycles
37
New cards
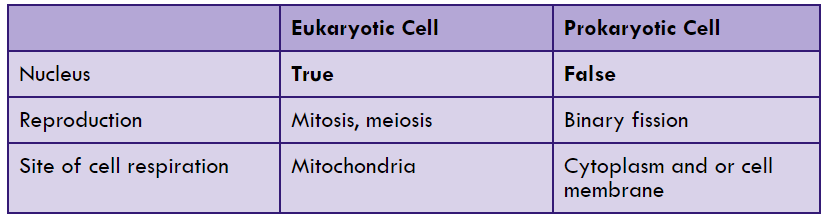
**EUKARYOTES**
* found in plants, animals, fungi, protists
* more complex
* with true-membrane-bounded nucleus
* with many organelles that allow them to be more diverse and complex, both morphologically and physiologically
* more complex
* with true-membrane-bounded nucleus
* with many organelles that allow them to be more diverse and complex, both morphologically and physiologically
38
New cards
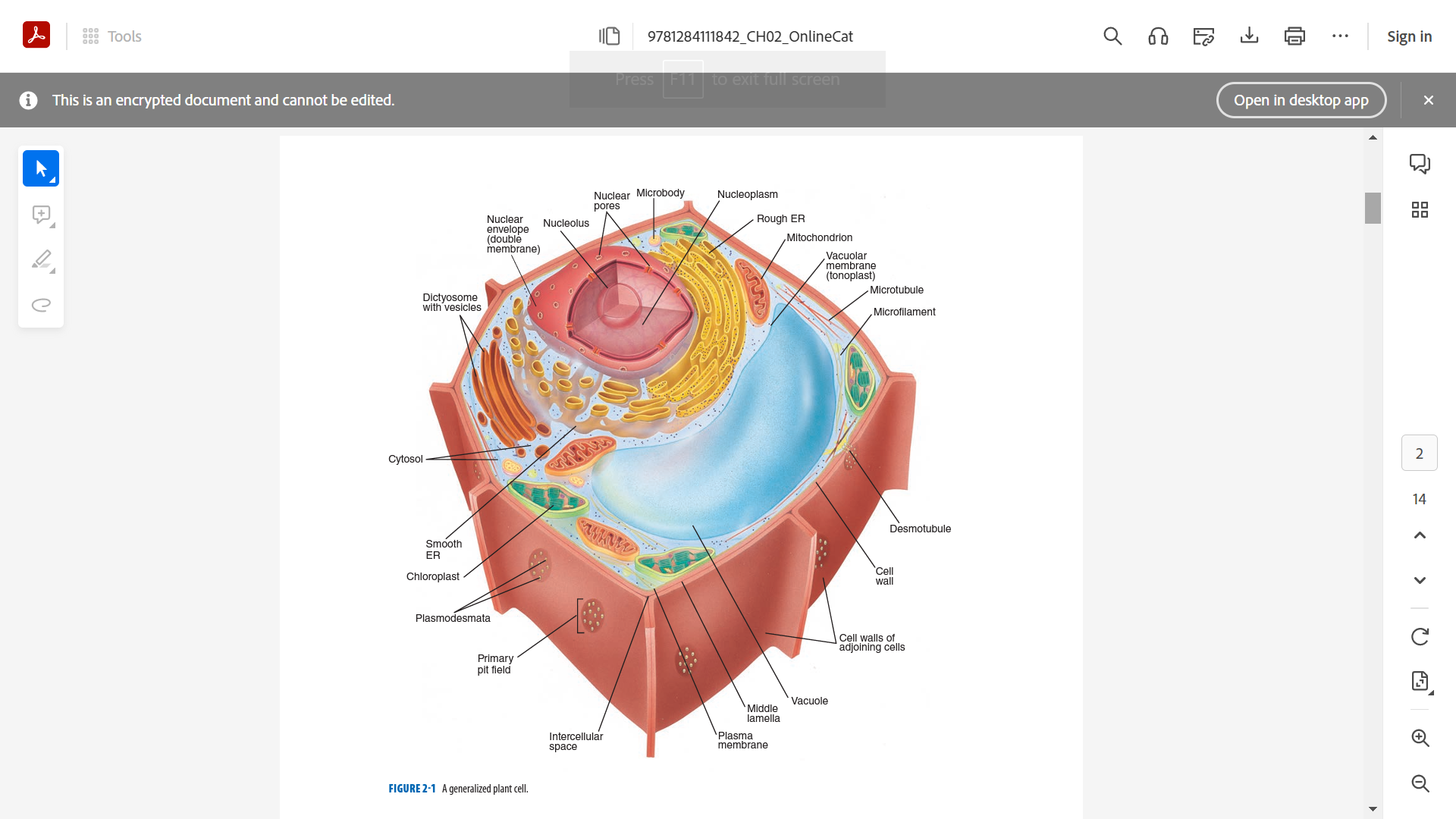
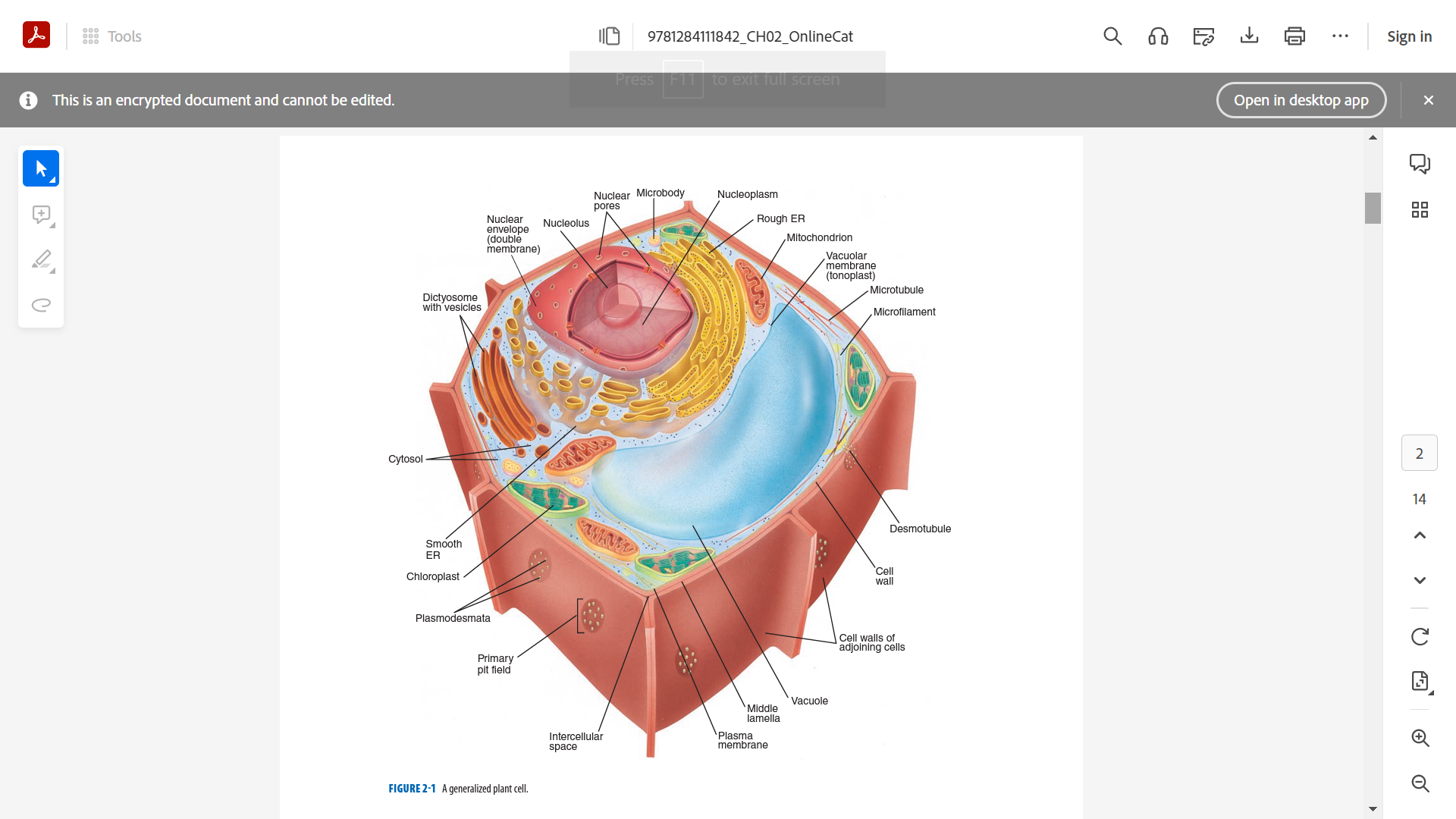
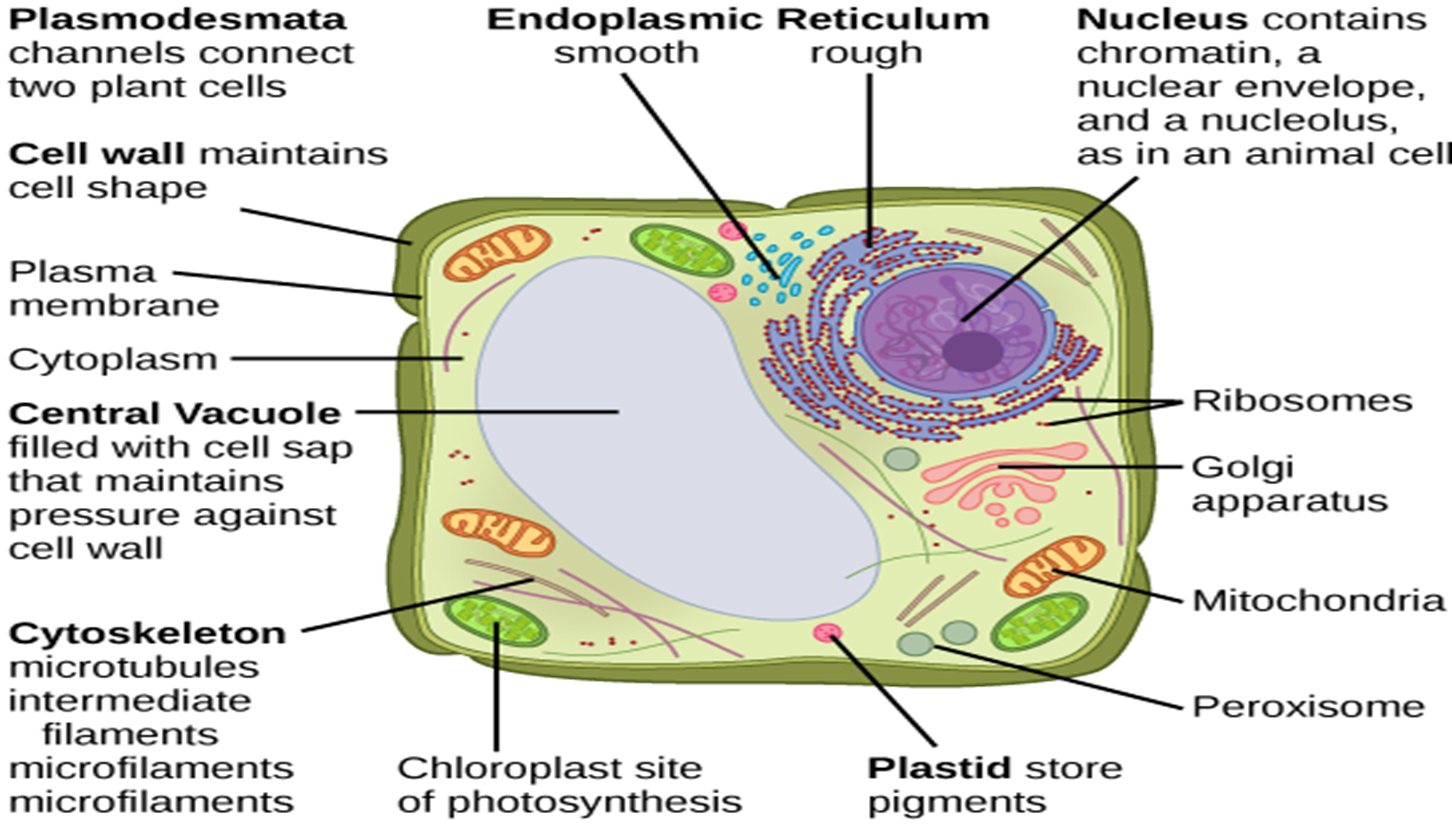
**CELL WALL**
* provides structure, support and protection
* surrounds the plasma membrane
* composed of 60% cellulose
* three layers: middle lamella, primary cell wall and secondary cell wall
* surrounds the plasma membrane
* composed of 60% cellulose
* three layers: middle lamella, primary cell wall and secondary cell wall
39
New cards
1. middle lamella,
2. primary cell wall
3. secondary cell wall
three layers of the cell wall
40
New cards
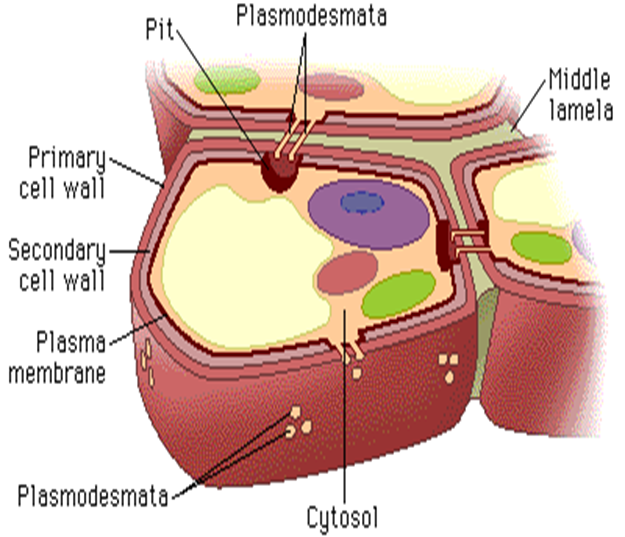
**MIDDLE LAMELA**
* cements cell walls of two adjoining cells together.
* pectin layer between cells.
* pectin layer between cells.
41
New cards
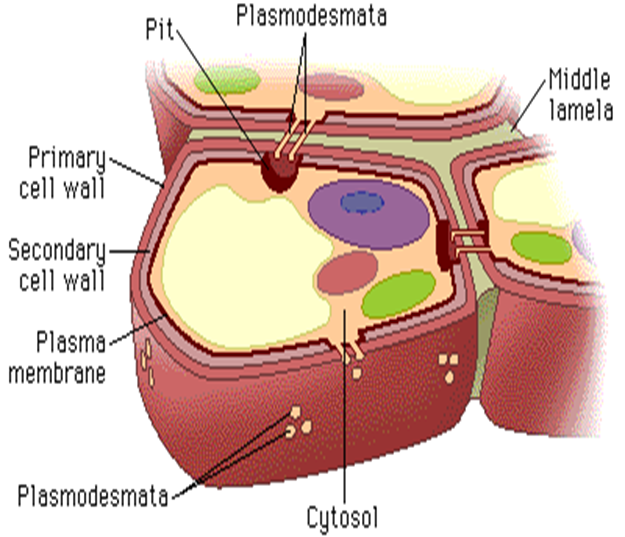
**PRIMARY CELL WALL**
* relatively thin and flexible and extensible layer
* composed of cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin
* common in young cells and cells in actively growing areas
* composed of cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin
* common in young cells and cells in actively growing areas
42
New cards
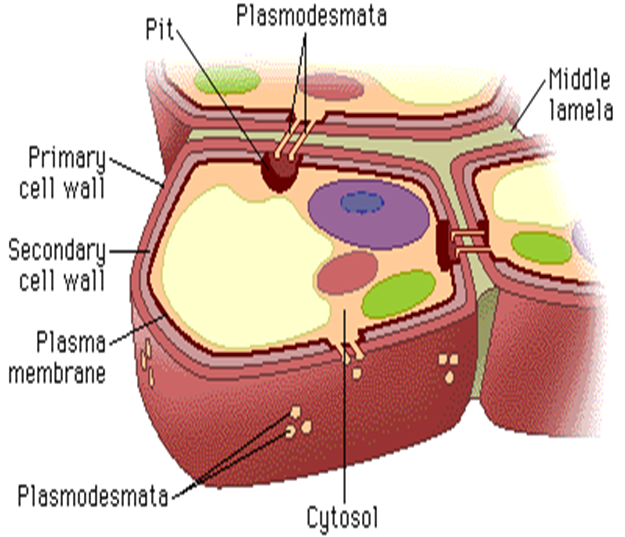
**SECONDARY CELL WALL**
* thick cell layer
* formed inside the primary cell wall
* more rigid than the primary cell wall
* with 25% lignin
* formed inside the primary cell wall
* more rigid than the primary cell wall
* with 25% lignin
43
New cards
**PLASMA MEMBRANE/CELL MEMBRANE**
* Plasmalemma
* Covers the surface of the protoplasm
* Selectively permeable
* Regulates the passage of substances in and out of the cell
* Covers the surface of the protoplasm
* Selectively permeable
* Regulates the passage of substances in and out of the cell
44
New cards
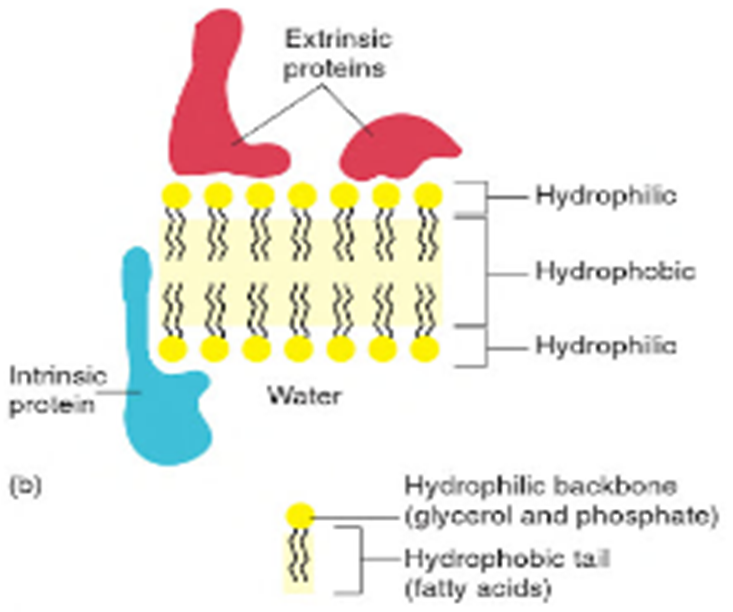
* Lipid bilaver
* Phospholipid molecules
* Proteins
* Phospholipid molecules
* Proteins
**COMPOSITION OF MEMBRANE**
45
New cards
46
New cards
**PROTOPLASM**
* Mass of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and water within a cell.
* Everything in the cell is protoplasm except for the cell wall.
* Cytoplasm and the nucleus.
* Everything in the cell is protoplasm except for the cell wall.
* Cytoplasm and the nucleus.
47
New cards
Protoplast
the protoplasm of a single cell.
48
New cards
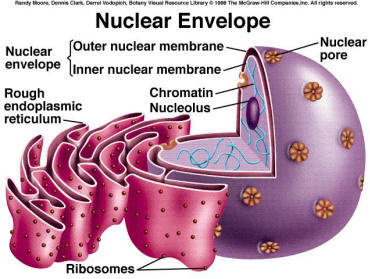
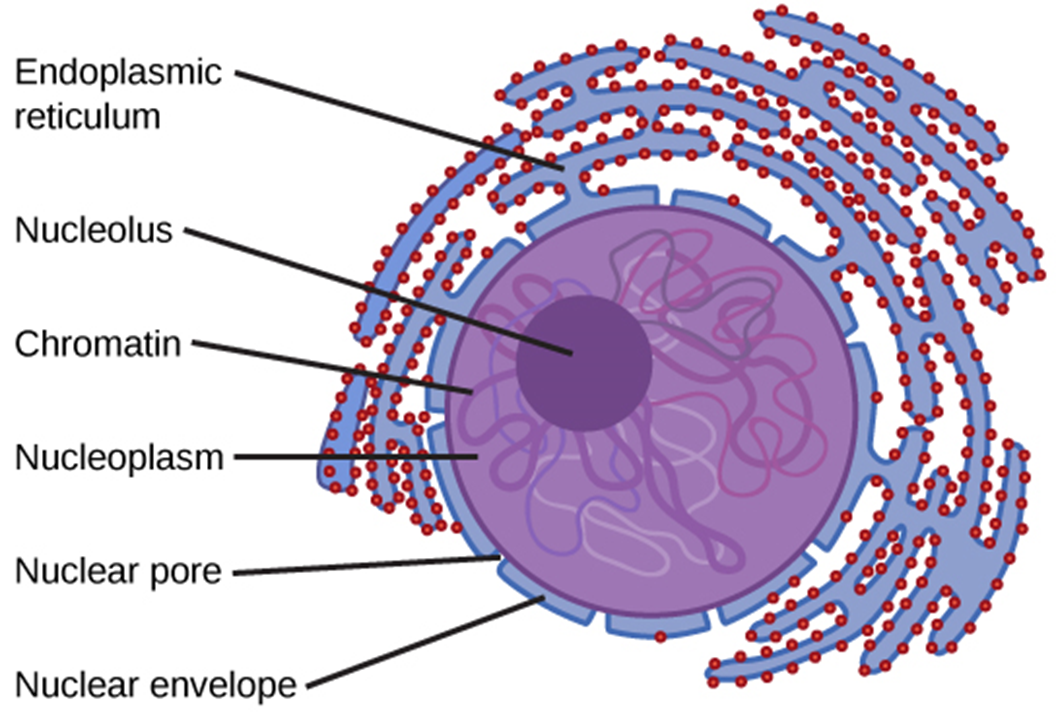
**NUCLEUS**
* Control center of the cell
* Permanent storage place of DNA
* Protein synthesis, cell division, growth and differentiation
* Permanent storage place of DNA
* Protein synthesis, cell division, growth and differentiation
49
New cards
**CENTRAL VACUOLE**
* with membrane or tonoplast
* the largest organelle
* stores both nutrient reserves, water products and wastes (membrane bound storage sac)
* provide structure and support for the growing plant
* the largest organelle
* stores both nutrient reserves, water products and wastes (membrane bound storage sac)
* provide structure and support for the growing plant
50
New cards
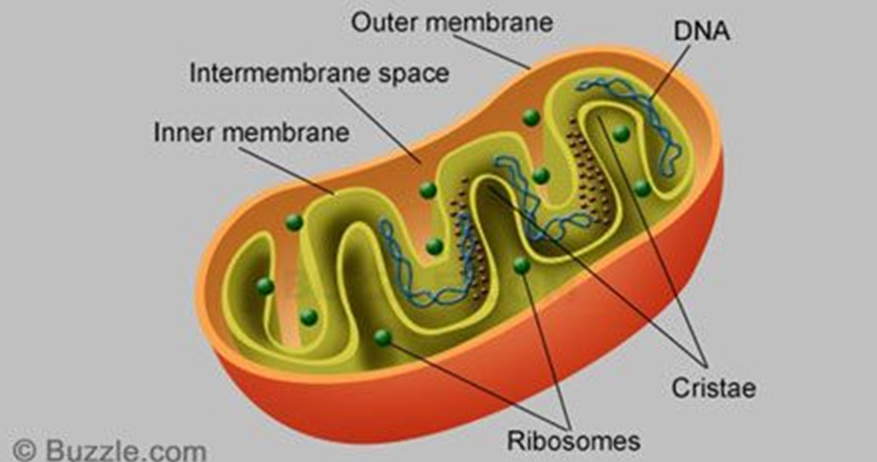
**MITOCHONDRIA**
* Powerhouse of the cell
* Break down fuel molecules (cellular respiration - glucose and fatty acids)
* Release energy (ATP)
* with own ribosomes (for protein synthesis) and DNA (for proteins and enzymes production)
* Break down fuel molecules (cellular respiration - glucose and fatty acids)
* Release energy (ATP)
* with own ribosomes (for protein synthesis) and DNA (for proteins and enzymes production)
51
New cards
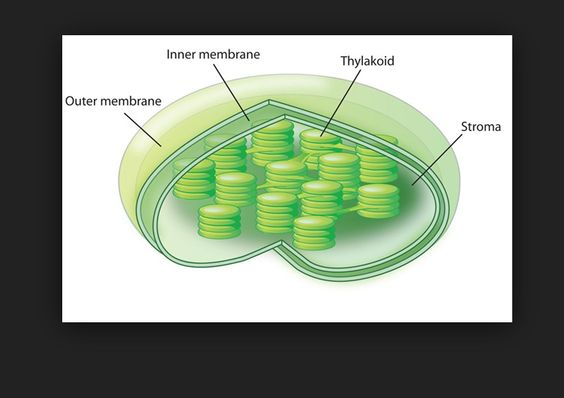
**PLASTIDS**
chloroplast
52
New cards
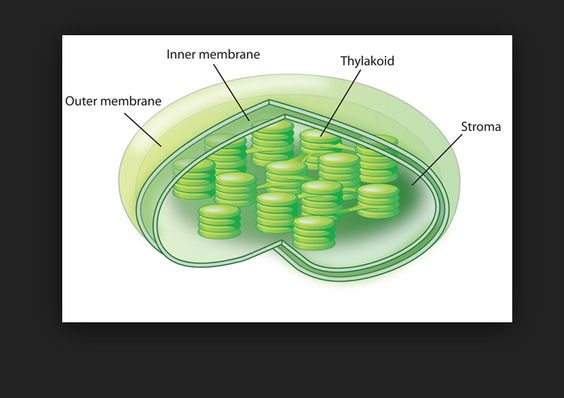
**CHLOROPLAST**
* green due to chlorophyll bodies
* larger than mitochondria
* cell may contain 50 chloroplasts
* larger than mitochondria
* cell may contain 50 chloroplasts
53
New cards
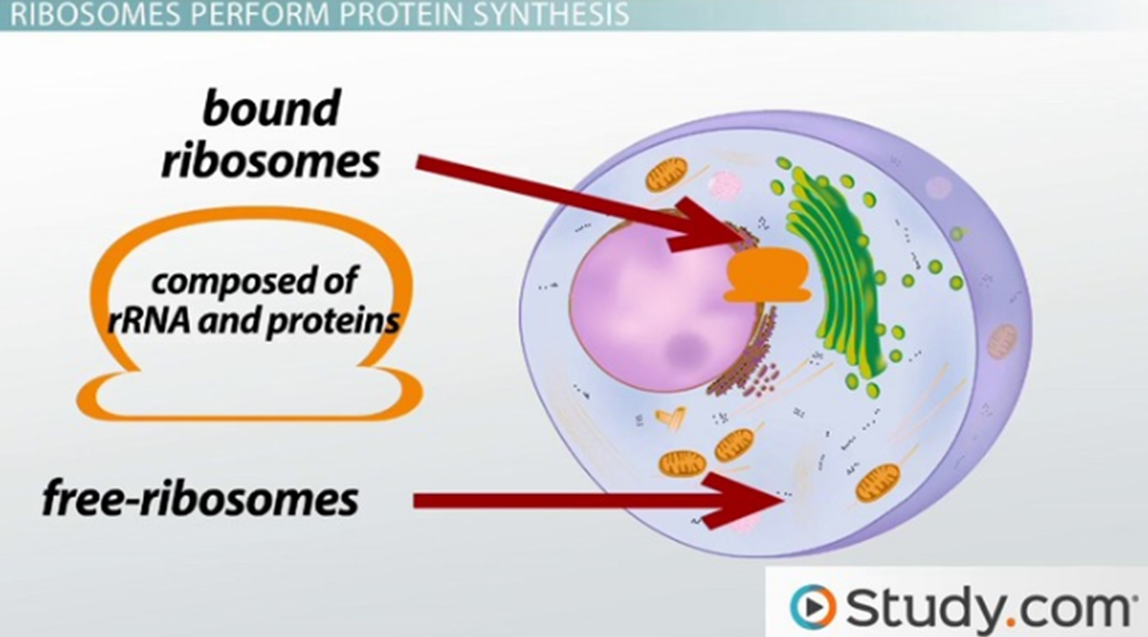
\
**RIBOSOMES**
54
New cards
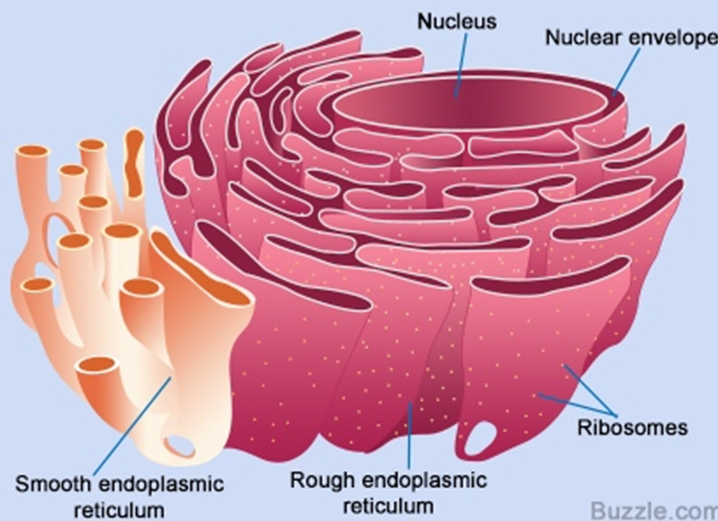
**ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER)**
* as manufacturing and packaging system
* rough ER (protein synthesis)
* smooth ER (for carbohydrate and lipid synthesis)
* rough ER (protein synthesis)
* smooth ER (for carbohydrate and lipid synthesis)
55
New cards
**DICTYOSOMES/GOLGI APPARATUS**
* Packaging and shipping station of cell.
* Two-sided.
* With membrane-bound vesicles.
* Cisternae
* Membrane bound vesicles (proteins, lipids and other substances)
* Two-sided.
* With membrane-bound vesicles.
* Cisternae
* Membrane bound vesicles (proteins, lipids and other substances)
56
New cards
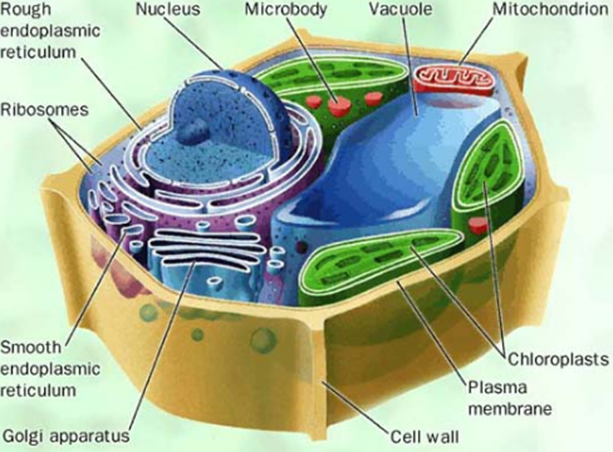
**MICROBODIES**
* smallest membrane-bound organelle.
* associated with ER, chloroplasts and mitochondria.
* two kinds: peroxisomes and glyoxysomes
* associated with ER, chloroplasts and mitochondria.
* two kinds: peroxisomes and glyoxysomes
57
New cards
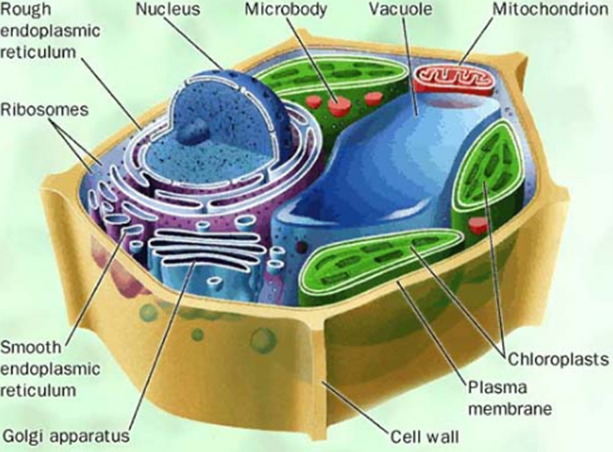
**PEROXISOMES**
* occur primarily in leaves
* break down some of the toxic products of cell
* break down some of the toxic products of cell
58
New cards
**GLYOXYSOMES**
* house the glyoxylic acid cycle
59
New cards
**CYTOSOL**
* the semi-fluid matrix between organelles
* intracellular fluid or the internal fluid of the cell.
* the main component is water
* large part of cell metabolism occurs here
\
* intracellular fluid or the internal fluid of the cell.
* the main component is water
* large part of cell metabolism occurs here
\
60
New cards
**MICROTUBULES**
* fibrous, hollow rods
* help support and shape the cell
* serve as a transportation function
* one of the cytoskeletons (filaments) of the cell
* help support and shape the cell
* serve as a transportation function
* one of the cytoskeletons (filaments) of the cell
61
New cards
**MICROFILAMENTS**
* thinnest filaments.
* help support the cell.
* function in cellular movement.
* also known as actin filaments.
* one of the cytoskeletons of the cell.
* help support the cell.
* function in cellular movement.
* also known as actin filaments.
* one of the cytoskeletons of the cell.
62
New cards
**PLASMODESMATA**
* bridges between two plant cells.
* allows molecules and substances to move back and forth.
* allows molecules and substances to move back and forth.
63
New cards
**GENES**
* a unit of heredity.
* are carried on DNA
* are carried on DNA
64
New cards
**DNA**
contained within __chromosomes__ as __chromatin__.
65
New cards
66
New cards
**CELL CYCLE (DIVISION)**
* This is the series of events that takes place in a cell leading to its division and duplication that produces 2 daughter cells.
67
New cards
1. INTERPHASE
2. M PHASE
**2 MAIN PHASES OF CELL CYCLE**
68
New cards
**INTERPHASE**
prepares cell for division.
69
New cards
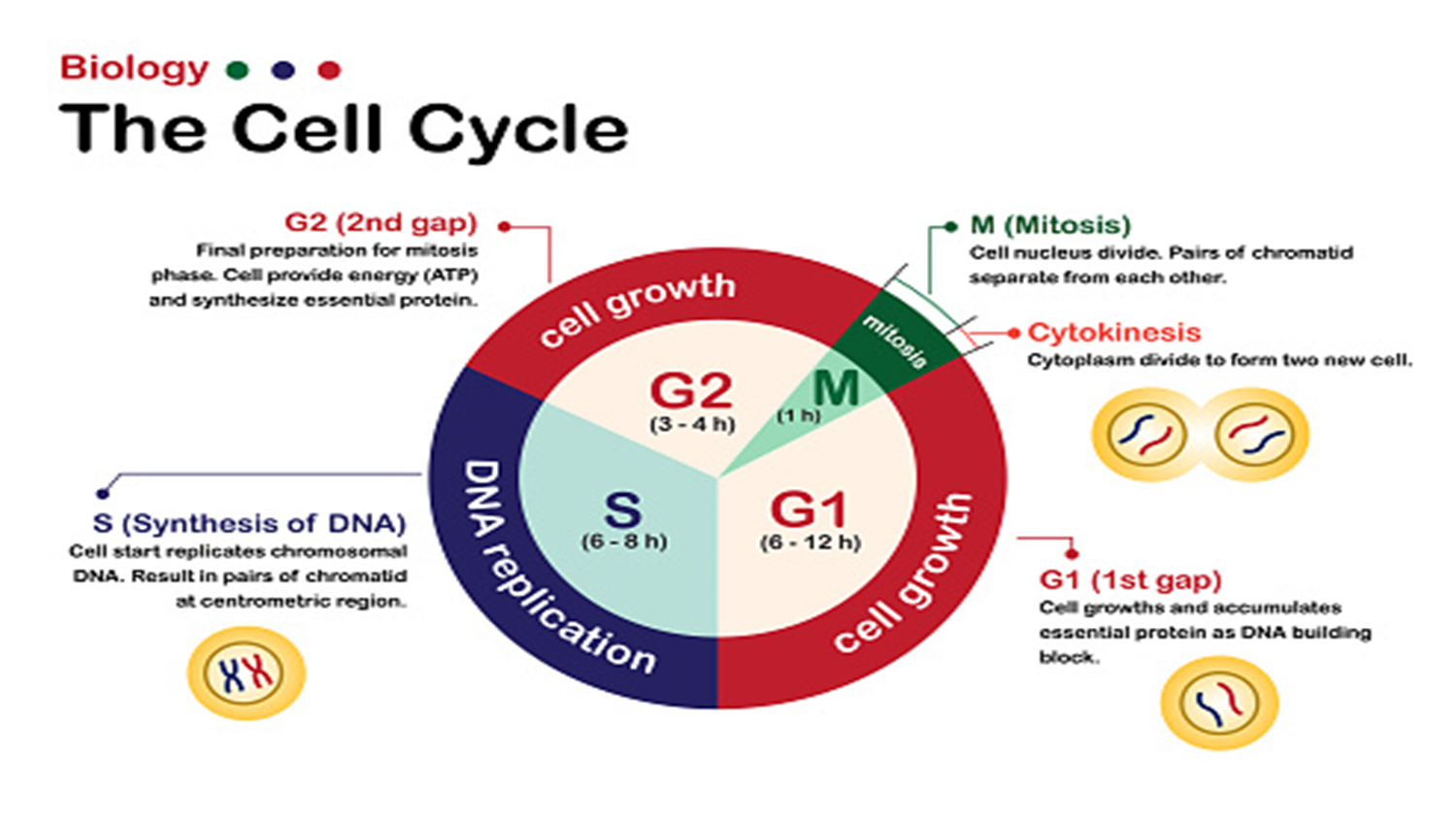
**M PHASE**
where division actually takes place.
70
New cards
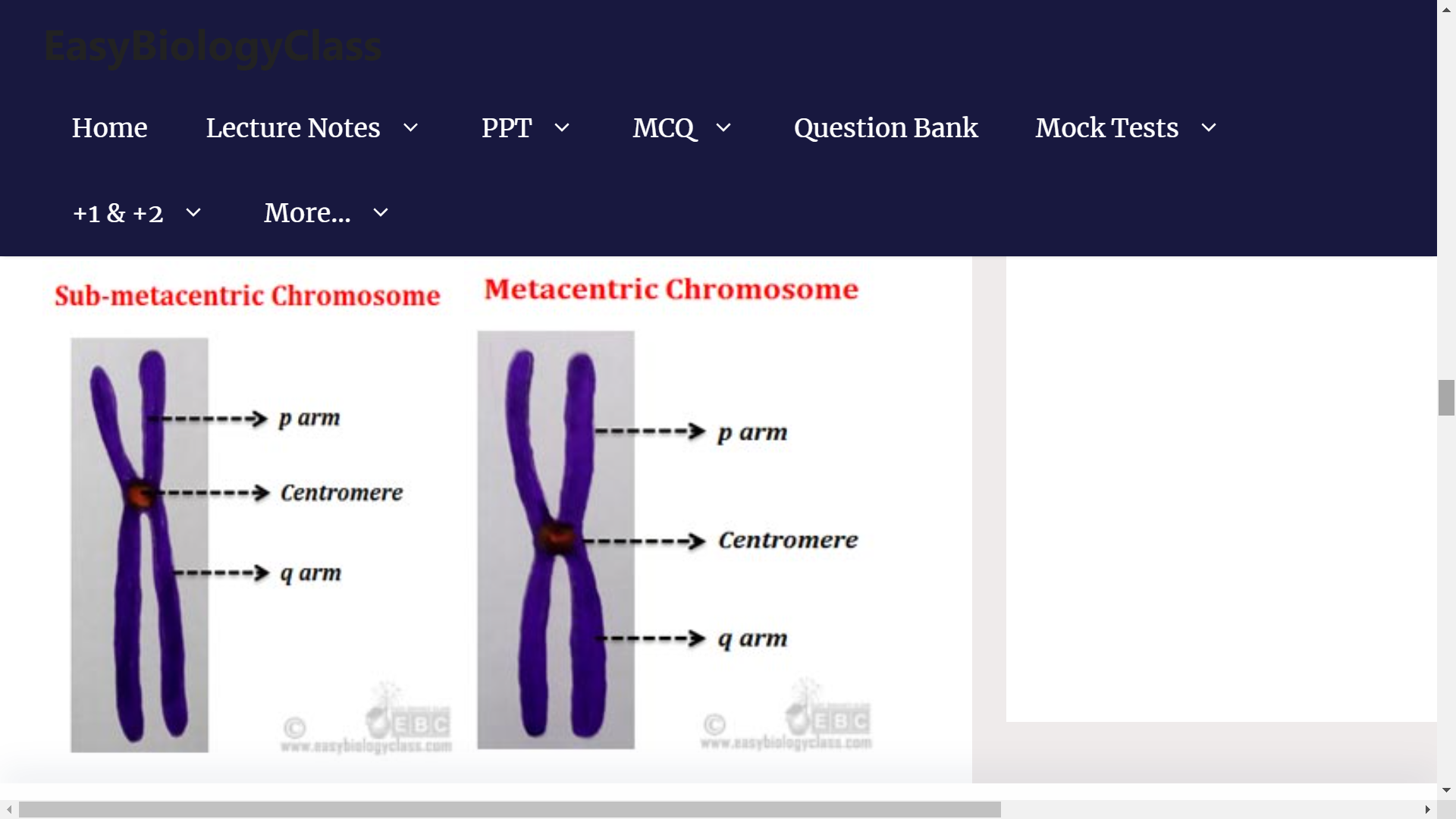
1. TELOMERE
2. CENTROMERES
**CHROMOSOME PARTS:**
71
New cards
**TELOMERE**
* chromosome tips
* Repeats
* Act as sort of biological clock
* Being whittled down at each Mitosis.
* Repeats
* Act as sort of biological clock
* Being whittled down at each Mitosis.
72
New cards
**CENTROMERES**
* middle
* Highly condensed
* Also repetitive sequence
* Region where spindle fibers attach
* Pulling chromatids apart during Mitosis
* Highly condensed
* Also repetitive sequence
* Region where spindle fibers attach
* Pulling chromatids apart during Mitosis
73
New cards
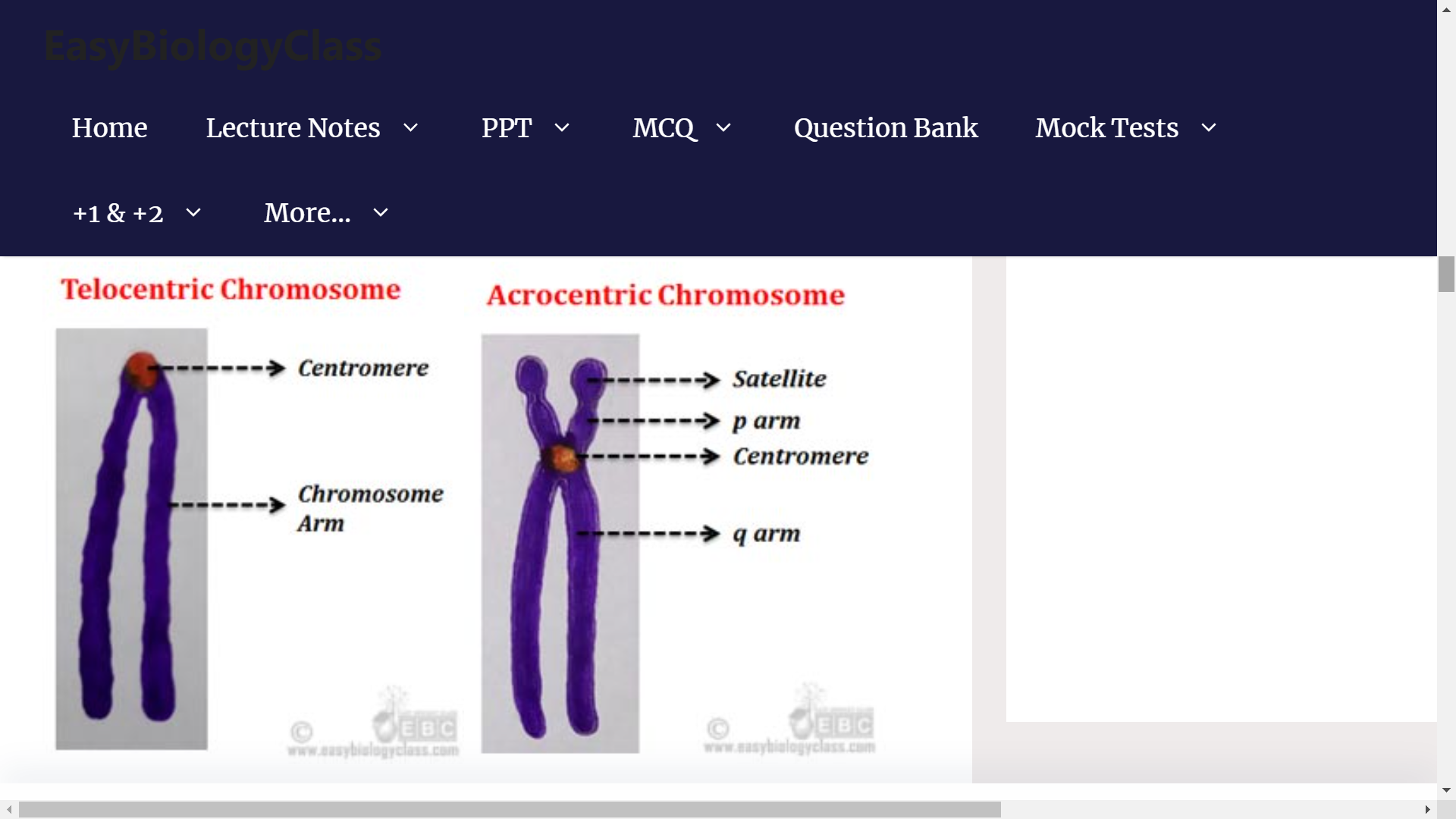
CLASSIFICATION OF CHROMOSOME
74
New cards
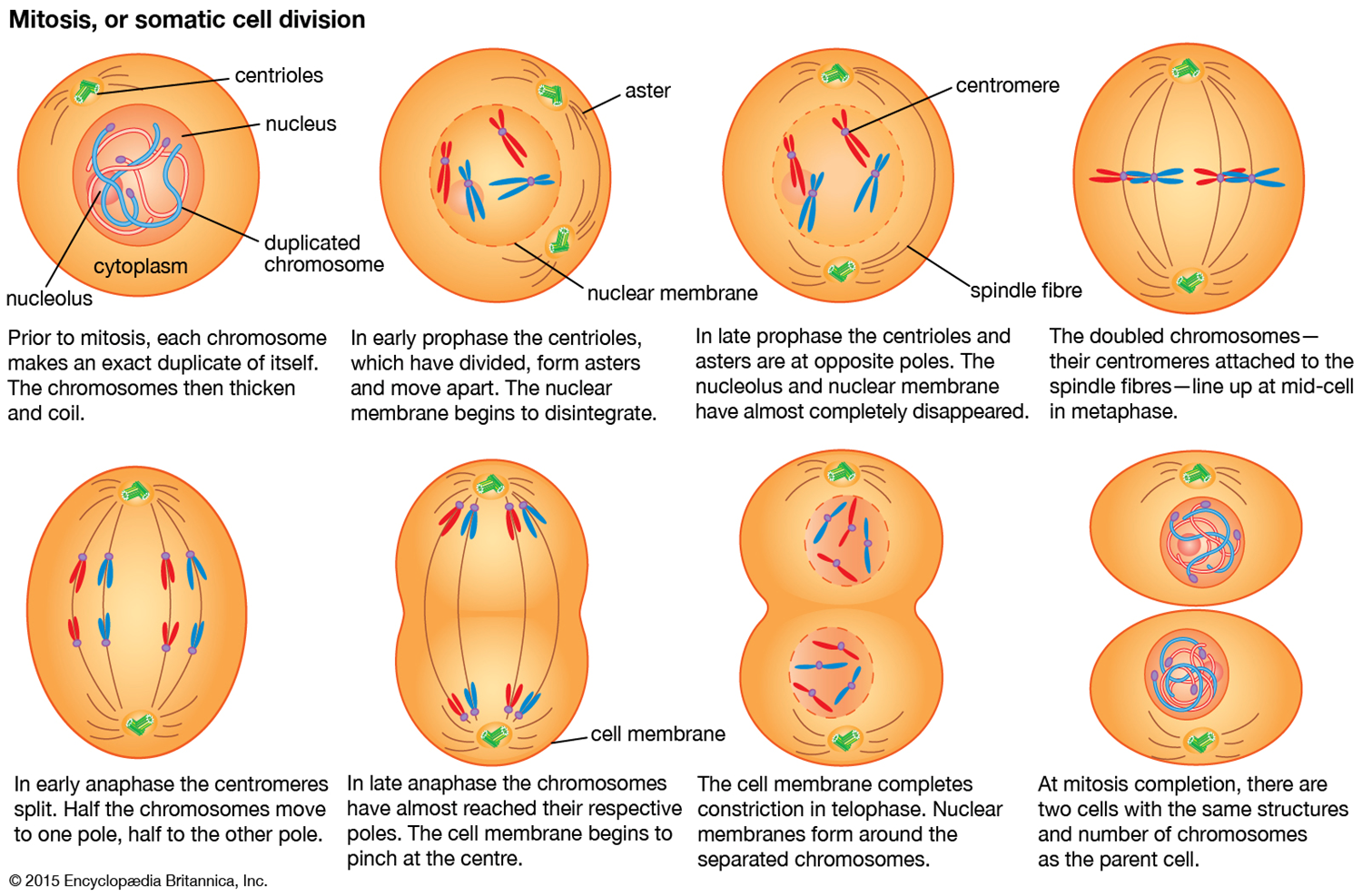
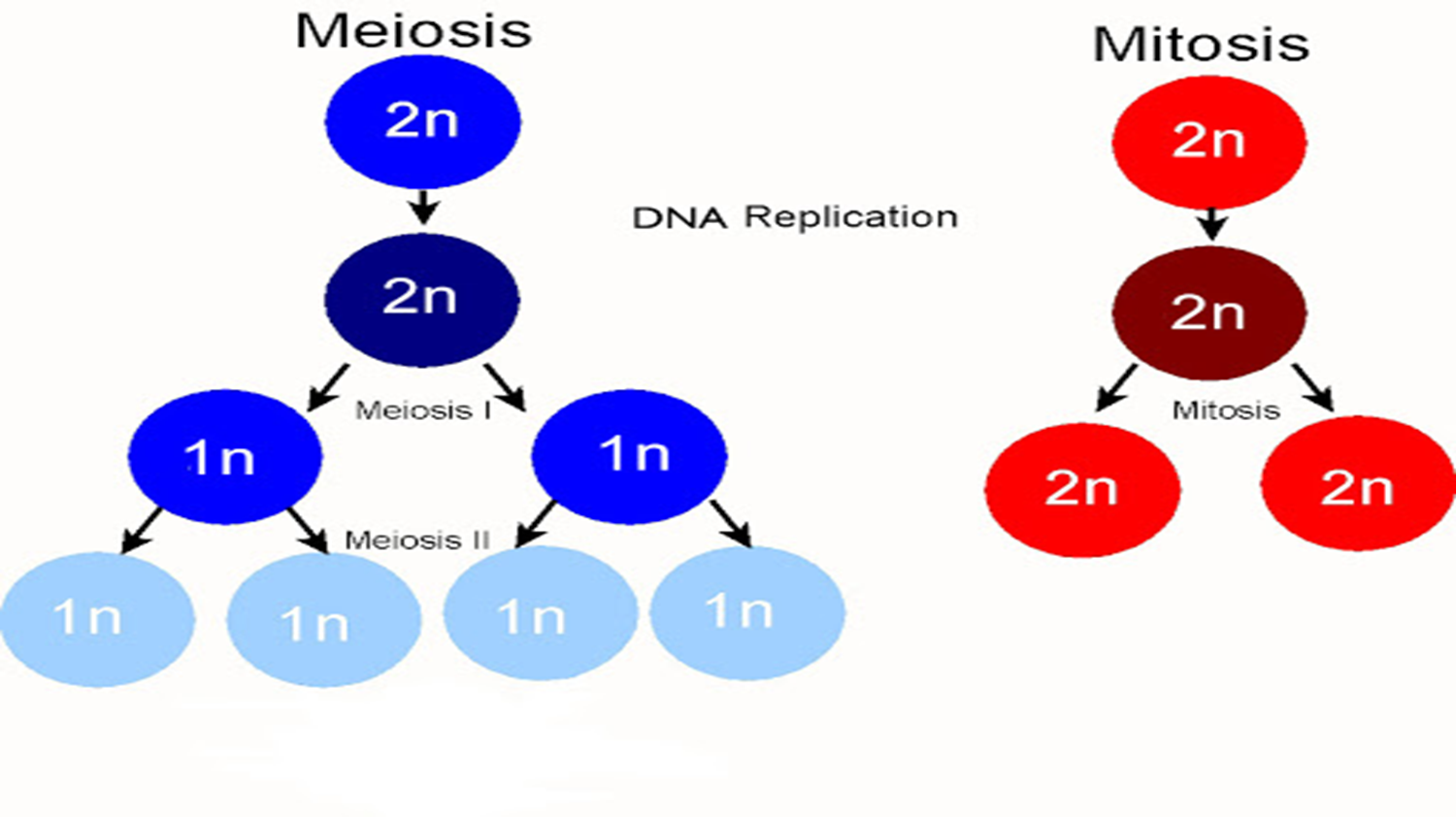
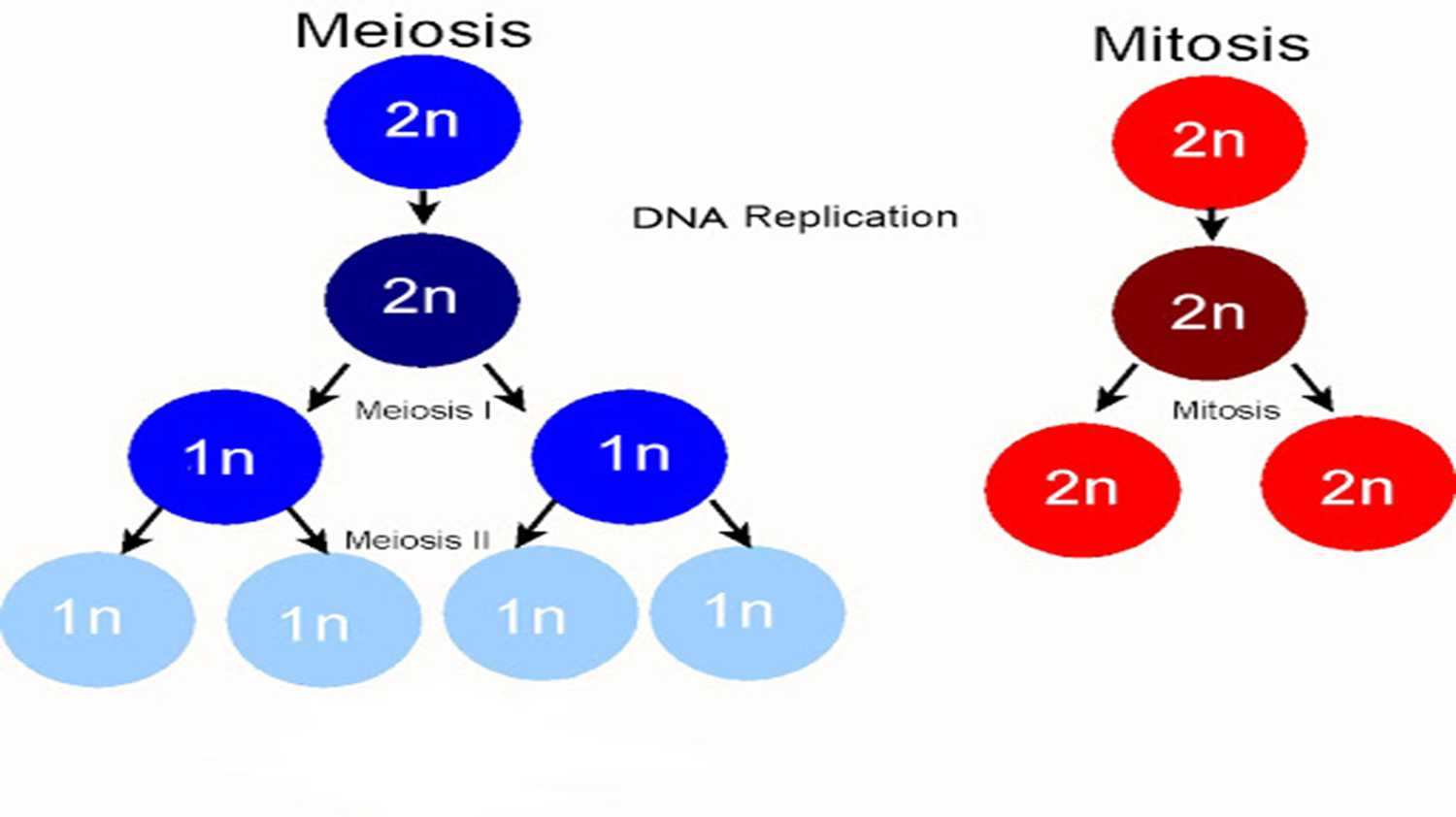
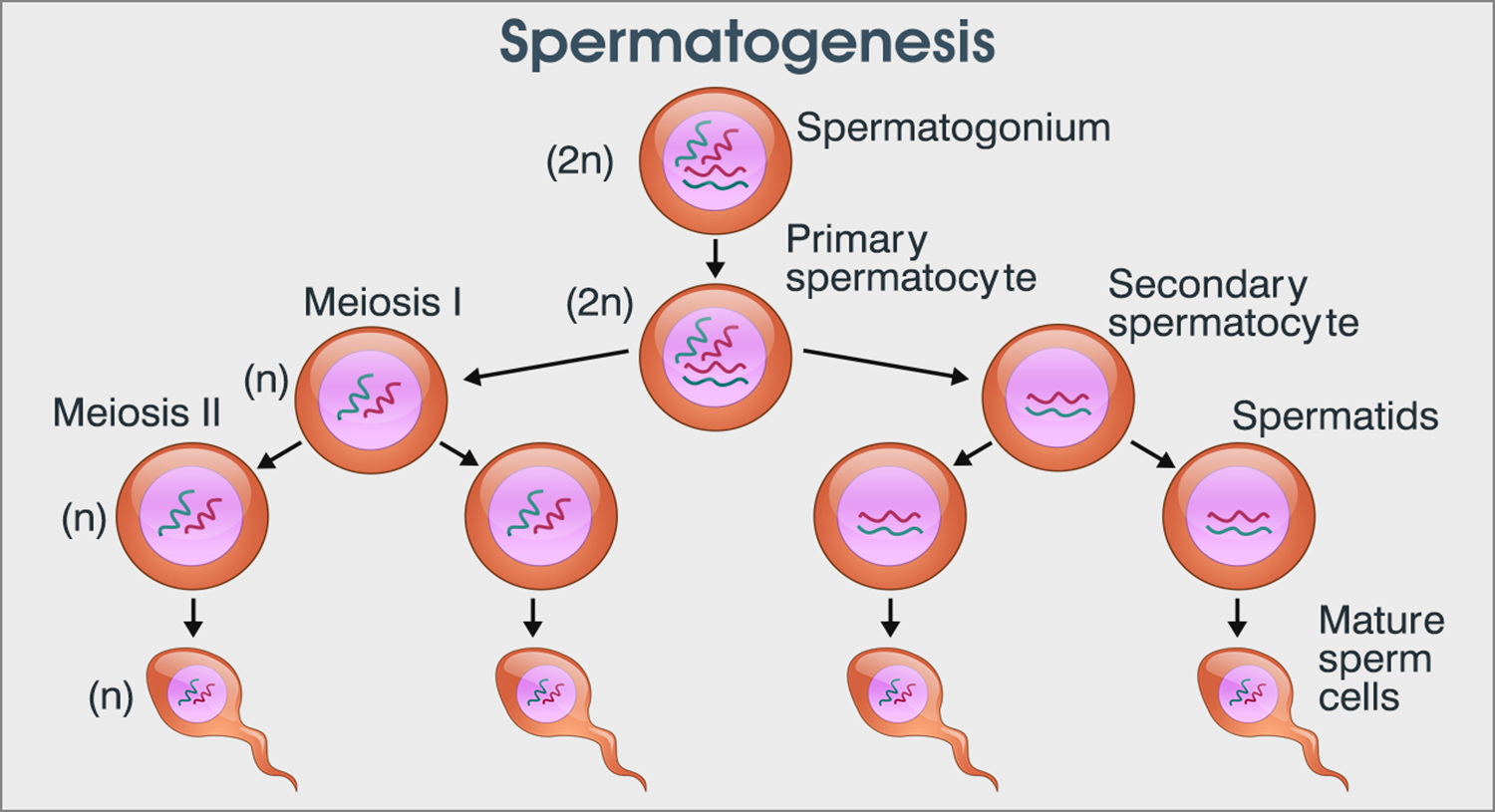
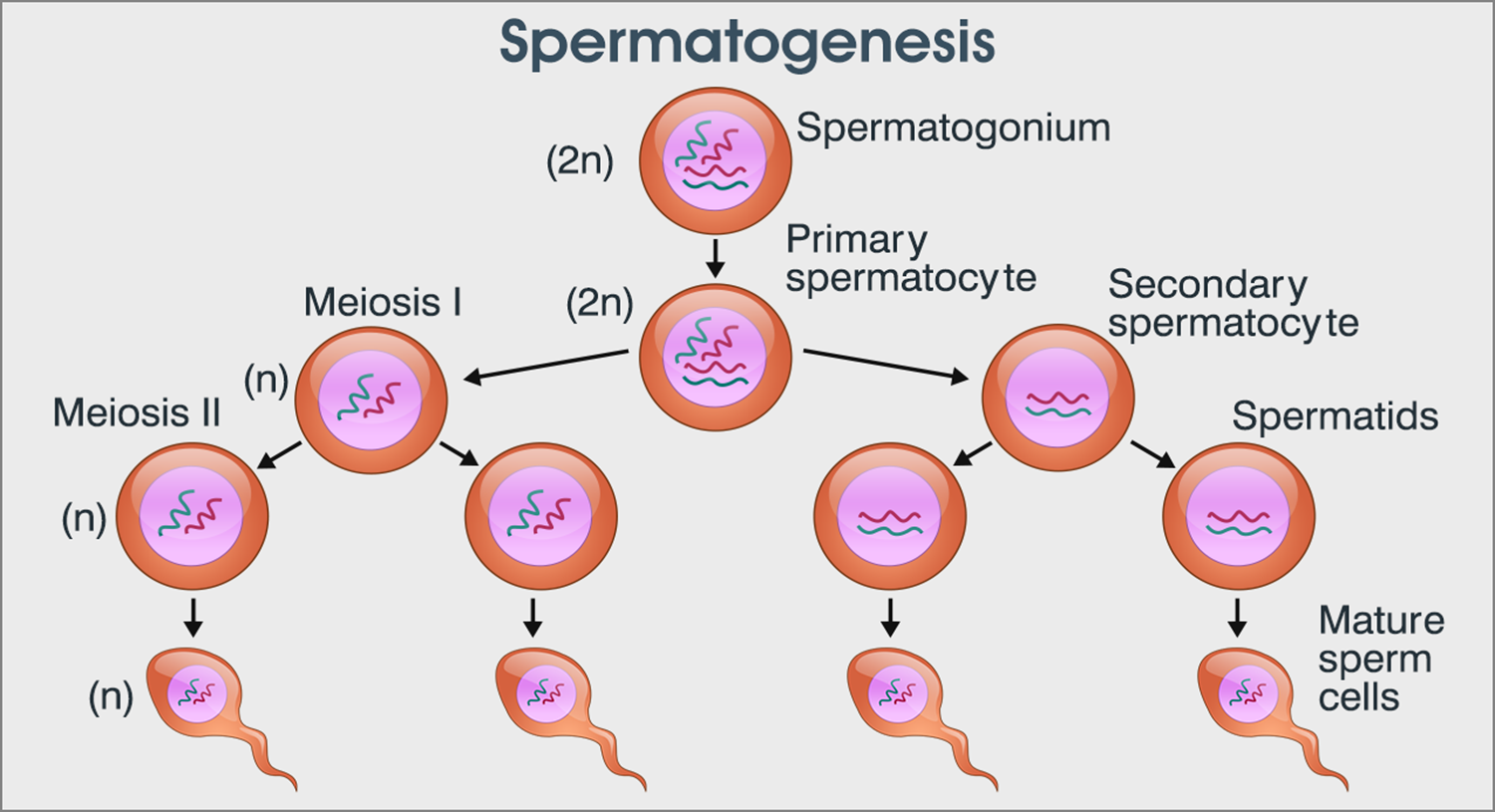
MITOSIS OR SOMANTIC CELL DIVISION
75
New cards
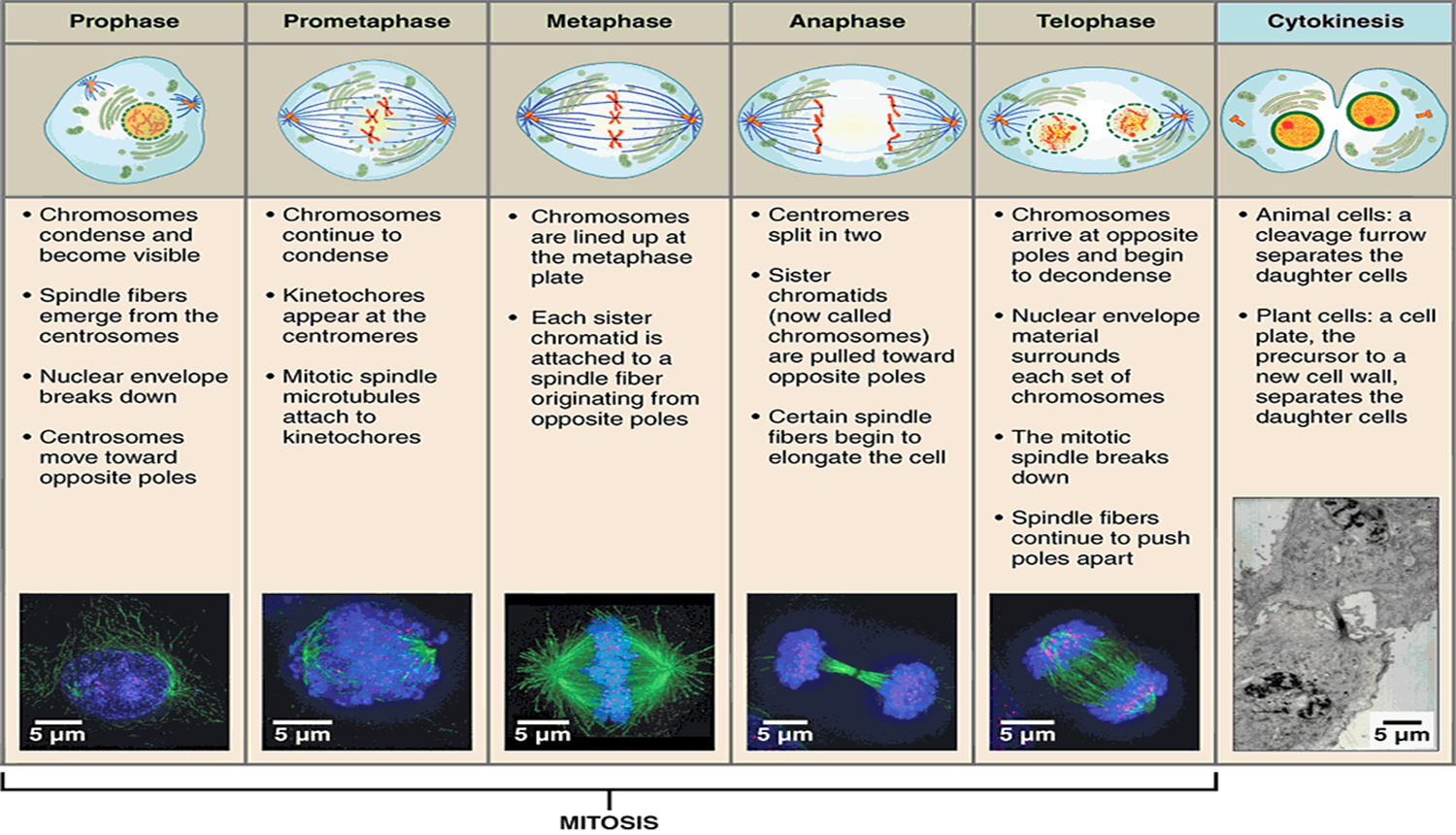
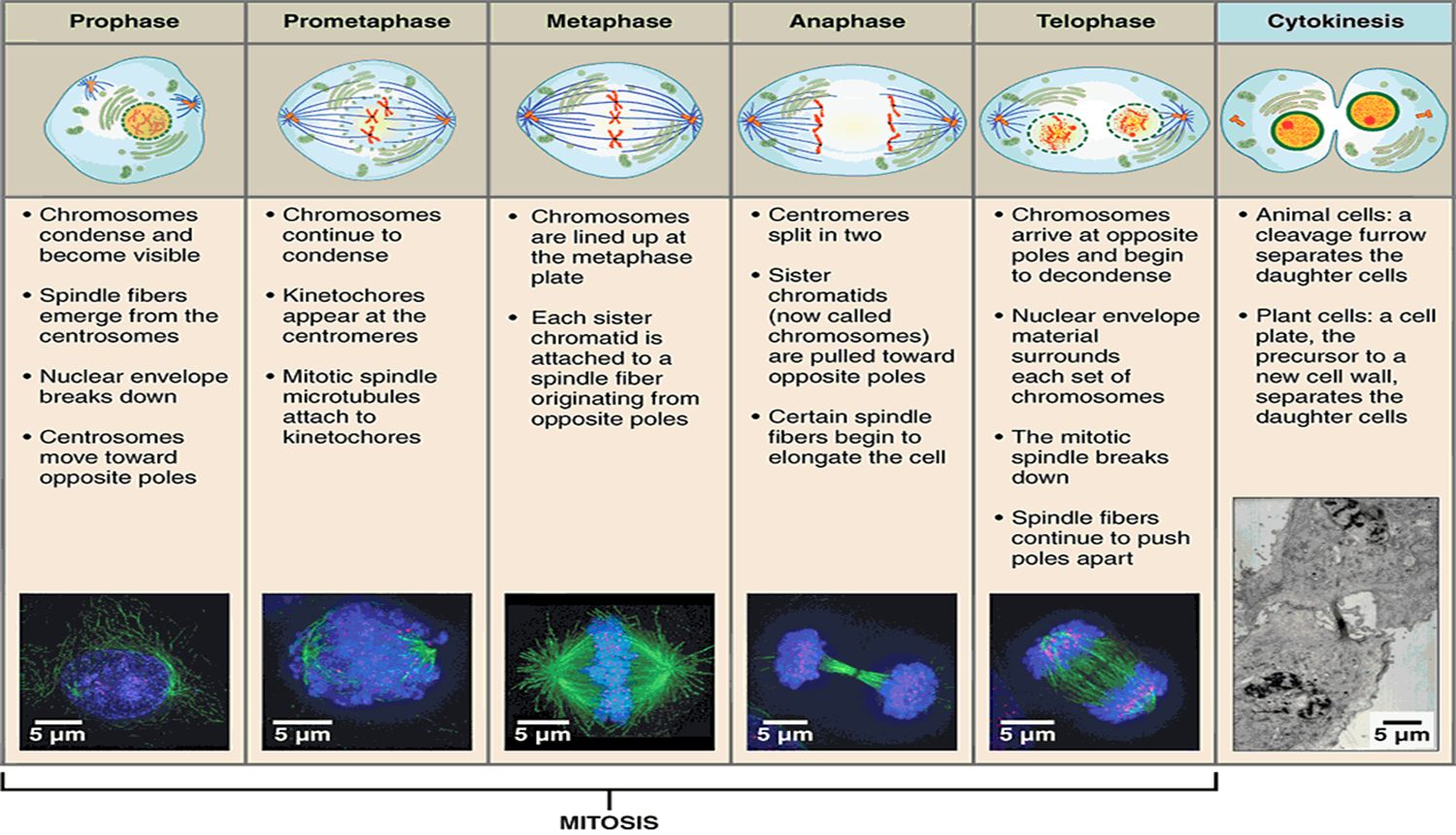
76
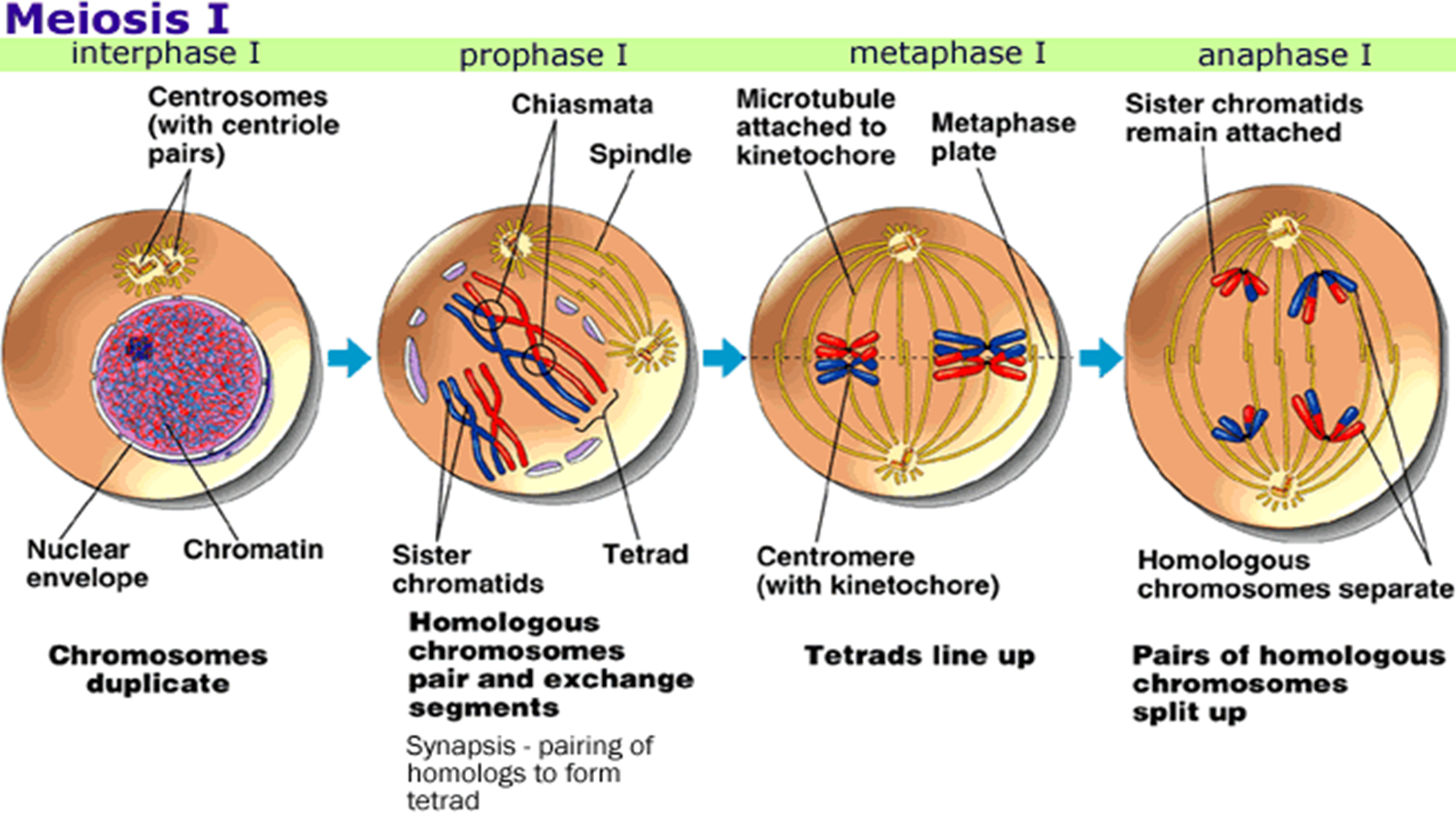
New cards
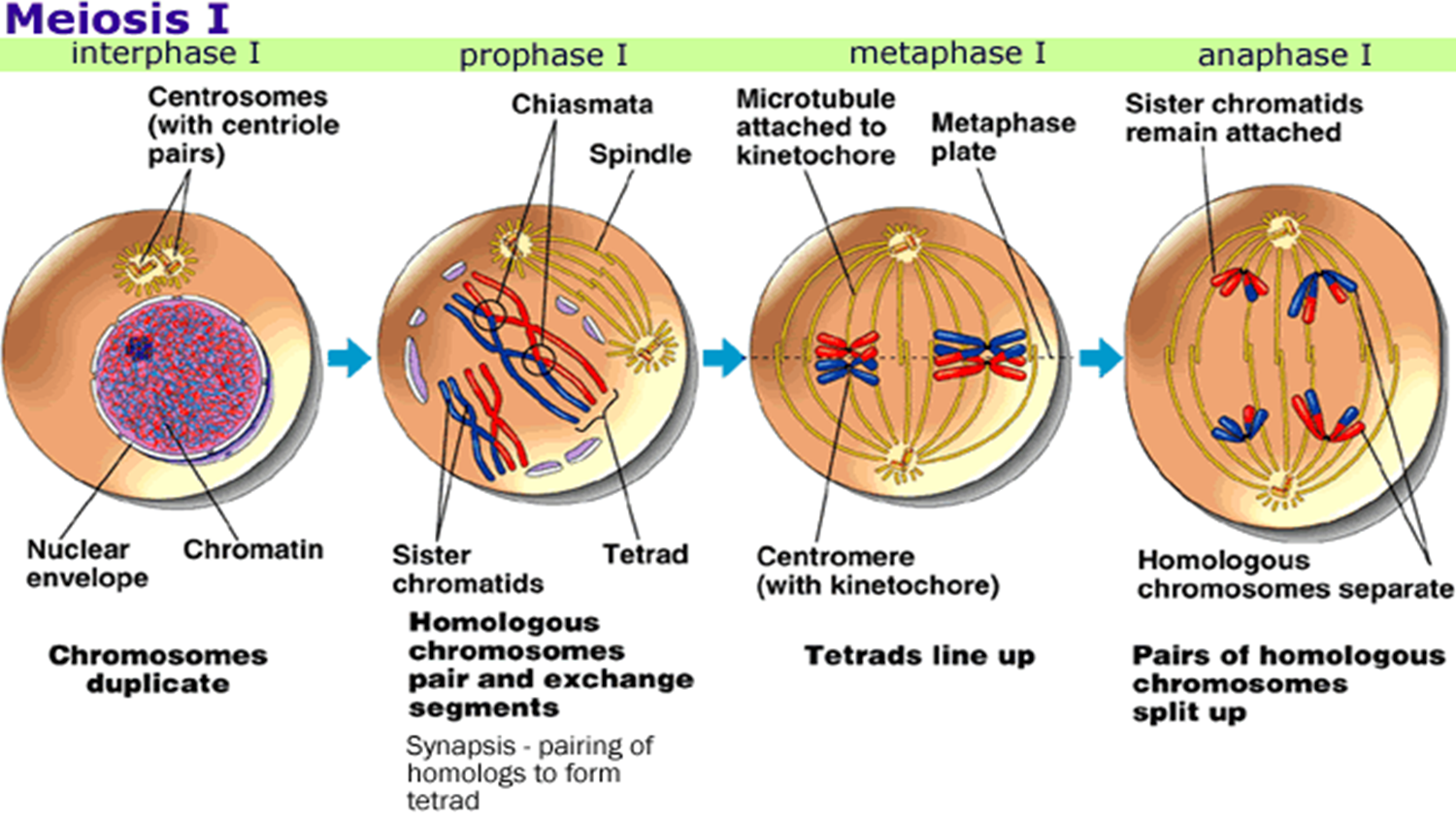
\
77
New cards
78
New cards
79
New cards
80
New cards
81
New cards
82
New cards
83
New cards
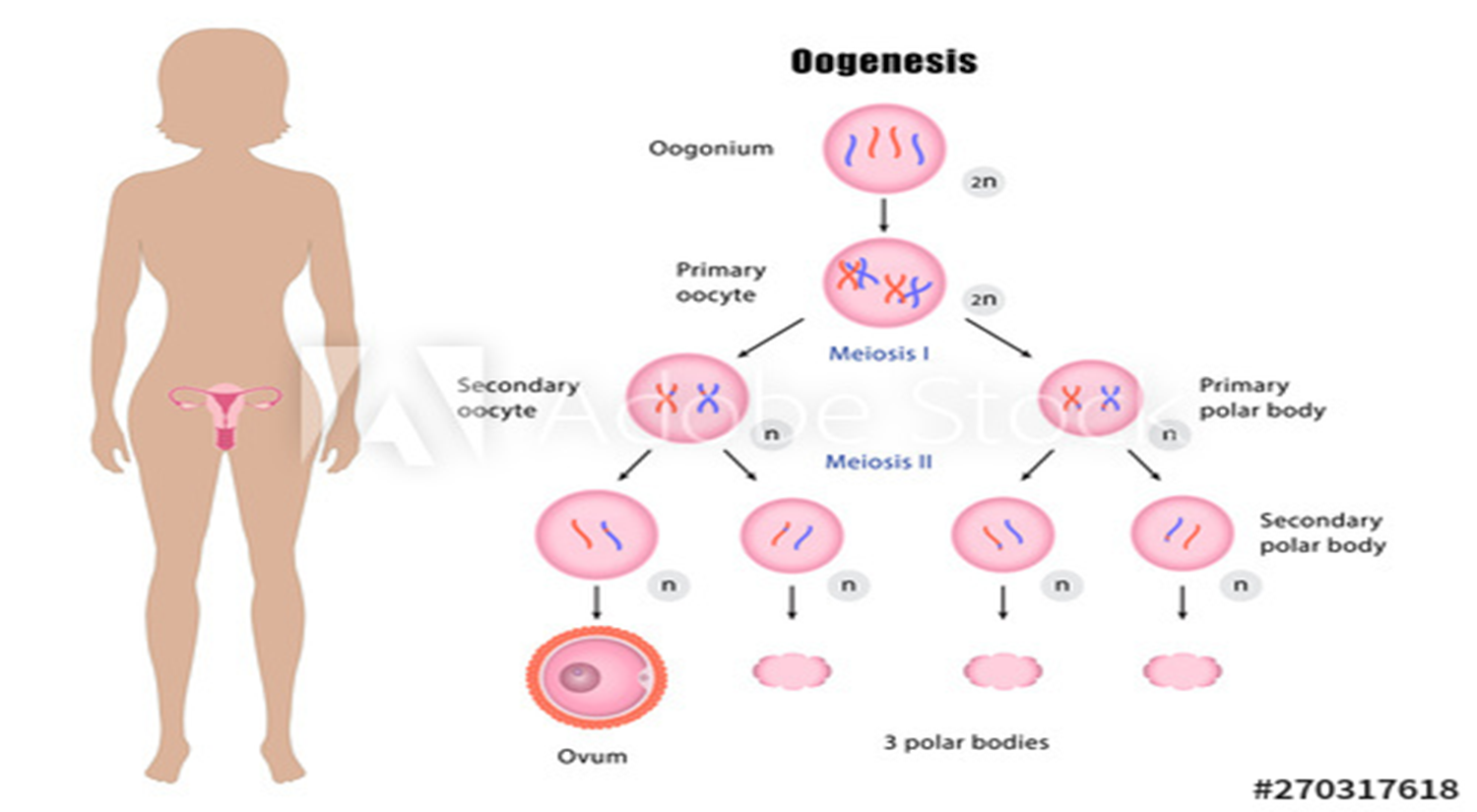
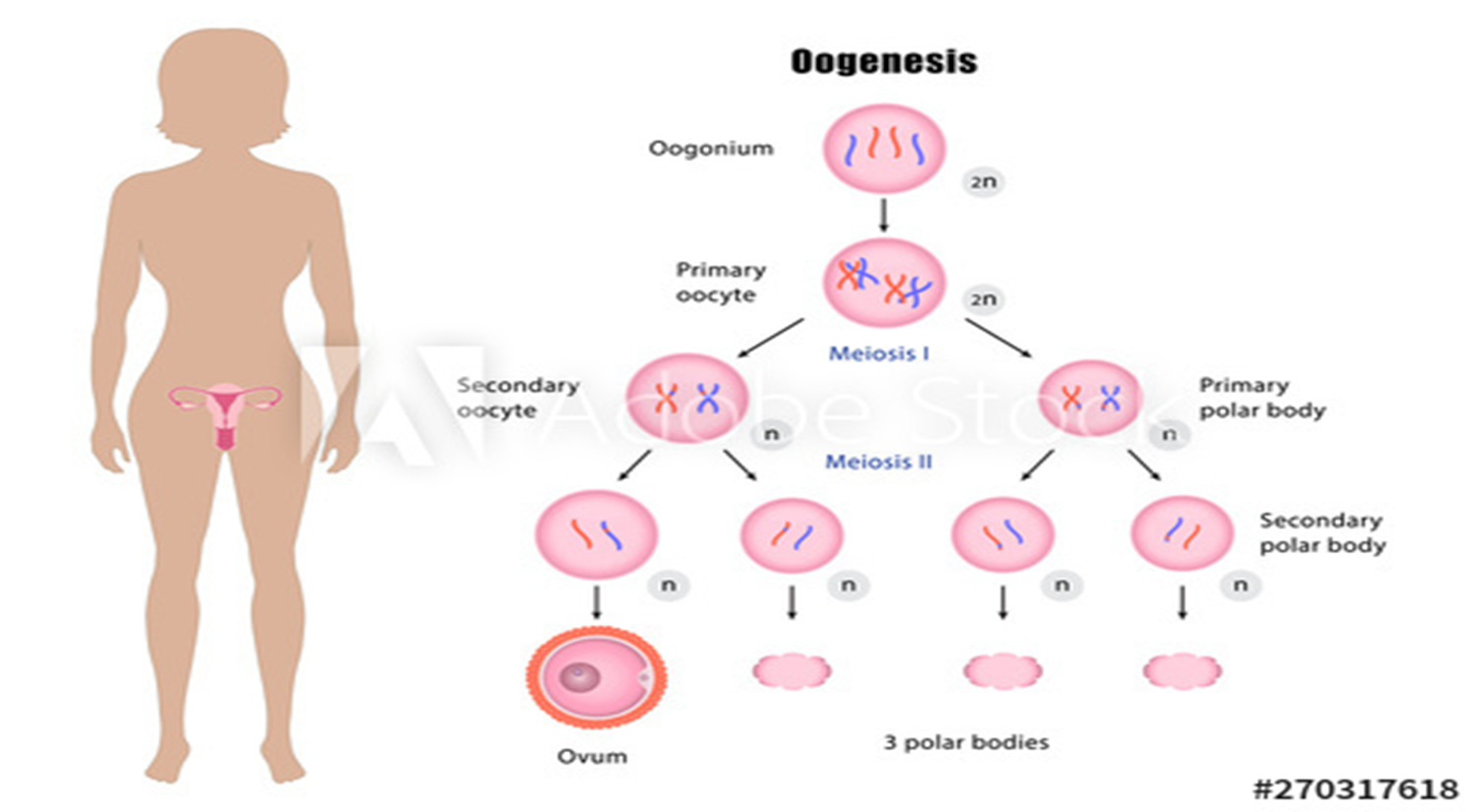
84
New cards
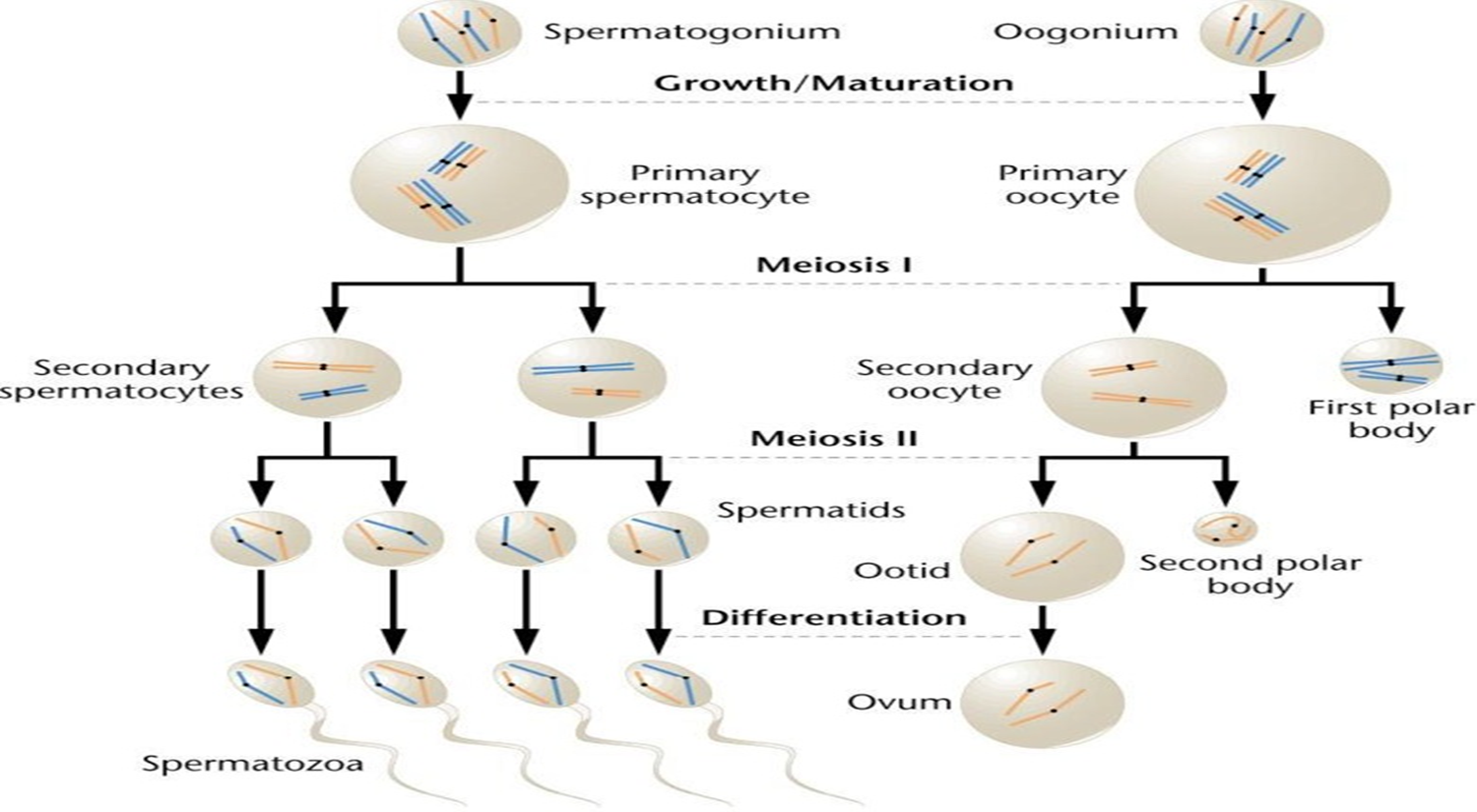
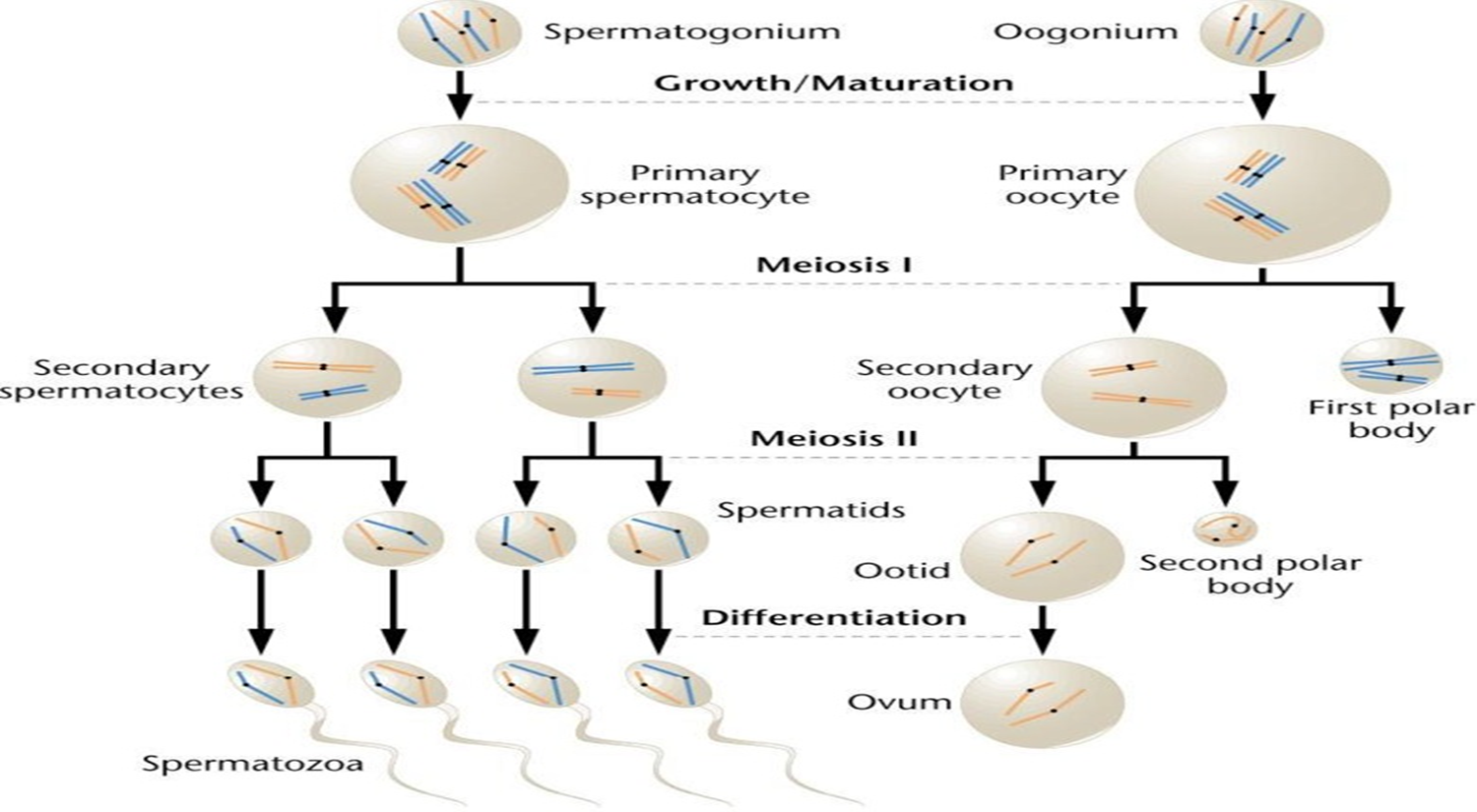
85
New cards
1. REPRODUCTION
2. GROWTH
3. REPAIR & REPLACEMENT
IMPORTANCE OF CELL DIVISION
86
New cards
**CHARACTER**
a heritable feature that varies among individuals (such as flower color).
87
New cards
**TRAIT**
each variant for a character, such as purple, or white color for flowers:
88
New cards
**HOMOZYGOTE**
An organism with 2 identical alleles for a character.
* it is said to be homozygous for the gene controlling that character.
* it is said to be homozygous for the gene controlling that character.
89
New cards
**HETEROZYGOTE**
An organism with 2 different alleles for a gene.
* It is said to be heterozygous for the gene controlling that character.
* Unlike homozygotes, heterozygotes are nat true-breeding.
* It is said to be heterozygous for the gene controlling that character.
* Unlike homozygotes, heterozygotes are nat true-breeding.
90
New cards
**TRUE BREEDING**
are plants that produce offspring of the same variety when they self-pollinate.
91
New cards
**MONOHYBRIDS**
are heterozygous for one character.
92
New cards
**DIHYBRIDS**
are heterozygous for 2 characters.
93
New cards
**PHENOTYPE**
the physical appearance. (color, etc.)
94
New cards
**GENOTYPE**
the genetic makeup. (Ex. PP and Pp).
95
New cards
**HYBRIDIZATION**
mating 2 contrasting, true-breeding varieties.
96
New cards
**P GENERATION**
true-breeding parents (parental).
97
New cards
**F1 GENERATION**
hybrid offspring or the P generation (first generation after crossing 2 parents).
98
New cards
**F2 GENERATION**
produced when F1 individuals self-pollinate or cross-pollinate with other Fl hybrids.
99
New cards
**GENE**
a unit of heredity that is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristic of the offspring.
100
New cards
**ALLELES**
* two forms of a gene dominant & recessive. A different form of the same gene.
* any 2 or more related genes of a trait
* any 2 or more related genes of a trait